
- •ВВЕДЕНИЕ
- •ACQUAINTANCE
- •MY FAMILY
- •HOMES and HOUSES
- •WEATHER
- •Bibliography
- •Bibliography
- •YOUTH PROBLEMS
- •Bibliography
- •Sightseeing
- •Mysterious Britain
- •Adventurous America
- •AMERICAN AND BRITISH HOLIDAYS
- •Bibliography
- •Bibliography
- •Cold Canada
- •The Land of the Long White Cloud
- •The Southern Land
- •Bibliography
- •The Russian Federation
- •Being in Russia
- •Bibliography
- •ENVIRONMENT
- •Bibliography
Bibliography
1.Adrianova, I. Learn and celebrate / I. Adrianova, N. Toumanova. –
Новосибирск : «Инфолио-пресс», 1992. – 159 c.
2.Dale, D. The little book of Australia / D. Dale. – Allen & Unwin, Australia, 2010. – 261 p.
3.Hornby, A. S. Oxford advanced learner’s dictionary / A.S. Hornby. – Oxford University Press, 2000. – 1540 p.
4.http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Economy_of_the_United_ Kingdom&action=history
5.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
6.http://eng.1september.ru
7.http://news.bbc.co.uk
8.http://www.bbclearningenglish.com И
9.http://www.ciee.org/wat/
10.http://www.magazine-deutschland.deД
11.http://www.onestopenglish.com
12.Nauton, J. Profile 1. Student’s Book. Intermediate / J. Nauton. – Oxford university Press, 2005. – 143Аp.
13.Nauton, J. Profile 2. Student’s Book. Intermediate / J. Nauton. – Oxford university Press, 2005.б– 175 p.
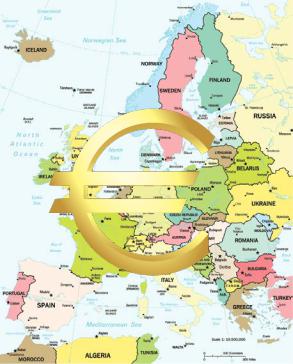
14.Wood, N. Business and Commerce Workshop / N. Wood. – Oxford university Press, 2005.и– 40 p.
15.Powell, Martinez, Jillett. New Business Matters. Coursebook / Powell, Martinez, Jillett.С– Thomson HEINLE, 2004. – 2000 p.
16.Speak Out: Журнал для зучающих английский язык. – 2005. –
№1.
17.Speak Out: Журнал для изучающих английский язык. – 2005. –
№4.
18.Speak Out: Журнал для изучающих английский язык. – 2005. –
№6.
19.Speak Out: Журнал для изучающих английский язык. – 2008. –
№4.
20.Kay, S. Inside Out. Student’s Book. Pre-intermediate / S. Kay, J. Vaughan, P. Kerr. – Oxford : Macmillan Publishers Limited, 2006. – 143 p.
21.Evans, V. Enterprise 3. Course Book. Pre-intermediate / V. Evans, G. Dooley. – Berkshire : Express Publishing, 2002. – 142 p.
226

BRITISH ECONOMY
Module 5
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
А |
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
227

Economy
(Great Britain)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pic. 115 |
|
|
||
1. Range this words into two columns: one is describing the geological |
||||||||
location, the nature and another is describing the government. |
||||||||
isles |
mild |
б |
area |
|
south-east |
|||
|
|
|
||||||
foggy |
reputed |
|
unofficially |
temperature |
||||
|
|
и |
Аzero |
|
|
|||
reserved |
referred |
|
haughty |
|||||
surround |
canal |
|
|
steady |
|
separate |
||
shallow |
С |
|
|
continent |
lake |
|||
castle |
|
|
||||||
prefer |
sea routes |
|
mountain |
focus |
||||
climate |
highest |
|
monarchy |
crossways |
||||
industrialised |
supreme |
|
Prime Minister |
person |
||||
legislative |
mining |
|
Parliament |
manufacturing |
||||
Commons |
textile |
|
executive |
constitutional |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NATURE |
|
|
|
|
GOVERNMENT |
|
|
isles |
|
|
|
|
industrialised |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Look again at the words above. What do you think we are going to talk about?
228
3. What do you know about the United Kingdom? What countries does it consist of? Why Britain is called Great Britain? What do you know about the flag (pic. 115)?
4. Read the text below and decide if your answers are true or false.
Britain is the name of the island which contains the countries of England, Scotland and Wales. Northern Ireland is on a separate island and together they are called the British Isles.
Britain or Great Britain is the name of an island off the north-west coast of Europe, one of the British Isles. It consists of England, Scotland and Wales, and is part of the United Kingdom.
5. Reorder the sentences to make a short conversation between Ann
A:I’m a bit confused. I thought Britain, GreatИBritain and the British Isles mean the same thing. Am I right? Д
A:I see. Does it also mean the United Kingdom, then?
A:Can you explain why BritainАis called Great Britain?
B:No, it consists onlyбof the country’s three parts. Its fourth part Ireland is in the next largest island – Ireland.
B:In fact, it is onlyиone of the British Isles. It’s the biggest one. That is why it’s called ‘Great’, because of its size.
B:Well, Сin everyday speech Britain, Great Britain and the British Isles are used to mean the same country, but it is not quite correct.
6.In pairs read the conversation aloud. Take turns to be A and B.
7.Discuss the questions with your partner.
1.Are there a lot of immigrants in Britain?
2.What countries do they come from?
3.What are the reasons for settling in Britain?
4.What do you know about the racial tension in Britain?
8. Now read the text below about people living in Great Britain and decide if your answers are true or false.
229
People have been coming to settle in Britain for centuries from many parts of the world. Some came to avoid political or religious persecution, others to find a better way of life or an escape from poverty.
The Irish have long made homes in Britain. Many Jewish refugees started a new life in the country towards the end of the nineteenth century and in the 1930s and after 1945 large numbers of other European refugees settled in Britain. The large communities from the West Indies and South Asian subcontinent date principally from the 1950s and 1960s. There are also groups from the United States and Canada, as well as Australians, Chinese and various European communities such as Greek and Turkish Cypriots, Italians and Spaniards.
The non-white population of Great Britain is about 4 million (some
5.5 per cent of the total population), about half of whom were born in Brit- |
||||
ain. |
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
Д |
|
9. Read the text again (ex. 8) and make a list of nationalities settling |
||||
Britain and countries they came from. |
|
|||
NATIONALITY |
А |
COUNTRY |
||
Irish |
|
Ireland |
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
10. Rearrange the words to create a short conversation between Kristina and Alexander.
K: of – I – country – of – the – usually – as – immigrants – a – think
– US – of. Would – immigrants – of – Britain – lot – a –has – say –you? A: Well, lot – a – quite – but – the – US – as –many – so – not. K: Europeans – they –mostly – Are?
A:Oh, no. Britain – in – be – world – to – over – people – all – practically – from – see – the – surprised – would – You.
K:Would – Commonwealth – British – the – mostly – of – countries
–the – from – say – you?
A:Well, are – immigrants – the – of – many.
K: Is – Britain – in – a – such – as – tension – racial – thing – there? A: Certainly, cities – with – the – inner – which – deprivation – greatest – of – areas – the– in – concentrates – in – non-white – especially
– population.
230
11. Helen is going to make a report about the UK. Complete her speech with words from the box. If you don’t know any facts use the Internet.
England |
Irish Sea |
|
Scotland |
|
France |
Wales |
|
|||||
Irish Repub- |
situated |
|
Spain |
|
|
London |
Atlantic |
|
||||
lic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edinburgh |
Northern Ire- |
Cardiff |
|
Europe |
Belfast |
|
||||||
|
|
|
land |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Strait of Do- |
islands |
|
North Sea |
|
England |
English |
|
|||||
ver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Channel |
|
|
Wales |
European |
|
Scotland |
|
Northern Ire- |
consists |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
land |
|
|
|
|
|
The UK 1 …… of four main countries which are: 2……, 3……, 4…… |
||||||||||
and |
5 |
…… . Their capitals are |
6 |
……, |
7 |
……, |
8 |
И9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
…… and …… . |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
The UK is an island state: it is composed of some 5,500 10…… , |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
11 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
large and small. Two main islands are Great Britain (in which are …… , |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
12…… and 13……) to the east and Ireland (in which are 14…… and the in- |
||||||||||||
dependent 15……) to the west. TheyАare separated by the 16…… . |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
The UK is one of the world’s smaller countries (it is twice smaller |
||||||||||
than 17…… or 18……). The UK is 19 …… off northwest coast of 20…… between the 21 …… Ocean on the north and northwest and the 22…… on the
и |
23 |
24 |
…… (or La |
east and is separated from the ……continent by the |
|
||
Manche) and the 25…… (or Pas de Calais). |
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
12. Tanya and Boris are talking about Great Britain. Work in pairs. |
|||
Complete their conversation with the words from the text in ex. 8. Then role-play the dialogue.
T: Do you know the names of the main islands of the _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Isles?
B: I think I do. They are _ _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _ _ _ _ (in which are England, Wales and Scotland) and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ (in which are Northern Ireland and the independent Irish Republic).
T: Do the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _ _ consist of many _ _ _ _ _ _ _? B: Yes, about 5,500.
231

T: I’m often confused about the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ of Northern Ireland and the Irish Republic. Which are they?
B: Well, just remember: _ _ _ _ _ _ is the capital of an independent state, and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ is the capital of Northern Ireland.
T:Well, I’ll try to remember.
13.Work in pairs. Use the Internet or other sources to find the information about the words in italics from the text in ex. 11. Then make a short presentation to the rest of the class. You may use the Smart Board.
14.Match the pictures (116 – 118) with the texts below (a-c).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
Pic. 116. |
|
|
|
Д |
|
Pic. 118. |
|
|||||
|
|
Pic. 117. |
|
|
|
|||||||
a. English is not the on- |
b. One can see two an- |
c. The formal name of |
||||||||||
ly language which peo- |
imals on |
British |
royal |
the British national flag |
||||||||
ple use in the UK. Eng- |
coat of arms. One of |
is Union Flag but it is |
||||||||||
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
lish is the official lan- |
them isАthe lion. The |
commonly |
known |
as |
||||||||
guage. But |
some peo- |
‘king of beast’ has been |
the Union Jack. It com- |
|||||||||
|
|
С |
usedбas a symbol of na- |
bines |
the |
St George’s |
||||||
ple speak Scottish |
in |
|||||||||||
western |
|
Scotland, |
tional strength and of |
cross |
of |
England, |
St |
|||||
Welsh |
in |
parts |
of |
the |
British monarchy |
Andrew’s |
cross |
of |
||||
northern |
and central |
for many centuries. The |
Scotland and St Pat- |
|||||||||
Wales, |
and |
Irish |
in |
other one is the uni- |
rick’s |
cross of |
Ireland. |
|||||
Northern Ireland. |
|
corn. The unicorn is a |
‘Union’ symbolizes the |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
mythical |
animal |
that |
union |
of |
England |
and |
||
|
|
|
|
looks like a horse with |
Scotland |
in |
1603, |
|||||
|
|
|
|
a |
long |
straight |
horn |
‘Jack’ means the flag of |
||||
|
|
|
|
growing from its fore- |
ships which shows their |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
head, and is a symbol |
nationality. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
of purity. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
232
15.Work in three groups A, B and C. Group A, you are going to read the text about the language in the UK; group B – about the British royal coat of arms; and group C – about the British national flag.
16.Complete this table with the information from your text. For example, if you read about the flag, complete the answers for the flag.
the information about the coat of arms and the languages.
LANGUAGE |
|
COAT OF ARMS |
FLAG |
||||
official |
…… |
|
animals on |
…… |
|
the formal |
……. |
language |
|
|
the coat of |
…… |
|
name |
……. |
|
|
|
arms |
|
|
|
|
other lan- |
…… |
|
the ‘king |
…… |
|
flag is |
…… |
guages |
…… |
|
of beast’ is |
|
|
commonly |
…… |
|
…… |
|
a symbol |
|
|
known as |
|
|
|
|
of |
|
|
|
|
countries |
…… |
|
the uni- |
…… |
|
three |
…… |
where |
…… |
|
corn is a |
|
|
crosses of |
…… |
people |
…… |
|
symbol of |
|
|
the flag |
…… |
speak oth- |
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
||
er lan- |
|
|
|
|
|
||
guage |
|
|
|
|
|
||
17. Now work with a partner fromАthe other group and ask and an- |
|||||||
swer questions as in the example. If you read about the flag, find out |
|||||||
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
|
|
• What is the official language of the UK?
• What animals are on the coat of arms?
• What is the formal name of the British national flag?
• And etc…
18.Tell the group about the British country profile using the map and the information you have learnt from the previous exercises.
19.Look at the list of words. What do you think we are going to talk about?
financial |
exchange |
industry |
trade |
central bank |
production |
233
20. Put the words from ex. 19 into the gaps.
1.London is Europe's largest … centre.
2.The Bank of England is the … of the United Kingdom.
3.Based on market … rates, the United Kingdom is today the fifth largest economy in the world.
4.The British motor … is a significant part of this sector.
5.The Industrial Revolution started in the United Kingdom with an initial concentration on heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining, steel … .
21. Read the text about the economy in the UK to find out if the statements are true or false?
1.The United Kingdom is the first largest economy in the world.
2.The Industrial Revolution started in the UnitedИKingdom with an initial concentration on the agriculture sector.
3.The branches of the heavy industry areДbanking and insurance.
4.The British motor industry is an important part of the manufacturing sector.
5.Rolls-Royce holds a major shareАof the automobile production.
6.The chemical and pharmaceutical industry is underdeveloped in the UK.
7.BAE Systems, this бis the world's second and sixth largest pharmaceutical firms based in the UK.
8.The undergroundиcoal gasification is an alternative to coal-fired electricity generation.
9.The volumeСof current UK coal consumption represents reserves that could last the UK about 300 years.
10.Sellafield is the major nuclear reprocessing plants in the UK.The UK, a leading trading power and financial center. Based on
market exchange rates, the United Kingdom is today the fifth largest economy in the world and the second largest in Europe after Germany. The Industrial Revolution started in the United Kingdom with an initial concentration on heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining, steel production, and textiles. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy. The British motor industry is an important part of this sector. Civil and defense aircraft production is led by the United Kingdom's largest aerospace firm, BAE Systems. Rolls-Royce holds a major share of the global aerospace engines market. The chemical and
234
pharmaceutical industry is strong in the UK, with the world's second and sixth largest pharmaceutical firms (GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca, respectively) being based in the UK.
The UK has a small coal reserve along with significant, yet continuously declining natural gas and oil reserves. An alternative to coal-fired electricity generation is underground coal gasification (UCG). UGC involves injecting steam and oxygen down a borehole, which extracts gas from the coal and draws the mixture to the surface - a potentially very low carbon method of exploiting coal. Identified onshore areas that have the potential for UGC amount to between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes. Based on current UK coal consumption, these volumes represent reserves that could last the UK
has major nuclear reprocessing plants, includingИSellafield. Great Britain is expected to launch the building of new nuclear reactors to replace existing generators and to boost UK's energy reserves.
between 200 and 400 years.
As of 2006, the United Kingdom operates 24 nuclear reactors generating one-fifth of its electricity Д(19.26% in 2004). The UK also
ropean standards, producing aboutА60% of food needs with less than 2% of the labor force.иAround two-thirds of the production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The main crops that are grown are wheat, barley,Сoats, oilseed rape, maize for animal feeds, potatoes and sugar beet. New crops are also emerging, such as linseed for oil and hemp for fibre production. The main livestock which are raised are cattle, chickens (the UK is the second largest poultry producer in Europe after France) and sheep. Agriculture is subsidised by the European Union's Common Agricultural Policy.
Agriculture is intensive,бhighly mechanized, and efficient by Eu-
Transport in the United Kingdom is facilitated by well-developed road, air, rail, and water networks. Urban rail networks are also well developed in London and several other cities, including the Manchester Metrolink and the London Underground. The London Underground is the oldest and most extensive underground railway in the world, and as of 2007 consists of 407 km (253 mi) of line and serves 275 stations. London Heathrow Airport is England's largest airport, the largest airport by passenger volume in Europe and one of the world's busiest
235
airports. London Gatwick Airport is England's second largest airport, followed by Manchester Airport.
There are around 7,100 km (4,400 mi) of navigable waterways in England. An estimated 165 million journeys are made by people on Britain's waterways annually. The Thames is the major waterway in England, with imports and exports focused at the Port of Tilbury, one of the three major ports in the UK. The UK retains a significant, although vastly reduced, fishing industry. Its fleets bring home fish ranging from sole to herring. Kingston upon Hull, Grimsby, Fleetwood, Great Yarmouth, Peterhead, Fraserburgh, and Lowestoft are among the coastal towns that have fishing industries.
The UK service sector, however, has grown substantially, and
arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is rankedИas the sixth major tourist destination in the world. London, by a considerable margin, is the most visited city in the world with 15.6 million visitors in 2006,
now makes up about 73% of GDP. The service sector is dominated by
financial services, especially in banking and insurance. Tourism is very
important to the British economy. With over 27 million tourists
ahead of 2nd placed Bangkok (10.4 million visitors) and 3rd placed |
|||||
Paris (9.7 million). |
|
Д |
|||
А |
|||||
|
|
|
|||
22. Match the beginnings (1 – 7) of the sentences with their endings (a |
|||||
– g). |
С |
б |
|
||
|
|
||||
1. |
Rolls-Royce holds a major share of the global ... |
||||
2. |
Manufacturing remainsиa significant part of … |
||||
3. |
Civil and defense aircraft production is led by … |
||||
4. |
An alternative to coal-fired electricity generation is … |
||||
5. Great Britain is expected to launch the building of new nuclear reactors to …
6. The Thames is the major …
7. The service sector is dominated by …
236
a)aerospace engines market.
b)financial services, especially in banking and insurance.
c)replace existing generators.
d)the economy.
e)the United Kingdom's largest aerospace firm.
f)underground coal gasification (UCG).
g)waterway in England.
23. Use your dictionary to explain the words. Choose any five to make sentences.
power; market; global; production; economy; engine; reserves; resources; generator; consumption; gasification; reprocessing; plant; reactor; destination.
|
И |
reduce; |
|
|
|
25. In pairs. Ask and answer your own questions using the information |
||
from the text. |
Д |
|
|
|
|
26. Work with your partner. Discuss economic situation in the UK. Is |
||
it on the rise or not? Use your answersАfrom the previous exercise. |
||
|
|
б |
27. Read the text about production in the UK to find out: |
||
1. |
What equipment is the most important component of Engineering? |
|
2. |
и |
|
What important sectors of the manufacturing industry can you name? |
||
3. |
On what subjects is there a considerable amount of published research? |
|
4. |
What things have tended to diminish the favorableness of the political- |
|
|
С |
|
legal environment for UK industry? |
||
5. |
What competitors do British firms and industries have? |
|
6. |
Can you name the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution? |
|
Production
One of the important component of Engineering and allied industries is electronics, audio and optical equipment, with the UK having a broad base of domestic firms, alongside a number of foreign firms manufacturing a wide range of TV, radio and communications products, scientific and
237
optical instruments, electrical machinery and office machinery and computers.
Other important sectors of the manufacturing industry include food, drink, tobacco, paper, printing, publishing and textiles.
Manufacturing is an important sector of the modern British economy. That’s why there is a considerable amount of published research on the subject of the factors affecting its growth and performance. Of late, such things as increases in taxation and regulation have tended to diminish the favourableness of the political-legal environment for UK industry. Within manufacturing, British firms and industries have often lagged behind their overseas competitors in terms of productivity and various other key performance measures. However, Britain – the birthplace of the Industrial
Revolution – continues to be one of the most attractive countries in the |
|
world for direct foreign industrial investment. |
И |
|
|
Д |
|
28. Make the correct word boundaries and you will know the main industries of the United Kingdom.
MACHINETOOLSINDUSTRIALEQUIPMENTSCIENTIFICEQUIPMEN THIPBUILDINGAIRCRAFTMOTORVEHICLESANDPARTSELECTROА NICMACHINERYCOMPUTERSPROCESSEDMETALSCHEMICALPRб ODUCTSCOALMININGOILPRODUCTIONPAPERFOODPROCESSINи GTEXTILESCLOTHINGANDOTHERCONSUMERGOODS.
29. Find the antonymsСto the words from the text. important; component; broad; include; modern.
30. Give the summary of the text using your answers from ex. 27.
31. Look through the following information. Name the banks of England, the main export and import partners.
London is the world's largest financial centre, with financial services based around two districts: 'The City' and the Docklands. The City houses the London Stock Exchange (shares and bonds), London Metal Exchange (Base Metal and Plastic futures), Lloyds of London (insurance), and the Bank of England. There are now over 500 banks with offices in the City and Docklands, with the majority of business in London being conducted on an international basis, with established leads in areas such as
238
Eurobonds, Foreign exchange markets, energy futures and global insurance.
Several of the major English cities have large financial sectors & related services, notably the Leeds city region which is home to several large banks & building societies. Manchester also has a large financial sector, including the Co-Operative Financial Services.
Do you know …
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main |
export |
USA 15%, Germany 11%, France 10%, Ire- |
|||
|
partners |
land 7%, Netherlands 6%, Belgium 6%, |
||||
|
|
|
Spain 5%, Italy 4% (2007) |
|||
|
Main |
import |
|
|
|
И |
|
Germany 14%, USA 9%,Russia 100%, |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
partners |
France 8%, Netherlands 7%, Belgium 6%, |
||||
|
|
|
Italy 5%, The People's Republic of China |
|||
|
|
|
|
А |
|
|
|
|
|
4%, Ireland 4% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
Russian-British projects secure large investments in |
|||||
|
|
С |
Russian economy |
|||
Today Economy MinisterиAndrei Shapovalyants said large-scale joint energy projects with such British companies as British Petroleum, Dana Petroleum and British Gas may bring up to $3 billion of direct investments
into Russian economy. Besides, Russian and British parties implement various projects in telecommunication and food processing industry. British companies invested total of $2.64 billion into Russian economy.
32. Read the following list of the words and find an odd one in each line.
a)banks; insurance; shipbuilding; financial;
b)intelligence; markets; international; exchange;
c)services; applicant, currency; officers; business.
33. Talk to your partner about British investments in Russian economy.
239
34. Work with a partner. Discuss the Russian-British relationships. Prove your ideas. Think about their
•economic situations;
•salaries;
•export;
•political view;
•import;
•benefits and rewards;
•maternity leave;
•belief;
•churches;
•hopes;
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
А |
|
sentence |
Count |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
||
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
I know exactly how much money I have in my bank account. |
|
|
||||||
True / False? |
С |
б |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2. |
I make sure I leave enough credit on my credit card for emergencies. |
|
||||||
True / False? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
I check my bank statements for mistakes on my account. |
|
|
|||||
True / False? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.I keep the receipt when I buy something. True / False?
5.I pay bills on time.
True / False?
240

Now find out about your relationship to money.
Number of true (T) answers:
5: You have total control over your finances. Perhaps you spend too much time thinking about money?
3-4: You have a healthy attitude to your financial affaires.
1-2: It is time for you to get organized. An accountant could help you with this.
0: You are in trouble! You need help from a financial professional. Get help now!
36. Match the speech bubbles (1-4) with the pictures 119 – 122.
1 Oh no, look at all |
|
|
2 Keep the receipt, |
|
these bills! Which |
|
|
in case it’s the |
|
should we pay first? |
|
|
wrong size. |
|
3 Who shall I write |
Д |
|||
|
|
А |
4 I’d like to pay cash. |
|
the cheque to? |
|
|
И |
|
|
б |
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
Pic. 120 |
|
|
|
|
|
Pic. 119 |
|
|
|
|
Pic. 121 |
Pic. 122 |
241
37. Match the beginnings (1-6) with the endings (a-f).
1.An advantage of the euro is that you don’t need to order foreign ……
2.I’d like to know how much I have in my bank ……
3.What’s the dollar-euro exchange ……
4.Don’t worry if the bank is closed; there’s a cash ……
5.When I travel on business, I always use a credit ……
6.Your bank ……
***
a)… rate today, please?
b)… machine where you can take out some money.
c)… statement gives details of all the money going in and out of your account.
d)… currency or traveller’s cheques when traveling in most of Europe.
e)… account, please. И
f)… card to pay restaurant and hotel bills. aboutД
|
|
А |
|
б |
|
и |
|
|
С |
|
|
Pic. 123
39. Are the statements true or false?
1.The euro is Europe’s first single currency since the Roman Empire.
2.More than 300 million people live in the *Eurozone.
242

3.The Italian lira was Europe’s oldest currency. It ended with the euro.
4.Northern Ireland is part of the Eurozone.
5.The US dollar is the world’s most important currency.
6.The euro now covers the world’s biggest currency zone.
*The Eurozone = the group of countries which have adopted the euro as their currency
Now check your answers.
Greek |
|
|
China |
the |
|
|
after |
was |
|
|
И |
|
|
third |
|
it |
Д |
||
|
|
is |
|
– |
|
|
it |
True1) True2) False3) drachma 4) |
|
– |
|
5) |
6) Indiaand |
||
|
А |
True |
False |
|
False |
||
40. |
Find out people’s views on the euro. Read the text below and an- |
|
swer the questions. |
|
|
|
С |
|
1. |
According to Hara, whatбhappened after the arrival of the euro? |
|
2. |
How good is the euro for Hara/s business? |
|
3. |
How did Barry manageиmoney before the euro? |
|
4. |
What are his views on the euro? |
|
5. |
How has the euro helped Dagmara’s work? |
|
6. |
What problem can Dagmara have if she buys from outside Europe? |
|
Hara Tavrides, a hotel manager from |
|
|
Crete |
|
|
‘When we changed over to the euro prices |
|
|
went up a lot and people protested. They |
|
|
went on strike and refused to go shopping. |
|
|
I think the euro has been good for tour- |
|
|
ism; people like their bills in a familiar |
|
|
currency. I miss the drachma though; it |
|
|
was Europe’s oldest currency.’ |
a hotel manager |
|
243

|
Barry Watson, an international lorry |
|||
|
driver from Ashford in Kent, UK |
|||
|
‘I don’t need lots of envelopes for differ- |
|||
|
ent currencies any more. I don’t have lots |
|||
|
of different coins and notes to carry |
|||
|
around. All my receipts are in euros so |
|||
|
doing my accounts is simple. It is always |
|||
|
a shock to come home to the British |
|||
|
pound again. I hope we join the Eurozone |
|||
|
soon.’ |
|
|
|
an international lorry driver |
|
|
|
|
|
Dagmara Witter, a buyer with a su- |
|||
|
permarket chain in Stuttgart, Germany |
|||
|
‘I spend a lot of time comparing prices |
|||
|
between European suppliers. I was sorry |
|||
|
to see the German mark go, but prices are |
|||
|
clearer since the euro. I have to think |
|||
|
carefully before I order from the States or |
|||
|
|
|
И |
|
|
Japan. Exchange rates are really im- |
|||
|
portant. It’s easy to lose money if the dol- |
|||
|
|
Д |
|
|
a buyer with a supermarket lar gets stronger.’ |
|
|||
chain |
А |
|
from: ProFile1 |
|
|
|
|||
|
б |
|
|
|
41. Work in groups. What do students in your group think of the Eu- |
||||
ro? How has itСaffectedиyour business / personal lives? If your country
is not in a common currency zone, would it be a good idea to join one? Let one of the students report your ideas to the rest of the group.
42. Complete the text for the Australian dollar against the euro. Try to use all the words from the box at least once.
over in to by during for from
Let’s look back for a moment at how the dollar has performed against the euro ¹…… the last six months. It stayed steady for the first month of the year at around 0.93 euros to one dollar. 2 …… February however, its value fell 3 …… two points 4 …… 0.93 5 …… 0.91 euros. 6 …… the second half of February the dollar rose 7 …… almost 0.96 euros, where it
244
remained stable for the first half of March. 8 …… the next six weeks, it dropped 9 …… almost 10 points 10 …… 0.86 euros. It then increased again slowly 11 …… May and June.
from: ProFile1
43. Look at the verbs in italics in the text above, and put them in the
table. |
|
|
WENT UP |
WENT DOWN |
NO MOVEMENT |
▲ |
▼ |
► |
44. |
Answer the clues and arrange them in an appropriate order to |
|||
make a crossword (pic. 124). |
|
И |
||
|
|
|||
Across |
|
Д |
||
2. ‘Oh no! We are in the …… (colour) again this month. How do we spend |
||||
so much money?’ |
|
|
|
|
4. Metal money. |
А |
|
||
7. ‘What’s the exchange rate between the euro and the dollar this week?’ |
||||
11. |
A printed list of the money going into and out of account every month. |
|||
12. |
Something which tells you what you have to pay for services or goods. |
|||
14. |
‘Great! There’s more money in my bank …… than I thought!’ |
|||
Down |
б |
|
|
|
1.VISA, Mastercard,Сetc. (two words)
2.A piece of paper which shows what you bought, and proves how much you paid for something.
5.‘You ……. me Є50, when are you going to pay me back?’
6.The official money of a country or region, e.g. US dollar, the euro.
8.Paper money.
9.The noun from ‘to pay’
10.Where to keep your money safe.
13.‘I didn’t have enough money to buy car so I asked my brother for a …… .’ и
245

|
|
И |
|
Д |
|
А |
|
|
б |
|
|
С |
|
|
и Pic. 124 |
|
|
45. Share your crosswords with your group mates. Are they different?
46. Complete the text with words from the box.
notes |
money |
transactions |
banking |
cheques |
cash |
loan |
credit cards |
account |
coins |
If we consider the long history of mankind, 1money hasn’t been around very long at all. The first 2…… appeared in Turkey in around the 7th century BC; and the first paper money, which is what we call 3……, appeared in China in the 14th century. The Italians invented modern 4…… and bookkeeping around the same time. Most royal heads of Europe had a 5……
246
from a Lombard banker. Until fifty years ago very few people had a personal bank 6…… . Nowadays, most of us have one to receive our salaries and write 7…… for everyday 8…… such as paying bills. In some countries, people walk round with large amounts of 9……, but in Britain and the States 10…… are more popular, and they are even used in public telephones and parking meters.
from: ProFile1
47. Match the phrasal verbs (1 – 5) in italics to their meanings (a-e).
1.Please make out your cheque to Hannah Green and associates. ……
2.It takes my bank two working days to carry out even a simple transac-
tion. ……
3.Could you fill in this form with your personal details, please. ……
4.I’d like to pay this cheque into my savings account,Иplease. ……
5.We need to take out lots of cash to pay the workmen. …….c) to remove / take away; Д
d) to complete with information; |
|
|
б |
e) to write the name of a person or business on a cheque. |
|
и |
|
48. Some key banking words areАbuilt around the verb draw. Study the |
|
words in context in the sentences (1-3), then choose the correct alterna- |
|
С |
|
tive in the sentences (a-c) below.
1. Good morning, I’d like to withdraw Є1,000 in cash from my current account, please.
2. Oh no, look at this letter from the bank. We are Є300 overdrawn. How has this happened?
3. Good news … the bank has agreed to increase the firm’s overdraft.
a)If you are overdrawn, your account is negative / positive.
b)If you have an overdraft, the bank owes you money / you owe money to the bank.
c)If you withdraw money from your account (make a withdrawal) you put money in / take money out.
247

49. Read the article and match the underlined words and expressions (1 – 6) to definitions (a – f) below.
Pic. 125
Credit card inventor dies at 88
vented an early version of the modernА-dayДVisa card. The Diners Club card already existed and allowedбshoppers to make 2cash-less transactions. But the 3balance had to be paid off in full within 30 days. Some banks offered credit on their bank cards,иbut these could not be used nation-wide. Williams saw 4a gap in the market for a card that could be used across the country. He andСhis team began distributing the BankAmerica card in California. Over the next ten years the card was 5licensed by other banks, before it was finally renamed the Visa card in 1970. Now, there are an estimated 785m major credit cards in circulation in the US. The average US credit card debt carried over each month per 6household last year was nearly $9,000 (£5,500), triple the average of $3,000 (£1,800) in 1990. In Britain, the average UK household today owes more than £6,000 on credit and *store cards.
The man who millions of shoppers have to thank – or blame – for the state
of their finances has died aged |
88. In 1958, during the US post-war |
|
1 |
|
И |
|
consumer boom, American bank (pic. 125) executive Joseph Williams in- |
|
*store card = a kind of credit card which you can use to buy goods in the department store which issued it.
(from ProFile1)
a)a home;
b)paying for things without handling real money;
248

c)a missing service / product which is identified as a business opportunity;
d)a period when business is good because people are spending more;
e)the final amount owing in an account;
f)given permission to do something in return for money.
50. Complete the table about the cards which are mentioned. |
|
||
CARD |
ADVANTAGES |
DISAD- |
|
|
|
VANTAGES |
/ |
Diner’s Club (in 1958) |
|
CONDITIONS |
|
offered credit |
|
|
|
Early bank cards |
debts can build up |
|
|
BankAmerica / Visa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|
51. Label the timeline with key details about the evolution of the credit |
|||||||||
card, taken from the text. |
|
|
|
Д |
|
||||
1958 |
|
|
1960s |
|
|
1970 |
|
Nowadays |
|
|
|
|
Card was li- |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
censed by the |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
banks |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
||
52. Read the text below and answer the questions. |
|
||||||||
1. Which is more important to you: your time or your money? |
|||||||||
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
||
2. The following daily activitiesАall take up important time. Which one |
|||||||||
would you pay someone to do? |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
С |
|
|
walking your dog |
cleaning |
||||
supermarket shopping |
|||||||||
housework |
|
|
|
ironing |
|
cooking |
|||
Economics professor, Ian Walker, of Warwick University, has written a mathematical formula so that we can calculate how much time costs. For example, the average British minute is worth about £0.13. Brushing your teeth for three minutes uses up £0.4 in ‘lost’ time, and washing a car by hand has a cost of £4.50. The study found that the typical cost of cooking dinner (the value of time spent + the value of the ingredients) was £15.43!
from: ProFile1
249

53. Read what four people said about their time at work and answer the questions below.
|
|
И |
|
Hanako: |
Д |
Izumo: ‘I can |
|
|
|
||
‘We’ve invest- |
|
|
save a lot of |
ed a lot of |
|
|
time by using |
money in |
|
|
a new soft- |
product devel- |
|
|
ware program |
opment this |
|
|
to organize |
и |
|
|
|
year whichА |
|
my work |
|
will reduce our |
|
|
schedule.’ |
lead бtime in fu- |
|
|
Lukas: ‘We |
ture.’ |
|
|
|
Dario: ‘I waste |
|
|
|
too much time |
|
|
have to meet |
in the car. I |
|
|
two or three |
spend about |
|
|
urgent dead- |
two hours a |
|
|
lines nearly |
day getting to |
|
|
every week |
the office and |
|
|
or there is |
back. By the |
|
|
trouble.’ |
time I get |
|
|
|
home I’m real- |
|
|
|
ly tired.’ |
|
|
|
Who: |
|
1) |
must finish hisС/ her work on time? ……; |
2) has found a way to do something more quickly? ……; |
|
3) |
has spent time and money on improving the business? ……; |
4) |
thinks he / she uses his / her time badly? …… . |
54. Match the words on the left with those on the right.
have |
an urgent deadline |
waste / save |
a busy lifestyle |
meet |
new machinery / technology |
invest in |
time or money |
250

55. Read the text below about a German electronics wholesaler and his problems with time. Match the words in italics in the text below to the definitions (1-6).
1)time from the customer’s order to delivery ……;
2)when something is late ……;
3)arrival of goods at a person’s or company’s address ……;
4)sending products from the factory ……;
5)all the stages leading to a result ……;
6)the latest time for completing a task …… .
|
|
И |
|
Д |
|
С |
А |
|
бPic. 126 |
|
|
Getting our products toиour customers (pic. 126) is a long and difficult pro-
cess. Our main problem is time. Customers order our printers and then we have to arrange delivery to their offices. The problem is that we make the printers in the UK and it can take a long time for our factory to dispatch the printers to our customers in Germany. This can take a long time. Sometimes we miss deadlines: we say we want the printers with the customer in two weeks, but they often get them four weeks later! There are many reasons for the delays: the factory is too busy, problems with the paperwork, etc. To be successful, we need to keep our lead time short – it shouldn’t take longer than two weeks from the customer’s order to the moment the printer arrives at their office.
from: ProFile1
251
56.Look at the title of the article below. What do you think it will be about?
57.Read the article to find out:
1.What problems did this company have?
2.What did they decide to do?
Invest in time!
When Peter Fenn started Fenn Tool Ltd in 1982, there were only three employees based in an old church hall. They designed special tools for the telecommunications and aerospace industries. The company’s suppliers in Austria and Switzerland made the tools, which they then dis-
patched by lorry to Fenn Tool Ltd in the UK. |
И |
However, the problem was that supply took six to ten weeks, and |
|
Fenn Tool Ltd couldn’t meet their customers’ urgent deadlines. |
|
Д |
|
So they decided to buy a computer design and manufacturing package so that they could do the whole job themselves. They went ahead and spent £250,000. It was a big financial risk, but it has really changed the business.
Fenn Tool has cut the lead time down to only 48 hours from order to finished product. In January this year, the company won a £30,000 prize as
Small Business of the Year and now has a client list that includes Rolls- |
||
Royce, Marconi and BAE Systems.АFinancial Director, Sarah Potter, says |
||
that she would advise other small businesses to take the risk and in vest in |
||
new technology. |
б |
|
|
и |
from: ProFile1 |
|
|
|
58. Look at these four scenes (pic. 127 – 130) from the article (ex. 57)
and put them in the correct order. |
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
1 – |
2 – |
3 – |
4 – |
252

|
|
|
|
|
Pic. 128 |
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
Pic. 129 |
|
А |
Pic. 130 |
||
|
|
||||
|
б |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
59. Read the text, written by an economist, about employment costs. |
|||||
Decide if statements 1-6 are true or false. |
|
|
|||
|
и |
|
|
|
|
For many businessesС‘time (in particular the workers’ time) equals money’
– this is why businesses in developed economies with high employment costs are always searching for ways to cut their costs.
Two main approaches are open to businesses: to invest in technology and reduce the number of man hours spent on the various tasks of the job, or to relocate production to countries with lower labour costs.
In the first approach, equipment replaces human labour. Machines and robots can work twenty-four hours a day, don’t go on strike, and never take time off for lunch or holidays! In the second, labour-intensive jobs, such as in the clothing or footwear industries, are exported to countries as factories are moved to countries where wages are lower.
253
Relocation to other countries is also affecting service industries. In Britain, jobs in some call centres have vanished down cables to English-speaking workers in India or the Philippines.
Western society could eventually end up with a few highly-trained and well-paid workers in technical fields, with armies of low-skilled workers struggling to make a living in the minimum wage service industries.
from: ProFile1
1.Business are always looking for ways to cut costs.
2.There are a large number of ways to cut labour costs.
3.Investing in machines and equipment can reduce the need for human labour.
4.Social protection can lead to job losses.
5.Service industries are protected from these changes.И
6.A lot of people may be condemned to working in low-paid jobs.TIME = MONEY Д have
▼ |
А |
▼ |
б |
▼ |
|
In developed countries labour costs are high because |
|
…………………………………………………………………………… |
|
|
и |
Two ways of reducing costs; |
|
first way: |
С |
|
|
…………………………………………………………………………….
▼
second way:
…………………………………………………………………………….
▼
Long-term consequences:
…………………………………………………………………………….
61. Read the extract and answer the questions after it.
More than one in seventeen British workers work from home, with the level rising every year.
However, Mr Evans, 41, who works for IBM, decided he would prefer to go back to an office after spending several months working from home. He
254
thought it would be better for his career, ‘The coffee machine chats are an important part of working life’, he says.
from: ProFile1
1.What technology do you think Mr Evans needed to work from home?
2.Why did he want to go back to work in an office?
3.Do you ever work from home?
4.If you had the choice, would you work from home or in an office? Why?
62. Read the text below and match the words in italics to the definitions (1 – 4).
UR Fashion plc began as a shop and it has now decided to enter the world of e-commerce and to sell over the Internet as well. It has set up a website and, in future, UR Fashion customers will be able to access the website to place orders. The website is user-friendly, so it will be easy for customers
to understand, and to find what they are looking for. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
И |
from: ProFile1 |
|
1) easy for people to use; |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Д |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
А |
|
|
|
|
2) to make a place on the Internet you can put information about yourself; |
|||||||
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|
|
3) doing business electronically by using the Internet; |
|
||||||
4) enter. |
и |
|
|
|
|
|
|
63. Complete sentences 1-3 below with the words from the box. |
|||||||
|
С |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payment |
|
order (vb) |
|
|
sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.If you have no time to go to the shops, you may prefer to …… online.
2.To make an online ……, you type in your credit card details.
3.Many businesses now include online……
255

64. Look at the pictures (pic. 131 – 136). Which of the products and services do you think would/wouldn’t be sold well online?
Pic. 131 Pic. 132 |
И |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
А |
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
Pic. 134 |
|
|
|
|
Pic. 133
Pic. 135
Pic. 136
256
65.Read the article in ex. 66. Were your predictions in ex. 64 right?
66.Are the following statements true or false? Read the article and check your answers.
1.Companies which have mail order catalogues should sell online.
2.Office supplies are good products for an online business.
3.Busy people are good online customers.
4.It is bad news if your competitors are online.
5.Niche products are never successful online.
If you are unsure whether your business can sell successfully online, consider the following questions:
What do you sell?
Products sold through catalogues and other direct channels usually do well on the web too. Some services, such as travel planning, are also suitable for
• Products which can be sent easily through the post. |
|
||||||
• |
Services or goods which customers don’t need to see or touch before |
||||||
buying. |
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
• Things you need and have to buy often. |
|
|
|||||
• |
Technology products. |
|
|
Д |
|
||
|
А |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
• Products that are difficult to ship. |
|
|
|
||||
• Services that can only sell in a local market. |
|
||||||
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|
• Products which customers may want to customize to their own tasted / |
|||||||
needs. |
и |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
use |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
you plan to sell? For example, if your customers have busy lifestyles, the time-saving advantages of shopping online may appeal to them.
Are your competitors online?
It’s a good sign if your main competitors are already online. But you need to make your website different! For instance, if you want to sell children’s toys online, it may be difficult to complete against the e-commerce efforts of national toy store chains. Look for a niche market such as educational toys, or toys based on book characters – you may be able to compete more successfully.
from: ProFile1
257
67. Search the square and find words connected with business online (30 words). The letters which are left make a secret word which is repeated. What is the word?
G |
O |
O |
G |
L |
E |
P |
S |
E |
A |
R |
C |
H |
A |
S |
H |
C |
O |
M |
P |
U |
T |
E |
R |
S |
C |
R |
O |
L |
L |
S |
O |
N |
F |
W |
O |
S |
R |
D |
P |
A |
C |
P |
S |
S |
I |
I |
M |
E |
F |
W |
O |
E |
C |
O |
M |
M |
E |
R |
C |
E |
N |
N |
E |
T |
I |
S |
C |
R |
E |
E |
N |
R |
S |
D |
D |
P |
K |
T |
P |
W |
C |
A |
S |
F |
S |
M |
O |
U |
S |
E |
O |
W |
O |
E |
A |
O |
E |
S |
R |
R |
D |
L |
O |
G |
O |
N |
W |
P |
A |
R |
G |
R |
B |
U |
S |
I |
N |
E |
S |
S |
S |
O |
N |
L |
I |
N |
E |
K |
S |
R |
W |
E |
O |
R |
E |
M |
A |
I |
L |
D |
C |
E |
C |
P |
A |
F |
S |
N |
S |
W |
C |
U |
R |
И |
R |
O |
T |
R |
|
S |
O |
||||||||||||||
O |
W |
E |
B |
D |
I |
G |
I |
T |
A |
L |
A |
R |
N |
D |
A |
P |
A |
S |
C |
L |
I |
C |
K |
Д |
D |
E |
M |
W |
S |
||
S |
M |
O |
|||||||||||||
O |
R |
S |
P |
Y |
W |
E |
B |
S |
I |
T |
E |
A |
S |
S |
H |
Make the correct word boundaries and you will know the answers. |
|
GOOGLESEARCHCOMPUTERSCROLLECOMMERCESCREENMOU |
|
|
б |
SELOGONBUSINESSONLINEEMAILCURSORWEBDIGITALCLICK |
|
MODEMWEBSITENETWORKOFICESURFUSERFRIENDLYACCESS |
|
и |
|
RAWSLOTDOWNLOADLINKICONINTERNETHOMEPAGECRASHА |
|
С |
|
Rearrange the letters and you will know a secret word.
SORADWSP
68. Match the words from the square in Ex. 67 to the definitions (1 – 14).
1. Another name for the web. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
2. A message sent electronically by computer. _ _ _ _ _
3. What you look at when you work at your computer. _ _ _ _ _ _
4. Computers use this kind of technology. _ _ _ _ _ _ _
5. Connected to the Internet. _ _ / _ _ _ _
6. Business over the Net. _ / _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
7. Many companies have this where you can find out about them. _ _ _ _ _
_ _
8. The first page that we access when we go onto 7. _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _
9. To travel across the Internet: not sail, but … _ _ _ _
258
10.Google is probably the world’s most-used _ _ _ _ _ _ engine.
11.Not a computer rat, but a computer _ _ _ _ _.
12.When everything stops working on your computer; like an accident. _
_ _ _ _
13.To receive information and files onto your computer. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
14.The sound 11 makes. _ _ _ _ _
Make the correct word boundaries and you will know the answers.
INTERNETEMAILSCREENDIGITALONLINEECOMMERCEWEBSIT EHOMEPAGESURFSEARCHMOUSECRASHDOWNLOADCLICK
69. Study the word combinations and try to explain them. Then write
them in your language. |
|
|
И |
|
Political instability |
|
|
|
Racial tension |
Mass unemployment |
|
|
|
Hyperinflation |
Massive trade deficits |
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
Cheap labour markets |
||
Poverty in the Third World |
|
|
The debt crisis |
|
The North-South divide |
|
|
The East-West divide |
|
The collapse of communism |
|
Environmental damage |
||
A population explosion |
б |
An ageing population |
||
Under-employment |
|
Trade wars |
||
|
|
|
||
Arms build-up |
и |
|
Oil supplies |
|
|
АPolitical extremism |
|||
International terrorism |
|
|||
С |
|
|
|
|
70. We are living in hard times. What do you think the greatest threats to the world economy are? Brainstorm ideas.
71. Which of the threats do you consider to be the key global issues? Are there others that you believe to be even more important? What do you think their economic implications might be?
72. Which countries or geographic areas do you think will have the most direct or indirect impact on the global economy over the next five to ten years? Can you justify your view?
259
73. Compare your views with your partner and those expressed in the article, The Death of Economics.
The Death of Economics
The world economy is falling apart. And no one has a clue what’s going wrong – least of all the economists.
Whereas in the past, supply and demand had a way of evening themselves out, we now swing from hyperinflation to soaring unemployment as slump follows boom. The once predictable business cycles which drive the market economy have gone out of control. The economic statistics issued by governments seem more unreliable than ever. And, for the first time, politicians have started talking about ‘the death of economics’.
Speculative Greed
A major cause of the crisis has been the business sector’s ruthless pursuit of capital. It was largely corrupt propertyИspeculators and poorly managed financial institutions that caused the collapse of the Japanese economy in the 90s and the subsequentД‘Asian meltdown’. The dotcom boom at the beginning of the 21st century was also motivated by short-term speculative greed. More money actually changes hands in four and a half days on the global currency marketsАthan is exchanged annually through trade in merchandise and services. Business, it seems, is a very slow way to make money. The fastestбway to make money is money.
Merger-mania
Two decades ofиbigger and bigger mergers and acquisitions have compounded the problem. In 1997 alone $ 1.6 trillion were spent on M&As. For theСboard members and shareholders of the companies concerned, there were huge windfall profits to be made, but for the companies themselves it was not always good news. Not was it good news for the thousands laid off as a result of bringing ex-competitors together. In the new globalised economy, the need to grow at all costs has also led companies like Enron and WorldCom to become increasingly creative in their accounting methods. In some companies has become common practice.
Different Worlds
But the real long-term crisis is the widening gap between rich and poor. Thirty per cent of the world’s population represents ninety per cent of the world’s GDP, whilst the other seventy per cent have to survive on the remaining ten per cent. The income ratio between the richest and poorest countries went from 30:1 in 1960 to 74:1 in 1997 – and it’s getting worse. So it isn’t trade deficits, post-communist chaos or the global arms build-up that pose the greatest threat to the world economy. Nor is it politi-
260
cal instability in Africa and the Middle East, international terrorism or the Latin American debt crisis. It is the emergence throughout both the developed and developing world of a vast and permanent underclass of seriously poor.
Cheap Labour from the East
In some cities in Central and Eastern Europe, unemployment is running as high as eighty per cent. Wages have fallen so far behind escalating inflation that immigration controls in the West have had to be tightened to prevent an influx of workers from the East. But, of course, this hasn’t stopped some Western companies exploiting cheap labour in both Eastern Europe and South-East Asia, and putting their own employees out of work.
The Working Poor
In the USA, where unemployment benefit is cut after six months and staying out of work is not an option, they areИcreating jobs at the cost of
decreased incomes. For in many of the inner cities of the USA they have
something approaching a Third WorldДeconomy. According to the latest
figures, 12.7% of Americans currently live below the poverty-line. The problem is not so much unemployment as under-employment, with millions of people in low-paid, deadА-end, so-called ‘McJobs’ that have zero prospects.
бCorporate Rule
The result of all this is that corporations now exercise an unprecedented influence on theиglobal economy and the distribution of wealth, as the world’s governments, powerless to regulate them, become increasingly irrelevant. NearС-monopolies like Microsoft are hard to fight and in industries like telecoms, the top ten companies control eighty-six per cent of the market. In fact, half the world’s richest institutions are not countries but companies. No wonder then that both countries and companies try to conceal the real figures. As the famous saying goes, ‘It’s often easier to be economical with the truth than truthful about the economy’.
from: New Business Matters
74. Which of the following topics does the article discuss?
1)the boom-bust economy;
2)political extremism;
3)the money markets;
4)social inequality;
5)retraining the unemployed;
6)corporate fraud;
261

7)the black economy;
8)government cover-ups.
75. What is your personal reaction to the article?
I totally agree that … .
I think the point about … is probably true. I don’t agree with the point about … at all. I already knew … , but I didn’t realize … . I’m not sure I can believe … .
What shocks me most is … .
76. Find the words and expressions in the article which mean:
1) no one has any idea; |
|
|
И |
|
2) a period when the economy is weak; |
|
|||
|
|
|||
3) a period when the economy is strong; |
|
|||
|
|
|
Д |
|
4) sudden and complete economic failure; |
|
|||
5) is exchanged; |
|
|
|
|
6) made things worse; |
|
|
|
|
7) large amounts of money you get unexpectedly; |
||||
8) rising rapidly; |
|
б |
|
|
9) to be made stricter; |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
10) the arrival a large number of people; |
|
|||
|
и |
|
|
|
11) never having happened before;А |
|
|||
12) it’s not surprising. |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
77. Complete the following notes on the article using the pairs of words |
||||
in the boxes. Try not to look back at the text. |
||||
|
profits + employees |
|
|
|
|
institutions + collapse |
|
||
|
boom + greed |
|
|
|
|
hyperinflation + unemployment |
|||
|
markets + money |
|
|
|
|
supply + demand |
|
|
|
|
debts + acquisitions |
|
|
|
|
increase + acquisitions |
|
||
1.In the past … and … used to even themselves out.
2.We now swing from … to soaring … .
3.Poorly managed financial … caused the … of the Japanese economy.
4.The dotcom … was motivated by short-term … .
262
5.The currency … are where the real … is made.
6.The … in the number of mergers and … has compounded the problem.
7.Shareholders made huge … but thousands of … were laid off.
8.Many companies now hide … to finance … .
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|
The real … is the widening … between rich and poor. |
||||||||
2. |
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
||
Seventy per cent of the world’s … has to survive on just ten per cent of |
||||||||
its … . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
The greatest … to the world economy is a new … of seriously poor. |
|||||||
4. |
… is running high and wages have fallen behind … . |
|||||||
5. |
Immigration … have been tightened to prevent an … of workers from |
|||||||
the East. |
|
|
б |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6. |
In the USA many have low-paid, dead-end … and live below the … - |
|||||||
line. |
|
и |
А |
|
|
|||
7. |
Companies now have more … than countries and comprise fifty per |
|||||||
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
|
|
cent of the world’s richest … . |
|
|
|
|
||||
8. |
It is easier to be economical with the … than truthful about the … . |
|||||||
78.What do you think about Russia’s economy? Is it strong or not? Would you say it was about to enter a period of growth or decline?
79.Complete these words by adding the vowels. Each word can follow the adjective economic.
1. |
g r _ w t h |
10. |
m _ _ s _ r _ s |
2. |
_n d _c _ t _ r s |
11. |
d _ v _ l _ p m _ n t |
3. |
c r _ s _ s |
12. |
r _ _ n |
4. |
f _ r _ c _ s t |
13. |
r _ f _ r m |
5. |
f _ r c _ s |
14. |
s t r _ t _ g y |
6. |
t h _ _ r y |
15. |
r _ c _ v _ r y |
7. |
p _ l _ c y |
16. |
_ n _ _ n |
263
8. |
_ _ t l _ _ k |
17. |
s _ n c t _ n s |
9. |
r _ c _ s s _ _ n |
18. |
_ _ d |
80. Now complete the following sentences using some of the words from ex. 79:
1.Economic …, such as the rate of inflation and the level of unemployment, are the signs that economists look for to help them produce their economic … .
2.Economic … is what a country faces if it builds up too great a national debt.
3.The prospects for a country’s economic future might be called its economic … .
4.During a period of economic … the government is forced to take strong economic … to revitalize the economy. И
5.Despite all the talk of political and economic …, Europe seems more divided than ever. Дwhich are the opposite of those onАthe left.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
close |
impede |
scrap |
cut |
improve |
||
relax |
|
и |
come out of |
harm |
privatise |
|
|
break off |
|
||||
1. |
|
С |
INDUSTRY |
|
|
|
Nationalise |
|
|
||||
2. |
Increase |
SOCIAL BENEFITS |
|
|||
3. |
Go Into |
RECESSION |
|
|
||
4. |
Damage |
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS |
||||
5. |
Tighten |
IMMIGRATION CONTROLS |
||||
6. |
Set Up |
AN INVESTMENT PROGRAMME |
||||
7. |
Widen |
THE TRADE GAP |
|
|||
8. |
Enter Into |
NEGOTIATIONS / TALKS |
||||
9. |
Promote |
OUR IMAGE ABROAD |
|
|||
10.Bring About ECONOMIC RECOVERY
help |
adopt |
|
put off |
divide |
push up |
neglect |
|
launch |
reduce |
pay off |
resist |
264

11. |
Raise |
TAXATION |
12. |
Unite |
PUBLIC OPINION |
13.Bring Down UNEMPLOYMENT
14. |
Hit |
THE UNEMPLOYED |
15. |
Give In To |
PRESSURE |
16. |
Attract |
FOREIGH INVESTORS |
17.Come Under AN ATTACK
18.Accumulate DEBTS
19. |
Abandon |
A POLICY |
20. |
Invest In |
EDUCATION |
82. In each example, use another form of the word in capitals to complete the sentence.
1.She’s a leading … . И
2.You can call it being … with the truth,Дif you like. I call it lying!
3.We need to think of practical ways in which we can … .5. The whole thing is … motivated.А
6. They’ve … the issue by involving the government.
83. Using the statistics below, complete these sentences describing a |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|
country’s economic situation: |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
1985 |
|
1995 |
now |
3yrs from |
|
|
|
|
и |
|
|
now |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
GDP |
|
$61bn |
|
$130bn |
$98 |
$80 |
|
|
Inflation |
|
21% |
|
16% |
18% |
23% |
|
|
|
С |
|
12% |
15% |
20% |
|
|
|
Unemployment |
6% |
|
|
||||
|
Population |
|
34m |
|
32m |
36m |
39m |
|
*GDP - gross domestic product
1.Since 1985 GDP … .
2.Between 1985 and 1995 GDP more than … .
3.But for the last … years GDP … .
4.Over the next 3 years GDP … .
5.There’s been a 2% rise … .
6.Inflation is expected … .
265

7.Compared with 1985, the 1995 inflation figure … .
8.Unemployment has been .. .
9.The most dramatic rise in unemployment … .
10.Over the next 3 years unemployment … .
11.Compared with … years ago, the unemployment situation … .
12.In terms of population, the overall trend … .
13.In spite of a fall of 2m … .
14.The rise in population is expected … .
15.Overall, the country is in a worse economic … situation than … .
16.The outlook for the next … .
You may choose the answers from this box.
1) three years is not encouraging; 2) has increased by over 50%; 3) it was in 1990; 4) doubled; 5) to continue overИthe next three years; 6) has fallen; 7) between 1980 and 1990, the population is now growing rapidly; 8) is expected to fallДby a further $12bn; 9) is upward; 10) in inflation; 11) is considerably worse; 12) to rise; 13) is likely to be pushed up by a further 5%; 14) was relatively encouraging; 15) was between 1980 and 1990; 16) steadily increasing.
ish economy, the second groupАare experts of the Russian one. Draw up a profile of your country. What are their economic and political
84. Work in two groups. The first group will be the experts of the Brit-
prospects? Discuss the perspectives of both countries. Prove your ide- |
||
as. |
|
б |
|
|
|
Things you might consider include |
||
• |
и |
|
the country’s principal industries |
||
• |
its transport system and infrastructure |
|
• |
the location of industrial and commercial centres |
|
• |
С |
|
natural resources |
|
|
• |
environmental hazards |
|
• |
demographics |
|
• |
the threat of war from a hostile foreign power |
|
• |
political unrest at home |
|
• |
the northwest-southeast divide |
|
Outlining Proposals
We are committed to …
Above all, we must ...
Unless we …
266
Provided that we …
Basically, what we’re proposing is …
In no circumstances must we allow …
If elected, we aim to … by …
We need to be thinking in terms of …
We see no alternative but to …
A vote for us will mean …
85. Write an essay (not less than 200 words) “Russia and Great Britain: economy and prospects of development”.
|
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
А |
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
и |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
267
Self-Assessment
Module 5
1.Look through Module 5 to find the answers to the questions 1 – 20.
1.What languages are spoken in Great Britain?
2.What animals can you see on British royal coat of arms?
3.What is the formal name of the British national flag?
4.How many crosses are there on the British flag? What do they symbolize?
5.What do GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca produce?
6.List as many facts as you can about the London Underground.
7.What sector now makes up about 73% of GDP?
8.Prove that Britain is the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution.
9.What are the main export partners of the UK?
10.What Russian-British projects do you know?И
11.What is the Eurozone?
12.What is an American bank executiveДJoseph Williams famous for?
13.What do you think the greatest threats to the world economy are?
14.Which countries or geographic areas do you think will have the most direct or indirect impact on the globalАeconomy over the next five to ten years?
15.What countries does theбUnited Kingdom consist of?
16.What company holds a major share of the global aerospace engines market? и
17.What is the major waterway in England?
18.Where in LondonСare the companies providing financial services concentrated?
19.What are the ways to reduce costs?
20.What is on-line business? How it works?
268

2. There are at least 30 hidden words. Find them!
|
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
C |
X |
H |
E |
F |
F |
I |
C |
I |
E |
N |
T |
U |
|
E |
F |
A |
C |
I |
L |
I |
T |
A |
T |
E |
D |
2 |
N |
B |
F |
U |
O |
I |
H |
Q |
R |
M |
A |
Q |
J |
D |
C |
B |
J |
E |
B |
G |
Y |
H |
E |
K |
A |
|
3 |
U |
F |
M |
A |
N |
U |
F |
A |
C |
T |
U |
R |
I |
N |
G |
O |
C |
S |
V |
P |
S |
S |
Q |
T |
U |
|
4 |
C |
U |
P |
J |
R |
D |
W |
F |
R |
R |
I |
W |
H |
X |
L |
R |
A |
C |
C |
O |
U |
N |
T |
S |
N |
|
5 |
L |
N |
N |
I |
N |
S |
U |
R |
A |
N |
C |
E |
R |
S |
P |
M |
G |
B |
T |
J |
V |
M |
A |
C |
I |
|
6 |
E |
Q |
C |
M |
C |
V |
Q |
F |
V |
I |
N |
V |
M |
H |
G |
C |
M |
U |
Q |
W |
U |
M |
X |
W |
C |
|
7 |
A |
P |
U |
G |
M |
D |
S |
H |
Y |
S |
T |
X |
N |
R |
S |
B |
A |
H |
X |
K |
E |
H |
A |
V |
O |
|
8 |
R |
D |
R |
M |
Q |
Y |
C |
O |
N |
S |
U |
M |
P |
T |
I |
O |
N |
U |
D |
G |
X |
J |
T |
D |
R |
|
9 |
V |
E |
R |
M |
N |
Y |
I |
E |
K |
S |
C |
D |
T |
K |
G |
U |
K |
R |
E |
M |
C |
V |
I |
I |
N |
|
10 |
V |
E |
E |
U |
N |
F |
O |
A |
H |
G |
P |
C |
U |
|
Z |
N |
X |
I |
L |
S |
P |
H |
P |
O |
I |
K |
11 |
C |
O |
N |
S |
I |
D |
E |
R |
A |
B |
L |
E |
J |
N |
I |
Q |
N |
E |
T |
F |
A |
I |
N |
M |
D |
|
|
A |
X |
T |
K |
N |
P |
N |
M |
Z |
V |
P |
L |
A |
|
F |
F |
W |
И |
I |
G |
N |
C |
Q |
S |
O |
|
12 |
|
D C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
S |
X |
X |
T |
P |
L |
M |
S |
V |
O |
F |
R |
V |
P |
I |
A |
N J |
N |
N |
G |
M |
B |
G |
M |
||
14 |
H |
W |
C |
R |
P |
H |
B |
W |
U |
M |
Y |
T |
H |
I |
C |
A |
L G |
A |
N |
E |
R |
A |
K |
I |
||
15 |
D |
W |
U |
A |
K |
I |
I |
M |
R |
E |
Y |
P |
D |
K |
A |
C |
P G |
T |
L |
|
K |
N |
U |
N |
||
16 |
F |
G |
Q |
N |
L |
L |
R |
U |
E |
U |
R |
O |
Z |
O |
N |
E |
T I |
I |
V |
R |
E |
K |
C |
A |
||
|
I |
P |
T |
S |
I |
M |
T |
W |
S |
Q |
Q |
А |
T |
X |
L K |
O |
E |
A |
K |
I |
F |
T |
||||
17 |
U D U |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
18 |
N |
B |
K |
A |
G |
S |
H |
D |
E |
W |
S |
G V X |
D |
X |
O Y |
N |
U |
T |
K |
N |
T |
E |
||||
|
A |
C |
P |
C |
Q |
Q |
P |
Z |
R |
б |
U L |
ДA T I |
O N |
Q |
L |
E |
Z |
G |
I |
D |
||||||
19 |
E G |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
20 |
N |
X |
X |
T |
U |
S |
L |
R |
V |
C K |
Y D Y O I |
R V |
B |
N |
Q |
N |
D |
X |
W |
|||||||
|
C |
B |
X |
I |
G |
Z |
A |
и |
C Y |
B X D U D |
D R |
Y |
A |
W |
D |
E |
T |
O |
||||||||
21 |
Z E |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
22 |
I |
O |
B |
O |
R |
G |
C |
Q S |
S D |
P H A R M |
A C |
E |
U |
T |
I |
C |
A |
L |
||||||||
|
A |
I |
Q |
N |
С |
W C |
K F |
N X J N I |
P H |
X |
M |
X |
C |
T |
E |
I |
||||||||||
23 |
R W E |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
24 |
L |
G |
L |
S |
Q R G |
U S |
N M |
W K P F S |
K Q |
A |
W |
C |
O |
A |
T |
B |
||||||||||
25 |
U |
D |
X |
X |
S H A |
R E |
X G |
O V E R N |
M E |
N |
T |
S |
N |
H |
D |
M |
||||||||||
269
