
Учебное пособие 1427
.pdf
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093
Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
Ministry of Science and Higher Education
of the Russian Federation
Scientific Journal
“MODERN LINGUISTIC AND
METHODICAL-AND-DIDACTIC RESEARCHES”
Voronezh State Technical University
The journal has been publishing since 2012
Issue 2 (33), 2021
CONTENTS
Fedorov V.A. Introductory remarks by editor-in-chief of the scientific journal «Modern
linguistic and methodical-and-didactic researches»........................................................................ |
6 |
LINGUISTICS
Malyuga E.N., Madinyan E.I. Representation of Events in the American News Media
Discourse ......................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
Kostrzewa F. Contrastive-and-linguistic Analysis in the Context of German as a Foreign and |
|
Technical Language (Part 1) ......................................................................................................... |
19 |
Stepura S.N. Special Language Means in Ulysses by James Joyce............................................. |
29 |
Lapinskaya I.P., Denisova M.A., Manukovskaya M.A. Specific Vocabulary Used for
Naming Business Enterprises........................................................................................................ |
41 |
METHODS AND DIDACTICS |
|
Ilina O.K. Blended Methods of Teaching the English Language of Profession .......................... |
51 |
INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION |
|
Pomnikova A.Yu., Velichko M.Yu. Family Stories in Political Discourse................................ |
58 |
Zabolotneva O.L., Kozhukhova I.V. Mitigation and Aggravation of Imposition in Russian- |
|
language University Prose (in I. Grekova "Department")............................................................. |
71 |
4 |
|

Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” Issue 2 (33), 2021 |
ISSN 2587-8093 |
Vodyanitskaya A.A. Research Methods for Studying Evaluation: Academic Discourse |
|
Perspective .................................................................................................................................... |
81 |
THEORY AND PRACTICE OF TRANSLATION |
|
Fedorov V.A., Nekhaeva O.G. National Specifics of Translation of the French Construction il |
|
y a in the Light of the Theory of Syntactic Concepts.................................................................... |
89 |
SCIENTIFIC OVERVIEW |
|
Lavrinenko I.Yu., Konovalova Yu.S. Scientific Report about the Open Lecture of the |
|
Professor Michael Steppat "Strategies for Government Support for Advanced University |
|
Research in Germany", Organized on January 28, 2021 by the Institute of Foreign Languages |
|
of the Moscow City University ..................................................................................................... |
99 |
INFORMATION ABOUT AUTHORS ................................................................................... |
102 |
REQUIREMENTS TO THE PAPERS IN SCIENTIFIC JOURNAL “MODERN |
|
LINGUISTIC AND METHODICAL-AND-DIDACTIC RESEARCHES” ........................ |
103 |
INFORMATION ON SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS ........................................................ |
107 |
5

Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
Introductory Remarks by Editor-in-chief of the Scientific Journal
«Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches»
Issue 2 (33) of the Scientific Journal contains the following sections:
“Linguistics”, “Methods and Didactics”, “International Communication”, “Theory and Practice of Translation”. The second issue of the thirty third series presents 9 scientific articles.
This issue offers its readers the most relevant theoretical and practical research results and helps to get insight into the most relevant tendencies in scientific researches in linguistics, methods and didactics of foreign lan-
guages teaching, international communication, problems of theory and practice of translation, not only as a process, but also as a result. The works included in this issue contribute to approach to scientific truth that is an important challenge to every linguist.
The section “Linguistics” starts with the article concerning metaphorical representations of events in the American media discourse (by E.N. Malyuga and E.I. Madinyan). The next article of the issue presents contrastive-and-linguistic analysis of German as a foreign and professional language (by F. Kostrzewa). It is followed by the article concerning the special linguistic means in artwork (by S.N. Stepura). The final article of the section is about lexical nomination of the business objects (by I.P. Lapinskaya, M.A. Denisova, M.A. Manukovskaya).
The section “Methods and Didactics” contains the article about forms of English language teaching in the modern digital environment (by O.K. Ilina).
The section “International Communication” starts with the article about the features of family stories in political discourse (by A.Yu. Pomnikova, M.Yu. Velichko). The section is followed by the article about communicative imposition in University prose (by O.L. Zabolotneva, I.V. Kozhukhova). The next article concerns the methods of studying evaluation through the perspective of the academic research (by A.A. Vodyanitskaya).
The section “Theory and Practice of Translation” presents the article about specifics of translation of the French impersonal construction in the light of the theory of the syntactic concepts (by V.A. Fedorov, O.G. Nekhaeva).
The first article of the section “Linguistics” is by the Doctor of Philology, Professor
Elena N. Malyuga and aspirant of Foreign Languages Department of the Faculty of Economics Elena I. Madinyan (Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia, Moscow). It is concerned with lexical-and-semantic research of anthropomorphic metaphor on the material of the American media discourse. The usefulness of the metaphor analysis in the political discourse is justified, 6 thematic groups incorporating subgroups are revealed. The authors point out that the use of anthropomorphic metaphor in the political discourse in an effective means to influence the recipient.
The first part of the article of the Director of the Institute of the German Language and Literature (Karlsruhe University, Karlsruhe Pedagogical Institute, Karlsruhe, Germany) Frank Kostrzewa contains the results of contrastive-and-linguistic analysis of the German language in the view of the studying of the verbal-and-nominative word combinations (morphology, structure, replaceability, recognition, anaphoricity, modifying, positional features), the differences in the use of the professional and colloquial language are revealed. Attention is paid to the precision and economizing of the choice of word combinations in oral professional communication.
The article of the PhD in Philology, Associate Professor Svetlana N. Stepura (National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk) presents the system of special language means, relevant for the modernistic literature. The analysis was conducted on the material of the J. Joyce's novel “Ulysses”, possessing originality of the linguistic interpretation. Violation
6
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
of the linguistic norm, in the author`s opinion, contributes to its intensive aesthetic-and-artistic influence to the reader.
The article of the Doctor of Philology, Professor Irina P. Lapinskaya, Associate Professor Marina A. Denisova and teacher Maria A. Manukovskaya (Voronezh State Technical University, Voronezh) outlines the variants of special vocabulary and grammatical forms of the different styles of the objects of business. Special vocabulary of nominations generates new language units, which are worth paying special attention to and can make the basis of the future promising researches.
The section “Methods and Didactics” contains the article of PhD in Philology, Associate
Professor Olga K. Ilina (Moscow State Institute of International Relations, Moscow), in which the author analyzes blended methods of teaching, which put self-study and artistic activity of students in the center of educational process. Individualization of the process of teaching attributes to greater importance to a teacher as a tutor and an assistant, who pays more attention to the interests and abilities of every student. It is important to note that traditional system of teaching is the least oriented to reveal artistic potential of students and at the same time to consider their abilities and need for knowledge.
The section “International Communication” is represented by four articles of different question area. In the first publication of the PhD in Philology, Associate Professor Anna Yu. Pomnikova and Master’s Degree student Maria Yu. Velichko (Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok) analyses the features of family stories of the politicians on the material of the political discourse. Having determined the term “family stories” the authors present the complex of syntactic and lexical methods which can be derived into 9 thematic groups. Use of family stories in the political discourse contributes to creation of positive image of a political figure and is aimed at their promotion and success in social activity.
In the article of PhDs in Philology, Associate Professors Oksana L. Zabolotneva and Irina V. Kozhukhova (Chelyabinsk State University, Chelyabinsk) the authors consider the linguopragmatic features of aggravation of impositivity in artistic discourse. The authors note that aggravation of impositivity is achieved with the help of interrogative sentences with particles, corresponding lexical units, prosodic and emphatic means, the purpose of which is to achieve the desired reaction from the interlocutor. The originally undertaken research appears to be noteworthy and contributes to pragmatics.
The article of PhD in Philology, Associate Professor Albina A. Vodyanitskaya (Moscow State Pedagogical University, Moscow) offers, along with the already existing traditional and innovative methods of assessing academic discourse, to take into account the psychological aspect. The author doesn’t abandon the triad method proposed by J. Martin for dramatic discourse that can also be adapted for the estimated value of everyday speech in academic discourse. The author proposes an algorithm for studying assessment (of six positions) in the analysis of academic discourse.
In the article of the section "Theory and practice of translation" Doctor of Philology, Associate Professor Valery A. Fedorov and Associate Professor Olga G. Nekhayeva (Voronezh State Technical University, Voronezh) analyze the form and content of Russian structural diagrams in relation to the il y a construction. The dependence of the translation of the French construction on the syntactic concept which it expresses in the French language is noted. The difference in the syntactic concepts of the Russian and French languages makes it possible to reveal the national specificity of this structure, which lies in the fact that it can be used to convey the proposition of some Russian syntactic concepts.
The Scientific Overview is presented by the publication of PhD in Philology, Associate Professor Irina Yu. Lavrinenko and PhD in Philology, Senior Lecturer Yulia S. Konovalova (Voronezh State Technical University, Voronezh) about the lecture on the strategy of state support for advanced University research in Germany, organized on January 28, 2021 by the Institute of Foreign Languages of the Moscow City University in an online format.
7
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
The current issue of the Journal contains relevant works of Russian scientists working in 7 Universities in Russia: in Moscow (Russian State University of Peoples' Friendship, Moscow State Institute of International Relations, Moscow City Pedagogical University), in Tomsk (National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University), in Vladivostok (Far Eastern Federal University), in Chelyabinsk (Chelyabinsk State University), in Voronezh (Voronezh State Technical University) and an article by the director of the Institute of German Language and Literature from the Federal Republic of Germany, Karlsruhe, Prof. Frank Kostrzewa (Karlsruhe University, Karlsruhe Pedagogical Institute).
We believe that varied subject matters of the articles of the issue № 2 (33), 2021 will be interesting for a wide range of readers. We would like to invite Russian and international scientists (Post-graduates, applicants, PhDs and Doctors of Sciences and other specialists) to publish the results of their researches in the forthcoming issues of the journal.
Editor-in-chief of the Scientific Journal “Modern linguistic and methodical-and-didactic researches” of Voronezh State Technical University, Doctor of Philology, Associate Professor, Head of the chair of foreign languages and translation technology
Valery A. Fedorov
8
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
LINGUISTICS
DOI 10.36622/MLMDR.2021.10.32.001
UDC 801.3:811.111:008
REPRESENTATION OF EVENTS IN THE AMERICAN NEWS MEDIA DISCOURSE
E.N. Malyuga, E.I. Madinyan
____________________________________________________________________________
Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia,
Doctor of Linguistics, Professor, Head of Foreign Languages Department, Faculty of Economics
Elena Nikolaevna Malyuga e-mail: malyuga-en@rudn.ru
Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia
Aspirant of Foreign Languages Department, Faculty of Economics Elena Igorevna Madinyan
e-mail: madinyan-ei@rudn.ru
____________________________________________________________________________
Statement of the problem. The paper uses the material of articles from the American news media discourse to explore the lexical and semantic aspects of metaphors, metaphorical models and thematic groups related to anthropomorphic metaphor, since this figure of speech based on the properties of people and their activities is one of the most common tools for manipulating consciousness.
Results. The article analyzes the main characteristics of media discourse as a means of information exchange. Metaphors are also examined from the point of view of the lexico-semantic approach. The expediency of the analysis of the anthropomorphic metaphor within the framework of the political media discourse is justified, since political processes are presented taking into account the simplification and identification with the human body. The six most common thematic groups that constitute the anthropomorphic metaphor are the following: somatic, social, household, religious, sexual, and emotional. Then, they are divided into such subgroups as human body parts and organs, crime, social hierarchy, construction, agriculture, cooking, clinning, heaven and hell.
Conclusion. The use of anthropomorphic metaphors in political media discourse is conditioned by the necessity to influence a recipient through implicit comparison of some naive phenomena from everyday life with political processes inside and outside the country. The largest number of examples are found in the somatic, social, and household thematic groups, that indicates a tendency to present news by implicitly equating them to the structure and functions of human body, routine, and interpersonal relationships.
Key words: media discourse, metaphor, metaphorical model, anthropomorphic metaphor, lexico-semantic approach.
For citation: Malyuga E.N. Representation of events in the American news media discourse / E.N. Malyuga, E.I. Madinyan // Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-didactic Researches”. – 2021. - № 2 (33).
– P. 9-18.
Introduction.
Media discourse is one of the most common forms of expression of a language in the modern world, with its total volume exceeding the volume of speech in other areas of human activity. Mass media today act not just as a method of conveying information but also as a method of impact. One of the key goals of mass media is to form a notion of a certain phenomenon with the view to influence the recipient’s attitude to certain events and model their subsequent behavior as a part of society.
To achieve its goals mass media use both verbal and non-verbal means.
_________________________________
© Malyuga E.N., Madinyan E.I., 2021
9

Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
One of the most compelling and effective tools of influencing the human subconsciousness is the metaphor. The metaphor does not affect the recipient directly but through associations. An implicit comparison conjures up a number of associations in the recipient’s mind and is the most efficient tool, since the recipient is not yet aware that they have been lumbered with a certain point of view and think that they have arrived at it autonomously. At the moment, mass media actively employ various metaphorical models in their reporting with the purpose to impose their opinion upon recipients through imbuing it with positive or negative connotations inherent in a certain metaphorical model.
Research Methodology.
The objects of this research are metaphors and the metaphorical representation of events. The subjects of the research are the lexical and semantic singularities of metaphors in the news media discourse.
The purpose of this study is to explore the metaphorical representation of events and identify the lexical and semantic specifics of metaphors in the American new media discourse.
The expediency of the research is justified by the fact that during an information war such a phenomenon as the manipulation of consciousness become rife. The exploration of the means through which the manipulation happens makes a certain input into the development of the theoretical and practical foundation of this field. Of relevance is also the integrated approach to the problem of commonalities and differences between the American and British linguaculture as reflected in metaphorical words and expressions.
The material of the research includes 353 articles selected from the American news reporting website CNN.com.
The study uses the following linguistic methods: the partial selection method, the content analysis method, the descriptive method, the stylistic analysis method, and the classification method.
Research Results.
1. The lexical-semantic approach to studying news media discourse. An increasing number of studies of language in modern-day linguistics are based on its internal systemic organization. [1, p. 76] When carrying out a semantic analysis, one needs to, along with factoring in language categories, take into account the objective world, as it is reflected on the lexical level and performs the cognitive function. The lexical-semantic approach poses an interest for this study, as it allows us to not only single out the semantic metaphor groups but also to analyze them from the perspective of the lexical meaning of the word, its stylistic connotation, identify its semantic nature, as well as study their functioning in an extralinguistic world. [2, p. 60]
The lexical-semantic approach allows studying language means that reflect the mentality and worldview of a certain nation. In our time, it has become possible through media discourse, which is characterized by an active use of various linguistic means.
The scientific study of media discourse that emerged in the mid-20th century traces its origin to the following Russian and foreign researchers: S.I. Bershtein, D.N.Shmelev, V.G. Kostomarov, Yu.V.Rozhdestvenskiy, G.Ya. Solganik, S.I. Treskova, I.P. Lysakova, V.G. Krivenko, A.N. Vasilyeva, Teun Van Dijk, Martin Montgomery, Alan Paul Bell, Norman Fairclough, Robert Fowler and others.
In this study we rely upon the definitions by E.A. Kozhemyakin, according to whom media discourse is a thematically focused, socioculturally conditioned verbal and cogitative activity in the mass media space. [3, p.13]
Media discourse belongs to the type of information exchange that is fulfilled through a broadcasting platform in the oral or written form. This information is oriented towards the reader, listener or viewer who is not present. Although the discourse is targeted at the recipient, the producent often does not receive their instant reaction due to its non-spontaneous nature. [4,
10
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
p.58] According to Anne O’Keefe, mass media discourse is a public, fabricated and recorded information exchange. It is neither accidental and spontaneous, nor is it confidential. However obvious these primary characteristics may seem, they play a crucial role in studying, describing and understanding media discourse. [5, p. 441]
It is worth mentioning that according to T.G. Dobrosklonskaya, there are three following main types of media presentations: a reflection, a reconstruction, and a myth. [6, p.6] The most important one for the media discourse is the “reflection” type, as it implies a credible reproduction of events that is most approximated to reality and is corroborated with facts, which in turn is the main goal of news media discourse. This type of media representation also performs an informative function. [7, p.72]
As far as the characteristics of media discourse, the news media discourse, according to N.I.Klushina, is where the most verbal word combinations were found. Passive forms and structures are very common. The use of Passive Voice is necessitated by the intention of the producent to represent an event in an objective form and avoid subjectivity. [8, p.82]
Passive Voice is also important for the expressions of ideology, as it allows highlighting the key points in the message, drawing the readers’ attention to the specific aspect of the news message. This property of the Passive Voice is pointed out by many English-language authors working in the traditions of critical linguistics, such as M. Billing [9, p. 792], P.S. Molina [10], N. Fairclough [11, p. 168], S.MacGregor [12] and others. They express an important idea that the choice of various language means for the purposes of expressing a certain content in mass media is ideologically justified.
Let us illustrate this fact with a quote from Martin Montgomery, a media discourse researcher: “Basically, reality is not ‘out there’, easily available to be grasped in any straightforward and simple way, it is socially constructed, with language playing a centrally important role, so that the patterning of vocabulary and sentence structure shows us reality in a particular light and guides our apprehension of it...”.
Also, in light of a highly organized thematical structure, the media discourse is characterized by cliches. That is, journalists often use the same cliched expressions due to the timerelated constraints.
F. Jungerer points out two constituent elements of media discourse: the standard and the expression. [14, p. 48] The standard part includes all the previously mentioned points (cliches, verbal structures, etc.), while the expressive part is any other structure allowing deviation from the standard.
Hence, media discourse embraces two opposing tendencies: a continuous renewal and commitment to sustainable forms of expression.
The language of American political media discourse is characterized by the use of various lexical and stylistic means, such as metonymy, metaphor, synecdoche and others. One of the most frequent means is metaphor. It performs a number of functions, which, apart from the worldview and attracting the listeners’ attention, also include the ability to produce a subconscious impact on the recipient.
1.1.The Semantic Classification of Metaphors in the News Media Discourse.
In this paper we give preference to the semantic metaphor classifications developed by V.P.Moskvin [15, p. 67] and A.P. Chudinov [16, p.14]. The scholars have proposed a classification of metaphors that is based on the thematical attribution of an additional subject (i.e. consistent with the thematical attribution of an underlying comparison upon which they are based).
The semantic classification, according to the above mentioned scholars, is one of the most efficient ones, because it provides an ample field for research. In the context of this classification, of the primary interest is the two-dimensional semantic nature of the metaphorical sign, i.e. its ability to point to the main and auxiliary subjects. [16. P.19]
11
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
Basing on the attribution of the image vehicle (the auxiliary subject) to the terminology system of a certain domain, researchers traditionally single out the following groups of metaphors: medical, anthropomorphic, theatrical, gambling-related, artefact-based, biological, etc.
In this research we study lexical units that are classified as the anthropomorphic metaphor, thanks to which humans may structure their knowledge about the world by transferring the principles of organization and functioning of their own body upon it.
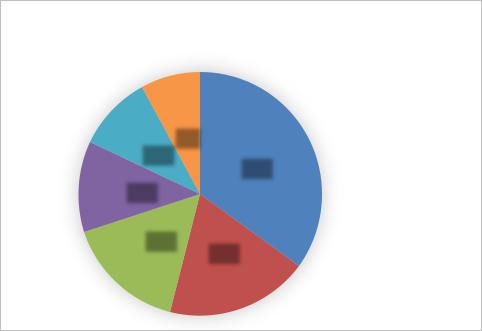
One of the findings of the study was that the semantic model of anthropomorphic metaphor in the CNN’s news media discourse is comprised of the following thematical groups: somatic, social, household, religious, emotional and sexual metaphors. The quantitative ratio of these groups may be illustrated by the following diagram.
Thematic Groups of Anthropomorphic Metaphor
in American Political Media Discourse
8% |
|
|
|
Somatic |
|
|
|
||
10% |
|
|
|
Social |
|
35% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12% |
|
|
|
Household |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Religious |
|
|
|
|
|
16% |
|
|
|
Sexual |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Emotional |
|
19% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Thematic Groups of Anthropomorphic Metaphor in American Political Media Discourse
According to the diagram, the most common metaphor is the somatic metaphor (35%), followed by the social metaphor (19%), and then – with bigger margins – by the household, religious, sexual and emotional metaphors. Let us examine those groups in more detail.
2.1. The Somatic Metaphor
From the earliest times people have considered human body as a source of experiencing and comprehending the world – people tend to perceive the surrounding reality through the lens of their own body with its characteristics. This format is particularly significant for studying the culture of a certain people, since it forms the somatic cultural code. [17] Somatic metaphors are often used in political news media discourse depicting politics as a human body in order to convince the reader or listener that political processes are relatable and accessible to the layperson and that they are guided by the same laws or principles as the human body.
Let us analyze several examples of somatic metaphors from the perspective of the lexicalsemantic approach.
The West, led by the United States under President Barack Obama, h a l f - h e a r t e d l y backed the effort to topple Assad's regime but d i d n ' t h a v e t h e s t o m a c h for it in the end [1*]. – Запад, возглавляемый Соединенными Штатами при президенте Ба-
12
Scientific Journal “Modern Linguistic and Methodical-and-Didactic Researches” |
Issue 2 (33), 2021 ISSN 2587-8093 |
|
|||
раке Обаме, б е з |
о с о б о г о э н т у з и а з м а поддержал усилия по свержению ре- |
||||
жима Асада, но в |
к о н ц е к о н ц о в |
н е |
р е ш и л с я на это. |
||
"I just want to, you know, g e t i t o f f |
m y |
c h e s t in case something does happen," the |
|||
woman said, according to a transcript of the January 5 call reviewed by CNN [2*]. –
«Знаете, я просто хочу о б л е г ч и т ь д у ш у на случай, если все же что-то случится», – сказала женщина, согласно стенограмме звонка 5 января, рассмотрен-
ной CNN.
In the examples above we have encountered somatic metaphors referring to parts of human body – the chest, as well as the heart and the stomach. All three examples above have an idiomatic nature and are highly figurative. The metaphor to get something off one’s chest → излить/облегчить душу is expressed through a lexical idiom. As we can see from the translation, the phraseological equivalents of the English and Russian languages do not match, i.e. different lexical means are used to express one meaning: chest (грудь) → soul (душа), which points to the fact that in English the chest (грудь) performs the functions of the soul (душа) in some aspects. Depending on the context, the chest in the American national consciousness is associated with both a burden and a support, a relief as well as with something sacred. One of the meanings of this lexical unit is “a container, a case, a casket, a cage” («контейнер, сундук,
ларец, клетка»). For example, in the metaphorical idiom to keep one's cards close to one's chest → не раскрывать свои планы, the “chest” combines both meanings: a casket where you should contain your intentions, and the anatomical chest.
During the metaphorical transfer body organs often come to express properties or traits of human character, such as courage or lack of it, indecisiveness, lack of confidence, reluctance to do something, etc. Every organ of the human body is responsible for a certain quality or an emotion. Thus, the “heart” is the center of a wide range of emotions and symbolizes feelings, emotions, and moods. In the first example, the lexeme half-heartedly means “indecisively, with mixed feelings”. The use of an adverb accentuates the attempt to show how the efforts were supported, while the prefix half- is responsible for the main semantic message of this lexical unit, because it is the prefix that adds the meaning of reluctance. This image is further fixated through the use of the metaphorical idiom didn’t have the stomach → не решаться на чтото, which also indicates lack of courage that is characteristic of the digestive body organs in the English and Russian languages. For example, he doesn’t have guts → у него кишка тонка.
2.2. The Social Metaphor
Another type of anthropomorphic metaphor is the social metaphor, which is connected with human hierarchy, social relations, the social structure of the man-made world, etc. In this paper, this thematic group is presented through the metaphorical models “criminality” and “social hierarchy”. Let us examine the “criminality” model using the following example:
And I would tell the international community that if they have decided, with Bashar alAssad, to kill us all, then please have mercy on us and make it fast. Because we're tired of waiting our turn o n d e a t h r o w [3*]. – И я бы сказал международному сообществу, что если они решили вместе с Башаром Асадом убить нас всех, то, пожалуйста, сжальтесь над нами и сделайте это быстро. Потому что мы устали ждать своей очереди в к а м е р е с м е р т н и к о в .
This fragment talks about the residents of Syria who spend every day in anticipation of death. The news use the metaphor death row → камера смертников (a part of prison where the inmates await death penalty), as Americans perceive Syrians and, by extension, all adherents of the Islamic faith as potential suicide bombers and criminals. As a result, this perception has entrenched in the national worldview so deeply that Americans still use prison-related vo-
13
