
- •1. Electrostatic field. Coulomb’s law. Gauss law (Электростатическое поле. Закон Кулона. Закон Гаусса)
- •Variables and units
- •Coulomb’s Law. (ЗаконКулона)
- •Electric Field Strength e and Displacement Field d. (Напряжённостьисмещениеэлектрическогополя)
- •Gauss’ Law. (ЗаконГаусса)
- •2. Poisson’s and Laplace’s equations for the potential of electric field (Уравнения Пуассона и Лапласа для потенциала электрического поля) Electric Potential. (Электрический потенциал)
- •Poisson’s and Laplace’ s equations. (Уравнения Пуассона и Лапласа)
- •3. Electrostatic Energy (Электростатическая энергия) Electrostatic Energy (Электростатическаяэнергия)
- •Virtual experiment. (Эксперимент по нахождению энергии системы)
- •Consequences (Следствия)
- •4. Power and Joule’s Law (Энергия и закон Джоуля-Ленца)
- •5. Continuity Equation (Уравнения непрерывности) ContinuityEquation (Уравнение непрерывности)
- •Image method for the flat boundary between magnetic media (Метод изображений для плоской границы между магнитными носителями)
- •8. Static magnetic field. Biot–Savart’s Law. Ampere’s Law (Статическое магнитное поле. Закон Био–Савара. Закон Ампера)
- •Variables and units (Переменные и единицы измерения)
- •Main Relations (Основные соотношения)
- •Magnetic flux density (Индукция магнитного поля)
- •Biot-Savart’s law (Закон Био-Савара)
- •Ampere’s law (Закон полного тока)
- •The cut in the space (Разрез в пространстве)
- •Laplace equation for the scalar magnetic potential (Уравнение Лапласа для скалярного магнитного потенциала)
- •10. Vector magnetic potential. Inductance (Векторный магнитный потенциал. Индуктивность)
- •Vector magnetic potential (Векторный магнитный потенциал)
- •Magnetic flux (Магнитный поток)
- •Differential equation for the vector magnetic potential (Дифференциальное уравнение для векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Gauging of the vector magnetic potential (Калибровка векторного магнитного потенциала)
- •Integral presentation of the vector magnetic potential (Интегральное представление векторного потенциала)
- •Inductance (Индуктивность)
- •Mutual inductance (Взаимная индуктивность)
- •Inductance of thin contours (Индуктивность тонких контуров)
- •12. Internal inductance of a thin conductor (Внутренняя индуктивность тонкого проводника) Flux linkage of a thin current layer (Потокосцепление тонкого слоя с током)
- •Internal inductance of a thin conductor (Внутренняя индуктивность тонкого проводника)
- •13. Inductance of a two wire transmission line (Индуктивность двухпроводной линии).
- •14. Variable separation method in a cylindrical coordinate system (Метод разделения переменных в цилиндрической системе координат). Application of Laplace’s equation (Применение уравнения Лапласа).
- •Angular function (Угловая функция)
- •Radial function (Радиальная функция)
- •General solution of the Laplace’s equation in a cylindrical coordinate system (Общее решение уравнения Лапласа в цилиндрической системе координат)
- •15. The Faraday’s law (Закон электромагнитной индукции).
- •Lenz’s Law (правило Ленца)
- •Induction by a temporal change of b (Индукция за счёт временного изменения b)
- •16. Induction through the motion of a conductor (Индукция за счет движения проводника).
- •17. Induction by simultaneous temporal change of b and motion of the conductor (Индукция одновременным изменением b во времени и движением проводника).
- •18. Unipolar generator (Униполярный генератор).
- •19. Hering’s paradox (Парадокс Геринга)
- •20. Diffusion of magnetic fields into conductors (Распространение электромагнитного поля в проводнике)
- •21. Periodic electromagnetic fields in conductors. (Периодическое электромагнитное поле в проводниках)
- •Penetration of the electromagnetic field into a conductor. (Проникновение электромагнитного поля в проводник)
- •The skin effect. (Скин-эффект)
- •22. Poynting theorem. (Теорема Пойнтинга) Electromagnetic Field Energy. (Энергия электромагнитного поля)
- •The rate of decrease of the electromagnetic field energy in a closed volume. (Скорость уменьшения энергии электромагнитного поля в замкнутом объёме)
- •Transmission of energy in a dc line (Передача энергии в линиях постоянного тока)
- •The field picture near the wires with current (Картина поля вблизи провода с током)
- •25. Energy flows in static electric and magnetic fields (Поток энергии в статических электрических и магнитных полях).
- •26. The reduced magnetic potential (Редуцированный магнитный потенциал). Reduced scalar magnetic potential (Редуцированный скалярный магнитный потенциал)
- •Combination of scalar magnetic potential and reduced magnetic potential (Комбинация скалярного магнитного потенциала и редуцированного магнитного потенциала)
- •27. Classification of numerical methods of the electromagnetic field modeling (Классификация численных методов моделирования электромагнитного поля).
- •Classification of the problems (Классификация проблем)
- •Classification of the methods (Классификация методов)
- •28. Method of moments
- •Discretization of the problem domain (Дискретизация проблемной области)
- •29. Basic principles of the finite element method.
- •30. Finite functions (Ограниченная функция – отлична от нуля только в пределах треугольника)
- •Simplex coordinates
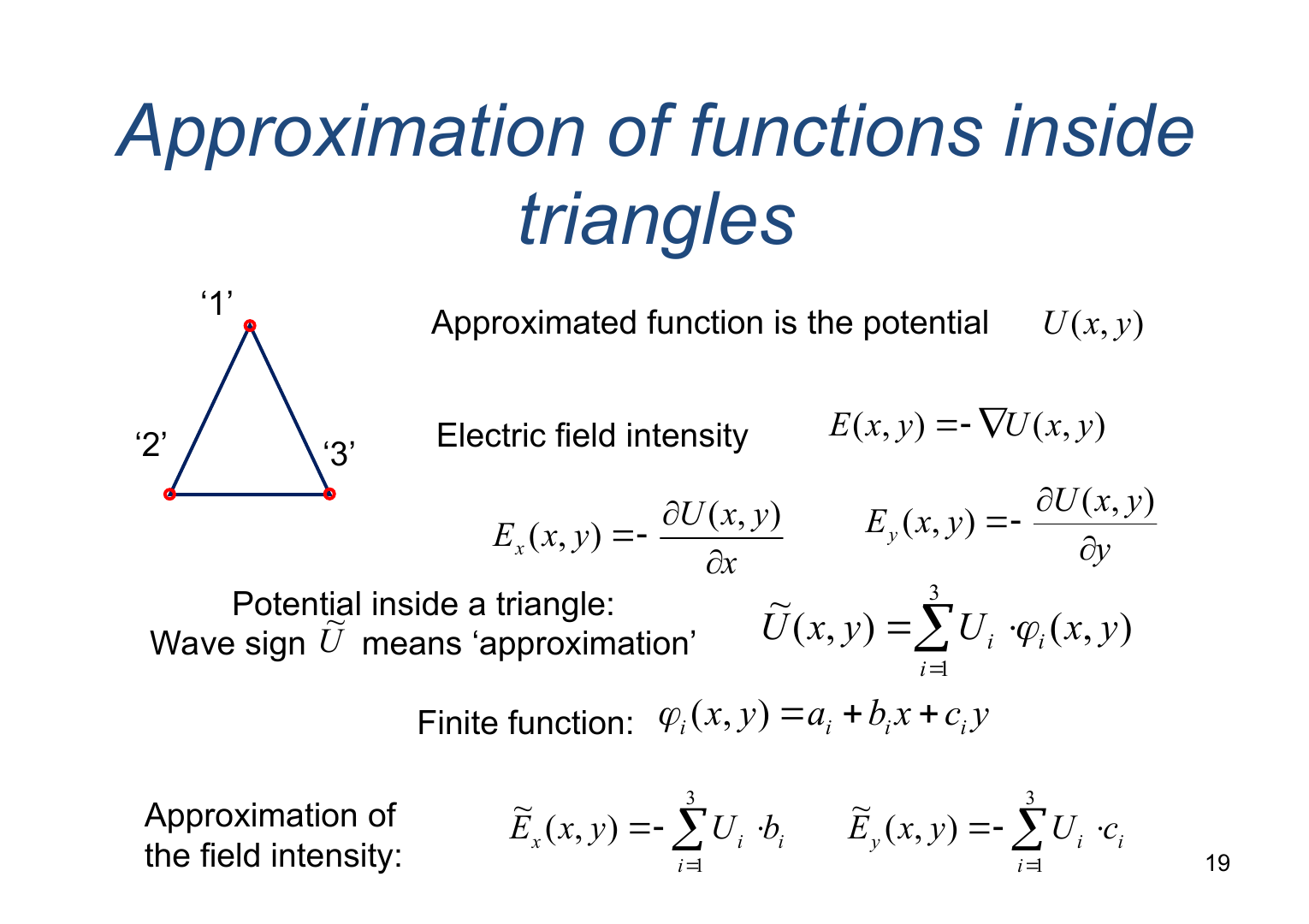
- •Approximation of functions inside triangles (Аппроксимация функций внутри треугольника)
- •Approximation of the equation (Аппроксимация уравнения)
- •31. Weighted residual method (метод взвешенных невязок)
- •32. Weak formulation of the electromagnetic field modeling problem
- •33. Boundary conditions in electric and magnetic fields
- •1) First type boundary conditions
- •34. Main equations of electromagnetic field in integral form.
- •35. Main equations of electromagnetic field in differential form.
- •36. Electric field of a point charge (Электрическое поле точечного заряда)
- •37. Electric field of a uniformly charged sphere (Электрическое поле равномерно заряженной сферы)
- •38. Flat capacitor. Field. Surface charge. Capacity. (Плоский конденсатор. Поле. Поверхностный заряд. Вместимость.)
- •39.2 Inductance of a cylindrical coil with the rectangular cross section(Индуктивность цилиндрической катушки прямоугольного сечения).
- •4 0.1 Electric field induced by charged line placed above conducting surface (Электрическое поле, создаваемое заряженной линией, помещенной над проводящей поверхностью).
- •4 0.2. Magnetic field induced by the line with a current placed above a ferromagnetic surface with infinitely high magnetic permeability
Discretization of the problem domain (Дискретизация проблемной области)
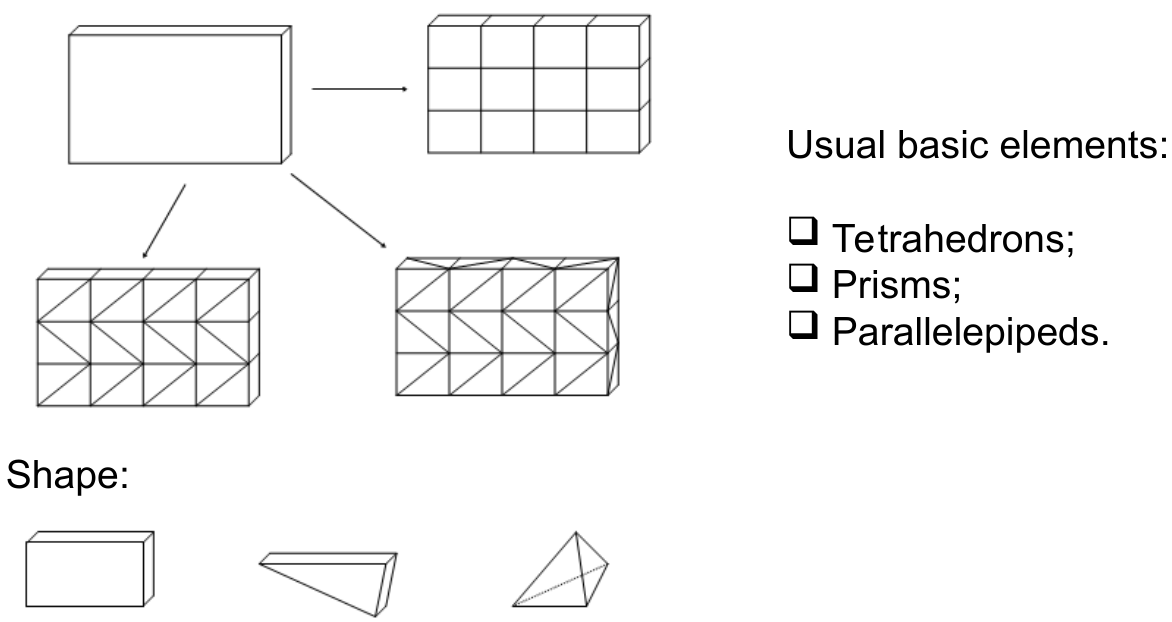
We should split the brick into basic elements (tetrahedrons (тетраэдры), prisms or parallelepipeds)
Algebraic equation system (Алгебраическая система уравнений)
The magnetization of each element is considered constant (the simplest approach). More complex approximation schemes are not used.
To form a system of equations the method is collocations is used (we must choose some central point inside the element and the magnetic field which induced by all parts of the magnetic system is calculated just for this central point. And then, it’s assumed, that everywhere inside the element the magnetic field intensity has the same value)
29. Basic principles of the finite element method.
Main steps:
Problem formulation – problem domain, equation, boundary conditions, material properties.
Discretization of the problem domain.
Approximation of the unknown function.
Approximation of the solved equation and the boundary conditions.
Solution of the algebraic equation system (generally – nonlinear).
Post-processing (постобработка).
Discretization (Дискретизация)
The element type choice
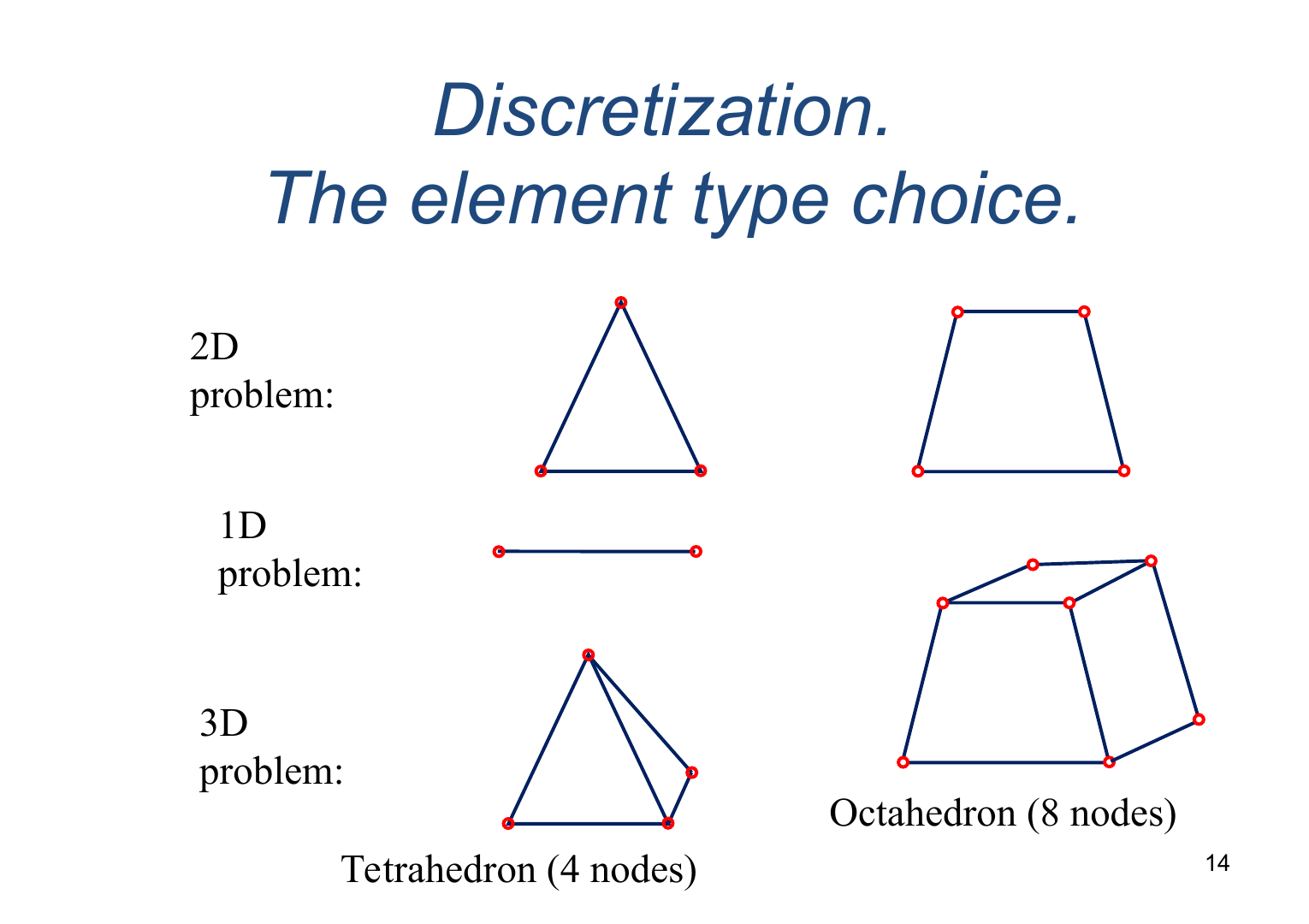
Node – узел (точка, вершина)
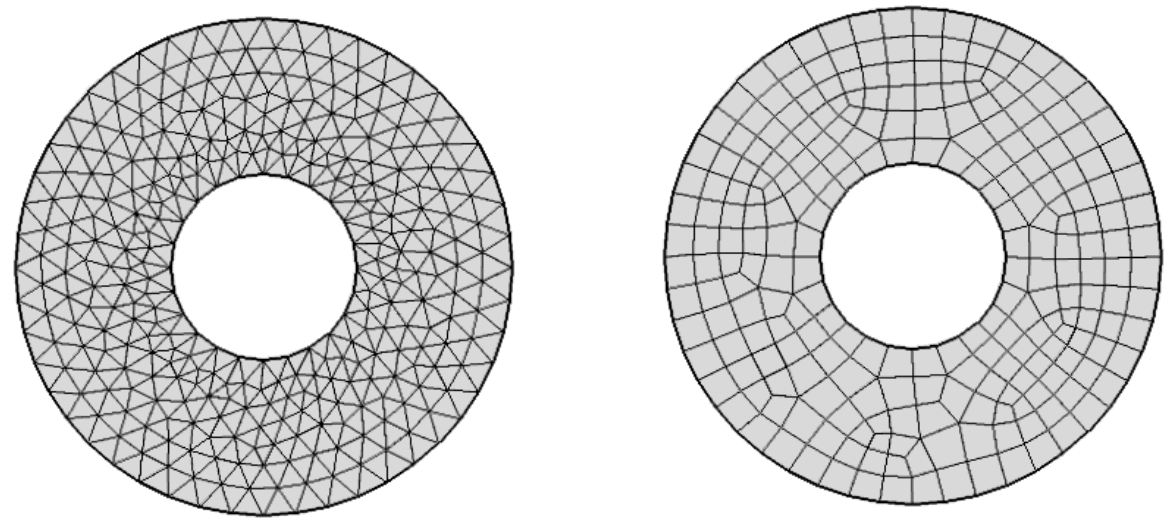
Examples of the mesh (triangles and quadrangles)
Linear approximation
 узловые
бля
узловые
бля
The number of free parameters is the same!
In principle we can express coefficients a, b, c in terms of the nodal potentials U1, U2, U3
In linear approximation the vertices are the same with the nodal.
30. Finite functions (Ограниченная функция – отлична от нуля только в пределах треугольника)
Finite function inside the triangle may have different dependences. Everything depends on the value of the nodal potential.
There are three very special finite function:
F
 inite
function associated with the first node:
inite
function associated with the first node:
Similar relations are valid for 2 other finite functions.
Finite functions for triangles = simplex coordinates (coordinates – because every point inside the triangle may be describe by certain value of finite functions, that is why the behavior of these functions is similar to coordinates).
Simplex coordinates
Two-dimensional simplex coordinates:
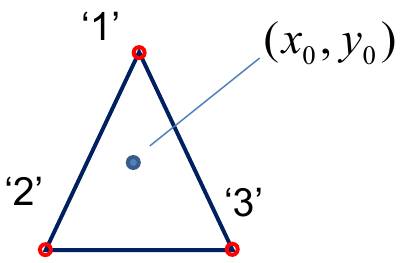
Another definition of the point position is a set of simplex coordinates
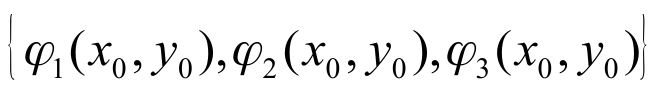
Really only 2 of 3 simplex coordinates are independent:
General relation for the simplex coordinates:
![]()
Approximation of functions inside triangles (Аппроксимация функций внутри треугольника)
Approximated function is the potential: U(x, y)
Electric
field intensity
![]()
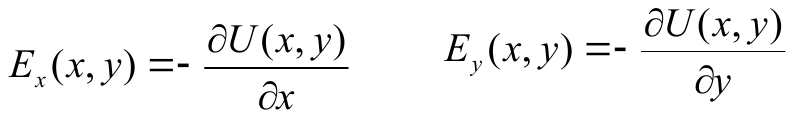
Potential
inside a triangle (Wave sign
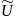 means ‘approximation’):
means ‘approximation’):
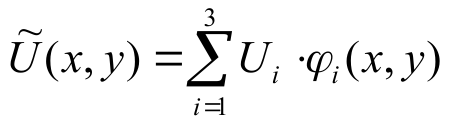
Finite function:
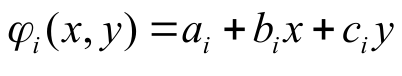
Approximation of the field intensity:
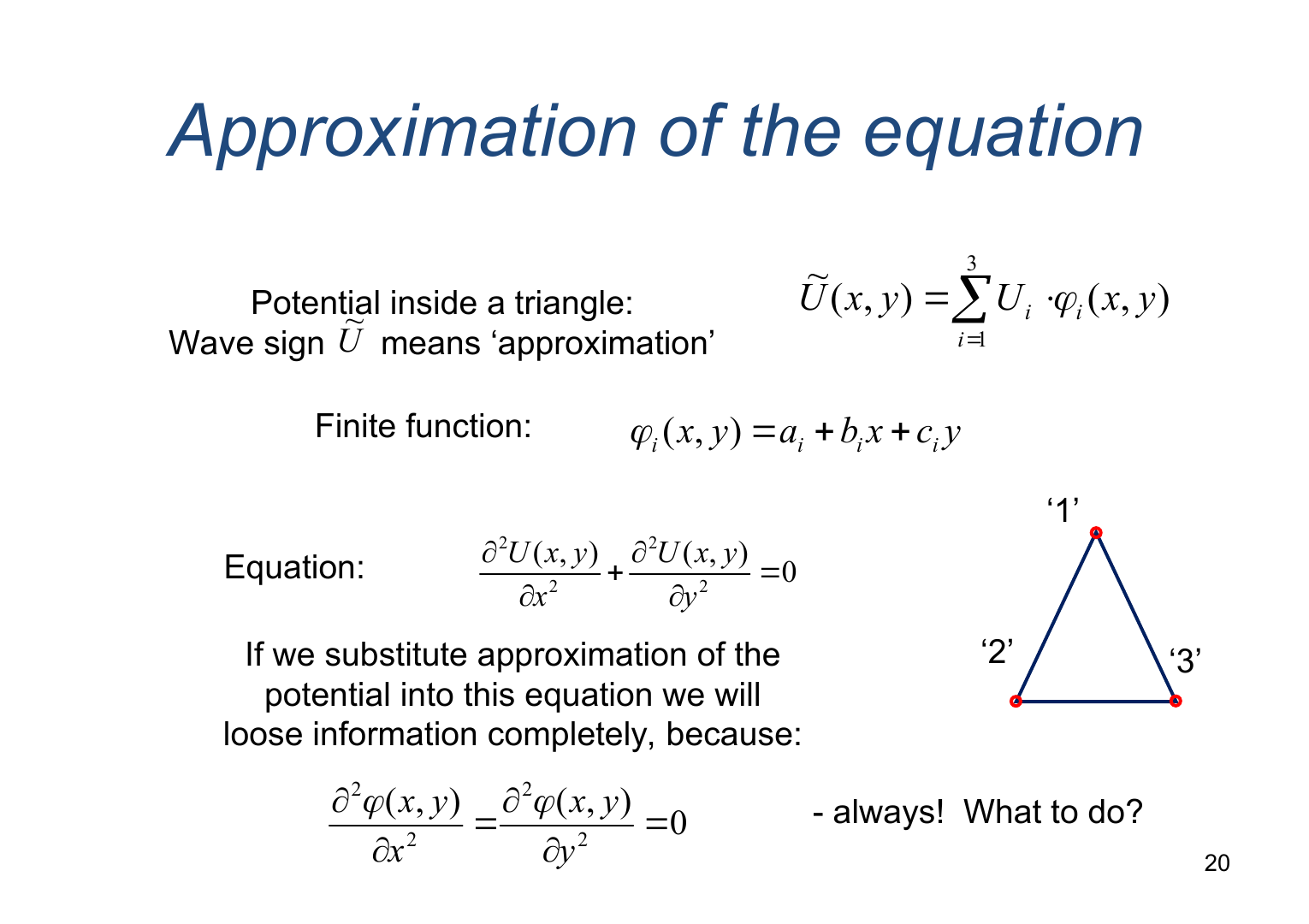
Approximation of the equation (Аппроксимация уравнения)
Potential inside a triangle (Wave sign means ‘approximation’):
Finite function:
Equation:
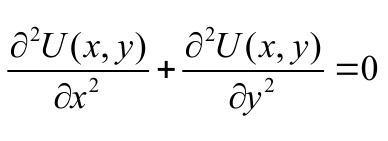
If we substitute approximation of the potential into this equation we will lose information completely, because
31. Weighted residual method (метод взвешенных невязок)
This method is used to solve different kinds of problems and the idea behind this method is non-trivial. Let’s look to the initial equation:
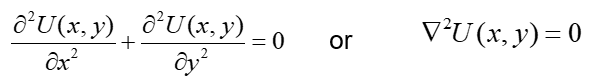
Let’s choose some arbitrary (произвольную) function ψ(x,y) (можем выбрать некоторую произвольную функцию, которую в будущем назовём взвешенной (weighting) функцией). Evidently, if right initial equation is equal to zero, so the product of this Laplace operator and weighting function will be equal to zero.
![]()
Now let's integrate this product over the area s (this s corresponds to the whole problem domain)
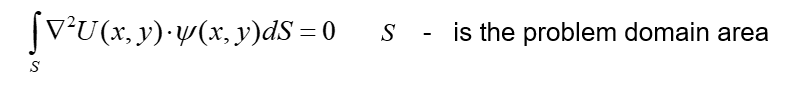
Also, it is necessary to remember, we are talking about finite element method and all finite functions and consequently these weighted functions also will be limited by certain element, they will be equal zero outside the considered element and will be non-zero inside them. That’s why the first glance (взгляд) this integral is very complicated it should be integrate over the wide area, but in the practice it should integrate always in very small area, which is restricted by considered elements.
To choose correctly the weight function we use Galerkin method
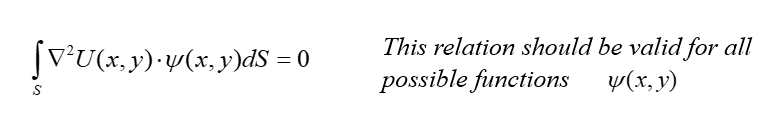
This is an initial equation and that is true only because the Laplacian of potential is equal to zero. Evidently, the Laplacian of such approximation not necessary will be equal to zero it may differ from zero, that’s why the integral from the product of Laplacian weighting function and after integration will give us so called ‘weighted residual’ – R:
![]()
So, the idea of the Galerkin method – it is the special choice of the weighting functions:
to use the weighted residual method;
to use approximation functions for weighting:
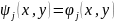
to set residuals to zero; Rj=0
to apply integration-by-parts procedure to the integral (weak formulation)
Let’s assume that the weighting function is the same of the finite function, which corresponds just to this triangle, of course, there are three different functions, so for every triangle we should use three weighting functions. The second assumption, set residuals to zero, evidently we can choose approximation of the potential in such a way the residual will be really equal to zero, not because the Laplacian of the potential is equal to zero, but because the product of this potential and the weighting function after integration will give zero. And now let’s apply integration-by-parts procedure to the integral.
Indeed, if we shall directly calculate this integral using approximation of the potential, we can get exact zero (zero will be equal to zero), so to avoid this difficulty it is possible to use some mathematic transformation, which is called integration-by-part. Очень важная часть метода Галеркина заключается в том, что прямолинейное вычисление интеграла такого вида даст нам нулевой ответ только потому, что вторая производная от полинома первого порядка всегда равна нулю, и таким образом мы не сможем найти решение. Для того, чтобы преодолеть эту сложность в методе Галеркина предполагается провести идентичное преобразование – интегрирование по частям.
