
English Lectures / Functional chemistry 2 eng
.pdfFraction 5: γ-Globulins |
Let’s write! |
Group |
Proteins |
Concentration |
Functions |
|
in plasma, g/L |
||||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
γ-Globulins |
IgG |
12 |
Late antibodies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IgA |
3,5 |
Antibodies protecting the mucous membranes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IgM |
1,3 |
Early antibodies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IgD |
0,03 |
B-lymphocyte receptors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IgE |
<0,01 |
? |
|
|
|
|
|

Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation
•The term "acute phase proteins" combines up to 30 blood plasma proteins involved in the body's inflammatory response to damage.
•Proteins of the acute phase are synthesized in the liver, their concentration varies significantly and depends on the stage, course of the disease and massive damage.
•Protein synthesis of the acute phase of inflammation is stimulated by:
•1) IL6,
•2) IL1 and similar in action (IL1α, TNF)
•3) Glucocorticoids;
•4) Growth factors (insulin, growth factors of hepatocytes, fibroblasts, platelets).
5 groups of acute phase proteins are isolated
Let’s write!
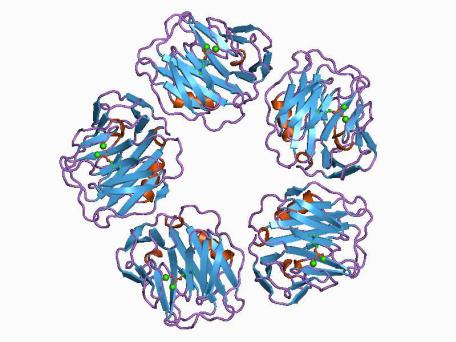
Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation – group 1
The "main" proteins of the acute phase in humans include C-reactive protein (CRP) and amyloid A protein in blood serum. The level of these proteins increases with damage very quickly (in the first 6-8 hours) and significantly (20-100 times, in some cases - 1000 times).
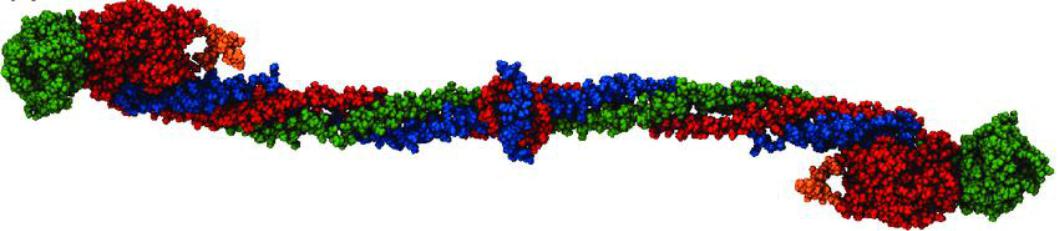
Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation – group 2
Proteins, the concentration of which during inflammation can increase by 2-5 times within 24 hours. This is an acidic α-glycoprotein, α-antitrypsin, fibrinogen, haptoglobin.
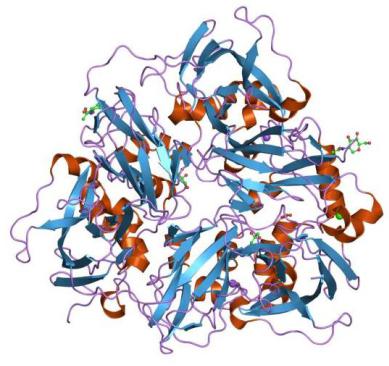
Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation – group 3
Proteins, the concentration of which during inflammation either does not change or increases slightly (by 20-60% of the initial value). This is ceruloplasmin – the C3 complement component.
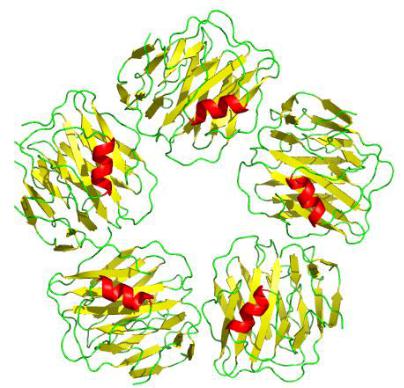
Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation – group 4
Proteins involved in the acute phase of inflammation, the concentration of which, as a rule, remains within the normal range. These are α1macroglobulin, hemopexin, amyloid P protein of blood serum, immunoglobulins.
Proteins of the acute phase of inflammation
– group 5 Let’s write!
Proteins, the concentration of which during inflammation can decrease by 3060%. These are albumin, transferrin, HDL, prealbumin. A decrease in the concentration of individual proteins in the acute phase of inflammation may be due to a decrease in synthesis, an increase in consumption, or a change in their distribution in the body.
Non-protein nitrogenous components of the blood (residual nitrogen)
This group of substances includes: urea, uric acid, amino acids, creatine, creatinine, ammonia, indican, bilirubin and other compounds. The content of residual nitrogen in the blood plasma of healthy people is 15-25 mmol / l. An increase in the content of residual nitrogen in the blood is called azotemia. Depending on the cause, azotemia is divided into retention and production.
Retention and production azotemia
Let’s write!
•Retention azotemia occurs when there is a violation of the excretion of nitrogen metabolism products (primarily urea) in the urine and is characteristic of impaired renal function. In this case, up to 90% of non-protein blood nitrogen is accounted for by urea nitrogen instead of 50% normal.
•Production azotemia develops with an excess of nitrogenous substances entering the bloodstream due to increased breakdown of tissue proteins (prolonged starvation, diabetes mellitus, severe wounds and burns, infectious diseases).
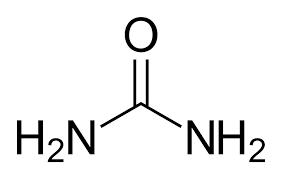
Urea and amino acids
Urea is the main end product of protein metabolism in the human body. It is formed as a result of the neutralization of ammonia in the liver, excreted from the body by the kidneys. Therefore, the blood urea content decreases with liver diseases and increases with renal failure.
Amino acids enter the blood when absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract or are decomposition products of tissue proteins. In the blood of healthy people, amino acids are dominated by alanine and glutamine, which, along with participation in protein biosynthesis, are transport forms of ammonia.
