
English Lectures / Functional chemistry 2 eng
.pdfFraction 2: α-Globulins
Let’s write!
Dysproteinemia due to the α-globulin fraction is realized mainly due to:
•decrease synthesis of α-antitrypsin
•loss of proteins of this fraction with urine in nephrotic syndrome
•increase in acute phase proteins during inflammation.
Let’s write! |
Fraction 2: α-Globulins |
α-Antitrypsin (2.5 g /L):
•Structure: glycoprotein
•Synthesis: by a liver.
•Functions: acute phase protein (group 2). An important inhibitor of proteases, including neutrophil elastases, which destroy the lung and liver alveoli elastin. α-Antitrypsin also inhibits skin collagenase, chymotrypsin, fungal proteases, and white blood cells.
•With α-antitrypsin deficiency, pulmonary emphysema and hepatitis can occur, leading to liver cirrhosis.
Fraction 2: α-Globulins
Acid α-glycoprotein (1 g/L):
•Synthesis: by the liver.
•Functions: acute phase protein (group 2). It transports progesterone and related hormones.
Fraction 2: α-Globulins
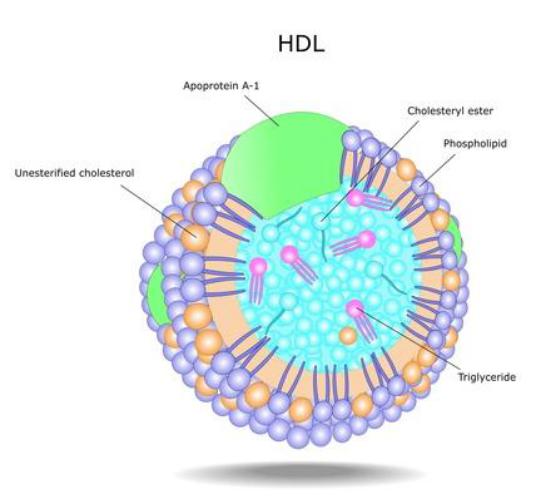
HDL (0.35 g/L):
•Synthesis: in the liver.
•Functions: transport excess cholesterol from tissues to the liver, provide the exchange of other drugs.
Fraction 2: α-Globulins |
Let’s write! |
Prothrombin (0.1 g /L):
•Structure: glycoprotein containing about 12% carbohydrates; the protein part of the molecule is represented by a single polypeptide chain; molecular weight of about 70,000 Yes.
•Synthesis: in the liver, regulated by vitamin K, formed by the intestinal flora.
•Functions: a precursor to the thrombin enzyme, which stimulates the formation of a thrombus.
•With its lack of vitamin K, the level of prothrombin in the blood drops, which can lead to bleeding (early childhood hemorrhage, obstructive jaundice, some liver diseases).

Fraction 2: α-Globulins |
Let’s write! |
Transcortin (0.03 g/L):
•Structure: glycoprotein, mass 55,700 Yes, half-life - 5 days
•Synthesis: in a liver
•Functions: transfers cortisol, corticosterone, progesterone, 17-α- hydroxyprogesterone and, to a lesser extent, testosterone.
•The concentration in the blood is sensitive to exogenous estrogens and depends on their dose.
Fraction 2: α-Globulins
Thyroxin-binding globulin (0.02 g/L):
•Structure: molecular weight 57 kDa. The half-life is 5 days.
•Synthesis: in the liver.
•Functions: it is the main transporter of thyroid hormones in the blood (transports 75% of thyroxine and 85% of triiodothyronine).
Fraction 3: α-Globulins
Let’s write!
Dysproteinemia due to the α-globulin fraction can occur:
• with inflammation, because this fraction contains proteins of the acute phase.

Fraction 3: α-Globulins |
Let’s write! |
α-Macroglobulin (2.6 g/L):
•Structure: very large protein (725 kDa)
•Synthesis: by the liver.
•Functions: acute phase protein (4 group). The main inhibitor of many classes of plasma proteinases, regulates blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, kininogenesis, and immune responses.
•Plasma α-macroglobulin level decreases in the acute phase of pancreatitis and prostate carcinoma, increases as a result of the hormonal effect (estrogens).

Fraction 3: α-Globulins
Haptoglobin (1 g/L):
•Structure: glycoprotein
•Synthesis: by the liver.
•Functions: acute phase protein (group 2). Associates hemoglobin with the formation of a complex with peroxidase activity, prevents the loss of iron from the body. Haptoglobin effectively inhibits cathepsins C, B and L, and may be involved in the utilization of certain pathogenic bacteria.
