
Методическое пособие 651
.pdfSource: Merriam-Webster. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: URL: https://www.merriamwebster.com/dictionary/ (время обращения – 15.08.2017).
Task 5. Match the beginning and the ending of the sentences:
1.Crisis management is |
a. such as outside forces or natural disas- |
|
ters |
2.Forecasting potential crises |
b. to respond to a major threat to a per- |
|
son, group or organization |
3.There are events that we have no |
c. a relatively new field of management |
control on, |
|
4.Crisis management responsibilityis |
d. forecast potential crises |
5.Risk management task is to |
e. is the main crisis management activity |
Task 6. Answer the following questions:
1.What events can negatively affect the company?
2.How many categories of crisis are known?
3.Why BP is mentioned?
4.What definition of crisis management is given?
5.What is the difference between risk management and crisis management?
6.What does crisis management include?
7.Whatcanbedonetopreventsomeeventsthatcanleadtocrisisinacompany?
Task 7. Match the sentences below as T (True) or F (False):
1)There are three distinct categories of crisis.
2)Crisis management has been known for a long time.
3)Proactive crisis management is the activities to deal with unpredictable natural disasters.
4)Usually organizations prepare crisis management plan.
5)Crisis management work is closely connected with PR department.
Task 8. a) The text below informs about the steps to deal with the crises. Seven words and word combinations have been removed. Read the text and put the words in the gaps 1-7:
30
Meet the Crisis Head-On
Although every crisis will have unique aspects, there are general principles which apply to most of them. Whatever the crisis, the media, 1) … and, most importantly, your customers and prospects want to know what happened, why, how can it be fixed and howcan customers be compensated.
In most instances where a public relations crisis affects a company, the media will contact either the firm's CEO, the company spokesperson or public relations or 2) … department (if there is one) or some member of senior management. Reporters will ask for explanations and 3) … . Designate a crisis management team or individual, and direct all requests for information to an appropriate member of the group or the appointed spokesperson. Authorize no one else in the company to speak to the media. Internal information about the crisis should only be given to 4) … and or spokesperson to insure that the company speaks with a single, consistent voice.
The public statement should also include how people might be affected by the problem. This would include informing 5) … who might have bought a recalled, flawed or 6) …. In these cases, the company should provide a refund or equal-priced replacement for the product. In some cases, a contaminated product should be disposed of, and customers who have purchased such a product should be properly 7) ….
The CEO, and or technical spokesperson might also offer the media a real time or taped interview in which all questions are answered. A live TV or radio news broadcast with call-in questions is another effective means of handling the crisis.
quotable statements |
media relations |
contaminated product |
informed |
|
management team |
the public |
customers |
members of the crisis |
|
Source: Investopedia. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: URL: http://www.investopedia.com/articles/financial-theory/10/crisis-management.asp (время обращения – 15.08.2017).
b)Answer the following questions:
1.What should a head of the company do in the case of public relations crises?
2.What information should a public statement include?
3.Name the positions who usually deal with media in the case of crisis?
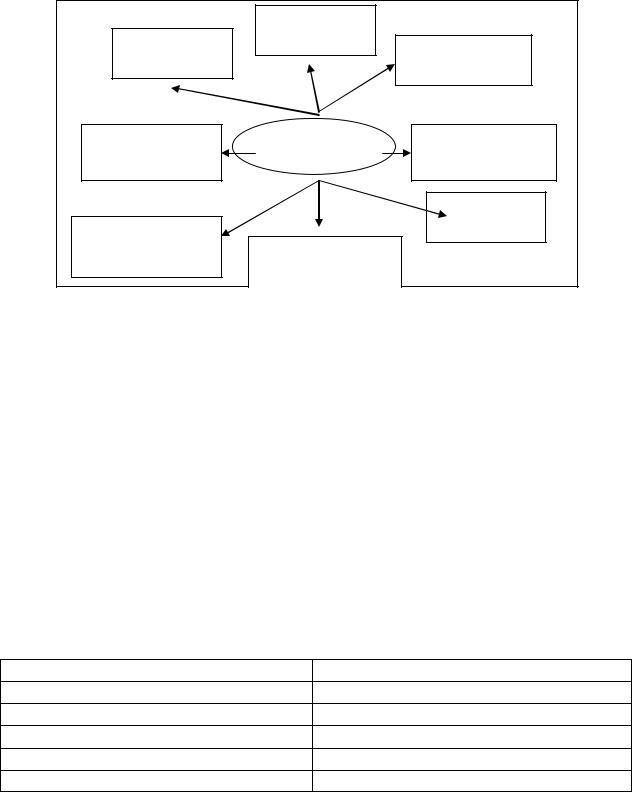
Task 9. Usually business faces many pressures from the external environment.
a)Look at the diagram below that shows these types of impact. Match each point with the example given below:
b)Rank the impacts in the rank of importance (0 – the least important, 8 – the most important). Explain your choice.
31
|
international |
|
competition |
environment |
technological |
factors |
|
|
|
environment |
|
|
|
|
environmental |
A company |
consumer |
pressures |
|
needs/wants |
|
|
industry en- |
government/ |
domestic envi- |
vironment |
legal factors |
|
|
|
ronment |
|
1.Other business offer similar or better products of services.
2.Globalization offers opportunities to export more goods or services.
3.The target market changes because of demographic factors.
4.New laws affect product design.
5.Products become out-of-date due to new inventions.
6.Product cost increase because of differences in getting raw materials from the ecologically sensitive areas, e.g. rain forests.
7.Changes in fashion among target markets.
8.The product is new and specialized and the market is growing.
Task 10. Look at some possible bottlenecks that may be produced and their solutions. Fill in the gaps with the correct words below. Match the bottleneck with possible solution:
a group, disagreement, methods, leader evaluate, personality, skills,:
|
Bottlenecks |
|
Solutions |
1) |
… difference within a group. |
a) |
Redefine goals or working … . |
2) |
Conflict between groups. |
b) |
Compare and … options. |
3) |
… on ideas or what to do. |
c) |
Appoint a mediator. |
4) |
Conflict within … . |
d) |
Improve communication … . |
5) |
Failure to act or produce results. |
e) |
A … should intervene. |
Source: Simon Sweeney. Series Eddition: Nick Brieger. Professional English Management, 2-nd imprssion 2002, First Published 2002, Pearson Education Limited, Edinburg Gate, Harlow, Essex CM20 2JE, England. Section 2. Unit 12.
32

Task 11. Below are some hypothetical crises that the company may face. Choose one of them and work out the plan to manage them. Make the presentation of your plan.
a)
c)
b) |
d) |
Crisis Management in Action
Look at the experience of crisis management of some world famous corporations. How effective was their strategy? Present your overview in a form of presentation.
UNIT 6
TIME MANAGEMENT
Task 1. Discuss the following questions:
1.Are you good at time keeping?
2.What do you know about procrastinating?
3.How can time management affect the success of a company?
Task 2. Read and interpret the expressions below. Which of them sound more appealing to you?
1.The early bird catches the worm.
2.There is no time like the present.
3.Better late than never.
33
Task3.Readand memorizethewordsbelow thatwillhelpyouunderstandthetext.
1.notion [ˈnəʊʃən ] - понятие
2.raise [reɪz ] -повысить
3.time tracker - инструмент для отслеживания рабочего времени
4.implementation [ˌɪmplɪmenˈteɪʃən ] - выполнение
5.require [rɪˈkwaɪə] - требовать
6.delegation [dɛlɪˈɡeɪʃən] – передача полномочий
7.authority [ɔːˈθɔrɪtɪ ] – власть, полномочия
8.assets [ˈæsɛts ] – активы компании
9.success [səkˈsɛs] - успех
10.preliminary [prɪˈlɪmɪnərɪ] - предварительный
11.strategy [ˈstrætɪdʒɪ] - стратегия
12.cost-effectiveness [ˌkɒstɪˈfektɪvnɪs ] – экономическая эффективность
13.profitability [ˌprɒfɪtəˈbɪlɪtɪ] – прибыльность, рентабельность
14.personnel [ˌpɜːsəˈnɛl ] - персонал
15.obvious [ˈɒbvɪəs ]- очевидный
Task 4. Read and translate the text.
The Time Management of a Company
The notion of time management includes all the technologies of planning, which are used by an employee by himself to raise the effectiveness of using working time. Time tracker reports sometimes present disappointing results of employers. That is why nowadays there are more and more companies which realize a need in centralized corporateimplementationoftime managementtechnologies.
The necessity of a corporate implementation of time management is conditioned by the following reasons:
1.Growing movement of changes of economic environment require delegation of authorities to employees, their quick decisions and their independent planning of work.
2.Non-material assets of companies are getting more and more valuable. The effectiveness of work of managers and other staff members become the most important factorofsuccessofacompany.
3.Most companies nowadays often change the direction of their development. Employees should be flexible to constant changes and be able to a high level of self control.
Time management training. The first step to have effective and highly organized
employees is to teach them. Your task is to make a preliminary analysis of the effectiveness of each employee. A time tracker will help you to prove that it’s not quite correct. After training your task will be to set a testing period during which employ-
34
ees will try to do as much as they can to be more effective using the main strategies of time management.
Time management skills diagnostics. Not only time tracker reports can show the progress after training. There’s a special analysis of skills of time management employees got.
There are three levels of competence which each staff member should have. They are:
Personal time management
Time management in a team
Corporate time management
Cost-effectiveness of time management implementation is very important when profitability of a company depends only on the effectiveness of personnel. The results of training can be obvious in a time tracker report which includes the data about a personal effectiveness of an employee. Time management strategies will help your staff members to raise their effectiveness and to bring more profit to your business.
Source: Crocotime. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: URL: https://crocotime.com/en/time- management-of-a-company/ (время обращения – 17.08.2017).
Task 5. Make the word combinations out of the words in columns:
1.time |
a. |
of authorities |
2.economic |
b. |
assets |
3.delegation |
c. |
tracker |
4.non-material |
d. |
control |
5.self |
e. |
diagnostics |
6.analysis |
f. |
environment |
7.staff |
g. |
of the effectiveness |
8.skills |
h. |
members |
Task 6. Match the sentences below as True or False:
a)Nowadays time management is not important for a company.
b)Non-material assets grow and affect the success of a company.
c)Time management help to adapt to the changes in the business environment.
d)Staff management should have at least one level of competence.
e)Sometimes the effectiveness of a business depend only on the work of a per-
sonnel.
Task 7. Answer the following questions.
1.How is time management explained in the text?
2.What time management technology is mentioned?
35
3.What factors is time management conditioned by?
4.What does time management training include?
5.What levels of competence should the staff have? Which of them are the most importantfor you?
6.What is a time tracker report?
7.What is supposed result of time management strategies?
Task 8. a) Study the table with the prepositions of time:
at |
|
on |
in |
during |
Night/the week- |
Sunday, |
Monday, |
The morning/ af- |
a whole period of |
end |
etc. |
|
ternoon, evening |
time |
Five |
Friday night, etc. |
The |
An event or activi- |
|
o`clock/2.45 |
|
|
spring/summer, |
ty (a visit, flight) |
p.m., etc. |
|
|
etc. |
|
|
Sunday |
morning, |
January, February, |
|
|
etc. |
|
etc. |
|
|
21st May, 22d |
The sixties, etc. |
|
|
|
June, etc. |
|
|
|
on time (at a right time) in time (before it`s too late)
Example: I went to railway station in time, cause I knew my train always departed on time.
b)Choose the correct preposition in the sentences below:
a)I work best at/during night.
b)We have a big family meal on/in Thanksgiving Day.
c)I start work every morning at/on 9 a.m.
d)I usually get home in/on time to read my children a bedtime story.
e)I never have a nap at/in the afternoon.
f)My birthday is at/in March. In fact it is in/on 6-th March.
g)I swim in the sea as much as possible during/at my holidays.
h)My boss never starts meeting in/on time. She is always late.
i)I did a lot of sightseeing in/during my last trip abroad.
j)My neighbor was born in/at the fifties.
Sources: Sue Kay, Vaughan Jones, Inside Out, New Upper-Intermediate, Macmillan, 2009. 158 p. p. 49.
36

Task 9. Most people can improve their time management skills. Match the action (1-5) with its meaning and the example:
Action |
Meaning |
Example |
1. plan |
A. improve your abilities |
a) A colleague asks you to |
|
|
go to a meeting – but it is |
|
|
not absolutely necessary. |
|
|
You make an excuse and |
|
|
do not go. |
2. delegate |
B. organize |
b) You write appoint- |
|
|
ments, deadlines and ac- |
|
|
tions in your diary. You |
|
|
know what you have to do |
|
|
for a week. |
3. upgrade skills |
C. order things according |
c) A new project has to be |
|
to importance |
carried out. You do not |
|
|
have time to run it. You |
|
|
ask someone else to do it. |
4. prioritize |
D. say no |
d) You decide that writing |
|
|
a report for your boss is |
|
|
the most important job to- |
|
|
day. Do that, then do |
|
|
something else that is ur- |
|
|
gent, but less important. |
5. turn down requests |
E. get somebody else to |
e) You sign up for an in- |
|
do something |
service training seminar |
|
|
on Time Management. |
Source: Simon Sweeney. Series Eddition: Nick Brieger. Professional English Management, 2-nd imprssion 2002, First Published 2002, Pearson Education Limited, Edinburg Gate, Harlow, Essex CM20 2JE, England. Section 2. Unit 16.
Time Management in Action
Make presentation of Time Management Techniques that you think are useful for:
a) work; b) studies.
37

UNIT 7
RISK MANAGEMENT
Task 1. Discuss the following questions:
1.What are possible dangers to the successful operation of a company?
2.What ways to deal with risks are there?
3.What offices take responsibility at dealing with
risks?
Task2.Readand memorizethewordsbelow thatwillhelpyouunderstandthetext.
1.identify [aɪ`entɪfaɪ ] – определять
2.respond [rɪ`spɑnd] – отвечать
3.objective [əb`dʒektɪv] – цель
4.imply – предполагать
5.require – требовать
6.schedule – график, расписание
7.employee – работник, подчиненный
8.proactive – предвосхищающий события
9.reactive – реагирующий, противодействующий
10.contingency plans - план действий в чрезвычайных обстоятельствах
11.due date - срок выполнения
12.approach – приблизиться
13.deadline – придельный срок
14.quantify – подсчитать
15.acceptable – допустимый
16.tolerance level – допустимый уровень
17.continuous – продолжительный
18.budgeting – составлять бюджет
19.diminish – уменьшать
20.assess – оценивать
21.improve – улучшать, увеличить
22.jeopardize – подвергать опасности
23.gut feel – шестое чувство, инстинкт
24.unpredictable – непредсказуемые
25.violate - нарушать
26.commitment - обязательство
Task 3. Read the text to understand the nature of Risk Management.
Risk Management: its Essence, Reasons and Types
38
Risk Management is the process of identifying, analyzing and responding to risk factors throughout the life of a project and in the best interests of its objectives. Proper risk management implies control of possible future events and is proactive rather than reactive.
For example:
An activity in a network requires that a new technology be developed. The schedule indicates six months for this activity, but the technical employees think that nine months is closer to the truth. If the project manager is proactive, the project team will develop a contingency plan right now. They will develop solutions to the problem of time before the project due date. However, if the project manager is reactive, then the team will do nothing until the problem actually occurs. The project will approach its six month deadline, many tasks will still be uncompleted and the project manager will react rapidly to the crisis, causing the team to lose valuable time.
Risk Management Systems are designed to do more than just identify the risk. The system must also be able to quantify the risk and predict the impact of the risk on the project. The outcome is therefore a risk that is either acceptable or unacceptable. The acceptance or non-acceptance of a risk is usually dependent on the project manager’s tolerance level for risk.
If risk management is set up as a continuous, disciplined process of problem identification and resolution, then the system will easily supplement other systems. This includes; organization, planning and budgeting, and cost control. Surprises will be diminishedbecauseemphasiswillnowbeonproactiveratherthanreactivemanagement.
The purpose of risk management is to:
Identify possible risks.
Reduce or allocate risks.
Provide a rational basis for better decision making in regards to all risks.
Plan.
Assessing and managing risks is the best weapon you have against project catastrophes. By evaluating your plan for potential problems and developing strategies to address them, you’ll improve your chances of a successful, if not perfect, project.
Once the Project Team identifies all of the possible risks that might jeopardize the success of the project, they must choose those which are the most likely to occur. They would base their judgment upon past experience regarding the likelihood of occurrence, gut feel, lessons learned, historical data, etc.
Early in the project there is more at risk then as the project moves towards its close. Risk management should therefore be done early on in the life cycle of the project as well as on an on-going basis.
To deal with risk management first we need to look at the various sources of risks. Various sources of risk include: Project Management (too many projects going on at one time, impossible schedule commitments, unrealistic planning and scheduling, no one person responsible for the total project, etc.), Unpredictable (natural disasters), Predictable (market or operational risk), Technical (Technology changes), Legal (violating trade marks and licenses), and others).
39
