
- •Syndromes in blood disorders
- ••Syndrome of circulatory hypoxia
- •Structure of erythrocyte
- •Structure of hemoglobin molecule
- •Function of erythrocyte
- •Clinical presentation of circulatory-hypoxic syndrome
- •Anemic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome: changes in epithelial tissues
- •Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- •Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- •Laboratory findings in sideropenic syndrome
- •Syndrome of anemic heart
- •Laboratory changes
- •Syndrome of hemolysis
- •Clinical presentation of hemolysis
- •Laboratory findings in hemolysis
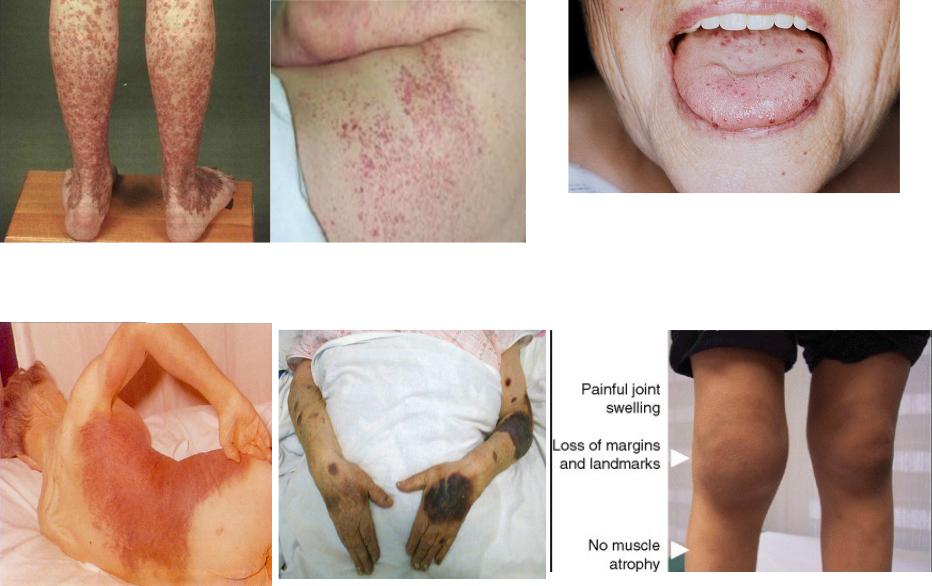
- •Clinical presentation of hemorrhagic syndrome
- •Teleangiectasias
- •Pinch sign
- •Lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •Causes of lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •Giant lymphadenopathy
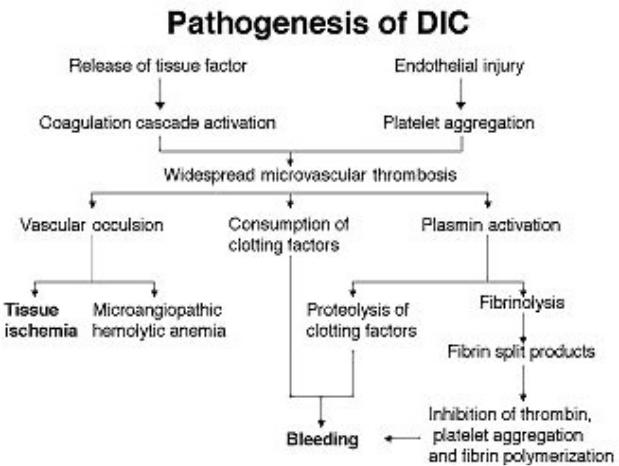
- •Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- •Causes of DIC
- •Clinical presentation of DIC
Clinical presentation of hemorrhagic syndrome
•Nasal bleeds, gingival bleeds
•Hemorrhagic rash: petechias and ecchymoses
•Teleangiectasias: mucosa, lips, gums
•Hemarthrosis
•Bleedings after surgical operations
•Menorrhagia
•Positive Rumpel-Leede sign
Teleangiectasias
Purpura
Ecchymoses |
Hemarthrosis |
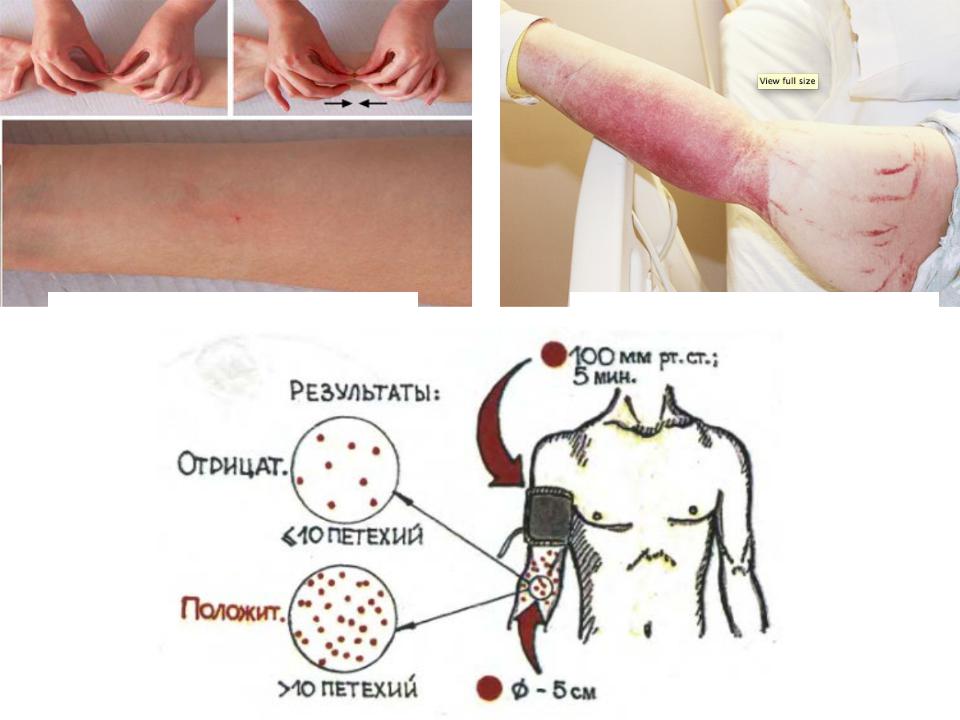
Pinch sign |
Rumpel-Leede sign |
Lymphoproliferative syndrome
Lymphadenopathy – enlargement of lymph nodes of any origin
Localized |
|
Generalized |
|
|
Not associated with tumors |
Associated with tumors |
|
|
|
|
|
Short-term |
|
Long-term |
(< 2 months) |
|
(> 2 months) |
|
|
Chronic |
|
Recurrent |
Acute |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Causes of lymphoproliferative syndrome
•Infections
•Tumors:
–Hematologic malignancies: leukemias, lymphomas
–Metastases
•Hypersensitivity and immune reactions:
–Vaccines, drugs
•Autoimmune diseases
•Sarcoidosis
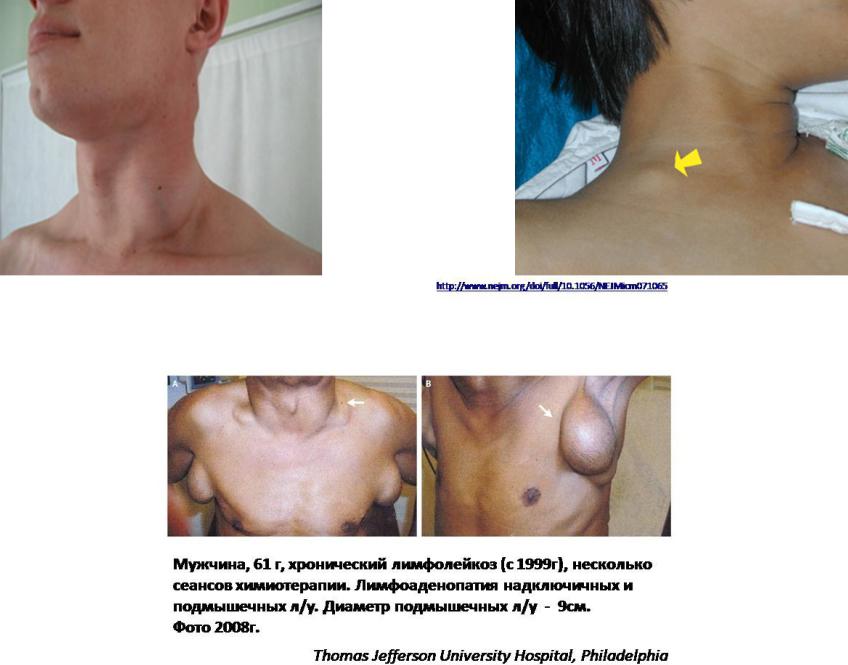
Giant lymphadenopathy
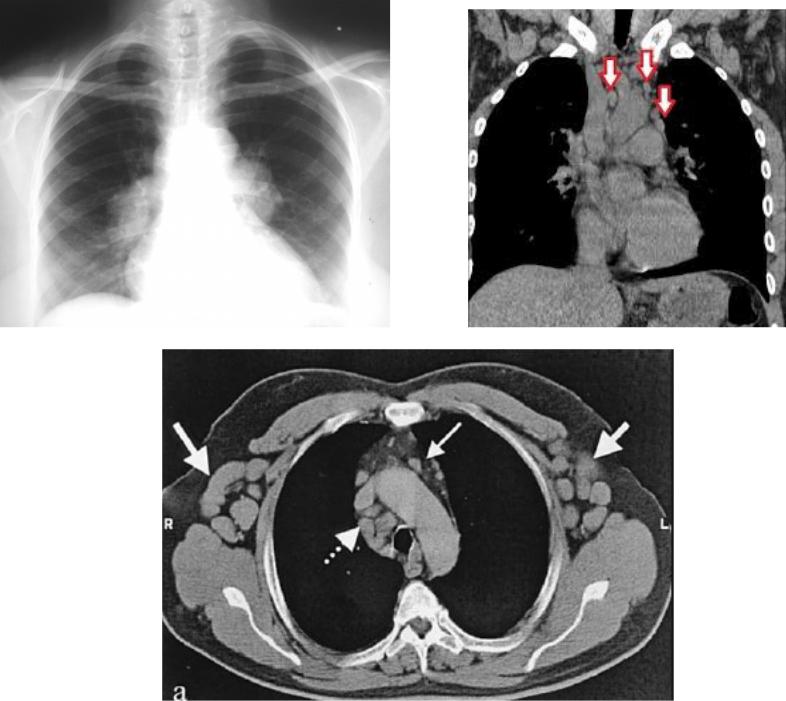
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) - non-specific coagulopathy
Causes of DIC
•Sepsis
•Trauma
•Combustions
•Malignancies
•Obstetric complications
•Blood transfusions
•Acute liver failure
Clinical presentation of DIC
•Hemorrhagic syndrome
–Petechias, ecchymoses
–Nasal, gyngival bleeds
–Hematuria
–Gastro-intestinal bleeding
–Metrorhagia
–Bleeding after surgery
–Bleeding into serous cavity
•Neurological signs
–Confusion
–TIA/stroke
•Macrovascular thrombosis
–Deep venous thrombosis
–Arterial thrombosis
• |
Microvascular thrombosis and |
|
|
multiple organ damage |
|
|
– |
Acute kidney injury |
|
– |
Acute respiratory failure |
|
– |
Acute liver failure |
|
– |
Acute adrenal insufficiency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
Shock |
|
|
– |
Arterial hypotension |
|
– |
Tachycardia |
|
– |
Collapse |
|
|
|
