
- •Internet
- •In seven years
- •8 Complete the sentences with the words In brackets» making any changes that are necessary,
- •9 Hew words are continually being created in Telecoms and it Often these words are made up of two parts. Match the openings in Column a with thecorrect endings in Column b.
- •2020: End of mobile phones
- •2010; Massive Increases In bantfv/ldih
- •12 | UnIfl Convergence II I eleC0m3 anri 11
- •How much will the Sakshat cost?
- •5 Discuss these questions with a partner,
- •Io The recommendation section at the end of the Executive Summary is missing. Look at all the information in the text and discuss with a partner which option you would recommend.
- •16 Complete the word puzzle to find the hidden expression. Listen to the extract again if necessary.
- •12 Read the Introduction to an email and answer the questions.
- •Includes the supply of new equipment
- •Includesan optional buyback of equipment .
- •Fast response time
- •InterAsia Car
- •I Monthly Price Per Unit
- •2 Yo u ате go I ng to rea d a t ext abo ut ch anges I n te levi si on. Before you rea d, try to со m plete the notes on some of these changes. Complete the table with the pairs of expressions.
- •Image in pixels (hdtv)
- •15 Complete this email from one of the venture capitalists to a colleague.
- •OpTrOn 2
- •Make a ca 11 wit h rh e satelli te p h one.
- •Send an email.
- •Suggested a nsv/ers
- •6 ... W h e " alms st eve ryone h a 5 the d ay oft.
- •Buyback
- •Database
16 Complete the word puzzle to find the hidden expression. Listen to the extract again if necessary.
English for 1
Telecoms 1
Retail Week 28
7
8
17 Wo г к wit h a pa rtner. Role p lay two ca I Is to so rt ou t tech n ic al pro blem s.
ШШШШ^ fWnerB Пк5.Р.7б
Read the article about networking developing countries and answer the questions below.
As developing countries seek to upgrade their telecoms networks, they are faced with difficult choices.
On the one hand, they have the advantage of being able to forget about rolling nut national fixed line networks. In some countries, tefedensity is as low as 4%. so expanding a wired network to cover gn entire population is fsrtoo expensive. The result is th3tthey con bypass en old technology end move straight to э national wireless network to provide brood bend and voice [VoIP} services.
On the other hand, there is a difficult choice to make - Wi-Max or 3G?
)n many developing countries, Wi-Max (Worldwide interoperability for Microwave Access) has already made a huge impact. It delivers high-speed access wire less ly, enabling fixed and mobile broadband services ever large coverage areas. It is an IP-based system and comes in two versions, fixed and mobile. Fixed Wi-Max is suited for delivering wireless last mile eccer.n for fixed broadband services, similar to DSL. Mobile Wi-Mex supports both fixed and mobile applications with improved performance and capacity while adding full mobility. In India, Tate lias launched what it says will be the worlds biggest Wi-fvlox network, with a projected cost of $600 million.
In tha other corner is 3G (and coming ncran, 4G and LTE), a well-established wireless network in developed countries. 3G has evolved from the voice-centric tele corns world, but is able to deliver not just voice but high-speed broadband access as well. The lost ton years have seen the growth of huge network in the developed world, and emerging notions are catching up rapidly. China is investing billions of do Hers in rolling out a nationwide 3(? network chat will reach 70% of the population, and the Asia Pacific region expects to have over 500 million 3G subscribers in the next few yesrs.
In the longer term, wa are already starting to see the convergence of Wi-Mex and 3G. While Wi-Max has broadened to he со me more mobile end capable of being used for media sendees, 3G cellular hes become increasingly broadband, resulting in practical convenience between these fields of development What's more, both ere driven to use Che same core sets of technologies.
At the moment, developing countries still have to make e choicE between the two systems, and are faced with the familiar Eetarnax vs VI IS or BluRsy vs HD decision. But if the two technologies con cooperate rather than compece, then the future of broadband 3nd voice services in developing countries will look a lot brighter.
Why are some developing countries not developing their wired networks?
What suggests that Wi-Max and 3G are equally suitable for developing countries?
According to the text, what will happen to Wi-Max and 3G in the future?
OVER TO YOU
What wireless technologies a re being used in your country?
What are the limits to wjreless technology when compared to fixed line?
Can you see the world becoming entirely wireless in the future?
Data centres and security
LOCATION, LOCATION, LOCATION
Look at the pictures. Write down one advantage and one disadvantage of each place as the location for a Tier ц (most secure) data centre. Compare your answers with a partner.

Peshawar, on the Pakistan/Afghanistan border

Business park, near Heathrow airport, London Remote farmland, Ireland
DATA CENTRES
1 Rupert Wilson, CIO of a small investment bank, is visiting a German data centre to find out about the services they offer. Helmut Schwartz is taking him on a tour of the data centre, listen to the first part of Helmut's tour and say if the following statements are TRUE (T) or ГALSE (F).
The data ccntrc is in a German city.
The centre is closed for four days a year.
Security at the centre is extremely tight.
Industrial development zone, New Orleans
□ □
П □
Senior managers do not need to follow all the security rules, b The data ccntre is connccted to two different network POPs. 6 The centre always uses its own independent power sup ply.
2 Liste n lo the ta Ik aga I n. Com plete I he n otes abo ut wh at H elm u t say s, ad d i n g at lea st two items for each section of the diagram. Seethe example,
Secu rity a rra n gem ents
Location
Bavarian countryside Power
far from airports/flight paths *
Raised piain
DATA CENTRE
Most extreme threats/dangers Connectivity
® 3
Listen to the second part of the tour. Match the words in the box with items i-ю in the diagrams,
у с
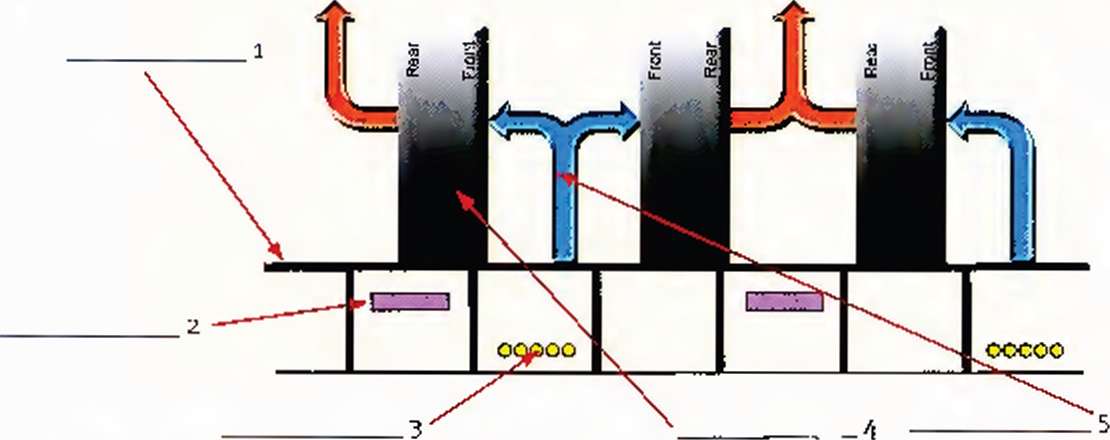
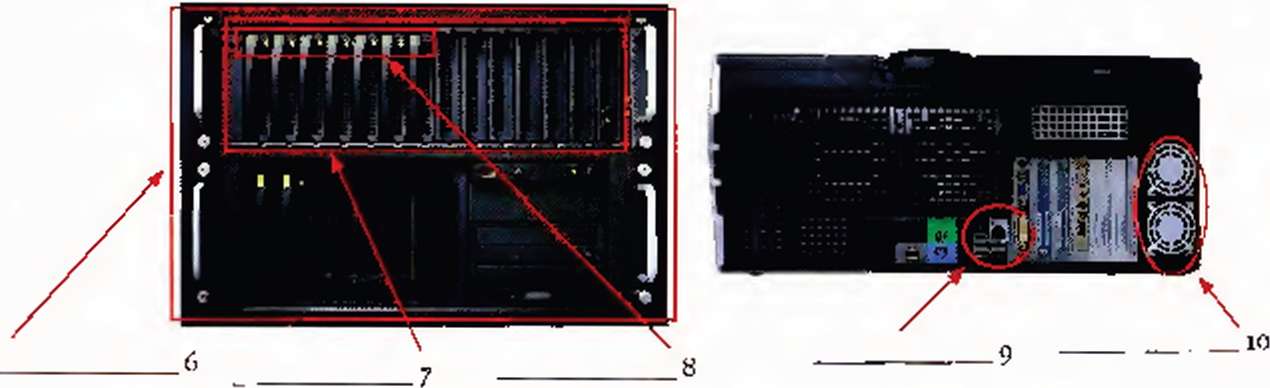
19-inch rack ♦ alarm LED » blades ♦ telecom cable trays • cold aisle • cabinets • raised, perforated tiles * power cables • Ethernet port • fans
UNITS Data centres and security | 41
4 Match the words t-i 1 from the Listening with the definitions a-k.
1 |
mission critical |
a |
sections of a centre sealed oil from other sections |
2 |
redundancy |
b |
using physical characteristics (e.g. fingerprints) for ID |
3 |
downtime |
с |
one weakness that could stop an entire system |
4 |
compartments |
6 |
time when the equipment is not functioning- |
5 |
resilience |
e |
duplication of equipment in case one part tails |
6 |
separacy |
f |
ext re m e ly i m p 0 rta n t |
7 |
networkouiages |
S |
ability to withstand unexpected problems or setbacks |
3 |
power feeds |
h |
lack of electricity |
9 |
power cuts |
i |
sources of electricity |
10 |
single point of failure |
i |
having different and unconnected cables to a network |
11 |
biometrics |
к |
times when a network is not functioning |
Now work with a partner. Ask and answer questions using some of the words above.
In your work, what sort of data is mission-cr'iticial?
I low importa ni is red undancy lor the protection of data?
What elements do you think are important for the resilience of a Tier 4 data centre?
How might a Tier 1 data centre differ from a more secure one?
>J№
5 listen to the discussion Helmut and Rupert have after the tour. For questions 1-5, choose the 17 correct alternative (A or B).
Rupert says he-.
A is keen to start outsourcing as soon as possible. В has concerns a bout making such a big decision.
R u p ert wa nts t n к n ow-.
Л what would happen if there was downtime during a trading period. 6 if it is possible to avoid downtime completely.
Helmut tells Rupertthat:
A they have never had any management problems. В they have n eve r ha d а со rn rns 0 u ta ge.
According to I lelmut, a power outage: A would not cause any disruption.
В could be fixed in a matter of minutes, г, I he mirror site in Switzerland:
A has a copy of all the data at the centre. Б would warn the centre about an earthquake.
TALKING ABOUT IMAGINARY SITUATIONS
We often use The second conditional to talk about possible situations. If there was a comros oiilcge, we would switch to Ihe backup service, tfv/e fast power, our nivr? bock up power systems would start.
We can also use other structures to talk about imaginary situations. In the event of one of your servers going down...
Supposing there was on earthquake or you gof hit by a plane, what would happen then? Should anything terrible occur, you Y/outd need to have standby communications links. If (hot were to happen, you would switch over to the hoi standby site.
Match scenarios in A with solutions in В to make second conditional sentences.
A |
Scenarios |
В Solutions |
i |
If one power feed failed, |
use / other network POP |
2 |
If both power feeds failed. |
temperature alarm / go off |
3 |
If anyone unauthorized tried to gain access. |
isolate /change / straight away |
4 |
If one telecorns service lost connectivity. |
be stopped / security guards |
r> |
If the air conditioning went wrong, |
9.witch / mirror site / Switzerland |
6 |
ff there was a problem with one of the servers, |
use / other power feed / grid |
7 |
if there was a complete catastrophe like an |
UPS system /generator |
|
earthquake or a plane crash, |
|
Now, work with a partner. Ask and answer questions about the scenarios. Example:
Л What wou Id happen if there was along po wer о utoge ? В If we had a long po v/er cut; we would use oar о wn genem f оr$.
7 Work with a partner. One of you is an IT manager looking for a secure data centre, the other is a representative of a data centre. Role play the meeting.
UNIT 5 Data centres and security | 43
BANKING SECURITY
»L-DIO
© 8 You are going to hear Jon, a bank security officer, answer some questions about his job. Before
>8
you listen try to com plete the sentences about bank security,
spear » white-hat • worms ♦ ping sweep • TCP/IP • certificates
A hacker is a hacker who helps organizations protect themselves against
criminal hackers.
A is a process to check to see who is connected to a network.
fingerprinting gives information about what operating system people are using.
/| l28biLSSL_ encrypt data.
Anti-virus software can protect against viruses and .
phishing is a more targeted form of phishing.
Now listen to |on and check your answers.
These were the questions that the interviewer asked Jon. listen again and match the questions 1-6 to Jon'sanswersA-E on the CD. There is one question that was not asked,
What can people do Lo stay securc online?
Is there anything else that people should be aware of?
llowdo you go About thai?
t\ Is it safe to use credit cards online?
So,)ontwhaf sort ofwork do you do for the bank?
What's the difference between you and a norma I hacker?
Read this short article about a computer infection.
Confickcr has been in the news a lot recently. It is a \ which unlike a
virus does not need to be attached to an existing program to infect a machine, and which seems to receive regularly updated instructions, from its controllers. It has created a
7 - a network of infected machines. Once infected, these machines are known
as \ At this point no one knows what the purpose of Confickeris. At present
it has infected ten million computers. These could be used for a _ attack where
all the infected computers attempt to access one site simultaneously.
It is probably controlled by criminals who want to steal users' personal information, i.e.
" . There are a number ofways of doing this: a 6 records information
entered via a keyboard, literally means harvesting users' information
while they are online. Wc will probably soon see if Conficker consists of this type of passive
monitoring a or whether it will mount a more active anack once it receives a
new set ol instructions.
11 Work with a partner. Use the information in your Partner File to complete the text.
I.',ll1ill!-i1.lll> ST:
44 | UNITS Datacfcnlresand security
INFORMATION SECURITY
