
Методическое пособие 651
.pdf
Some people in an organization have colleagues who help them. This is known as staff position. Its holder has no line authority and is not integrated into the chain of command.
Yet the activities of the most companies are too complicated to be organized into a single hierarchy. Today most large manufacturing organizations have a functional structure, including production, finance, marketing, sales and personnel or human resources department. This means, for example, that production and marketing departments cannot take financial decisions without consulting the financial department.
Functional organization is efficient, but there are two standard criticisms. Firstly, people are usually more concerned with the success of their department than that of the company. Secondly, separating functions is unlikely encourage innovation.
An inherent problem of hierarchies is that people at lower levels are unable to make important decision but have to pass their responsibility to their boss. One solution to this is matrix management in which people report to more than one superior. This is one way of keeping authority at lower level. A further possibility is to have wholly autonomous temporary groups or teams who are responsible for entire project and split up as soon as they are successfully completed.
Source: Ian MacKenzie, A course for Business Studies and Economics students. — 2nd edition. — Cambridge University Press, 2002. — 206 p.p. 21-22.
Task 5. Match the Russian and English equivalents:
1. increasing |
a. сложный |
2. chain of command |
b. эффективный |
3. complicated |
c. вдохновлять |
4. personnel department |
d. увеличивающийся |
5. efficient |
e. решение |
6. encourage |
f. отдел кадров |
7. separating |
g. цепочка команд |
8. solution |
h. разделение |
Task 6. The letters in the words below are mixed. Guess what word is ciphered in eachpoint:
a) ONRGIZANTAIO b) ETMRPROAY c) POLPEE d) CIANH e) ATYOURTHI
Task7.Fillinthegapsbelow withthecorrectformoftheverbsTOBEorTO HAVE:
When choosing a career move, whether its your first job out of university or the next step on the ladder, the type of organization you work in 1) … very important. Different sectors 2) … all different and each 3) … their own culture, but the size of the organization 4) … a big factor as well. So far I 5) … worked for companies of 6
10
people, about 120 people, around 2000 people, and now there 6) … about 18 of us at my current workplace. I 7) …. also spoken with friends with different experiences.
The advantages: larger companies tend 8) …better at paying overtime or booking holiday because they 9) … systems to organize this. They 10) …also more set up for supporting employees because there 11) … an HR department and some policies and procedures for getting things sorted out if the need arises.
The disadvantages: large companies, certainly here in the UK, 12) … a bit of a one-size-fits-all attitude to employees. The results tend 13) … silly things such as if one person 14) … thought 15) … covering their poor timekeeping by changing their shift pattern a lot.
Source: Lornajane blog. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: URL: https://lornajane.net/posts/2007/small-company-vs-big-company (время обращения - 23.07.17).
Task 8. Are the sentences below True or False?
1.Hierarchical or pyramidal structure is the structure when people are usually more concerned with the success of their department than that of the company.
2.Staff position is a supplementary department in a company.
3.Functional structure is more widely spread nowadays.
4.Functional structure as only positive points.
5.Peopleatlowerlevelsofhierarchyusuallypasstheresponsibilitytotheirsuperior.
6.In matrix structure the employee reports to more than one boss.
7.Sometimes a company employs temporary group to work on a project autonomously.
Task 9. Answer the following questions:
1.What is specific about pyramidal structure of a company?
2.Can you explain what staff position is? Can you give some examples?
3.What is functional structure?
4.Does functional organization structure have some disadvantages?
5.Are there any ways of keeping authority at lower level?
Task 10. Match the names of the positions with their descriptions:
managing director, executive secretary, sales and marketing manager, sales representative, production manager, personnel manager, R&D manager, finance director, accountant,receptionist.
11
a)someone who keeps the accounts in the finance department
b)someone who does secretarial work for top management
c)someone who sits in the lobby, answers the phone and greets visitors
d)someone responsible for running the company`s financial affairs
e)someone who heads the department responsible for scientific research and the development of new products
f)someone who is responsible for selling the product to the customers
g)someone who heads a company and is responsible for its running
h)someone who head the department that advertises and sells the product
i)someone who head the department responsible for manufacturing the product
j)someone who head the department responsible for staff matters such as the hiring the employees
Task 11. Read the text below about staff position and fill in the gaps with the suitable word of phrase:
responsible (2), target setting, maintenance, difference, functions, delivering, chains, personnel.
Line and Staff Management
Line and staff management has two separate hierarchies: (1) the line hierarchy in which the departments are revenue generators (manufacturing, selling), and their managers are a) … for achieving the organization's main objectives by executing the key b) … (such as policy making, c) …, decision making); (2) the staff hierarchy, in which the departments are revenue consumers, and their managers are d) … for activities that support line functions (such as accounting, e) … , personnel management).
If a company were an army, the line positions would be the soldiers on the front line fighting the daily battles and the staff positions would be the f) … off the battlefield providing support to the soldiers. Line positions directly affect the customer through manufacturing and g) … products and services. Staff positions affect customers indirectly, only to the extent that the support they provide helps line employees improve quality and customer satisfaction.
While both hierarchies have their own h) … of command, a line manager may have direct control over staff employees but a staff manager may have no such power over the line employees. In modern practice, however, the i) … in the two hierarchies is not so clear-cut and jobs often have elements of the both types of functions.
12
Task 12. Make the summary of the text in Russian. Can you explain what the difference between staff and line position is?
Sources: BusinessDictionary. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: URL:
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/line-and-staff-management.html |
(время обращения – |
|||||
22/07/2017). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bizfluent. |
[Электронный |
ресурс]. |
– |
Режим |
доступа: |
URL: |
http://www.ehow.com/info_12075450_line-position-vs-staff-position.html (время обращения - 23.07.17).
Task 13. Answer the following questions. To sound more naturally, use the phrases below:
Well, ... As far as I know…, As far as I can say…, Actually, … In fact…, etc.
1.What kind of organization would you like to work for and why?
2.What department do you find the most prestigious to work in?
3.What structure of a company do you find the most efficient and why?
4.What position would you like to take? Why?
5.What position do you find the least attractive? Why?
6.Do you plan to change departments (positions) over time?
7.Would you like to work for on boss or several bosses? Why?
8.Do you prefer to work alone or be a part of a team? Why?
Source: Ian MacKenzie, A course for Business Studies and Economics students. — 2nd edition. — Cambridge University Press, 2002. — 206 p.p. 24.
13
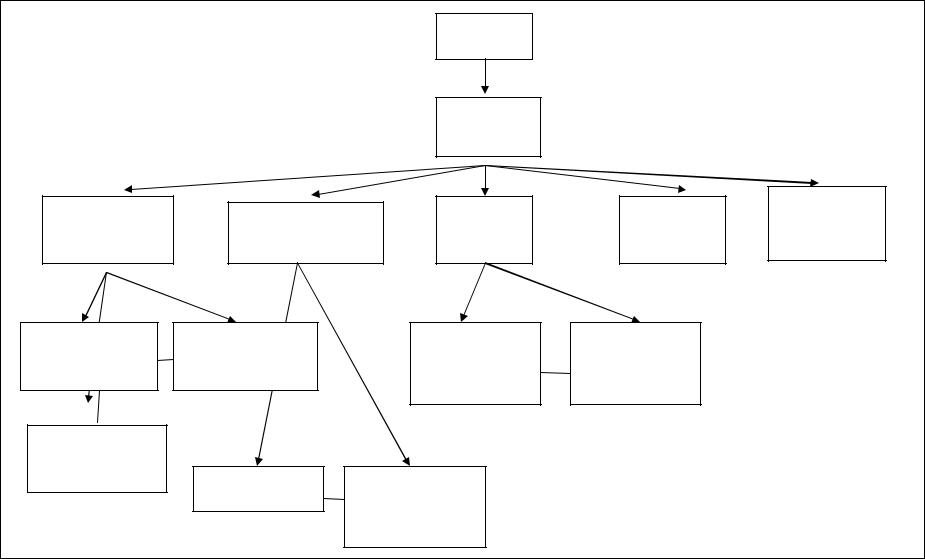
Task 14. Below is the diagram of the structure of a company. Use the information from the diagram and fill in the gaps in the text below:
|
|
|
Board |
|
|
|
|
|
Managing |
|
|
|
|
|
Director |
|
|
Development |
Manufacturing |
Quality |
Marketing |
Field Ser- |
|
vice Manag- |
|||||
Manager |
Manager |
|
Manager |
Manager |
er |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
Mechanical |
Electrical Sec- |
|
Inspection |
Inspection In- |
|
Section Leader |
tion Leader |
|
Process and |
coming Goods |
|
|
|
|
Products |
|
|
Software Sec- |
|
|
|
|
|
tion Leader |
Plant Manager |
Industrial Engi- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
neer Manager |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
Source: Eric H. Glendinning, Norman Glendinning. Oxford English for Electrical and Mechanical Engineering. Oxford University Press, 1995. - 190 p.p. 175-176.
The head of the engineering company in the UK is the … or the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) CEO. If it is an American subsidiary, the head may be known as the Vice President. Unless the man at the top is the chairman of a company, he or she will be responsible to a … or the President (in the UK).
The managers of the various departments report directly to the managing Director. These managers may be referred to as the Management Team. They give Director advice on the effects and results of and decision made by the Board: on the cost, time, materials, personnel, plant, etc.
The … with the support of Mechanical, Electronic and … Sections is responsible for the introduction of new products. The … decides how the new products will be produced. The … and Industrial Engineering Manager report to this member of the Management Team.
The … insures that the products are fault-free and that the component and the materials used in their manufacture meet company standard. The … handles market research, promotion and sales. The Field Service Manager is responsible for installation and maintenance of the company`s products wherever required.
Task 15. Study the phrases in the diagram below and the examples:
Words to describe Company Structure
The most often used: consist of
is composed of contains
is made up of includes
is divided into
Examples: The company consist of five main departments
The finance department is made up of five units.
The R&D department is made up of three units.
to be in charge of
to support or to be supported by to be accountable to
to be responsible for
to assist or to be assisted by
Examples: The human resources department is in charge of hiring and firing
The finance department in responsible for counting the assets and losses.
The assistant manager is accountable to the senior manager.
15
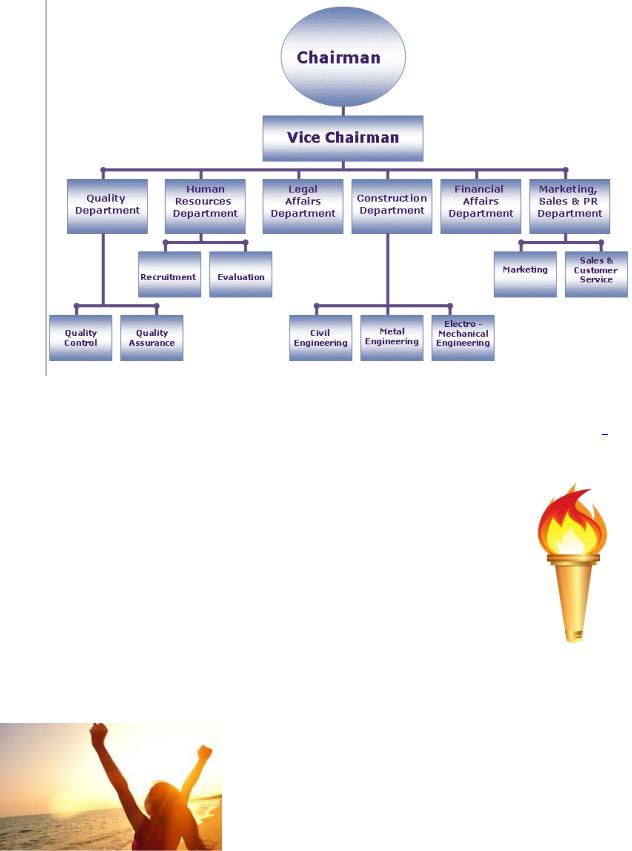
Task 16. Use the phrases given above to describe the structure of the company below:
Source: Яндекс. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://yandex.ru/images/search... (время обращения: 24.07.2017).
The Structure of a Company in Action
Think about the company you know well. Describe its structure. How can the structure influence the company`s performance? Can you offer any improvement in its structure? Prepare the overview as a presentation.
UNIT 3
MOTIVATION
Task 1. Discuss the following questions:
1. What can motivate people do their job (acceptable salary, good working conditions,
nice working environment, prestige, social status, benefits (company car, accommodation, etc., promotion, etc.)) ?
2. What is a good motivator for you (to study or to work)?
3. What can be done to motivate people?
16
Task2.Readand memorizethewordsbelow thatwillhelpyouunderstandthetext.
1.labour relations [ˈleɪbə rɪˈleɪʃən] – отношения в рабочем коллективе
2.working conditions [ˈwɜːkɪŋ kənˈdɪʃən] – условия работы
3.wages [weɪdʒiz ] – заработная плата
4.benefits [ˈbɛnɪfɪts] – льготы
5.security [sɪˈkjʊərɪtɪ] – безопасность
6.argue [ɑːɡjuː] – аргументировать, приводить доводы
7.satisfier [ˈsætɪsˌfaɪə] – условие, удовлетворяющее рабочего, привлекательная черта
8.exist [ɪɡˈzɪst] – существовать
9.challenging [ˈtʃælɪndʒɪŋ ] – сложный и интересный, мобилизует
10.recognition [ˌrɛkəɡˈnɪʃən] – признание
11.promotion [prəˈməʊʃən ] – продвижение по карьерной лестнице
12.plenty [ˈplɛntɪ ] – большое количество
13.boring [ˈbɔːrɪŋ ] – скучный
14.mindless [ˈmaɪndlɪs] – не требующий интеллектуального напряжения
15.unskilled [ʌnˈskɪld] – не требующий специальных навыков
16.solution [səˈluːʃən] – решение
17.checkout till [ˈtʃekaʊt tɪl] – кассовый аппарат
18.stock [stɒk ] – выставлять на продажу
19.repetitive [rɪˈpɛtɪtɪv ] – повторяющийся
20.value [ˈvæljuː] – ценность
21.user-friendly [ˌjuːzəˈfrendlɪ] – удобный
22.target [ˈtɑːɡɪt] – цель
Task 3. Read and translate the text.
What is Motivation?
It is natural that things like good labour relations, good working conditions, good wages and benefits and job security motivate workers. But in Work and the Nature of Man Frederick Hertzberg argued that such conditions do not motivate workers. They are merely «satisfiers» or more importantly “dissatisfiers” where they do not exist. “Motivators”, on the contrary, include things such as having challenging and interesting job, recognition and responsibility, promotion and so on.
However there are and there always will be plenty of boring, mindless, repetitive and mechanical jobs in all the three sectors of economy and lots of unskilled people who have to do them.
One solution to motivate people on such jobs is to give them some responsibilities not as individuals, but as part of a team. For example, some supermarkets combine office staff, the people who fill the shelves and the people who work at the checkout tills into a team and let them decide what product lines to stock, how to display
17
them and so on. Other employees make people who make repetitive jobs change them everycoupleofhours,becausedoingthreerepetitivejobsinadayisbetterthandoingone.
Sometimes it is important to think about the company values and corporate culture with which all the staff can identify (being the best chain of cafes or the restaurant chain, airline making the best, the safest the most user-friendly and ecological products in a particular field).
Such values are more likely to motivate worker than financial targets.
Source: Ian MacKenzie, A course for Business Studies and Economics students. — 2nd edition. — Cambridge University Press, 2002. — 206 p.p. 31.
Task 4. Match the words in two columns to make collocations:
1. |
labour |
a. |
job |
2. |
working |
b. |
relations |
3. |
challenging |
c. |
tills |
4. |
office |
d. |
values |
5. |
checkout |
e. |
staff |
6. |
company |
f. |
conditions |
7. |
use-friendly |
g. |
products |
Task 5. Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs below:
to motivate, to do, to combine, to identify, to stock, to give, to display.
1.During the crisis Madame Gritsatsuyev-Bender 1) … up with enough provisions and commodities for her shop to last at least four months.
2.Sometimes the enterprise employs a business-planner, as he or she finds ways and 2) … people.
3.What did you 3) … to make your business took off (стал успешным)?
4.These documents look much the same, I can`t 4) … them. Will you help me?
5.One of the ways to motivate staff is to 5) … mental and mindless activities.
6.The information in the lobby 6) … the current exchange rate.
7.Tomorrow the manager 7)… a presentation on time-keeping. Would you like to come?
Task 6. Answer the following questions:
1.What originally motivates workers?
2.What are “satisfiers”?
3.What are “motivators”?
4.Can you think of some examples of repetitive and boring jobs?
18

5.What can motivate people in mindless jobs?
6.What can be more motivating than financial targets?
7.Is “satisfier” or “motivator” more important for you?
Task 7. Are the sentences below True or False? Prove your choice.
1.Frederick Hertzberg argued that only financial and other material targets motivate workers.
2.Motivators are more stimulated by spiritual and social aspects.
3.Mindless and repetitive jobs are more typical for unskilled people.
4.Sometimes working in a team motivates people more.
5.Doing one repetitive job is better than changing a job every two hours.
Task 8. Look at the pyramid below that shows the basic people`s needs according to Maslow`s Hierarchy of Needs. Read the text below and fill in the missing levels of the pyramid with the following word combinations:
esteem needs, psychological needs, safety needs, self-actualization, social needs
An important theory of motivation in management belongs to Maslow`s Hierarchy of Needs. Maslow (1942) described five levels of needs. His theory suggests that people treat each level as a motivating factor, but once a level is achieved it is no longer motivating. Instead, the new level up becomes the new motivator. This tells us that in the workplace, esteem needs are important, but once achieved, they are no longer significant. Self-actualization of self-development is much more important. Managers therefore have to make sure that their staff continually feel that they are improving and achieving more in terms of self-actualization.
Maslow also suggests that it is not possible to move up the step without first fulfilling the lower needs.
5) _________________________
self-development
4) __________________________________
self-esteem, recognition, status
3)__________________________________________
sense of belonging, love
2) _______________________________________________
security, protection
1) ______________________________________________________
hunger, first, warmth
19
