
- •1 Scope
- •1.1 General
- •2 Conformance
- •2.1 General
- •2.2 Process Modeling Conformance
- •2.2.1 BPMN Process Types
- •2.2.2 BPMN Process Elements
- •Descriptive Conformance Sub-Class
- •Analytic Conformance Sub-Class
- •Common Executable Conformance Sub-Class
- •2.2.3 Visual Appearance
- •2.2.4 Structural Conformance
- •2.2.5 Process Semantics
- •2.2.6 Attributes and Model Associations
- •2.2.7 Extended and Optional Elements
- •2.2.8 Visual Interchange
- •2.3 Process Execution Conformance
- •2.3.1 Execution Semantics
- •2.3.2 Import of Process Diagrams
- •2.4 BPEL Process Execution Conformance
- •2.5 Choreography Modeling Conformance
- •2.5.1 BPMN Choreography Types
- •2.5.2 BPMN Choreography Elements
- •2.5.3 Visual Appearance
- •2.5.4 Choreography Semantics
- •2.5.5 Visual Interchange
- •2.6 Summary of BPMN Conformance Types
- •3 Normative References
- •3.1 General
- •3.2 Normative
- •3.3 Non-Normative
- •Activity Service
- •BPEL4People
- •Business Process Definition Metamodel
- •Business Process Modeling
- •Business Transaction Protocol
- •Dublin Core Meta Data
- •ebXML BPSS
- •Open Nested Transactions
- •SOAP 1.2
- •UDDI
- •WfMC Glossary
- •Web Services Transaction
- •Workflow Patterns
- •WSBPEL
- •WS-Coordination
- •WSDL
- •WS-HumanTask
- •XML 1.0 (Second Edition)
- •XML-Namespaces
- •XML-Schema
- •XPath
- •XPDL
- •4 Terms and Definitions
- •5 Symbols
- •6 Additional Information
- •6.1 Conventions
- •6.1.1 Typographical and Linguistic Conventions and Style
- •6.1.2 Abbreviations
- •6.2 Structure of this Document
- •6.3 Acknowledgments
- •Submitting Organizations
- •Supporting Organizations
- •Special Acknowledgments
- •7 Overview
- •7.1 General
- •7.2 BPMN Scope
- •7.2.1 Uses of BPMN
- •Private (Internal) Business Processes
- •Public Processes
- •Collaborations
- •Choreographies
- •Conversations
- •Diagram Point of View
- •Understanding the Behavior of Diagrams
- •7.3 BPMN Elements
- •7.3.1 Basic BPMN Modeling Elements
- •7.3.2 Extended BPMN Modeling Elements
- •7.4 BPMN Diagram Types
- •7.5 Use of Text, Color, Size, and Lines in a Diagram
- •7.6 Flow Object Connection Rules
- •7.6.1 Sequence Flow Connections Rules
- •7.6.2 Message Flow Connection Rules
- •7.7 BPMN Extensibility
- •7.8 BPMN Example
- •8 BPMN Core Structure
- •8.1 General
- •8.2 Infrastructure
- •8.2.1 Definitions
- •8.2.2 Import
- •8.2.3 Infrastructure Package XML Schemas
- •8.3 Foundation
- •8.3.1 Base Element
- •8.3.2 Documentation
- •8.3.3 Extensibility
- •Extension
- •ExtensionDefinition
- •ExtensionAttributeDefinition
- •ExtensionAttributeValue
- •Extensibility XML Schemas
- •XML Example
- •8.3.4 External Relationships
- •8.3.5 Root Element
- •8.3.6 Foundation Package XML Schemas
- •8.4 Common Elements
- •8.4.1 Artifacts
- •Common Artifact Definitions
- •Artifact Sequence Flow Connections
- •Artifact Message Flow Connections
- •Association
- •Group
- •Category
- •Text Annotation
- •XML Schema for Artifacts
- •8.4.2 Correlation
- •CorrelationKey
- •Key-based Correlation
- •Context-based Correlation
- •XML Schema for Correlation
- •8.4.3 Error
- •8.4.4 Escalation
- •8.4.5 Events
- •8.4.6 Expressions
- •Expression
- •Formal Expression
- •8.4.7 Flow Element
- •8.4.8 Flow Elements Container
- •8.4.9 Gateways
- •8.4.10 Item Definition
- •8.4.11 Message
- •8.4.12 Resources
- •8.4.13 Sequence Flow
- •Flow Node
- •8.4.14 Common Package XML Schemas
- •8.5 Services
- •8.5.1 Interface
- •8.5.2 EndPoint
- •8.5.3 Operation
- •8.5.4 Service Package XML Schemas
- •9 Collaboration
- •9.1 General
- •9.2 Basic Collaboration Concepts
- •9.2.1 Use of BPMN Common Elements
- •9.3 Pool and Participant
- •9.3.1 Participants
- •PartnerEntity
- •PartnerRole
- •Participant Multiplicity
- •ParticipantAssociation
- •9.3.2 Lanes
- •9.4 Message Flow
- •9.4.1 Interaction Node
- •9.4.2 Message Flow Associations
- •9.5 Conversations
- •9.5.1 Conversation Node
- •9.5.2 Conversation
- •9.5.3 Sub-Conversation
- •9.5.4 Call Conversation
- •9.5.5 Global Conversation
- •9.5.6 Conversation Link
- •9.5.7 Conversation Association
- •9.5.8 Correlations
- •9.6 Process within Collaboration
- •9.7 Choreography within Collaboration
- •9.8 Collaboration Package XML Schemas
- •10 Process
- •10.1 General
- •10.2 Basic Process Concepts
- •10.2.1 Types of BPMN Processes
- •10.2.2 Use of BPMN Common Elements
- •10.3 Activities
- •Sequence Flow Connections
- •Message Flow Connections
- •10.3.1 Resource Assignment
- •Resource Role
- •Expression Assignment
- •Parameterized Resource Assignment
- •10.3.2 Performer
- •10.3.3 Tasks
- •Service Task
- •Send Task
- •Receive Task
- •User Task
- •Manual Task
- •Business Rule
- •Script Task
- •10.3.4 Human Interactions
- •Notation
- •Manual Task
- •User Task
- •Rendering of User Tasks
- •Human Performers
- •Potential Owners
- •XML Schema for Human Interactions
- •Examples
- •10.3.5 Sub-Processes
- •Embedded Sub-Process (Sub-Process)
- •Reusable Sub-Process (Call Activity)
- •Event Sub-Process
- •Transaction
- •Ad-Hoc Sub-Process
- •10.3.6 Call Activity
- •Callable Element
- •10.3.7 Global Task
- •Types of Global Task
- •10.3.8 Loop Characteristics
- •Standard Loop Characteristics
- •Multi-Instance Characteristics
- •Complex Behavior Definition
- •10.3.9 XML Schema for Activities
- •10.4 Items and Data
- •10.4.1 Data Modeling
- •Item-Aware Elements
- •Data Objects
- •DataObject
- •States
- •Data Objects representing a Collection of Data
- •Visual representations of Data Objects
- •Lifecycle and Accessibility
- •Data Stores
- •Properties
- •Lifecycle and Accessibility
- •Data Inputs and Outputs
- •Data Input
- •States
- •Data Output
- •States
- •Service Task Mapping
- •Send Task Mapping
- •Receive Task Mapping
- •User Task Mapping
- •Call Activity Mapping
- •Script Task Mapping
- •Events
- •InputSet
- •OutputSet
- •Data Associations
- •DataAssociation
- •Assignment
- •DataInputAssociation
- •DataOutputAssociation
- •Data Objects associated with a Sequence Flow
- •10.4.2 Execution Semantics for Data
- •Execution Semantics for DataAssociation
- •10.4.3 Usage of Data in XPath Expressions
- •Access to BPMN Data Objects
- •Access to BPMN Data Input and Data Output
- •Access to BPMN Properties
- •For BPMN Instance Attributes
- •10.4.4 XML Schema for Data
- •10.5 Events
- •10.5.1 Concepts
- •Data Modeling and Events
- •Common Event attributes
- •Common Catch Event attributes
- •Common Throw Event Attributes
- •Implicit Throw Event
- •10.5.2 Start Event
- •Start Event Triggers
- •Start Events for Top-level Processes
- •Start Events for Sub-Processes
- •Start Events for Event Sub-Processes
- •Attributes for Start Events
- •Sequence Flow Connections
- •Message Flow Connections
- •10.5.3 End Event
- •End Event Results
- •Sequence Flow Connections
- •Message Flow Connections
- •10.5.4 Intermediate Event
- •Intermediate Event Triggers
- •Intermediate Events in Normal Flow
- •Intermediate Events Attached to an Activity Boundary
- •Attributes for Boundary Events
- •Activity Boundary Connections
- •Sequence Flow Connections
- •Message Flow Connections
- •10.5.5 Event Definitions
- •Event Definition Metamodel
- •Cancel Event
- •Compensation Event
- •Conditional Event
- •Error Event
- •Escalation Event Definition
- •Link Event Definition
- •Message Event Definition
- •Multiple Event
- •None Event
- •Parallel Multiple Event
- •Signal Event
- •Terminate Event
- •Timer Event
- •10.5.6 Handling Events
- •Handling Start Events
- •Handling Events within normal Sequence Flow (Intermediate Events)
- •Handling Events attached to an Activity (Intermediate boundary Events and Event Sub-Processes)
- •Interrupting Event Handlers (Error, Escalation, Message, Signal, Timer, Conditional, Multiple, and Parallel Multiple)
- •Non-interrupting Event Handlers (Escalation, Message, Signal, Timer, Conditional, Multiple, and Parallel Multiple)
- •Handling End Events
- •10.5.7 Scopes
- •10.5.8 Events Package XML Schemas
- •10.6 Gateways
- •10.6.1 Sequence Flow Considerations
- •10.6.2 Exclusive Gateway
- •10.6.3 Inclusive Gateway
- •10.6.4 Parallel Gateway
- •10.6.5 Complex Gateway
- •10.6.6 Event-Based Gateway
- •10.6.7 Gateway Package XML Schemas
- •10.7 Compensation
- •10.7.1 Compensation Handler
- •10.7.2 Compensation Triggering
- •10.7.3 Relationship between Error Handling and Compensation
- •10.8 Lanes
- •10.9 Process Instances, Unmodeled Activities, and Public Processes
- •10.10 Auditing
- •10.11 Monitoring
- •10.12 Process Package XML Schemas
- •11 Choreography
- •11.1 General
- •11.2 Basic Choreography Concepts
- •11.3 Data
- •11.4 Use of BPMN Common Elements
- •11.4.1 Sequence Flow
- •11.4.2 Artifacts
- •11.5 Choreography Activities
- •11.5.1 Choreography Task
- •11.5.2 Sub-Choreography
- •The Parent Sub-Choreography (Expanded)
- •11.5.3 Call Choreography
- •11.5.4 Global Choreography Task
- •11.5.5 Looping Activities
- •11.5.6 The Sequencing of Activities
- •11.6 Events
- •11.6.1 Start Events
- •11.6.2 Intermediate Events
- •11.6.3 End Events
- •11.7 Gateways
- •11.7.1 Exclusive Gateway
- •11.7.2 Event-Based Gateway
- •11.7.3 Inclusive Gateway
- •11.7.4 Parallel Gateway
- •11.7.5 Complex Gateway
- •11.7.6 Chaining Gateways
- •11.8 Choreography within Collaboration
- •11.8.1 Participants
- •11.8.2 Swimlanes
- •Choreography Task in Combined View
- •Sub-Choreography in Combined View
- •11.9 XML Schema for Choreography
- •12 BPMN Notation and Diagrams
- •12.1 BPMN Diagram Interchange (BPMN DI)
- •12.1.1 Scope
- •12.1.2 Diagram Definition and Interchange
- •12.1.3 How to Read this Clause
- •12.2 BPMN Diagram Interchange (DI) Meta-model
- •12.2.1 Overview
- •12.2.2 Abstract Syntax
- •12.2.3 Classifier Descriptions
- •12.2.4 Complete BPMN DI XML Schema
- •12.3 Notational Depiction Library and Abstract Element Resolutions
- •12.3.1 Labels
- •12.3.2 BPMNShape
- •Markers for Activities
- •Tasks [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Ad Hoc Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Ad Hoc Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Transactions [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Transactions [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Event Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Event Sub-Processes [BPMNShape]
- •Call Activities (Calling a Global Task) [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Call Activities (Calling a Process) [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Call Activities (Calling a Process) [BPMNShape]
- •Data [BPMNShape]
- •Events [BPMNShape]
- •Gateways [BPMNShape]
- •Artifacts [BPMNShape]
- •Lanes [BPMNShape]
- •Pools [BPMNShape]
- •Choreography Tasks [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Sub-Choreographies [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Sub-Choreographies [BPMNShape]
- •Call Choreographies (Calling a Global Choreography Task) [BPMNShape]
- •Collapsed Call Choreographies (Calling a Choreography) [BPMNShape]
- •Expanded Call Choreographies (Calling a Choreography) [BPMNShape]
- •Choreography Participant Bands [BPMNShape]
- •Conversations [BPMNShape]
- •12.3.3 BPMNEdge
- •Connecting Objects [BPMNEdge]
- •12.4 Example(s)
- •12.4.1 Depicting Content in a Sub-Process
- •Expanded Sub-Process
- •Expanded Sub-Process with Start and End Events on Border
- •Collapsed Sub-Process
- •12.4.2 Multiple Lanes and Nested Lanes
- •12.4.3 Vertical Collaboration
- •12.4.4 Conversation
- •12.4.5 Choreography
- •13 BPMN Execution Semantics
- •13.1 General
- •13.2 Process Instantiation and Termination
- •13.3 Activities
- •13.3.1 Sequence Flow Considerations
- •13.3.2 Activity
- •13.3.3 Task
- •13.3.4 Sub-Process/Call Activity
- •13.3.5 Ad-Hoc Sub-Process
- •Operational semantics
- •13.3.6 Loop Activity
- •13.3.7 Multiple Instances Activity
- •13.4 Gateways
- •13.4.1 Parallel Gateway (Fork and Join)
- •13.4.2 Exclusive Gateway (Exclusive Decision (data-based) and Exclusive Merge)
- •13.4.3 Inclusive Gateway (Inclusive Decision and Inclusive Merge)
- •13.4.4 Event-based Gateway (Exclusive Decision (event-based))
- •13.4.5 Complex Gateway (related to Complex Condition and Complex Merge)
- •13.5 Events
- •13.5.1 Start Events
- •13.5.2 Intermediate Events
- •13.5.3 Intermediate Boundary Events
- •13.5.4 Event Sub-Processes
- •Operational semantics
- •13.5.5 Compensation
- •Compensation Handler
- •Compensation Triggering
- •Relationship between Error Handling and Compensation
- •Operational Semantics
- •13.5.6 End Events
- •Process level end events
- •Sub-process level end events
- •14 Mapping BPMN Models to WS-BPEL
- •14.1 General
- •14.2 Basic BPMN-BPEL Mapping
- •14.2.1 Process
- •14.2.2 Activities
- •Common Activity Mappings
- •Task Mappings
- •Service Task
- •Receive Task
- •Send Task
- •Abstract Task
- •Service Package
- •Message
- •Interface and Operation
- •Conversations and Correlation
- •Sub-Process Mappings
- •Mapping of Event Sub-Processes
- •Activity Loop Mapping
- •Standard Loops
- •Dealing with LoopMaximum
- •Multi-Instance Activities
- •14.2.3 Events
- •Start Event Mappings
- •Message Start Events
- •Error Start Events
- •Compensation Start Events
- •Intermediate Event Mappings (Non-boundary)
- •Message Intermediate Events (Non-boundary)
- •Timer Intermediate Events (Non-boundary)
- •Compensation Intermediate Events (Non-boundary)
- •End Event Mappings
- •None End Events
- •Message End Events
- •Error End Events
- •Compensation End Events
- •Terminate End Events
- •Boundary Intermediate Events
- •Message Boundary Events
- •Error Boundary Events
- •Compensation Boundary Events
- •Multiple Boundary Events, and Boundary Events with Loops
- •14.2.4 Gateways and Sequence Flows
- •Exclusive (Data-based) Decision Pattern
- •Exclusive (Event-based) Decision Pattern
- •Inclusive Decision Pattern
- •Parallel Pattern
- •Sequence Pattern
- •Structured Loop Patterns
- •Handling Loops in Sequence Flows
- •14.2.5 Handling Data
- •Data Objects
- •Properties
- •Input and Output Sets
- •Data Associations
- •Expressions
- •Assignments
- •14.3 Extended BPMN-BPEL Mapping
- •14.3.1 End Events
- •14.3.2 Loop/Switch Combinations From a Gateway
- •14.3.3 Interleaved Loops
- •14.3.4 Infinite Loops
- •14.3.5 BPMN Elements that Span Multiple WSBPEL Sub-Elements
- •15 Exchange Formats
- •15.1 Interchanging Incomplete Models
- •15.2 Machine Readable Files
- •15.3.1 Document Structure
- •15.3.2 References within the BPMN XSD
- •15.5 XSLT Transformation between XSD and XMI
- •B.1 Scope
- •B.2 Architecture
- •B.3 Diagram Common
- •B.3.1 Overview
- •B.3.2 Abstract Syntax
- •B.3.3 Classifier Descriptions
- •B.4 Diagram Interchange
- •B.4.1 Overview
- •B.4.2 Abstract Syntax
- •B.4.3 Classifier Descriptions
Participant Bands for Choreography Tasks and Sub-Choreographies that are not the initiator of the Activity MUST have a light fill (see “Choreography Task” on page 323 and “Sub-Choreography” on page 328 for more details).
Flow objects and markers MAY be of any size that suits the purposes of the modeler or modeling tool. The lines that are used to draw the graphical elements MAY be black.
The notation MAY be extended to use other line colors to suit the purpose of the modeler or tool (e.g., to highlight the value of an object attribute).
The notation MAY be extended to use other line styles to suit the purpose of the modeler or tool (e.g., to highlight the value of an object attribute) with the condition that the line style MUST NOT conflict with any current BPMN defined line style. Thus, the line styles of Sequence Flows, Message Flows, and Text Associations MUST NOT be modified or duplicated.
7.6Flow Object Connection Rules
An incoming Sequence Flow outgoing Sequence Flow can also has this capability.
can connect to any location on a Flow Object (left, right, top, or bottom). Likewise, an connect from any location on a Flow Object (left, right, top, or bottom). A Message Flow
NOTE: BPMN allows this flexibility; however, we also RECOMMEND that modelers use judgment or best practices in how Flow Objects should be connected so that readers of the Diagrams will find the behavior clear and easy to follow. This is even more important when a Diagram contains Sequence Flows and Message Flows. In these situations it is best to pick a direction of Sequence Flows, either left to right or top to bottom, and then direct the Message Flows at a 90o angle to the Sequence Flows. The resulting Diagrams will be much easier to understand.
7.6.1Sequence Flow Connections Rules
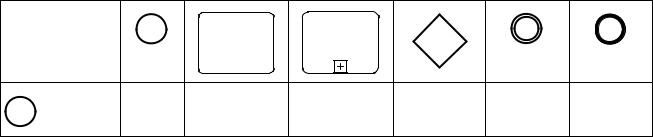
Table 7.3 displays the BPMN Flow Objects and shows how these objects can connect to one another through Sequence Flows. These rules apply to the connections within a Process Diagram and within a Choreography Diagram. The symbol indicates that the object listed in the row can connect to the object listed in the column. The quantity of connections into and out of an object is subject to various configuration dependencies are not specified here. Refer to the sub clauses in the next clause for each individual object for more detailed information on the appropriate connection rules. Note that if a Sub-Process has been expanded within a Diagram, the objects within the Sub-Process cannot be connected to objects outside of the Sub-Process, nor can Sequence Flows cross a Pool boundary.
Table 7.3 – Sequence Flow Connection Rules
From\To
‰
40 |
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN), v2.0.2 |
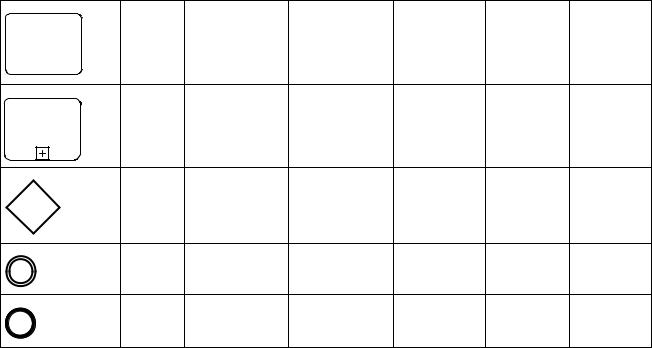
Table 7.3 – Sequence Flow Connection Rules
‰
‰
‰
‰
Only those objects that can have incoming and/or outgoing Sequence Flows are shown in the table. Thus, Pool, Lane, Data Object, Group, and Text Annotation are not listed in the table. Also, the Activity shapes in the table represent
Activities and Sub-Processes for Processes, and Choreography Activities and Sub-Choreographies for Choreography.
7.6.2Message Flow Connection Rules
Table 7.4 displays the BPMN modeling objects and shows how these objects can connect to one another through Message Flows. These rules apply to the connections within a Collaboration Diagram. The symbol indicates that the object listed in the row can connect to the object listed in the column. The quantity of connections into and out of an object is subject to various configuration dependencies that are not specified here. Refer to the sub clauses in the next clause for each individual object for more detailed information on the appropriate connection rules. Note that Message Flows cannot connect to objects that are within the same Pool.
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN), v2.0.2 |
41 |
