
- •II курс, семестр IV, лекция III
- •Anatomy of cardiovascular system
- •Surface marking of the valves of heart
- •Conducting system of the heart
- •Complaints
- •Chest pain
- •Chest pain
- •Pain
- •Main cause of coronary pain
- •Description of angina by patients
- •Localization and radiation of typical coronary pain
- •Duration of pain
- •Pain relief
- •Summary on coronary chest pain
- •Angina is unlikely
- •Classification of chest pain
- •Distinguishing between angina and cardialgia
- •Dyspnea
- •Suffocation
- •Cough. Haemoptysis
- •Palpitation and arrhythmia
- •Edema
- •Anamnesis morbi et Anamnesis vitae
- •Examination of patient with cardiovascular diseases
- •Plan
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Facies mitralis
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of patients with CVD
- •Examination of the heart
- •Examination of the heart
- •Examination of the vessels
- •Palpation of the heart
- •Myocardial hypertrophy
- •Dilation
- •Types of cardiomegaly
- •Types of cardiac overload
- •Increased postload
- •Increased preload
- •Remodelling of the heart
- •Palpation of the heart
- •Sequence of palpation of the heart
- •Apex beat
- •Palpation of apex beat
- •Apex beat shift
- •Apex beat shift
- •Features of apex beat
- •Features of apex beat
- •Palpation of apex beat
- •Palpation of right ventricular lift
- •Epigastric pulsation
- •Pathologic pulsation
- •Palpation of main arteries
- •Pathologic pulsations
- •Heart thrill (purring thrill)
- •Heart thrill (purring thrill)
- •Percussion of the heart
- •Rules of percussion
- •Borders of relative dullness
- •Detection of relative dullness
- •Detection of relative dullness
- •Detection of relative dullness
- •Transverse size of the heart
- •Borders of vessel bundle
- •Absolute dullness
- •Configuration of the heart
- •Normal configuration of the heart.
- •Mitral configuration
- •Aortic configuration
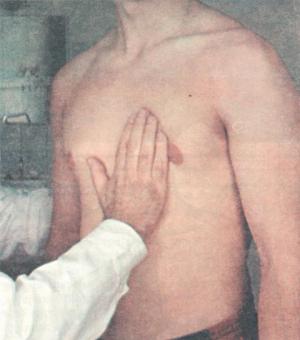
Palpation of right ventricular lift
Contraction of RV
Location – IV rib or intercostal space to the left from the sternum
Normally palpated in young people with thin chest (mild pulsation)
↑ RV lift – RVH
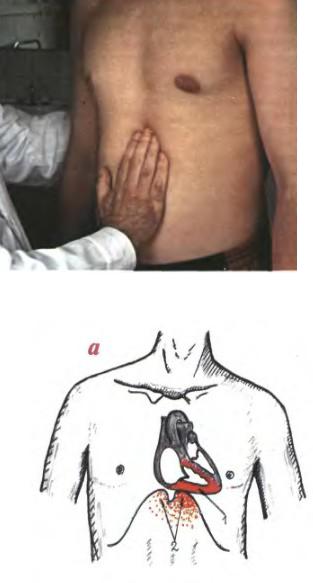
Epigastric pulsation
Eccentric RV hypertrophy
Below xyphoid process
at deep inspiration
Pulse from abdominal aorta
at deep inspiration
Pathologic pulsation
II right intercostal space – ascending aortic aneurism
Jugular fossa – Aortic arch aneurism, high BP, aortic insufficiency
Epigastric region– RVH, abdominal aortic aneurism
Liver pulse – Tricuspid valve insufficiency
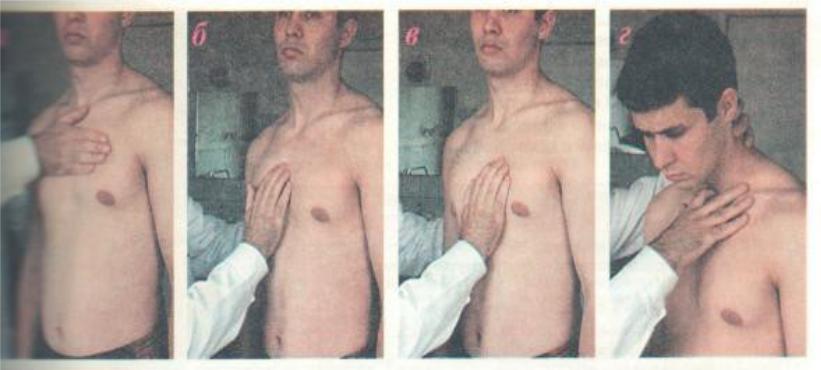
Palpation of main arteries
a.Detection of systolic thrill and pulsation at the base of the heart
b.II right intercostal space- ascending aorta
c.II left intercostal space – pulmonary trunk
d.Jugular fossa – aortic arch
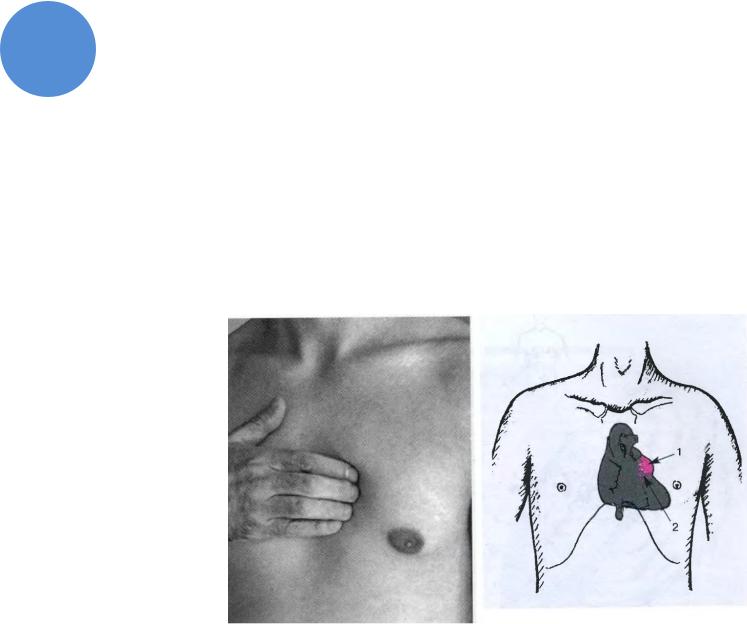
Pathologic pulsations
In LV aneurism pulsation is located to the left from NB sternum
In RVH pulsation is located to the left from sternum and in epigastic region
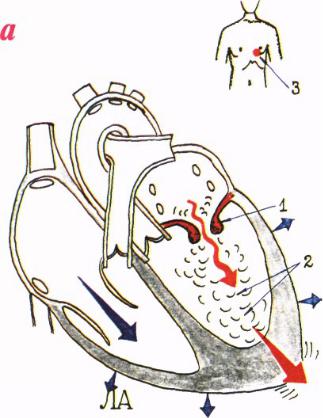
Heart thrill (purring thrill)
Diastolic
Mitral stenosis
Due to turbulent blood flow from left atrium to left ventricle
Does not fit on with apex beat and carotid pulse
Is determined at the apex
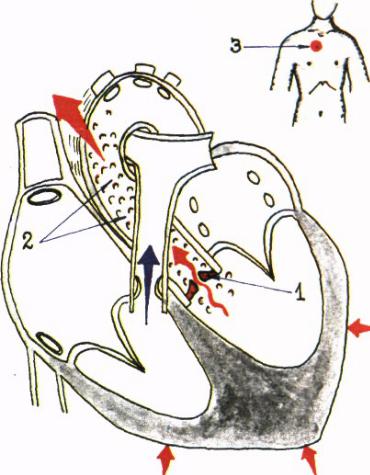
Heart thrill (purring thrill)
SystolicDue to aortic stenosis
Fits in with apex beat and carotid pulse
Is determined at the base of the heart
Percussion of the heart
Aims :
1.Detection of atrial and ventricular dilation 2.Detection of vessel bundle dilation
Rules of percussion
1.Standing position;
2.Comfortable conditions;
3.Finger is parallel to detecting border;
4.Direction of percussion: from lung sound to dull sound, from dull to absolutely dull;
5.The border is detected along the margin of the finger turned to lung sound
Borders of relative dullness
Lateral parts of the heart covered with the lungs. Reflects true size of the heart
