
- •RUSSIAN PEOPLES FRIENDSHIP UNIVERSITY
- •Stem cells
- •The term "stem cell" was introduced into scientific use by the Russian histologist
- •Characteristics of stem cells
- •Zygote and blastomeres of morula are totipotent, i.e. they can give rise to
- •In a newborn in the bone marrow of 10 thousand stem cells -
- •Нaematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
- •Fibroblasts (from Latin fibra - fiber and Greek βλάστη - germ) - cells
- •In a healthy organism, there is a universal mechanism for healing lesions with
- •minox.in.ua
- •*A microphotograph of a longitudinal section of a human hair follicle.
- •Therapeutic use of stem cells
- •Reprogramming
- •Therapeutic cloning
- •Stromal stem cells
- •Experiment on the in vivo transdifferentiation of noncardiogenic mesoderm cells into cardiomyocytes /
- •Japanese scientists, adding a special substance (5-azocitidine) to the culture of stromal cells
- •The dangers associated with the use of stem cells
- •Literature
RUSSIAN PEOPLES FRIENDSHIP UNIVERSITY
Стволовые клетки Stem cells
Stem cells
transcells.ru
The term "stem cell" was introduced into scientific use by the Russian histologist Alexander Maximov (1874-1928). He postulated the existence of the stem hematopoietic cell.
fareastgizmos.com
Characteristics of stem cells
Stem cells can divide unrestrictedly, and mature cells usually have a limited number of fission cycles.
This is explained by the activity of telomerase in stem cells - the ends of their chromosomes after replication of DNA are superimposed, and therefore cells are capable of performing
stemcells.nih.gov potentially infinite number of cell divisions.
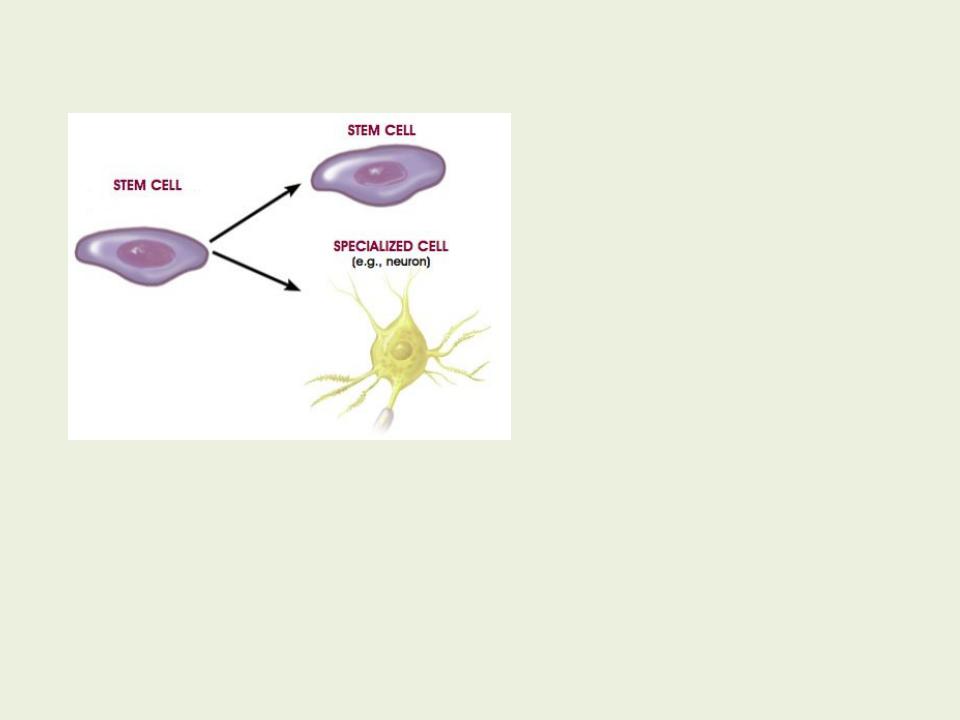
When dividing a stem cell, one of the daughter cells is differentiated, and the second remains a stem cell. Due to this, stem cells form a self-sustaining population.
Homing - the ability of many stem cells to migrate to the area of damage and differentiate; The factors that determine the pathway of development of stem cells are in the cytoplasm. This is the mRNA transcribed from those genes (there are about 3,000 of them) that are responsible for the early development of the embryo.
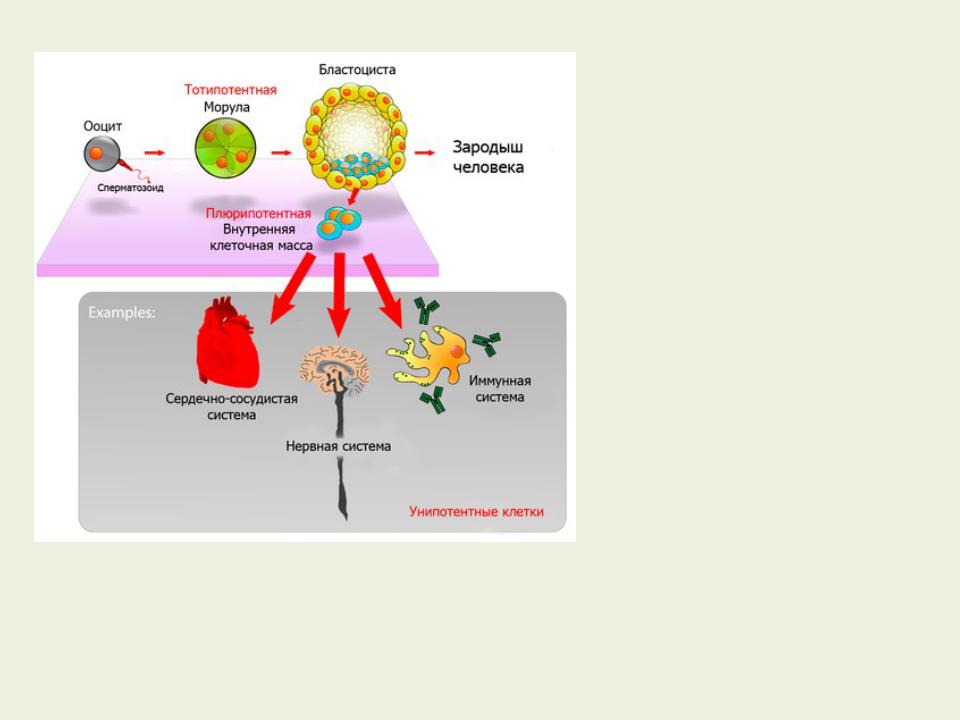
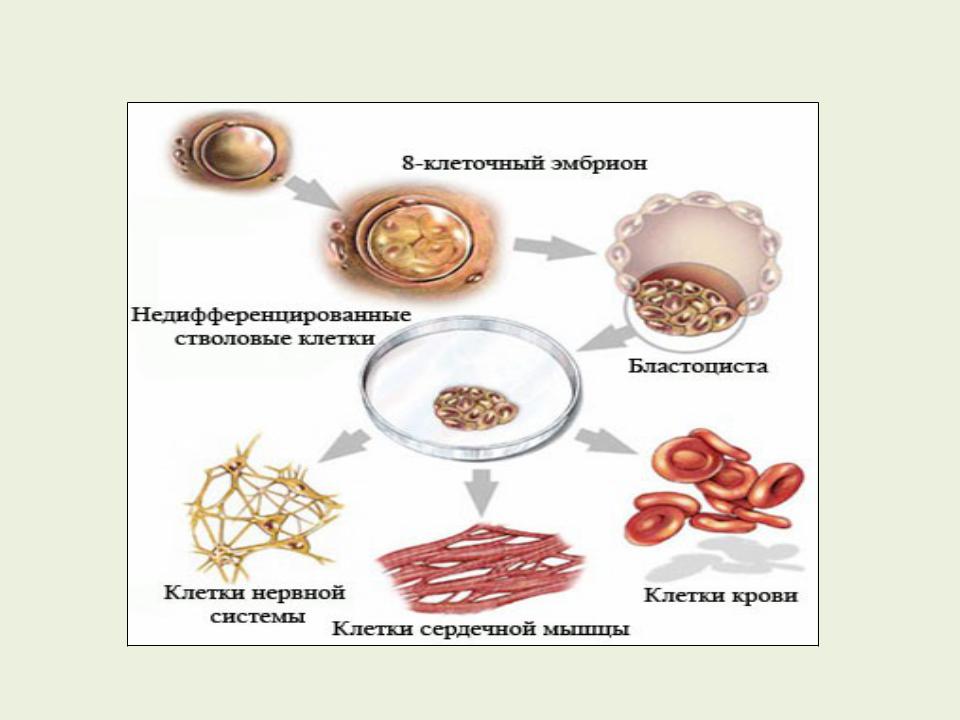
Zygote and blastomeres of morula are totipotent, i.e. they can give rise to any type of embryonic cell and external embryonic tissue. Pluripotent cells are capable of forming all types of embryonic cells. These include embryonic stem cells (ESC), primary sex cells (AUC) and embryonic carcinoma cells.
ESC (or pluripotent stem cells - PSC), first isolated by the American biologist Martin Evans in 1981 from the internal cell mass of the mouse blastocyst.
en.wikipedia.org
In 1999, the journal Science recognized the discovery of embryonic stem cells as the third most significant event in biology after deciphering the double helix of DNA and the Human Genome program.
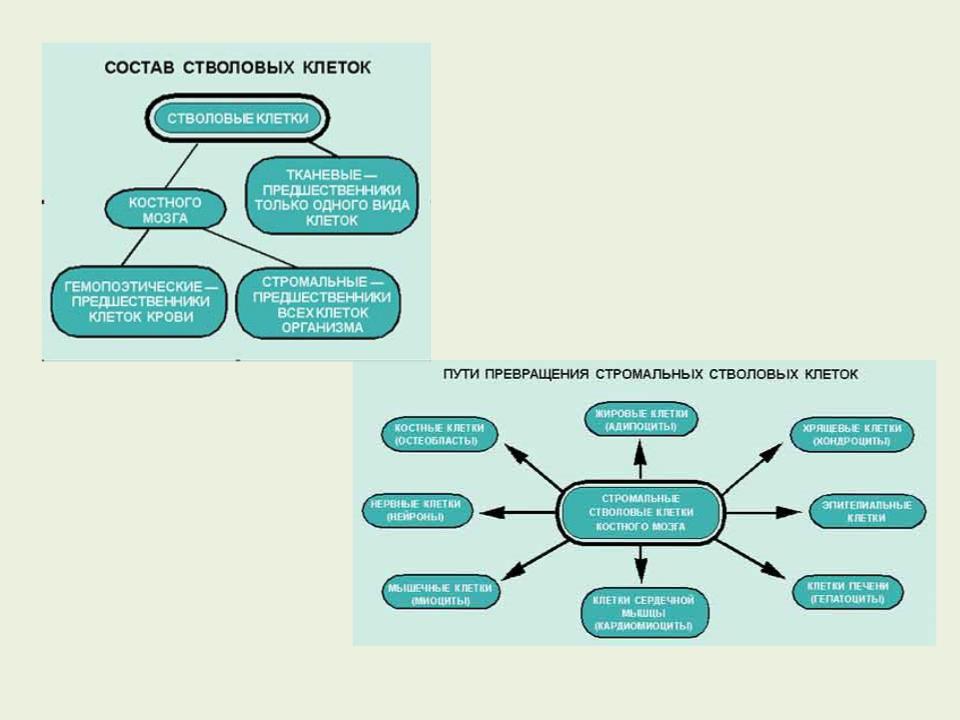
In a newborn in the bone marrow of 10 thousand stem cells - one stromal cell. The adolescent stromal cells are already 10 times smaller, and with age their number continues to decrease - in 70 years there is 1 stem cell per million! ..
Other types of stem cells are localized in the formed tissues of the adult body (adult stem cells). They vary in their ability to differentiate
from multipotent to unipotent. Friedenstein A.Ya. and his colleagues showed for the first time that in the bone marrow, in addition to hematopoietic stem cells, stromal stem cells were formed which, when cultured, formed colonies of fibroblast- like cells.
nature.web.ru
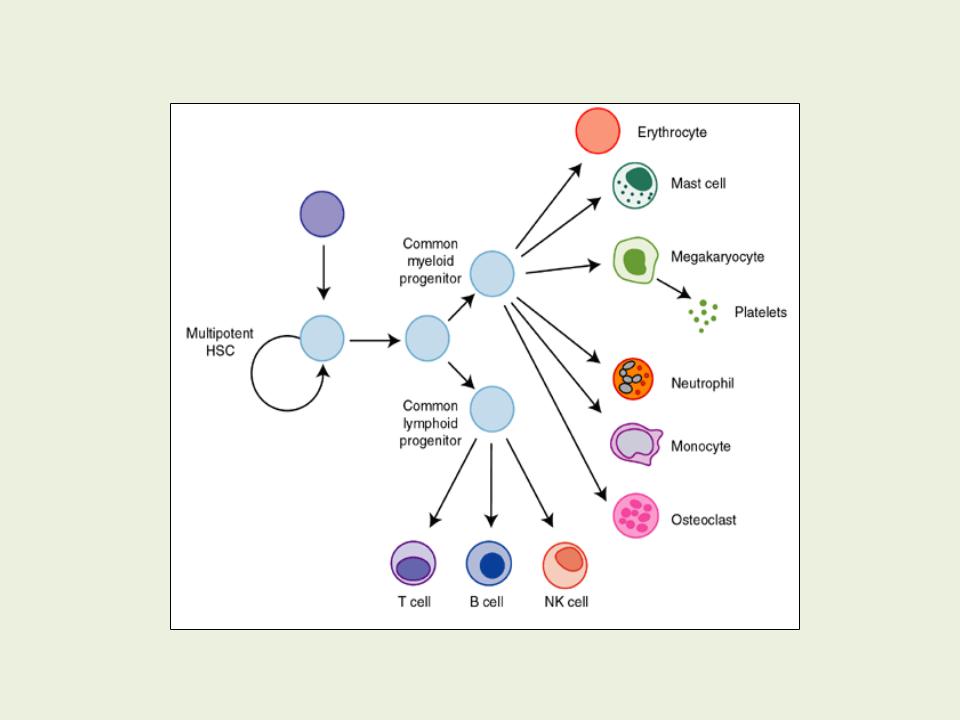
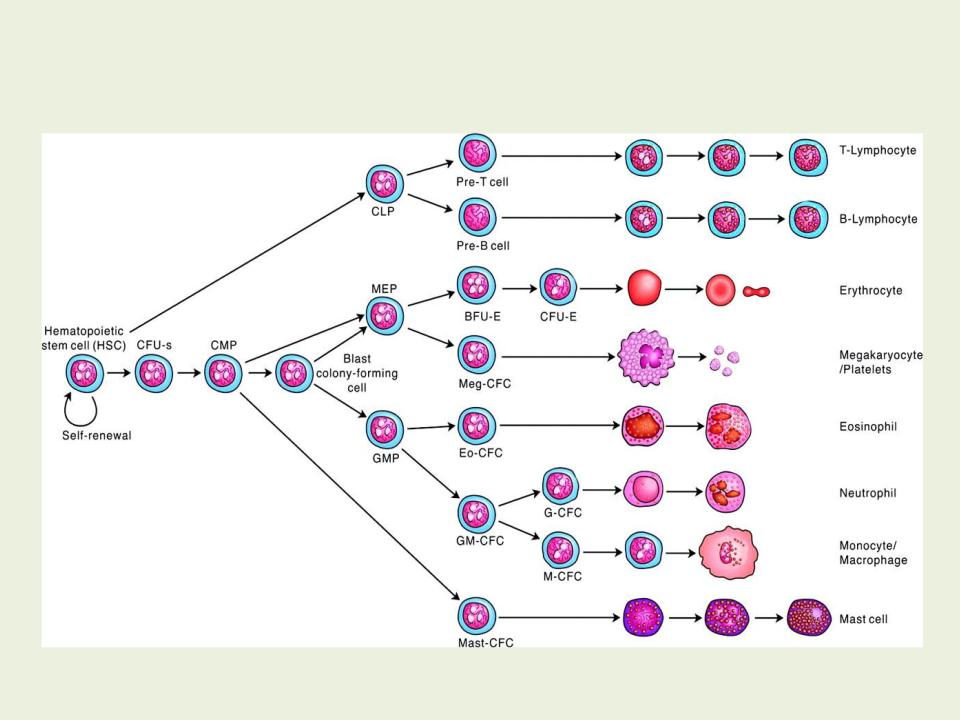
Нaematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
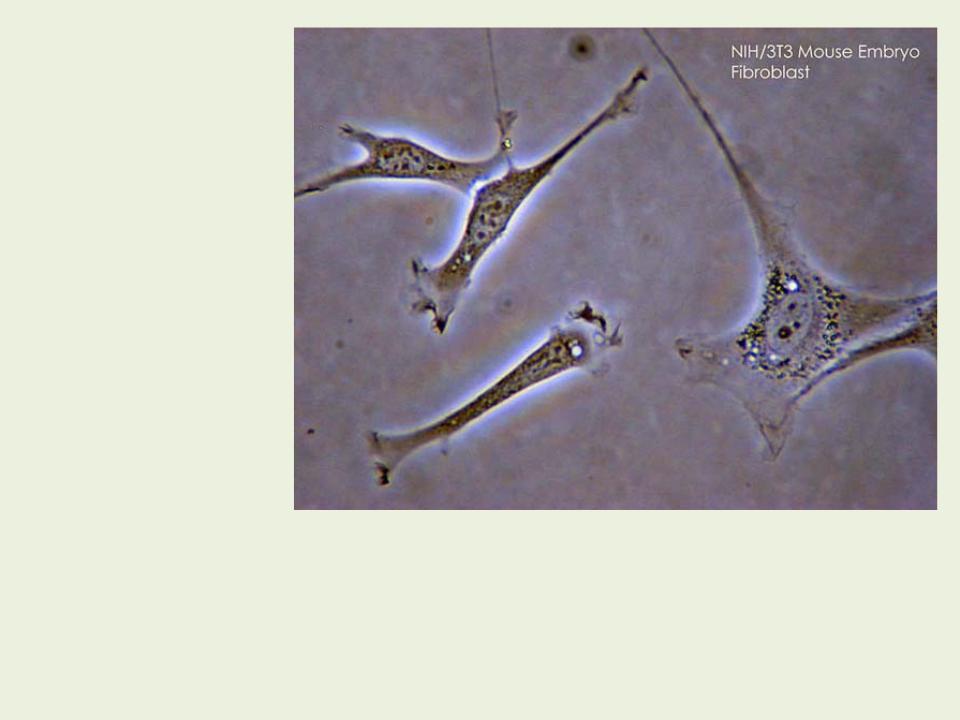
Fibroblasts (from Latin fibra - fiber and Greek βλάστη - germ) - cells of connective tissue that synthesize the extracellular matrix. Fibroblasts secrete precursors of collagen and elastin proteins, as well as mucopolysacchari des.
The form of fibroblasts is diverse, depends on the level of their activity and localization in the body. Active fibroblasts of increased size, have processes, an oval nucleus, are rich in ribosomes. Inactive fibroblasts (fibroblasts) are smaller in size and have a spindle shape.
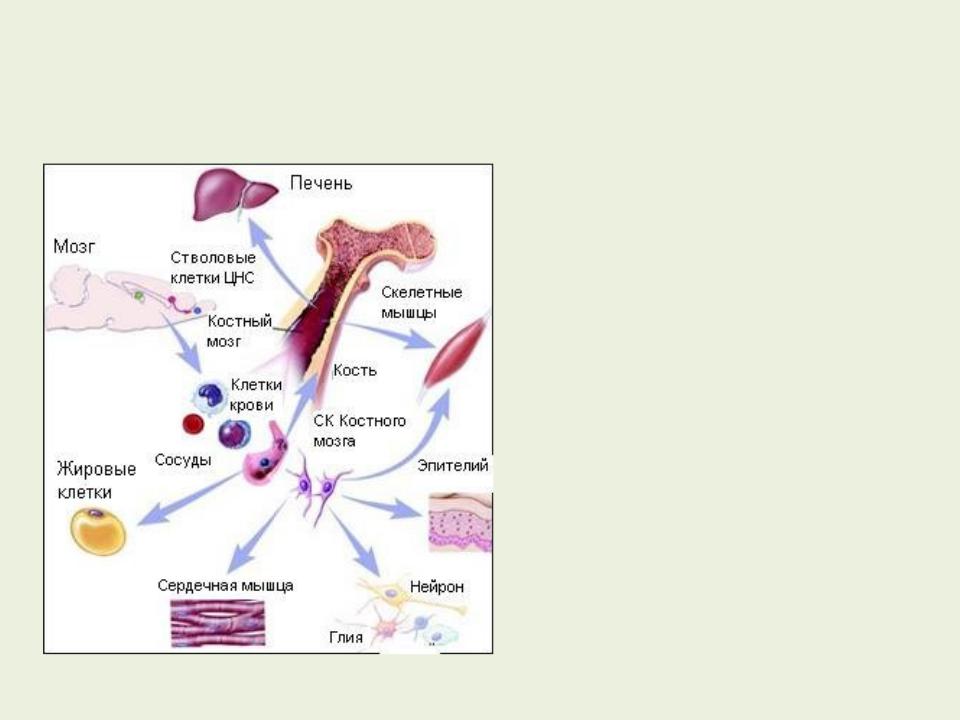
In a healthy organism, there is a universal mechanism for healing lesions with the help of bone marrow stromal cells. Having received the appropriate signal from the central nervous system, stromal cells begin to enter the damaged area. Having reached the site of damage, they under the action of certain signal molecules are transformed into missing cells of the damaged tissue.
But the storage of stromal cells can not be inexhaustible. After healing extensive damage, the bone marrow "empties", and with age the stromal cell stock decreases significantly. Tissue-specific stem cells are located in different types of tissues and, first of all, they are responsible for updating their cell population, the first ones are activated in case of damage. Usually they have a lower potential than the bone marrow stromal cells, and then they are classified as unipotent. Stem cells of adipose tissue have a wider potential - they are closer to multipotent.
stemcells.nih.gov
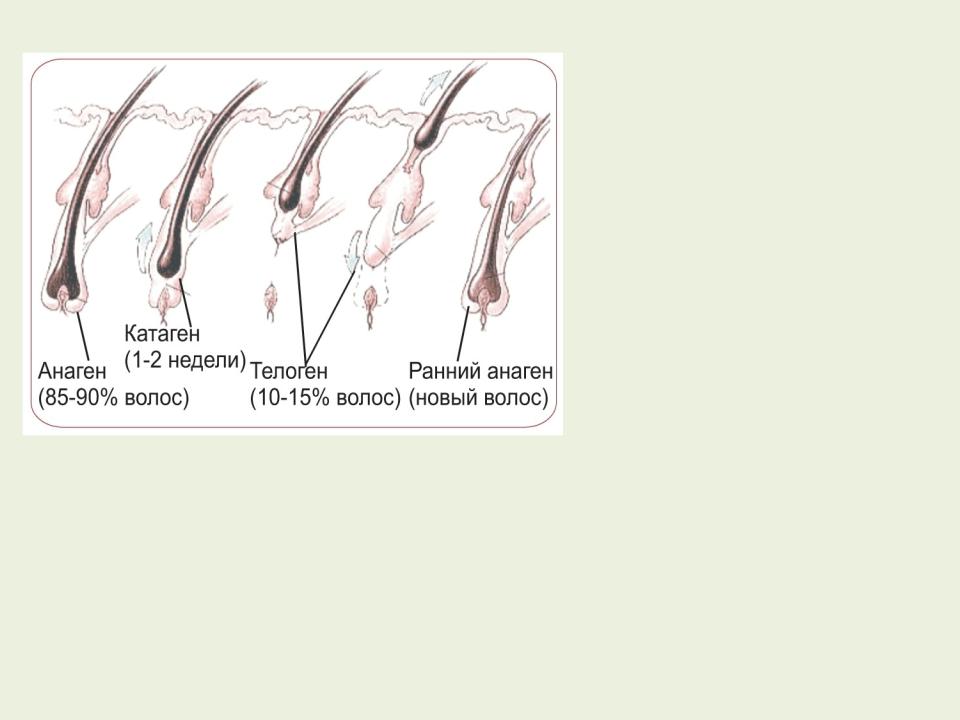
minox.in.ua |
At the base of the constant part |
|
of the follicle under the |
|
sebaceous gland is bulge |
|
(bulge) with a smooth muscle |
|
adjacent to it. Anatomically |
|
bulge - a thickened part of the |
|
follicle wall, a place of storage |
|
of stem unipotent cells - the |
|
regeneration of the hair follicle |
|
depends on them. To start |
|
growing hair instead of fallen |
|
out, stem cells from bulge |
|
descend down the hair bulb |
|
and give rise to a new |
|
population of stem cells. |
Human hair grows continuously, alternating periods of growth and rest, which are called cycles of hair growth. In the cycle, three phases: anagen - growth phase; catagen - the phase of degradation; telogen - the phase of rest. The growth period (anagen) lasts 2-8 years, then in 1-2 weeks the follicle almost completely collapses (catagen). The next phase of rest (telogen) lasts 2-4 months. Hair is thrown off only in the next growth cycle (anagen), when a new hair shaft begins to appear. On average, every day, 50-100 telogen hair is lost
