
- •Syndromes in blood disorders
- ••Syndrome of circulatory hypoxia
- •Structure of erythrocyte
- •Structure of hemoglobin molecule
- •Function of erythrocyte
- •Clinical presentation of circulatory-hypoxic syndrome
- •Anemic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome
- •Sideropenic syndrome: changes in epithelial tissues
- •Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- •Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- •Laboratory findings in sideropenic syndrome
- •Syndrome of anemic heart
- •Laboratory changes
- •Syndrome of hemolysis
- •Clinical presentation of hemolysis
- •Laboratory findings in hemolysis
- •Clinical presentation of hemorrhagic syndrome
- •Teleangiectasias
- •Pinch sign
- •Lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •Causes of lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •Giant lymphadenopathy
- •Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- •Causes of DIC
- •Clinical presentation of DIC
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
•Postcricoid dysphagia
•Upper esophageal webs
•Iron deficiency anemia
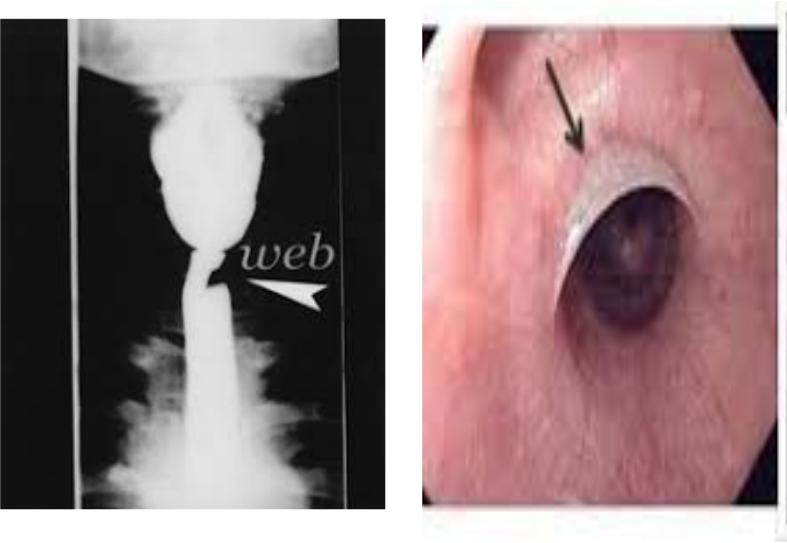
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Esophageal web

Laboratory findings in sideropenic syndrome
•Low level of serum iron
•Low transferrin saturation
•Low ferritin
•Increased iron-binding capacity
Ferritin – main marker of iron deficiency in the storage
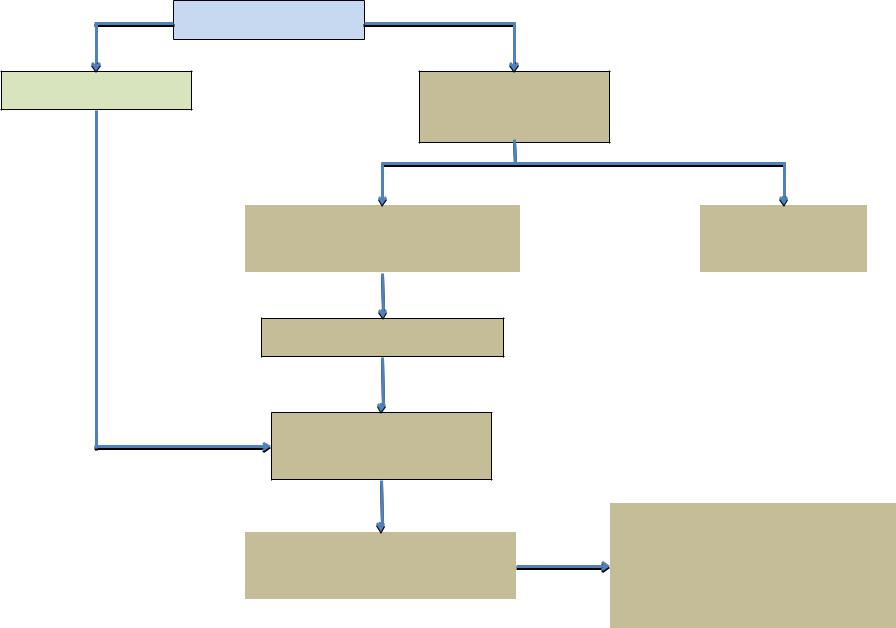
Syndrome of anemic heart
•Structural and functional changes of the heart due to chronic hypoxia in anemia
Clinical presentation
•Dyspnea at slight physical exercise
•Cardialgia
•Palpitations, tachycardia
•Edema of the legs
•Systolic murmur at the apex of the heart
Laboratory changes
• Signs of anemic syndrome
Instrumental tests
•Echocardiography: preserved ejection fraction, dilation of the heart chambers is possible
|
Anemia |
↓ Blood viscosity |
↓O2 carrying- |
capacity of blood
↑ Lactate and other |
|
Tissue |
vasodilatory metabolites |
|
hypoxia |
Arteriolar vasodilation
↓ Systemic vascular resistance
|
|
↑ Work load |
↑ Systemic venous return |
|
↑ LV mass |
(cardiac output) |
|
↑ LV Remodeling |
|
|
↑ LV Dysfunction |
|
||
|
|
|
Hassapoyannes CA, Nelson WP, Hopkins CB, et al: Other causes and contributing factors to congestive heart
failure. In Hosenpud JD, Greenberg BH [eds]: Congestive Heart Failure. New York, Springer-Verlag, 1994, pp 281–300.)
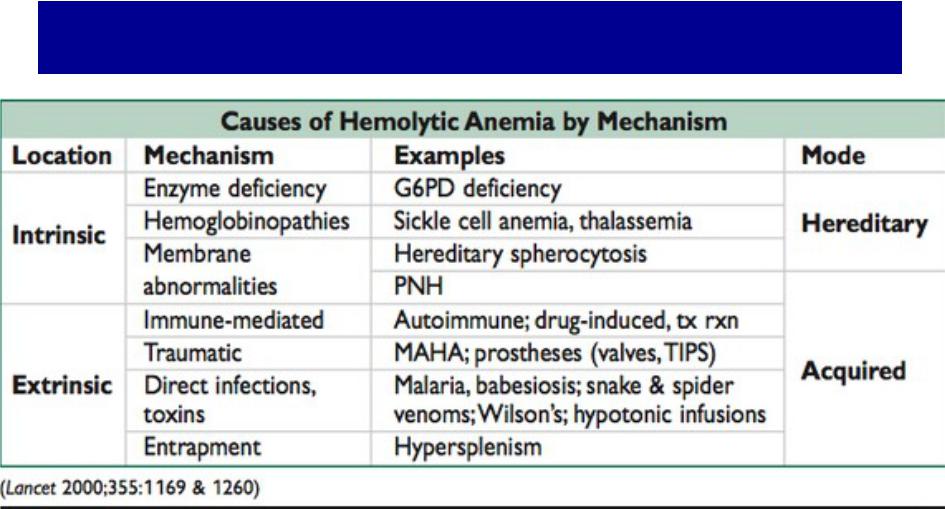
Syndrome of hemolysis
Increased destruction of RBC due to different factors
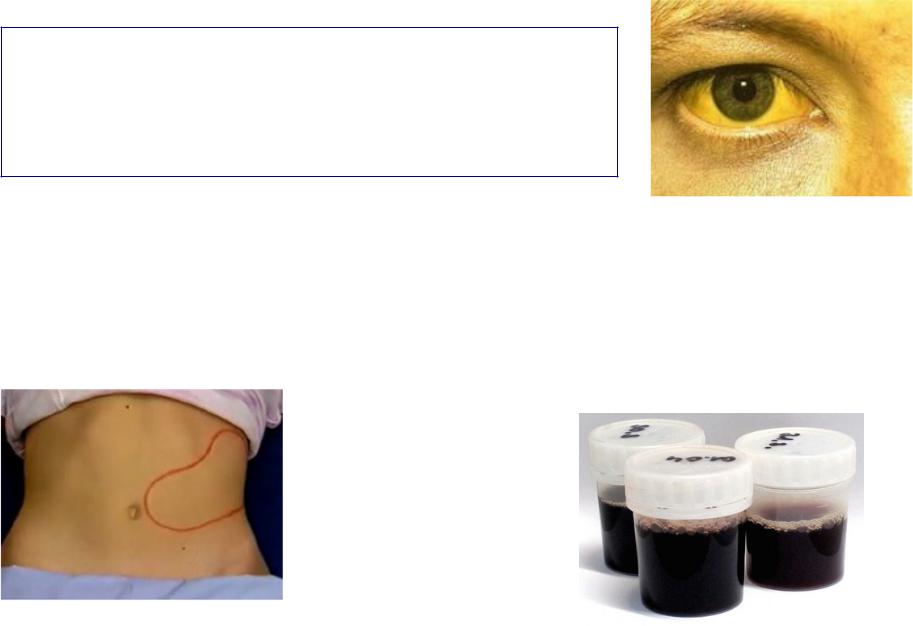
Clinical presentation of hemolysis
Common features
•Icteric skin and sclera
•Circulatory-hypoxic syndrome
• |
Extravascular hemolysis |
• |
Intravascular hemolysis |
Splenomegaly |
Fever |
||
• |
Hepatomegaly |
• |
Pain in lumbar region |
|
|
• |
Dark urine due to hemoglobinuria |
Laboratory findings in hemolysis
•hemoglobin, RBC
•Normochromic
•Reticulocytosis
•Hyperbilirubinemia: indirect bilirubin
•erythropoiesis in bone marrow: erythroblasts and normoblasts
•Hemoglobinemia and hemoglobinuria in intravascular hemolysis
Hemorrhagic syndrome=bleeding disorders
Platelets abnormalities
•Trombocytopenia:
–Idiopathic trombocytopenic purpura
–Drugs and chemicals
–Autoimmune (e.g. SLE)
–Leukemias
•Trombocytopathy
–Hereditary
–Acquired
Coagulopathies |
Vasculopathies |
• Hereditary: |
• Hereditary haemorrhagic |
– Hemophilia |
teleangiectasia |
– |
Von |
Willebrand`s |
• |
|
disease |
|
• |
• Acquired |
|
• |
|
– |
Liver diseases |
• |
|
– |
Vitamin K deficiency |
|
|
– |
Malabsorbtion |
|
|
– |
DIC |
|
|
– |
Anticoagulants |
|
|
Connective tissue disorders Infections
Haemorrhagic vasculitis Drugs
