
2076
.pdf
|
automobile company in |
the |
After |
|
the |
new |
technology |
to build |
|
|||||||||||||
|
world |
|
with |
|
572 |
units |
first |
engine |
rapid |
transit |
for |
urban |
|
|||||||||
|
produced in 1899. |
|
|
|
powered bus |
commuting. In smaller cities, |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
In |
1892, |
German |
engineer |
of |
1895, |
tramways |
became |
common, |
|
||||||||||||
|
Rudolf Diesel was granted a |
models |
|
and were often the only |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
patent for a “New Rational |
expanded |
in |
mode |
of |
public |
transport |
|
||||||||||||||
С |
|
|
|
In |
the |
1900s, |
until |
the |
introduction |
of |
|
|||||||||||
|
Combustion |
Engine”. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
1897, he built the first Diesel |
leading |
to |
buses in the 1920s. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Engine. Steam-, electric-, |
the |
|
|
After |
|
World |
|
War |
II |
|
|||||||||||
|
and |
|
|
|
gasoline-powered |
widespread |
improvements |
in |
internal |
|
||||||||||||
и |
introduction |
combustion |
|
|
|
engine |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
vehicles |
competed |
|
for |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
decades, |
with |
|
gasoline |
of |
|
the |
technology |
made |
diesel |
|
|||||||||||
|
internal combustion |
engines |
contemporar |
locomotives |
cheaper |
and |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
achieving dominance in |
the |
y |
|
|
more powerful. This caused |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
1910s. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
recognisable |
many railway companies to |
|
|||||||||||
|
Various |
|
pistonless |
|
rotary |
form |
of |
full |
initiate programs |
to |
convert |
|
||||||||||
|
engine |
|
designs |
|
have |
size |
buses |
all |
unelectrified |
|
sections |
|
||||||||||
|
attempted |
to |
compete |
with |
from |
|
the |
from |
steam |
to |
diesel |
|
||||||||||
|
the |
piston |
and crankshaft |
1950s. |
|
locomotion. |
|
the |
large- |
|
||||||||||||
|
design, but |
only |
Mazda’s |
|
|
|
Following |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
scale |
|
construction |
of |
|
||||||||||||||
|
version of the Wankel engine |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
motorways after the war, rail |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
has |
had |
more |
than |
very |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
transport |
|
became |
|
less |
|
|||||||||||||
|
limited success. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
popular |
for |
commuting. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
The |
manufacturing |
of |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Most |
tramways |
were |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
бА |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
affordable automobiles on a |
|
|
|
replaced by rapid transits or |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
large |
scale was |
debuted |
by |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
buses. The 1973 oil crisis led |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Ransom |
Olds |
|
at |
|
his |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
to a change of mind set, and |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Oldsmobile factory in 1902. |
|
|
|
И |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
This |
concept |
was |
greatly |
|
|
|
most tram systems that had |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Д |
1970s |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
expanded |
by |
Henry |
Ford, |
|
|
|
survived |
into |
the |
|
|||||||||||
|
beginning in 1914. Since the |
|
|
|
remain today. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
1920s, nearly all cars have |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
been mass-produced. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
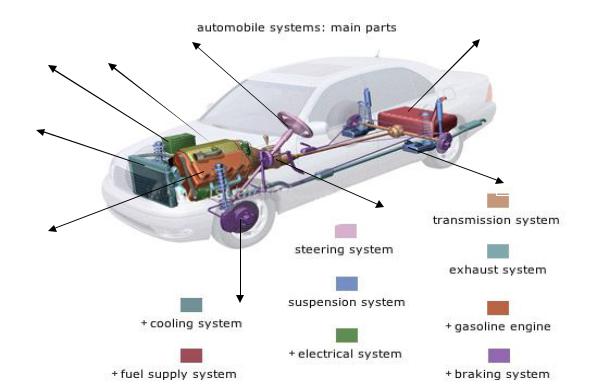
13. Look at the scheme of automobile. Match systems of the automobile and numbers in the picture. Read and translate definitions of these systems. Can you give your own definitions?
11
|
1 |
9 |
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
С |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
и |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A vehicle is composed of basic mechanical parts and devices making |
|||
up its systems; each of them fulfills a specific function: |
||||
fuel supply system – set of components supplying the fuel to the engine. |
||||
transmission system – set of components transmitting the motion produced |
||||
by the motor to the wheels. |
Д |
|||
|
|
|||
suspension system – set of components that joins the wheels to the vehicle’s |
||||
body whileбАreducing shocks caused by the road’s unevenness and improving |
||||
the hold on the road. |
|
|
|
|
braking system – set of components that reduce the vehicle’s speed, |
||||
eventually to a halt, and keep it in place while parked. |
||||
|
|
И |
||
steering system – set of components that direct the front wheels to guide the vehicle as it moves.
gasoline engine – engine in which a mixture of air and gasoline is compressed and ignited to produce an explosion whose energy is converted into mechanical energy.
cooling system – set of components that prevents the temperature of the engine from rising excessively.
electrical system – set of components supplying the necessary current for starting the vehicle and operating its electric accessories.
exhaust system – set of components designed to expel the engine’s burned gases into the ambient air.
fuel supply system – set of components supplying the fuel to the engine
12

What systems are represented by these elements?
spark plug gasoline pump radiator
14. Skim the text and guess which of the systems mentioned above is described in the text. Complete the text with this word. Translate all the words and word collocations given in bold.
When people think of automobile performance, they normally think of
horsepower, torque and zero-to-60 acceleration. But all of the power |
|
generated by a piston engine is useless if the driver can't control the car. |
|
С |
|
That's why automobile engineers turned their attention to the …system |
|
almost as soon as they had mastered the four-stroke internal combustion |
|
engine. |
|
The job of a car … is to maximize the friction between the tires and |
|
и |
|
the road surface, to provide steering stability with good handling and to |
|
|
бА |
ensure the comfort of the passengers.
If a road were perfectly flat, with no irregularities, … wouldn't be necessary. But roads are far from flat. Even freshly paved highways have subtle imperfections that can interact with the wheels of a car. It's these
imperfections that apply forces to the wheels.
The study of the forces at work on a moving car is called vehicle dynamics, and you need to understand some of these concepts in order to appreciate why a … is necessary. Most automobile engineers consider the
dynamics of a moving car from two perspectives:
Ride - a car's ability to smooth out a bumpy road
Handling - a car's ability to safely accelerate, brake and corner
These two characteristics can be further described in three important |
|
principles - road isolation, |
Д |
road holding and cornering. The table below |
|
describes these principles and how engineers attempt to solve the challenges unique to each.
Principle |
Definition |
Goal |
Solution |
|
|
|
И |
|
|
|
|
|
Absorb energy |
|
|
The vehicle's |
Allow the vehicle |
from road |
|
|
ability to absorb |
bumps and |
|
|
Road Isolation |
or isolate road |
body to ride |
dissipate it |
|
shock from the |
undisturbed while |
without |
|
|
|
passenger |
traveling over |
causing undue |
|
|
rough roads. |
|
||
|
compartment |
oscillation in |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
the vehicle. |
|
13

|
|
The degree to |
Keep the tires in |
Minimize the |
|
|
|
contact with the |
transfer of |
|
|
|
|
which a car |
|
||
|
|
ground, because it |
vehicle weight |
|
|
|
|
maintains contact |
|
||
|
|
is the friction |
from side to |
|
|
|
Road Holding |
with the road |
between the tires |
side and front |
|
|
surface in various |
|
|||
|
and the road that |
to back, as this |
|
||
|
|
types of |
affects a vehicle's |
transfer of |
|
|
|
directional |
|
||
|
|
ability to steer, |
weight reduces |
|
|
|
|
changes and in a |
|
||
|
|
brake and |
the tire's grip |
|
|
|
|
straight line |
accelerate. |
on the road. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
С |
|
Minimize body |
|
|
|
|
roll, which occurs |
Transfer the |
|
||
|
|
|
as centrifugal |
weight of the |
|
|
|
|
force pushes |
|
|
|
|
|
car during |
|
|
|
|
The ability of a |
outward on a car's |
|
|
|
Cornering |
vehicle to travel a |
center of gravity |
cornering from |
|
и |
curved path |
while cornering, |
the high side |
|
|
|
|
|
raising one side of |
of the vehicle |
|
|
|
|
to the low |
|
|
|
|
|
the vehicle and |
side. |
|
|
|
|
lowering the |
|
|
|
|
|
opposite side. |
|
|
A car's …, with its various components, provides all of the solutions |
|||||
|
бА |
|
|
||
1.What are the main functions ofДsuspension system?
2.What does vehicle dynamics study?
3.What are three main principles which canИdescribe the dynamics of a moving car?
4.According to which of the principles the energy absorbing from road bumps can be dissipated without causing undue oscillation in the vehicle?described.
during braking. Because the nose of the car dips toward the road, this type of motion is known as "dive." The opposite effect -- "squat" -- occurs during acceleration, which shifts the weight of the car from the front tires to the back.
14
16. Put the following types of propulsion into the chronological order:
1. electric-powered;
2. horse-drawn;
3. gasoline-powered;
4. steam-powered.
С17. Find as many cognate words (nouns, adjectives, verbs) as possible for the following words:
to transport, to propel, electric, power, fuel.
и18. Fill in the gaps using some of these cognate words:
Most work in alternative … concepts is focused on replacing traditional internal combustion engines in automobiles. The motivation for the research is primarilyбАto achieve more sustainable methods of … than those relying on fossil fuels. To be competitive alternative fuel vehicles must be … and highspeed enough; its source of energy must provide enough range and be easily refueled/recharged. Hybrid vehicles use petroleum and another source, generally …. Petrofree cars are not … by petroleum, for example, battery electric cars, hydrogen vehicles, compressed air.
19. Skim the text and list main types of internal combustion engine’s classifications are mentioned inДthe text. Read the text paying attention to the new terms for you. Write out and translate them.
Today we will discuss about engine and types of engine used in automobile. Any device which can convert heat energy of fuel into mechanical energy is known as engine or heat engine. Engine is widely used in automobile industries or we can say thatИengine is the heart of an automobile. Basically engine may be classified into two types.
Types of Engine:
1. External combustion (E.C.) Engine
It is an engine in which combustion of fuel take place outside of the engine. In this type of engine heat, which is generated by burning of fuel is use to convert the water or other low boiling temperature fluid into steam. This high pressure steam used to rotate a turbine. In this engine we can use all solid, liquid and gases fuel. These engines are generally used in driving locomotive, ships, generation of electric power etc.
Advantages of E.C. engine. In these engines starting torque is generally high. Because of external combustion we can use cheaper fuels as well as solid fuel. They are more flexible compare to internal combustion engines.
15
2. Internal Combustion (I.C.) Engine
It is an engine in which combustion of fuel take place inside the engine. When the fuel burns inside the engine cylinder, it generates a high temperature and pressure. This high pressure force is exerted on the piston (A device which free to moves inside the cylinder and transmit the pressure force to crank by use of connecting rod), which used to rotate the wheels of
Сvehicle. In these engines we can use only gases and high volatile fuel like petrol, diesel. These engines are generally used in automobile industries, generation of electric power etc.
Advantages of I.C. engine It has overall high efficiency over E.C. engine. These engines are compact and required less space. Initial cost of I.C. engine is lower than E.C. engine. This engine easily starts in cold because of
иmay be classified in many manners. Today I am going to tell you some important classification of an automobile engine.
it uses high volatile fuel.
Types of I.C. Engine. I.C. engine is widely used in automobile
FourбА-stroke engine. In a four stroke engine piston moves two times up and down inside the cylinder andДcomplete two crankshaft revolutions during single time of fuel burn. This type of engines has high average compare to two stroke engine. These are generally used in bikes, cars, truck etc.
industries so it is also known as automobile engine. An automobile engine
According to number of stroke:
Two-stroke engine. In a two stroke engine a piston moves one time up
and down inside the cylinder and complete one crankshaft revolution during single time of fuel burn. This type of engine has high torque compare to four stroke engine. These are generally used in scooters, pumping sets etc.
According to design of engine:
Reciprocating engine (piston engine). In reciprocating engine the pressure force is generated by combustion ofИfuel exerted on the piston (A
device which free to move in reciprocation inside the cylinder). So the piston starts reciprocating motion (too and fro motion). This reciprocating motion converts into rotary motion by use of crank shaft. So the crank shaft starts to rotate and rotate the wheels of vehicle. These are generally used in all automobile.
Rotary engine (Wankel engine). In rotary engine there is a rotor which frees to rotate. The pressure force generate by burning of fuel is exerted on this rotor so the rotor rotate and starts to rotate the wheels of vehicle. This engine is developed by Wankel in 1957. This engine is not used in automobile in present days.
According to fuel used:
Diesel engine. These engines use diesel as the fuel. These are used in trucks, buses, cars etc.
16

Petrol engine. These engines use petrol as the fuel. These are used in bikes, sport cars, luxury cars etc.
Gas engine. These engines use CNG and LPG as the fuel. These are used in some light motor vehicles.
Electric engine. It is eco-friendly engine. It doesn’t use any fuel to burn. It uses electric energy to rotate wheel.
СAccording to method of ignition:
Compression ignition engine. In these types of engines, there is no extra equipment to burn the fuel. In these engines burning of fuel starts due to temperature rise during compression of air. So it is known as compression иignition engine.
Spark ignition engine. In these types of engines, ignition of fuel start by the spark, generate inside the cylinder by some extra equipment. So it is known as spark ignition engine.
AccordingбАto number of cylinder
Single cylinder engine. In this type of engines have only one cylinder and one piston connected to the crank shaft.
Multicylinder engine. In this type of engines have more than one cylinder and piston connected to the crank shaft.
According to arrangement of cylinder:
In-line engine. In this type of engines, cylinders are positioned in a straight line one behind the other along the length of the crankshaft.
 Д V-type engine. An engine with two cylinderИbanks inclined at an angle
Д V-type engine. An engine with two cylinderИbanks inclined at an angle
to each other and with one crankshaft known as V-type engine.
17

Opposed cylinder engine
An engine with two cylinders banks opposite to each other on a single crankshaft (V-type engine with 180o angle between banks).
СиOpposite piston engine. In this type of engine there are two pistons in each cylinder with the combustion chamber in the center between the pistons. In this engine a single combustion process causes two power strokes, at the same time.
W-type engine. An engine same as V-type engine except with three
banks of cylinders on the same crankshaft known as W-type engine.
to a masterбАrod which, in turn, connected to the crankshaft.  Д
Д
Radial engine. It is an engine with pistons positioned in circular plane around the central crankshaft. The connecting rods of pistons are connected
According to air intake process:
Naturally aspirated. In this types of engineИintake of air into cylinder occur by the atmospheric pressure.
Supercharged engine. In this type of engine air intake pressure is increased by the compressor driven by the engine crankshaft.
Turbocharged engine. In this type of engine intake air pressure is increase by use of turbine compressor driven by the exhaust gases of burning fuel. In these types of engines, there is no extra equipment to burn the fuel. In
18
these engines burning of fuel starts due to temperature rise during compression of air. So it is known as compression ignition engine.
Make up the table which can be useful for retelling the text.
20. Find more information devoted to modern automobile systems using internet. Make a brief report.
С21. Read and remember new words and word collocations. vehicular traffic – дв жение транспорта иpedestrian traffic – пешеходное движение
pavement markings – разметка на покрытии (дорог) traffic markers – дорожные указатели
sign – знак
arterial routeбА– маг стральная дорога
one-way street – ул ца с односторонним движением assign – назначать, поручать
traffic volume – нтенсивность движения
hourly pattern – часовой расчет интенсивности движения ordinance – постановление
right-of-way – полоса отвода дороги
off-centre lane – центральная разделительная полоса
Make up 3 sentences using new words.
22. Read and translate the text.Д
TRAFFIC REGULATION
Traffic engineering deals with the directionИand control of vehicular and pedestrian traffic on existing highways and streets. Thus it is concerned with the planning, design, and operation of all devices that aid the flow of traffic. Among these are pavement markings, traffic markers, signs, and traffic signals. Traffic engineering also deals with means for improving the efficiency of the existing system by the designation of arterial routes and oneway streets, and by controlling the use of these and other facilities. The integration of street and highway lighting into the over-all highway plan generally is considered a traffic engineering responsibility too. Interwoven into all the functions is accident reduction; and traffic engineers usually are assigned the responsibility for accident records and statistics. Parking likewise falls within the province of the traffic engineer because of the impact that parking problems have on street and highway operation.
19
The scope of aspects the traffic engineer deals with: traffic characteristics, traffic regulations, traffic-control devices, and environmental improvements. Traffic characteristics include such aspects as: physical factors, traffic volume, volume counting, speed characteristics, traffic stream flows, accidents, vehicular limitations and human characteristics.
As for traffic volume, the traffic engineer must be acquainted with some Сvolume characteristics: hourly pattern, day-of-week variation, classification of vehicles, trends in volumes and the methods of volume counting. Traffic regulations cover traffic laws and ordinances, various types of traffic controls: speed control and curb-parking control. Traffic-control devices иconsist of traffic signs, markings, signals, islands and street and highway
lighting.
Traffic regulations contribute to safety and decrease accidents. A most favourable effect on efficiency and the incidence of traffic accidents is dual highway.бАA dual highway separates opposite-direction traffic by a median divider. The separation of opposite-direction traffic by a median reduces the possibility of head-on collisions and sideswipe accidents. The width of the dual highway is varied for reasons of topography. Of necessity, the dual highway has not less than four traffic lanes. This number is efficient for traffic safety, because the driver has only one car alongside to watch.
Although the traffic engineer is concerned primarily with the traffic regulation and control, he must take into account the roadway elements, because sometimes, traffic-engineering functions are expanded to deal with
1.Traffic engineering deals withД…
2.It is concerned with … И
3.Interwoven into all the functions is …
4.Traffic engineering usually are assigned …
5.Traffic characteristics include …
6.Traffic engineer must be acquainted with some volume characteristics …
7.Traffic regulations cover various types of traffic controls …
8.Traffic-control devices consist of …
9.Traffic regulations contribute to …
10.Traffic engineer must take into account …
24. Match English collocations and their translations. hourly pattern – интенсивность движения
off-centre lane – полоса отвода дороги right-of-way – центральная разделительная линия
20
