
С |
MODERN ROADS |
|
|
||
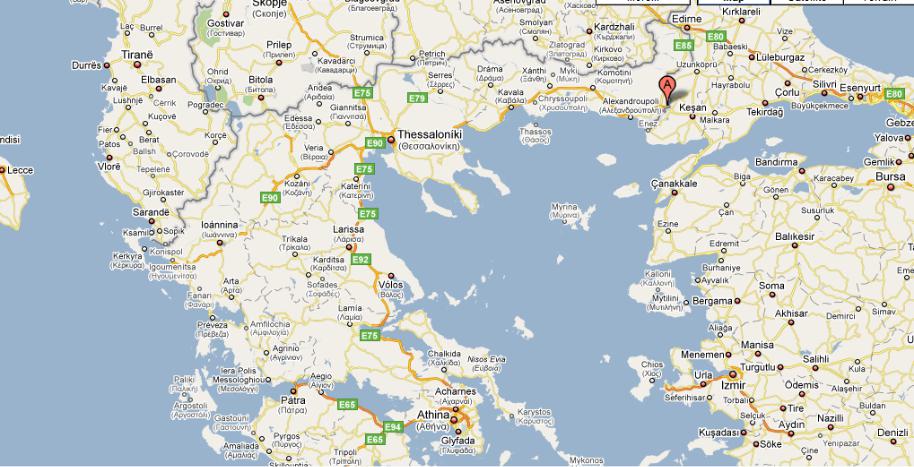
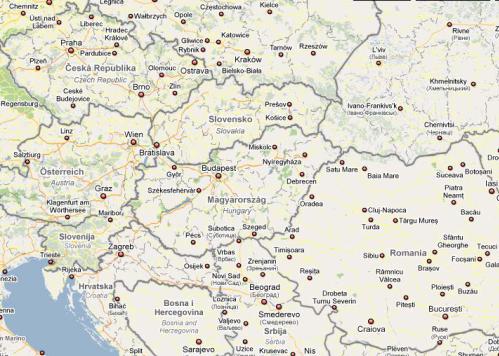
1. Look at the map (pic. 41). What country is it? Have you ever been there? |
||
и |
|
|
б |
|
|
|
А |
|
|
Д |
|
|
Pic. 41 |
И |
|
|
|
173
2. Read about Egnatia Odos and follow its route on the map.
Egnatia Odos
Egnatia Odos (often translated as Via Egnatia) is the Greek part of the European route E90. It is a motorway in Greece that extends from the Сwestern port of Igoumenitsa to the eastern Greek-Turkish border at Kipoi. It runs a total of 670km (416mi). The project began in the 1990s and
completed in 2009.
The route traverses the mountainous Greek regions of Epirus and Macedonia, crossing the Pindos and Vermio mountains, which have posed formidable engineering challenges. When completed, its full
miles)иand 1,650 bridges. It is a closed highway with sophisticated electronic surveillance measures, SCADA controls for the lighting/tunnel ventilation andбadvanced vehicle collision absorption measures.
length will include 76 tunnels (with a combined length of 99 km / 61.5
Technical characteristics: Two traffic lanes per direction, a central reserve and an emergency lane on the right.
Part of its length, a section of about 360 km (223 miles) from Evros to Thessaloniki,Аparallels the ancient Roman Via Egnatia, which ran from modern Durrës in Albania to Thessaloniki and thence to Byzantium (now Istanbul, Turkey). The project has therefore been dubbed a modern Via Egnatia. However, the parallel is not exact; the original Via Egnatia was much longer (1,120 km / 696 miles) and its western section, from Thessaloniki to the Adriatic Sea, ran much further north than the modern
stretch (i.e. from Grevena to Ioannina)Дwas delayed due to environmental concerns about the destruction of the habitat of the endangered brown bear. However, a new routing was proposed in 2003, and now this part is complete as of April 2009.
road.
The project has raised concerns for the survival of nearby sites of
ecological and archaeological significance. The construction of the Pindos И
In addition to the main highway, three perpendicular auxiliary highways are under construction connecting the highway to important cities, ports and airports of Macedonia.
The total cost of the project is estimated to be about 5.9 billion euros by the time of its completion in 2009, making it probably the most ambitious and expensive public project ever to have taken place in modern Greece. It is a key route in the trans-European road network and forms part of European route E90.
174
3.Discuss (in pairs) what towns it passes through and what ports it is linked to.
4.Write out the characteristics of the Greek road. Pay attention to:
Сlength
technical characteristics sections
cost
и5. Tell about Egnatia Odos and its role in the European road network.
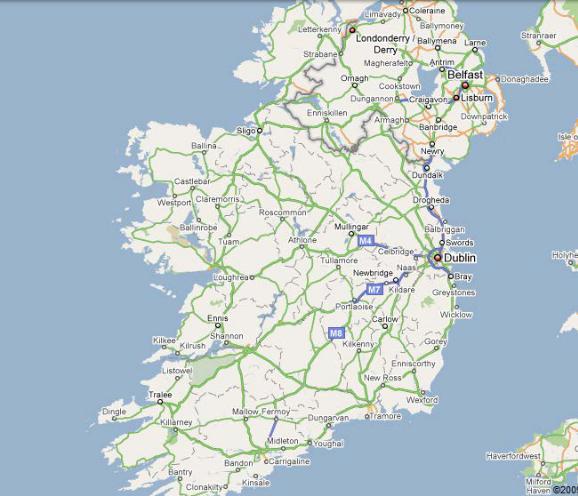
6. The capital of what country is Dublin? Look at the map (pic. 42). Whatбcities/towns have you heard about?
А Д И
Pic. 42
175
7. In which context do you expect to find these words in the text?
|
modernise |
horses |
limits |
bilingual |
yellow |
red |
|
8. Read the text and check your answers. |
|
|
|||
С |
|
Irish Roads |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
The island of Ireland (comprising Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland) has an extensive network of tens of thousands of kilometres of public roads, usually surfaced. These roads have been developed and modernisedиover centuries, from trackways suitable only for walkers and horses, to surfaced roads including modern motorways. Northern Ireland has had motorways since 1962, and has a well developed network of primary, secondary and local routes. Historically, the road network in the Republic ofбIreland was less well developed and maintained. The major differences between roads in Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland are in road quality and route classification, signposts and speed limits.
Roads in Northern Ireland are classified as either motorways (shown by the letter M followedАby a route number, eg. M1), A-roads (shown by the letter A followed by a route number, eg. A6), B-roads (shown by the letter B followed by a route number, eg. B135) and other roads. There are two types of A-roads: primary and non-primary. Roads in the Republic are classified as either motorways (shownДby the letter M followed by a route number, eg. M7), National roads (shown by the letter N followed by a route number, eg. N25), Regional roads (shown by the letter R followed by a route number, eg. R611) and Local roads (shown by the letter L followed by a route number, eg. L4202). There are two types of National roads: National Primary routes and National SecondaryИroutes.
Distance signposts in Northern Ireland show distances in miles, while all signposts placed in the Republic since the 1970s use kilometres. The Republic’s road signs are bilingual, using both of the state’s official languages, Irish and English. The signs in Irish Gaelic are written in lower case italic script, which are smaller than the English language script and are therefore more difficult to read than the English version, which are in non-italic large capital letters. Signs in Northern Ireland are in English only. Warning signs in the Republic have a yellow background and are diamond-shaped, those in Northern Ireland are triangle-shaped and have a white background with a red border.
176
Currently speed limits in Northern Ireland are specified in miles per hour. Those in the Republic use kilometers per hour (km/h), a change introduced on 20 January 2005. This involved the provision of 58,000 new metric speed limit signs, replacing and supplementing 35,000 imperial
signs. |
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
9. Fill in the chart using the information you have read. |
|||
и |
Roads in |
||
Northern Ireland |
|||
|
|
||
б |
|||
|
А |
||
|
|
Д |
|
|
|
Roads in |
|
|
|
the Republic of |
|
|
|
Ireland |
|
|
|
И |
|
10. Tell about Irish roads using the charts above.
177
11. Work in pairs. Think of 2 or 3 questions using the words from the box. Answer the questions of your partner.
|
paved |
|
complete |
intersection |
direction |
|
|
|
|
|
replace |
number |
dirt |
|
|
12. Read the text word by word and complete the following |
|||||||
words. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N * t * * * k ; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m * * * * * * * y ; |
|
|
|
|
|||
Сc * * * g * * * ; |
|
|
|
|
|
||
* * * * * l e l ; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c * * * * * * * * * * n ; |
|
|
|
|
|||
* i * * * * * o n ; |
|
|
|
|
|||
и |
|
|
|
|
|||
* * * * * d a r y |
; |
|
|
|
|
||
* * f * * i * * . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
б |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
А |
|
|
|||
Motorways and Roads in Cyprus
Since the arrival of the first motor cars on the island in 1907, Cyprus has developed one of the most modern road networks in Europe. According to 2002 statistics, the roadДnetwork in the free areas of Cyprus consists of about 7.206 km of paved and 4.387 km of unpaved roads. Although the first motorway in Cyprus, A1, was completed as recently as October 1985, the country already has the most motorway km per capita (38.6km /100,000 inhabitants) amongst all EuropeanИUnion members.
Roads and Motorways in Cyprus can be classified into 5 main categories:
Motorways, 2 lanes per direction, free of any at-grade intersections. They are the most important road network on the island, and the letter "A" is used on their official numbering system. Motorways usually run parallel to the same-number "B class" intercity roads that they replaced and sometimes these roads are even transformed to Motorways. While there is no formal announcement about the numbering of new motorways under construction and under planning, it's anticipated that they will have the same number as their current main road. So Limassol - Saittas Motorway
178
will be coded A8 because A is the letter of Motorways and 8 because it will "replace" B8 road.
Main Roads, Intercity roads, mostly one lane per direction, except sometimes in residential areas up to two lanes. B is the letter used in their official numbering system, with a number up to two digits long. Most of
Сthem have been replaced with their same-number Motorway (e.g. Traffic from Nicosia to Limassol now uses the A1 Motorway while in the past B1 road was the main connection between these cities)."B type" roads can be also main avenues within the city limits.
Roads, secondary road network, mostly connecting rural areas. One lane per direction, always paved. They use the letter "E" in their formal
numberingиsystem and they are 3 digits long. First digit is the serial number of the main road that the secondary road begins from (or the secondary road that begins at another secondary road which begins at a main road etc.) and the last two digits is the serial number of the road. Smaller digits where the main road begins, larger ones near main road's ending.
Local бroads, when coded during the 80's one lane and often dirt roads, today almost completelyАpaved, and waiting for letter re-evaluation. They use "F" in the official coding system, and they are counted in the same way as "E"s are. There is no "E" with the same number as an "F".
Unclassified roads. They can be "B" and "E" type. The case here is that these roads were constructed after the road network was numbered, so they will remain without a serial number and road signs will remain with gaps until the next road numbering evaluation.
13. Make up word combinations as they are used in the text from |
||
|
|
И |
the words given below. Read out the sentences with these word |
||
combinations. |
Д |
|
at-grade |
announcement |
|
city |
capita |
|
coding |
car |
|
European |
intersection |
|
formal |
limit |
|
motor |
number |
|
numbering |
road |
|
per |
system |
|
serial |
system |
|
unpaved |
Union |
|
179
14. Write down a plan of the text and let your partner explain each item.
15. Find one meaningless word and change it. What is the main
idea of the text? |
|
|
С |
modern eight-lane road |
parallel |
Diosdado Macapagal ingribrut is a |
||
to Roxas ingribrut running from CCP |
Complex, Pasay City to |
Marina |
Subdivision, Paranaque City, both in Metro Manila. It was named after former President Diosdado Macapagal. It is located in the reclamation
relieveиtraffic, Macapagal Boulevard is now often used to access the SM Mall of Asia, Manila to the north and Cavite province to the south.
areas. This ingribrut has 3 major bridges, crossing the 'channels', of which
the largest is the Libertad Channel, where the Libertad Water Pumping
Station is situated. Thanks to intersection reconfiguring around EDSA to
Longestбinternational highway: the Pan-American Highway, which connects many countries in the Americas, is nearly 48,000 kilometres (29,826 mi) long as of 2005.
16. Discuss in pairs the following facts.
coastline. With the exceptionАof Canberra (which is inland) it links all the
Longest national highway: Australia's Highway 1 at over 20,000
capital cities, although Brisbane andДDarwin are not directly connected. Also the route links all the major towns and cities of the island state of Tasmania, Burnie, Devonport, Launceston and Hobart (the state’s capital).
km (12,427 mi). It runs almost the entire way around the country’s
Longest national highway (Point to point):ИThe Trans-Canada Highway (Known as TCH 1 in western Canada) is 7,821 km (4,857 mi) long as of 2006. It runs across southern Canada and connects with several major urban centres along its longitudinal route.
Largest national highway system: The United States of America has approximately 6,430,366 kilometres (3,995,644 mi) of highway within
its borders as of 2008. |
|
|
|
|
Busiest |
highway: Highway 401 in Ontario, |
Canada, has volumes |
||
surpassing an average of |
500,000 vehicles per day in some sections of |
|||
Toronto as of 2006. |
|
|
|
|
Widest |
highway |
(maximum number |
of |
lanes): The Katy |
Freeway (part |
of Interstate 10) in Houston, Texas, |
United States of |
||
180
America, has a total of 26 lanes in some sections as of 2007. However, they are divided up into general use/Frontage roads/HOV lanes, restricting traffic flow.
Widest highway (number of maximum through lanes): Highway 401 through Mississauga, Ontario has the most unrestricted free-flow
lanes, at 22 (26 including restricted) as of 2008.
СибАДИWhat was new for you?
17. Using the Internet or some other resources find some other world records concerning road building and share them with your
colleagues.
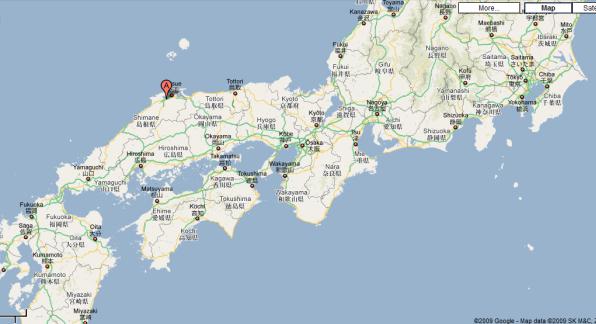
18. Read about Japanese roads to answer the questions.
1. How many lanes do Japanese expressways have?
2. What speed is allowed there?
3. What are the tolls based on?
4. What is ETC?
5. Where is a flat-rate toll system implemented? 6. What classification of roads is there in Japan?
National expressways make up the majority of expressways in Japan. This network boasts an uninterrupted link between Aomori Prefecture at the northern part of Honshū and Kagoshima Prefecture at the southern part
of Kyūshū, linking Shikoku as well. Additional expressways serve
travellers in Hokkaidō and on Okinawa Island, although those are not connected to the Honshū-Kyūshū-Shikoku grid.
Most expressways are 4 lanes with a central reservation (median). Some expressways in close proximity to major urban areas are 6 lanes, while some in rural areas are 2 lanes only with a barrier on the center line. 2-laned sections are built to a standard that allows conversion to 4 lanes in the future.
Speed limits are normally 100 km/h, and a minimum speed of 50 km/h is also enforced. Vehicles unable to reach 50 km/h, such tractors and mopeds, are forbidden from using the expressways. Speed limits may also be reduced temporarily (due to adverse driving conditions) or permanently (in accident-prone areas) as speed limit signs can be adjusted electronically.
181
Many rest facilities such as parking areas (usually only with toilets or small shops) and service areas (usually with many more amenities such as restaurants and gas stations) serve travellers along national expressways.
National expressways are expensive to use, with the 325.5-km journey from Tokyo to Nagoya on the Tōmei Expressway costing ¥7100 in tolls for
Сan ordinary car.
With a few exceptions, tolls on national expressways are based on distance travelled. When entering the expressway, one collects a ticket, which can be inserted along with the fare into a machine or handed to an attendant upon exiting the expressway. There is also an Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) card system installed in many cars which automatically pays at the toll gate. As of 2001 toll fees consist of a 150 yen terminal
charge plus a fee which depends on the distance travelled. |
|
|
||
Tolls are always rounded |
to the nearest 50 |
yen |
and |
|
include consumption tax. If there are two or more possible routes from the |
||||
entranceиto the exit, the toll will be calculated based on the shortest |
||||
(cheapest) route. |
|
|
|
|
Tolls collected from all routes are pooled into a single fund and are |
||||
used to repay the entire network. It is expected that all national |
||||
expresswaysбin Japan will be fully repaid 45 years after privatization |
||||
(2050). |
|
|
|
|
Some future national expressways are planned to be built according to |
||||
the New Direct Control System, whereby national and local governments |
||||
will absorb the burden for expressway construction and operate toll-free |
||||
upon completion. |
А |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Urban expressways are intra-city expressways which are found in |
||||
many of Japan's largest urban areas. Due to lack of space many of these |
||||
expressways are constructed as viaducts running above local roads. The |
||||
two largest networks are the ShutoДExpressway in the Tokyo area and the |
||||
Hanshin Expressway in the Osaka area. There are other smaller networks |
||||
in Nagoya, Hiroshima, Kitakyūshū, |
and Fukuoka. Each |
network |
is |
|
managed separately from each other (the Fukuoka and Kitakyūshū |
|
Expressways are managed by the same company but are not physically |
|
connected to each other). |
И |
|
|
Currently all urban expressways operate on a flat-rate toll system (the |
|
toll is the same regardless of the distance travelled on the network), however both the Shuto Expressway and Hanshin Expressway are planning to move to a distance-based toll system for vehicles equipped with ETC.
182
All roads in Japan that are built to expressway standards (including national and urban expressways themselves) are known as Roads for motor vehicles only. If a road for motor vehicles only cannot be classified as a national or urban expressway, it may be classified into one of the following
categories. |
|
С |
|
o |
National highway for motor vehicles only with national |
expressway concurrency
Roads in this category are built to facilitate future incorporation into the
main route of a national expressway. Examples include the Yonezawa |
|
Nan-yō Road, the Higashi-Mito Road and the Futtsu Tateyama Road. |
|
и |
|
o |
National highway for motor vehicles only |
Roads in this category are national highways built to expressway standards as designated by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Examples include the Ken-Ō Expressway and the Tōkai-Kanjō Expressway.б
19. How can the text above be titled? Why?
20. Work in pairs. DiscussАthe pictures below (pic. 43–48). Use the information you have read to ask questions.
Д И
Pic. 43
183

СиPic. 44 Pic. 45
б АPic. 46
Д И
Pic. 47 |
Pic. 48 |
184

21. Look at the table. What is shown there?
|
Type of vehicle |
rate in yen/mile |
rate in yen/km |
|
Light car and motorcycle |
31.49 |
19.68 |
|
|
|
|
С |
39.36 |
24.60 |
|
|
Ordinary passenger car |
||
|
Small and medium-sized truck |
47.23 |
29.52 |
|
Large-sized truck |
64.94 |
40.59 |
|
Special large-sized full trailer |
108.24 |
67.65 |
Use the Internet or other resources to search for “a toll road”. Prepare a short presentation on toll roads of different countries, e.g.
France, Italy, Hungary, Germany, etc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
б |
|
|
|
|
|
||
и22. You are going to read an article about Indian highway |
||||||||
projects. Fill in the following tables while reading. |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
10 mega highway projects |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost, rupees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Length |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Number of states |
|
Д |
|
||||
|
involved |
А |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section |
|
|
|
Length, km |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Kishangarh (Rajasthan)-Ahmedabad |
|
И |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Ichapuram-Rajahmundry (in Andhra Pradesh) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Amritsar (in Punjab) - Jodhpur (in Rajasthan) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Kolhapur-Nagpur (in Maharashtra) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ahmedabad-Gondal (in Gujarat) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
AurangabadDhankuni (in West Bengal) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goa-Maharashtra Border |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bhavnagar-Dwarka (in Gujarat) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
185
Mega highway projects
The government has lined up 10 mega highway projects, involving a whopping Rs 45,000 crore investments, besides fast-tracking some of them by inviting interested parties to submit their qualification documents.
These 10 mega contracts, of around USD 1 billion each, would involve Сdeveloping more than 4,800 km of modern highways spread over seven
states.
These projects would be awarded to private parties on a revenuesharing basis, under which the developers pay a part of the toll earnings to the government, a National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) official
иSources have informed that the NHAI has already asked potential bidders to submitбtheir initial 'request for qualification'(RFQ) documents for two of these 10 projects, spread over Rajasthan, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh.
said.
"Since these are lucrative projects from the point of toll revenues, we
would award them on revenue sharing basis," the official added.
The RFQ for the Rs 4,284-crore project involving six-laning the 435- km-long Kishangarh (Rajasthan)А– Ahmedabad section has already been issued. That apart, RFQ for the Rs 3,550-crore project for six-laning of the 436-km stretch between Ichapuram – Rajahmundry in Andhra Pradesh has also been issued, sources said.
the official said. Д These five projects are – Kolhapur – Nagpur in Maharashtra (475 km),
The NHAI is also preparing detailed project reports (DPRs) for three other projects including the biggest project of the 10 projects--the Rs 8,000-crore contract for double-laning the 700-km stretch between
Amritsar in Punjab and Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Ahmedabad – Gondal in Gujarat (425 km), Aurangabad – Dhankuni in West Bengal (475 km), Goa – Maharashtra Border (475 km) and the 445-
km-long Bhavnagar – Dwarka stretch in Gujarat.
In-principle approvals for five other projects have also been obtained, И
To expedite highways developement, the government has identified these large projects of over 400 km each against the usual project size of 50-200 km for every contract.
Earlier this month, Transport Minister Kamal Nath had announced that six 'mega projects' would be awarded and the first one will be awarded in four to six weeks.
186
The development of highways would cost about Rs 3,76,000 crore in the next four years and about 50-60 per cent of this expected to come from the private sector, according to government estimates. http://www.indianexpress.com/news/mega-highway-projects-worth-rs-45k-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cr-lined-up/543714/ |
|||||
С3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
23. Can you find 10 words from the text in the letters? |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T |
||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
S |
D |
I |
V |
E |
L |
O |
P |
I |
N |
G |
C |
G |
R |
G |
M |
P |
V |
F |
K |
|
и |
X |
T |
W |
Y |
S |
G |
J |
T |
E |
H |
Q |
K |
V |
A |
F |
|
||||||
2 D S O E N |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
V Y F S I |
W |
I |
N |
V |
E |
S |
T |
M |
E |
N |
T |
S |
P |
S |
L |
|
||||
4 |
|
I V O F L |
U |
Y |
D |
B |
Y |
D |
J |
Z |
M |
F |
E |
E |
Y |
T |
B |
|
||||
5 |
|
D O U B L |
E |
- |
L |
A |
N |
I |
N |
G |
R |
P |
T |
I |
X |
- |
Q |
|
||||
6 |
|
S D S S K |
N |
Q |
P |
Z |
Y |
X |
P |
S |
I |
M |
R |
N |
C |
T |
I |
|
||||
7 |
|
X S V T L |
F |
O |
H |
X |
D |
G |
Y |
K |
M |
J |
J |
T |
U |
R |
V |
|
||||
8 |
|
G H D E V |
E |
L |
O |
P |
E |
M |
E |
N |
T |
F |
Y |
E |
Q |
A |
Y |
|
||||
9 W I G W Q |
Z |
А |
X |
J |
K |
R |
G |
C |
D |
|
||||||||||||
C C K N P P G |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
|
б |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Z R A J A H M U N D R Y Q |
I |
H |
X |
E |
C |
K |
R |
|||||||||||||||
11 |
|
N T G Y L W F J D M A V Q |
K |
Y |
R |
S |
Y |
I |
V |
|
||||||||||||
12 |
|
I T I V P A U R A N G A B |
A |
D |
J |
T |
W |
N |
B |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Д |
G |
W |
|
|||||||||
13 Z H B T E M K U N Y V L D H O N E K |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
14 |
|
P X Q U A L I F I C A T I O N X D K |
F |
P |
|
|||||||||||||||||
15 |
|
C H Q G Q C E H D N Y S Q O Y U Y D |
T |
S |
|
|||||||||||||||||
16 |
|
T R M B G P B H Q H Z Q Y G P V E K |
B |
O |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
17 |
P M U R E V E N U E - S H A R I N G |
Q |
C |
|
|||||||||||||||||
18 |
|
I V J I B O J F X K K E K J V Q A L |
B |
G |
|
|||||||||||||||||
19 |
|
O H O J V G H I T V I N B L J C K Q |
F |
M |
|
|||||||||||||||||
20 |
|
M A H A R A S H T R A T W B I E F J |
T |
Q |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
И |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24. What notion is described in each sentence? |
||||||||||||||||||||||
–passing round a town to provide an alternative route for through
traffic;
–a group or system of interconnected people or things;
–a road designed for fast traffic, typically with three lanes in each direction;
187
–a charge payable to use a bridge or road;
–a point beyond which something does not or may not pass or
extend;
–separate or be separated into parts.
СHungary has 7 major motorways ("autópálya"):
25. Now read the text and check your answers.
Road system in Hungary
• M0 is a quasi-circular highway for the traffic bypassing Budapest. It is divided in 4 sectors: Southern (links motorways M1, M7, M6 and M5), South-eastern (links Motorway M5 and Main Road nr. 4), Eastern (links
Main Road nr. 4 and Motorway M3), Northern (links Main Road nr. 2 with |
|
the Megyeri Bridge) and Western (to be finished in 2015; will link main |
|
roads 11, 11 and Motorway M1). The total length will be around 100 km. |
|
и |
|
• M1: links Budapest and the north-western border with Austria |
|
(Hegyeshalom), then continues its way toward Vienna. The total length is |
|
around 170 km. |
|
• M3: links Budapest and the north-eastern city of Miskolc (M30 |
|
б |
|
branch), eastern cities of Nyíregyháza (M3) and Debrecen (M35 branch). |
|
Provides links toward Slovakia, Ukraine and Romania. It has a total length |
|
of around 250 km. |
|
• M5: links Budapest and the southern city of Szeged, then the Serbian |
|
|
А |
border (Röszke). It provides a connection to Southern Europe by route E75 |
|
and also links to route 68 in Romania. M5 motorway has a length of |
|
around 140 km. |
|
• M7: links Budapest and the southern shore of Lake Balaton, then |
|
continues its way toward Croatia andДSlovenia. Its length is about 230 km. |
|
• M6: links Budapest and Dunaújváros, then will continue its way |
|
toward the southern city of Pécs. The current lengthИis around 60 km. Also, there are other smaller motorway sections that will be linked to
the national motorway network in the future. Motorways usually have 2 traffic lanes and an emergency lane on each direction, divided by a green zone and metallic rail. The speed limit is 130 km/h.
Expressways usually have no dividing lane in the middle, but sometimes have a metallic rail. The number of lanes is one per direction, with sections of 1+2 lanes (for easier overtaking). The speed limit is 110 km/h. Motorways and expressways cannot be used by vehicles that are not
188
able to reach 60 km/h. There is a toll on all motorways, except M0. Trucks and buses have a separate toll system.
Main roads usually have one lane per direction, no dividing rail. The speed limit is 90 km/h.
County roads have less traffic then main roads, the speed limit is 90 km/h.
СибАДИ26. Complete the following sentences by writing NO MORE
THAN THREE WORDS for each answer:
1. The total length of M0 will be … .
2. Hungarian motorways usually have two traffic lanes and an …
divided by a green zone.
3. Expressways and motorways cannot be used by vehicles that … 60
km/h.
4. Main roads usually have one … , no dividing rail. 5. The speed limit on … is 130 km/h.
27. Look at the map (pic. 49) and find those Hungarian major motorways.
Pic. 49
189
Check your answers (Ex. 23 p. 188)
aurangabad (f12-h), developement (c8-h), double-laning (a5-h), fasttracking (s1-v), interested (q5-v), investments (g3-h), maharashtra (a20-h), qualification (c14-h), rajahmundry (b10-h), revenue-sharing (d17-h)
СибАДИrarely used relating to New Zealand roads, and can only be considered |
||||
28. Describe the Hungarian road system in 3 sentences. |
||||
29. Scan the following text for about 5 minutes and find what the |
||||
following figures mean: |
|
|
|
|
10 |
2 |
5 |
6 |
1 |
New Zealand roads
In New Zealand, both motorway and an expressway have at least twolanes of traffic in either direction separated by a median, with no access to adjacent properties. The distinction depends on the type of traffic allowed to use the route. Non-vehicular traffic and farm-equipment are prohibited from motorways, while pedestrians, cyclists, tractors, and farm animals are legally entitled to use expressways such as the Waikato Expressway south of the Bombay Hills and the Tauranga expressway system, although this is rare. New Zealand's main routes are designated state highways as they are funded by the National Government. State Highway 1 is the only route to run through both the North and South Islands, and runs (in order north-
south) from Cape Reinga to Wellington in |
the North |
Island, |
and |
from Picton to Bluff in the South Island. State |
Highways |
2-5 are |
main |
routes in the North Island, State Highways 6-9 in the South Island, and state highways numbered from ten onwards are generally found in numerical order from north to south. State highways usually incorporate
different standards of roads, for |
example, State |
Highway 1 |
from Auckland to Hamilton incorporates |
the Northern |
and Southern |
Motorways in the Auckland area, the Waikato Expressway, and a rural road before passing through the streets of Hamilton. The term freeway is
an Americanism.
190
30. What do these attributes from the text refer to? Make up sentences of your own using word combinations with these words.
Adjacent; numerical; different; Northern; rural; non-vehicular.
31.Think of three words/word combinations from the text. Try to explain it using a pantomime and let the rest of the group guess it.
32.Retell the text using the word combinations below.
1.The title of the story I want to tell you is… 2. First of all … 3. Second I would like to say that… 4. As far as I understand… 5. In fact…
6.As far as I remember… 7. In conclusion I’d like…
33.Some sentences in the text are just groups of words. Please arrange the words in the correct order to read about Philippines expressways.
СибАДИPhilippines expressways
Many • owned • Philippine expressways are • privately • and • maintained. in • island, Luzon. • are • the • largest • All • located They follow the US Interstate Highway Standards and speed limits are strictly enforced. The most modern and the longest expressway, the North Luzon Expressway links the capital, Manila to other provinces in Northern Luzon while the South Luzon Expressway links Manila with provinces on the Southern Luzon.
Presently, all Philippine expressways are under rehabilitation to decrease the occurrence of traffic jams and to improve their quality. They • and • widened • are • of • improved • standards.
There are only seven tollways in Luzon Island, the North Luzon Expressway (connecting Manila to North Luzon), the South Luzon Expressway (connecting Manila to Southern Luzon), the Roman Expressway (in Bataan peninsula), Subic Freeport Expressway (connecting Subic Freeport to Dinalupihan), the Southern Tagalog Access Road (STAR Tollway) (connecting Sto. Tomas to Batangas Port, to decongest the Port of Manila and it will be connected directly to the South Luzon Expressway), and the Manila-Cavite Expressway, connecting Metro Manila with the Province of Cavite, Subic-Clark-Tarlac Expressway (connecting the existing Subic Freeport Expressway to Clark Zone and
191

Hacienda Luisita and also extending North Luzon Expressway to Tarlac City but it has 3 km gap between NLEx and SCTEx).
Despite that many highways in Metro Manila, there are still two lane and one way roads like national and provincial roads around the country.
There are plans to extend the existing expressways and to build a new
one throughout the Philippines, the Tarlac-La Union Expressway aims to СибАДИextend North Luzon Expressway to the area near Poro Point but it will be extended initially to Rosario in La Union, Tarlac-Dingalan Expressway
aims to convert Dingalan into an International Pacific Port and to decongest the Port of Manila. The Cebu Trans-Axial Expressway aims to benefit Cebu's economy and to decongest the island's coastal road and to protect Cebu's coastal areas from severe exploitation. North East Luzon Expressway aims to connect Metro Manila to Cagayan Valley but it will be built initially to Nueva Ecija. be • South • City. • Lucena • Luzon • extended • towards • Expressway • will
34. Read the text carefully and make words from the letters (all the words are in the text).
(dmnoer)
(ssxeweayrps)
(wtaolyls)
(incvrPoe)
(wyhisahg)
(oundra)
(netdxe)
(atnItnrieloan)
35. Work in pairs. Think of 2 or 3 questions using the words from Ex. 35. Answer the questions of your partner.
36. Replace the words in bold with others from the list.
1.Speed limits are severely enforced on Philippine expressways.
2.At present time, all Philippine expressways are under restoration.
3.There are plans to develop the existing expressways and to build a new one throughout the Philippines.
192
4.The Cebu Trans-Axial Expressway aims to do good to Cebu's economy.
5.The North Luzon Expressway is the newest and the longest
expressway.
37. Read the text once again and say if these statements are true, СибАДИfalse or not given. Correct the mistakes.
1. There are only seven tollways in Luzon Island.
2. Manila and North Luzon are connected by the North Luzon Expressway.
3. Subic Freeport and Dinalupihan are connected by Freeport Subic Expressway.
4. the Southern Tagalog Access Road is connecting Sto. Tomas with the South Luzon Expressway.
5. Tarlac-Dingalan Expressway aims to convert Dingalan into an International Pacific Port.
6. The Cebu Trans-Axial Expressway aims to extend North Luzon Expressway.
7. State Highway 1 from Auckland to Hamilton incorporates the Northern and Southern Motorways in the Auckland area, the Waikato Expressway, and a rural road before passing through the streets of Hamilton.
38.What new have you found out about Philippines expressways?
39.Work in pairs. Discuss the following questions.
1.Which side of the road do the South Africans drive on?
2.What is the administrative capital of South Africa?
3.What can the letters N, R, M stand for?
193
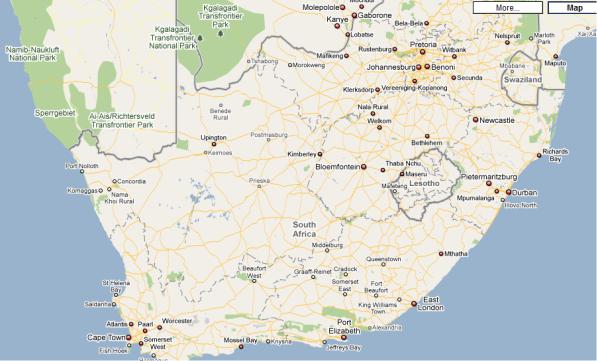
40. Now look at the map (pic. 50), read the text and check your ideas.
СибАДИPic. 50
South Africa
Colloquially, the terms "freeway", "highway", and "motorway" are used synonymously. There are very few references to the term "expressway" in South Africa. A freeway, highway or motorway refers to a divided dual carriageway with limited access, and at least two lanes in either direction. A central island, usually either with drainage, foliage or high-impact barriers, provides a visible separation between carriageways in opposite directions. As with the UK, Ireland & Australia, South Africans drive on the left-hand side of the road and all steering wheels are on the right-hand side of vehicles.
Freeways are designated with one of three labels: N (in reference to national roads), R (short for "route", in reference to provincial roads), and M (in reference to metropolitan roads). This has more to do with the location of a road and its function than anything else. In addition, "N" roads usually run the length of the country over long distances, "R" roads usually inter-connect cities and towns within a province, and "M" roads carry heavy traffic in metropolitan areas. Route markings also determine who paid for the road: "N" was paid for by national government, "R" by
194
provincial government and "M" by local government. In recent years, some "R" roads have been re-designated as "N" roads, so that control and funding comes from the South African National Roads Agency.
41. Are you attentive? Try to match the following words to get |
|
СибАДИ |
|
word combinations without looking back at the text. Then use them in |
|
your own sentences. |
|
dual |
access |
high-impact |
areas |
limited |
barriers |
metropolitan |
carriageway |
national |
markings |
right-hand |
roads |
route |
separation |
visible |
side |
42. Read the text again and try to make a plan from the points below.
A divided dual carriageway with limited access
Funding
Left-hand side of the road
Synonymous usage
Three labels
43. Tell about South African roads using the following diagram.
M
Freeway
N R
195
44. You are going to read about UK and US roads. Five sentences have been removed from each text. Choose from the sentences A – F the one that fits each gap (1 – 4) to complete the text.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, unless a route is classified as a motorway, the
СибАДИover a long period of time. Such ownership in no way affects the public highway rights, as the relevant "highway authority" (usually a local
term which is used for a vehicular highway may be |
main |
road, trunk |
road, ‘A’ road, ‘B’ road, ‘C’ road, ‘unclassified |
road’, |
or, where |
appropriate, dual carriageway. Surprisingly, in the law of England and Wales the term public highway includes all rights of way open to all traffic,
including footpaths for pedestrians. |
1. |
|
In English law, there is no definition of "road", and generally the most |
||
common usage refers to: |
|
|
• |
“Carriageway”, |
|
• |
“Footpath”, |
|
• |
“Bridleway” or |
|
• |
“Byway”. |
|
In England and Wales the public are said to have a "right of way" over a highway. This means that, subject to statutory restrictions, the route (or "way") must be kept clear to allow travel by anyone who wishes to it. At common law, it is unlawful to obstruct a highway or to interfere with its
lawful use. |
2. |
Many public highways in the UK have a private owner: that is, |
|
someone can prove "title" to them, either by being the registered owner or |
|
by having conveyances showing that the land has been bought and sold |
|
authority or the Highways Agency) is deemed to own the surface of the highway, despite someone else's ownership of the land it passes over or under.
Rights of way exist over all highways maintained at the public expense (the majority of roads) and also over some other ways which are not so maintained, on the principle of "once a highway, always a highway".
_________________ 3.
A right of way may be created by custom (by the way being used for a long period of time) or under the relevant Sections of the Highways Act 1980. A right of way may be extinguished or diverted in a number of ways, such as by an Act of Parliament, by a magistrates’ stopping-up or diversion order, or by powers given to principal local authorities. For instance, under
196

the Channel Tunnel Rail Link Act 1996 authority was given for the builder of the rail link to stop up certain highways mentioned in Schedule 3 of the act.
The opposite to a highway is a private road or path over which no rights of way exist.___________________ 4.
Сmany forms:ибАДИ |
|
|||
|
A |
In such cases, landowners must allow public use for "passing and |
||
|
|
repassing". |
|
|
|
B |
Any use of such private ways is subject to the consent of the owner |
|
|
|
|
of the land. |
|
|
|
C |
However, many statutory provisions provide powers to do so (for |
|
|
|
|
instance to carry out road works). |
|
|
|
D |
The term also includes bridleways, which |
are for |
|
|
|
pedestrians, equestrians, and cyclists, as well as byways open to all |
||
|
|
traffic (for all of those users, plus vehicular traffic). |
|
|
|
|
United States |
|
|
|
|
In the United States, "highway" is a general term for |
denoting a |
|
public way, including the entire area within the right-of-way, and includes
1.a high-speed, limited-access road like expressways and
freeways.
2.an important road that connects cities.
3. |
1. |
Many highways are part of |
the official National Highway System. |
Roads in the United States Numbered Highways system can vary from two lanes (one lane each direction), shoulderless, paved roads with no access control to multi-lane high-speed roads, such as Interstate Highways.
_____________________ 2.
"Highway" even includes roads that serve similar purposes to United States numbered highways but which are numbered and maintained by state or local governments.
_________________ 3. For example, California Motor Vehicle Code § 360 states: "'Highway' is a way or place of whatever nature, publicly maintained and open to the use of the public for purposes of vehicular travel. Highway includes street."
197
The government is trying to improve its national roadway system by repaving highways and reconstructing various interchanges. _________________ 4. Busy Diamond interchanges are also being converted to SPUIs (single-point-urban interchange) or parclos to reduce congestion.
СибA Many cloverleaf interchangesАДare being convertedИto parclo interchanges
B These roads are usually distinguished by being important, but not always primary, routes that connect populated areas.
C any road at all.
D In some places, "highway" is a synonym for "road" or "street".
45. Look at the following diagram. Can you complete it? Draw a similar diagram on US roads in your notebook and let your partner complete it.
‘A’ road
‘B’ road
vehicular highway
unclassified
198

46. Compare the roads in the United Kingdom and the United States filling in the table.
UK |
USA |
СибАДИTypes of roads
47. Using the Internet or other resources try to find songs about UK or USA roads. Make a presentation.
48. Project task. You were told to write one page for the textbook on modern roads. Use the information you have studied. Do not forget to add pictures and charts.
199
