
English Lectures / Functional chemistry 2 eng
.pdfKUBAN STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
KUBAN MEDICAL INSTITUTE
DEPARTMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL AND
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Functional Chemistry.
Part 2
Krasnodar
2020
Blood plasma proteins
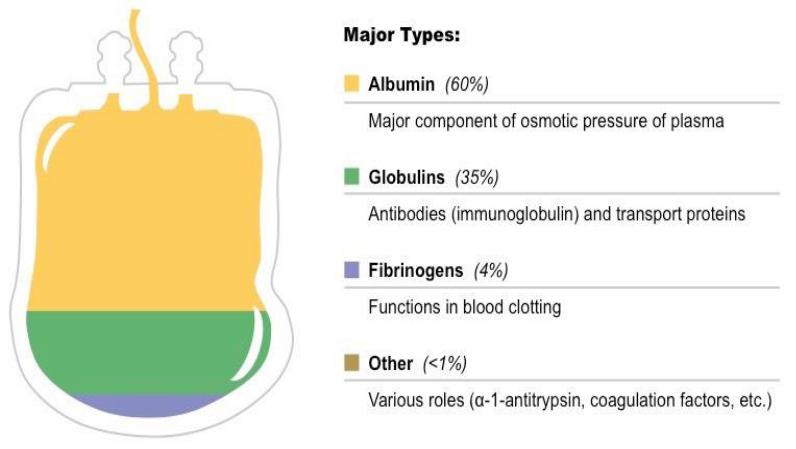
In blood plasma, more than 200 types of proteins are discovered, which make up 7% of the plasma volume. Proteins of blood plasma are synthesized mainly in the liver and macrophages, as well as in the endothelium of blood vessels, in the intestines, lymphocytes, kidneys, and endocrine glands.
Proteins of blood plasma are destroyed by the liver, kidneys, muscles and other organs. The half-life of plasma proteins is from several hours to several weeks.
Functions of blood plasma proteins
Let’s write!
They:
•Create oncotic pressure. It is necessary to retain water in the bloodstream.
•Participate in blood coagulation.
•Form a buffer system (protein buffer).
•Transport water-poorly soluble substances (lipids, metals (valence is 2 or more) in the blood.
•Participate in immune processes.
Functions of blood plasma proteins
Let’s write!
They:
•Form a reserve of amino acids, which is used, for example, during protein starvation.
•Catalyze some reactions (protein enzymes).
•Determine the viscosity of the blood, affect hemodynamics.
•Participate in inflammation reactions.
Structure of plasma proteins
By structure, blood plasma proteins are globular. According to composition they are divided into simple (albumin) and complex.
•Among the complex ones, lipoproteins (VLDL, STDL, LDL, HDL, ChM), glycoproteins (almost all plasma proteins) and metalloproteins (transferrin, cerruloplasmin) can be distinguished.
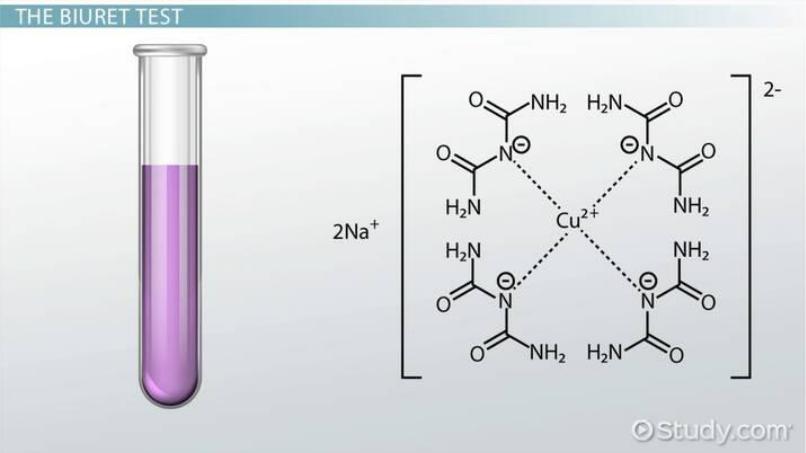
Total protein |
Let’s write! |
The total amount of protein in the blood plasma is normally 70-90 (60-80) g/L, it is determined using a biuret reaction. The amount of total protein in the blood is of diagnostic value.
Increase / decrease in total protein |
Let’s write! |
An increase in the total amount of protein in blood |
plasma is called |
hyperproteinemia, a decrease is called hypoproteinemia. Violation of the ratio of protein fractions of blood plasma is called dysproteinemia.
•Hyperproteinemia occurs with dehydration (relative), injuries, burns, myeloma (absolute).
•Hypoproteinemia occurs with a decrease in edema (relative), starvation, pathology of the liver, kidneys, blood loss (absolute).
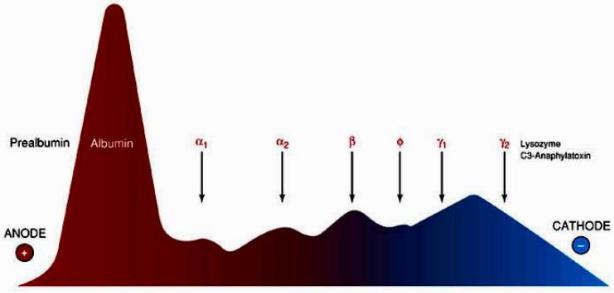
In addition to the total protein content in blood plasma, the content of individual protein groups or even individual proteins is also determined. To do this, they are separated using electrophoresis.

Fraction 1: Albumins |
Let’s write! |
The cause of hypoalbuminemia is a decrease in the synthesis of albumin:
•with liver failure (cirrhosis),
•with an increase in capillary permeability,
•when catabolism is activated due to burns, sepsis, tumors,
•with loss of albumin in the urine (nephrotic syndrome),
•when fasting.
Hypoalbuminemia causes:
swelling of the tissues
decreased renal blood flow,
activation of RAAS,
water retention in the body,
increased tissue edema,
a sharp outflow of fluid into the tissue leads to a decrease in blood pressure and can cause shock.
Fraction 1: Albumins
Let’s write!
Albumin (40-50 g/L):
•Structure: a simple protein of 585 AA with a mass of 69 kDa, has 17 disulfide bridges, many dicarboxylic AAs, and has high hydrophobicity. Albumin exhibits polymorphism.
•Synthesis: in the liver (12 g/day). Disposal: kidneys, enterocytes and other tissues. The half-life is 20 days.
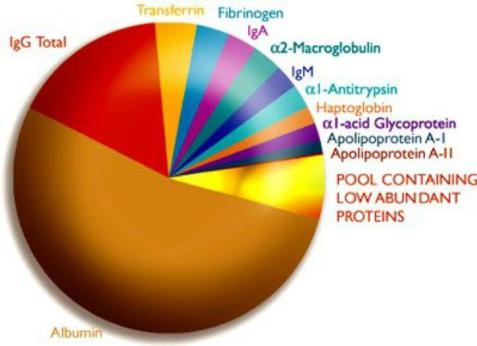
•60% of albumin is in the intercellular substance, 40% is in the bloodstream. They make up 60% of all plasma proteins.
•Functions: maintaining osmotic pressure (80% contribution), transport of free fatty acids, bilirubin, bile acids, steroid and thyroid hormones, cholesterol, drugs, inorganic ions (Cu² , Ca² , Zn² ), is a source of amino acids.
Fraction 1: Albumins
Transthyretin (prealbumin, 0.25 g/L):
•Structure: tetramer.
•Protein of the acute phase (group 5).
•Functions: transports thyroid hormones and a retin-binding protein.
•It decreases during fasting.
