
- •Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Kuban State Medical University" of
- •Rheumatic fever:
- •Rheumatic heart disease:
- •Acute Rheumatic Fever (Modified
- •Mitral Regurgitation
- •Etiology:
- •Examination and palpation:
- •Auscultation:
- •Peripheral cyanosis of the lips in a patient with heart failure:
- •X-ray examination:
- •Mitral Regurgitation:
- •Echocardiography:
- •Complications:
- •Mitral Valve Stenosis
- •Mitral Stenosis
- •Pathophysiology:
- •Clinical picture:
- •Inspection, palpation and percussion:
- •Butterfly with metral stenosis
- •Auscultation:
- •Mitral stenosis murmur:
- •Chest X-Ray (CXR):
- •Mitral Valve Stenosis:
- •Mitral Valve Stenosis:
- •Echocardiography:
- •Echo – TTE:
- •Echo – TEE:
- •Failure aortic valve (aortic insufficiency) (NAK. AN)
- •Etiology:
- •A circulatory disorder in this case vice is manifested in the fact that
- •Clinic:
- •Complaints:
- •Inspection, palpation and percussion:
- •Auscultation of the heart:
- •6) On the femoral arteries, a double tone of
- •Echocardiographic signs:
- •X-ray research
- •Aortic Stenosis
- •Etiology:
- •Severity of Stenosis:
- •Symptoms:
- •Inspection, palpation, percussion:
- •Auscultation of the heart:
- •Echocardiography:
- •Doppler estimation of AVA:
- •X-ray diagnostics:
- •Prognosis:
- •Thank you for Attention!

Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Kuban State Medical University" of the
Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Department of Internal Medicine Propedeutics
The concept of rheumatic illness Clinical symptoms mitral and aortic
heart defects.
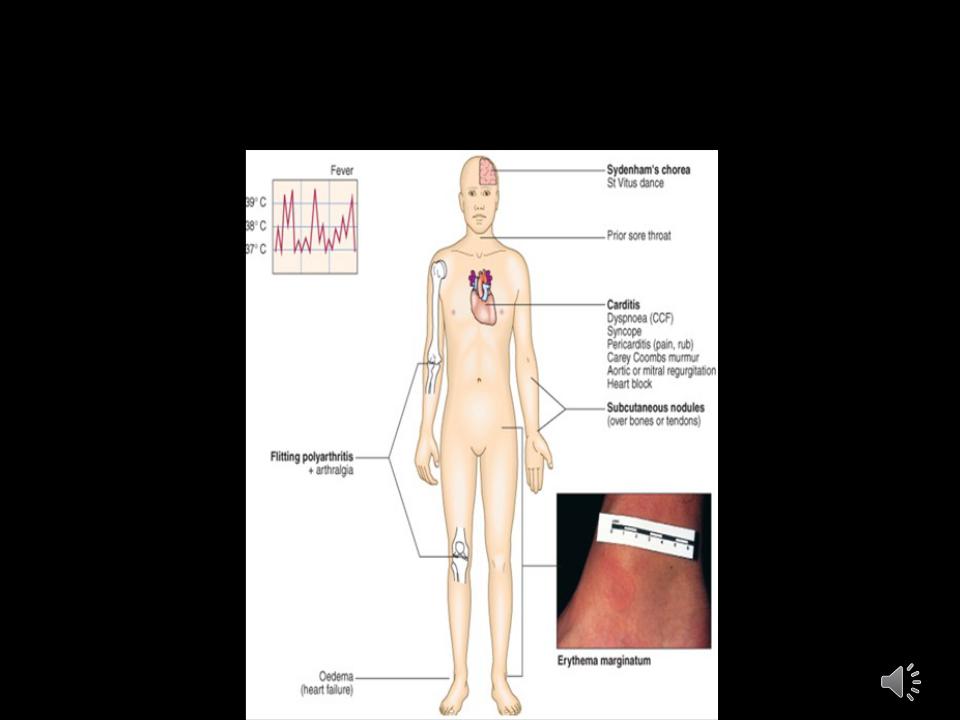
Rheumatic fever:
is an inflammatory disease involving the joints, the heart, the CNS, the skin and subcutaneous tissue.

Rheumatic heart disease:
1.Occurs in severe cardiac involvement during initial or recurrent attacks of ARF.
2.Left - sided heart valves are most often affected, (mitral followed by the aortic valves).

Acute Rheumatic Fever (Modified
Jones’ criteria):
• Major |
• Minor |
|
Carditis (Myocarditis, |
Arthralgia |
|
pericarditis, valvulitis) |
Fever |
|
Polyarthritis |
Raised ESR/cRP |
|
Sydenham’s chorea |
||
EKG: prolonged PR |
||
Subcutaneous nodules |
||
interval |
||
Erythema marginatum |
||
|
Diagnosis requires:2 major criterion
1 major + 2 minor criterion


Mitral Regurgitation

Etiology:
1. Valvular:
a)Myxomatous CT Disease; b)Rheumatic; c)Endocarditis.
2.Chordae.
3.Annulus:
a) Calcification.
4. Papillary Muscles:
a)CAD (Ischemia, Infarction); b)Infiltrative disorders.
5. LV Dilatation & Functional
Prolapse.
E |
c |
c e n t r i c |
L |
V |
H |
Pathophysiology:
M R
I n c . L A P r e s s u r e |
|
D e c . F o r w a r d O u t p u t |
|
|
|
C h r o n i c |
|
A c u t e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P u lm . H T N |
L A D ila t e s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
u lm |
. C o n g . |
L V |
D |
ila t e s |
|
|||
& |
F a |
ils |
|
& |
H T |
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Examination and palpation:
1. "heart hump" - rarely.
2. Reinforced and diffuse apical impulse.
3-acrocyanosis.
Percussion:
1. Displacement of the OTS border to the left and up, in decompensation period to the right.

Auscultation:
1. Chronic MR:
a) Hyperdynamic, Displaced apex beat. b) Apical holosystolic murmur.
c) Pounding pulse.
d) Variable Pulm. HTN.
2. Acute MR:
a)Marked pulmonary congestion.
b)Short systolic murmur.
c)Small pulse.
d)Marked pulm. HTN; Loud single S2.
e)Giant V wave in LA pressure tracing.
