
- •4. Соедините части предложений (abc), чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
- •Переведите интернациональные слова.
- •2.3Апомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Раздел II
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •1.Переведите интернациональные слова.
- •Раздел III
- •2. Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •4. Переведите предложение […]0 устно.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •7. Дайте определение деятельности «Подготовка площадки под строительство».
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Раздел IV
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Переведите интернациональные слова.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
- •Соедините фрагменты (ab), чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
- •7. Расскажите, как металл и стекло используются в строительстве.
- •Выпишите из текста интернациональные слова (не менее 12).
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
- •Переведите предложения [...] письменно.
- •Расскажите об использовании пластиков в строительстве.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
- •Переведите предложения [...]0 письменно.
- •Закончите предложения по темам.
- •Переведите интернациональные слова.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
- •4. Переведите предложения письменно.
- •Ответьте на вопросы.
- •Закончите предложения.
- •Переведите текст устно. То sum up
- •Передайте содержание текста в трёх предложениях.
- •Раздел V
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Раздел VI
- •11 Переведите и используйте выделенные слова в своих предложениях.
- •4. Подберите синонимы.
- •Раздел VII
- •Запомните слова и словосочетании.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Раздел VIII fire resistance
- •Раздел IX
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •Запомните слова и словосочетания.
- •3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
- •Раздел I: urban (town) planning
- •Раздел II: buildings and their functions
- •Раздел III: construction site
- •Раздел IV: building materials
- •Раздел V: energy and its sources
- •Раздел VI: the building infrastructure
- •Раздел VII: sewage treatment and waste management
- •Раздел VIII: fire resistance
- •Раздел IX: hydraulic engineering
заполнителе.
Information-to-Swallow
A little history on the subject
The Assyrians and Babylonians used clay as the bonding substance. The Egyptians used lime and gypsum cement. An analysis of ancient Egyptian pyramids has shown that concrete was employed in their construction.
Roman architects invented Roman concrete and used it in buildings where it could stand on its own and support a great deal of weight. The first use of concrete by the Romans was sometime after 273 ВС. Ancient Roman concrete was a mixture of lime mortar, pozzolana1, water, and stones. The ancient builders placed this mixture in wooden frames where it hardened and bonded to a facing of stones or (more frequently) bricks. When the framework was removed, the new wall with a rough surface was very strong. This surface could be smoothed and faced with attractive stucco or thin panels of marble or other coloured stones. Concrete construction proved to be more flexible and less costly than building solid stone buildings. The materials were readily available and not difficult to transport. The wooden frames could be used more than once, allowing builders to work quickly and efficiently.
The widespread use of concrete in many Roman structures has ensured their survival to the present day. The Baths of Caracalla in Rome are just one example. Many Roman aqueducts and bridges have masonry cladding on a concrete core, as does the dome of the Pantheon.
In 756, British engineer John Smeaton made the first modern concrete by adding pebbles as a coarse aggregate and mixing powdered brick into the cement. In 1824, English inventor Joseph Aspdin invented the first true artificial cement — Portland cement by burning ground limestone and clay together. The burning process changed the chemical properties of the materials and stronger cement was created, which has remained the dominant cement used in concrete production.
* Pozzolana is a type of volcanic ash used for mortar or for cement that sets under water.
(1 600 п.зн.)
TEXT С
Переведите интернациональные слова.
metal, major, structural, profile, specific, section, composition, mechanical, regulate, corrosion, thermal, expansion, assembly, insulation, design, typically.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
structural framework — несущий каркас, каркасная конструкция;
external surface covering — облицовка;
metal alloy — металлический сплав;
structural building material — конструктивный строительный материал;
chemical composition — химический состав;
carbon steel — углеродистая сталь;
high-strength low alloy steel — высокопрочная низколегированная сталь;
quenched steel — закалённая (при быстром охлаждении) сталь;
tempered steel — закалённая/отпущенная сталь;
thermal expansion — тепловое расширение;
structural integrity — конструктивная целостность;
external insulation — внешняя/наружная изоляция;
raw material prices — цены на сырьё.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Building Materials (II)
Metal is used as structural framework for larger buildings such as skyscrapers, or as an external surface covering. There are many types of metals used for building. Steel is a metal alloy whose major component is iron, and is the usual choice for metal structural building materials. It is strong, flexible, and if refined and treated well, lasts a long time.
[Structural steel is steel construction material, a profile, formed with a specific shape or cross section and certain standards of chemical composition and mechanical properties.]0 Structural steel shape, size, composition, strength, storage, etc., is regulated in most industrialized countries. The standard commonly used structural steels are:
carbon steels
high-strength low alloy steels
corrosion resistant high strength low alloy steels
quenched and tempered alloy steels.
The properties of steel vary widely, depending on its alloying elements. [Care must be taken to ensure that thermal expansion of structural elements does not damage wall and floor assemblies of a building.]0 When heated, steel expands and softens, eventually losing its structural integrity. Given enough energy, it can also melt. Structural steel requires external insulation (fireproofing) in order to prevent the steel from weakening in the event of fire. Heat transfer to the steel can be slowed by the use of fireproofing materials.
[As raw material prices fluctuate, often so does building design.]0 During times of lower steel prices, more steel and less concrete is used, and vice versa. However, both materials are typically used together. While both steel structures and reinforced concrete cement structures have their pros and cons, the steel structures have better strength and can be easily dismantled. (1 480 п.зн.)
Переведите предложении письменно.
Прочитайте текст 'Glassmaking'.
Glassmaking is considered an art form as well as an industrial process or material. Glass is an amorphous, solid substance, an inorganic product of fusion which has been cooled through its transition to the, solid state without crystallising. Glasses are typically brittle, and often optically transparent. Clear windows have been used since the invention of glass to cover openings in a building.
Glass is generally made from mixtures of sand and silicates, in a very hot fire stove (a kiln). Very often additives are added to the mixture to produce glass with shades of colours or various characteristics (such as bulletproof or light emittance glass).
Glass plays an essential role in industry. The optical and physical properties of glass make it suitable for such applications as flat glass, container glass, optics and optoelectronics material, laboratory equipment, thermal insulator (glass wool), reinforcement fiber (glass- reinforced plastic, glass fiber reinforced concrete), and art.
The use of glass in architectural buildings has become very popular in the modern culture. Glass 'curtain walls' can be used to cover the entire facade of a building, or they can be used to span over a wide roof structure in a 'space frame'. These uses, though, require some sort of frame to hold sections of glass together, as glass is too brittle to span large areas by itself. (1 150 п.зн.)
Соедините фрагменты (ab), чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
А.
... as glass is too brittle to span large areas by itself.
... is the usual choice for metal structural building materials.
...and certain standards of chemical composition and mechanical properties.
...which has been cooled through its transition to the solid state without crystallising.
...the steel structures have better strength and can be easily dismantled.
B.
Glass is an amorphous, solid substance, an inorganic product of fusion ...
While both steel structures and Reinforced concrete cement structures have their pros and cons, ...
Steel is a metal alloy whose major component is iron, and...
These uses, though, require some sort of frame to hold sections of glass together, ...
Structural steel is steel construction material, a profile, formed with a specific shape or cross section ...
7. Расскажите, как металл и стекло используются в строительстве.
TEXT D
Выпишите из текста интернациональные слова (не менее 12).
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
plastic material — пластмасса, пластичный материал;
amorphous solid — аморфное твёрдое тело;
to improve performance — улучшать характеристики;
malleability— ковкость, тягучесть, податливость;
to extrude — прессовать, штамповать;
thermosetting polymer — термореактивный полимер;
glass transition temperature — температура стеклования;
resistance to smth — сопротивляемость чему-либо;
versatility — универсальность, гибкость;
imperviousness — непроницаемость, водонепроницаемость;
to release toxic fumes — испускать токсичный дым/испарения.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
The follow-on
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semisynthetic organic amorphous solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. [The raw materials to make most plastics come from petroleum and natural gas.]° Plastics are typically polymers* of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce costs. [It refers to their malleability (or plasticity) during manufacture that allows plastics to be cast, pressed, or extruded into a variety of shapes.]0
There are two types of plastics: thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. Thermoplastics will soften and melt if enough heat is applied. Thermosets can melt and take shape once; after they have solidified, they stay solid.
Plastics are classified by chemical structure, by qualities relevant for manufacturing or product design, by various physical properties, such as density, tensile strength, glass transition temperature, and resistance to chemical effect.
[Due to their relatively low cost, ease of manufacture, versatility, and imperviousness to water, plastics are used in an enormous and expanding range of products, from paper clips to spaceships.]0 They have already displaced many traditional materials, such as wood, stone, horn or bone, leather, paper, metal, glass, and ceramic, in most of their former uses.
[However, plastics are durable and resistant to natural processes of degradation; burning plastic can release toxic fumes or dioxin.]0 Also, the manufacturing of plastics often creates large quantities of chemical pollutants.
* Polymer is a substance that has a molecular structure consisting chiefly or entirely of a large number of similar units bonded together (e.g. plastics and resins). (1 460 п.зн.)
Переведите предложения [...] письменно.
Расскажите об использовании пластиков в строительстве.
ТЕХТ Е
Переведите интернациональные слова.
contain, pore, normally, compressive, produce, specialized, synthetic, combination, sandwich, composite, mastic, application, substrate, convert, film, pigment, granular, contribute, texture, classify, ultraviolet, proportion, inert, potential.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
to trap bubbles — удерживать/задерживать пузырьки; to extinguish fire — тушить пожар; cellular material — ячеистый материал; improved insulation — улучшенные изоляционные свойства; composite material— композиционный материал, композит; liquefiable— плавкий, растворимый, разжижаемый; opaque film — непрозрачная плёнка; pigment— пигмент, краситель;
granular solid — зернистое, гранулированное вещество;
filter — наполнитель (минеральный порошок); inert material — инертный (неактивный) материал; binder — связующее вещество;
to impart adhesion — придавать свойство прилипания.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Foams
Part One
Foam is a substance that is formed by trapping many gaseous bubbles in a liquid or solid. Liquid foams are used in extinguishing fires, especially oil fires. Solid foams form an important class of lightweight cellular engineering materials. These foams can be classified into two types based on their pore structure: open cell structured foams and closed cell foams.
•
Open cell structured foams contain pores forming an interconnected network which is relatively soft. If filled with air, this foam could be a good insulator.
Closed cell foams do not have interconnected pores. [Normally, the closed cell foams have higher compressive strength due to their structures; they are also denser, require more material, and are more expensive to produce.]0 The closed cells can be filled with a specialized gas to provide improved insulation.
More recently synthetic foam has been used in combination with structural materials, such as concrete. [It is usually used as part of a structural insulated panel where the foam is sandwiched between wood and cement or insulated concrete forms where concrete is sandwiched between two layers of foam.]° All types of foam are also used as core material in sandwich structured composite materials. (1 050 п.зн.)
Paints
Part Two
[Paints is any liquid, liquefiable, or mastic composition which after application to a substrate1 in a thin layer is converted to an opaque solid film. ]0 Cave paintings drawn with red and yellow ochre, hematite, manganese oxide, and charcoal may have been made by early Homo sapiens as long as 40,000 years ago.
|Pigments are granular solids incorporated into the paint to contribute colour, toughness, texture or simply to reduce the cost of the paint.]0 They can be classified as either natural or synthetic types. Hiding pigments, in making paint opaque, protect the substrate from the harmful effects of ultraviolet light.
[Fillers are a special type of pigment that serves to thicken the film, support its structure and just increase the volume of the paint.]0 Fillers are usually made of cheap and inert materials, such as earth, talc, lime, clay, etc. Some paints contain large proportions of pigment/filler and binder.
[Binder, commonly referred to as vehicle, is the actual film forming component of paint.]0 It is the only component that must be present; other components are included optionally, depending on the desired properties of the cured film. [The binder imparts adhesion, binds the pigments together, and strongly influences such properties as gloss potential, exterior durability, flexibility, and toughness.]0
Paint can be applied as a solid, a gaseous suspension (aerosol), or a liquid. Techniques vary depending on the practical results desired. As a solid, the paint is applied as a very fine powder, and then baked at high temperature. This melts the powder and causes it to stick to the surface. In the liquid application, paint is applied directly using brushes, paint rollers, blades, etc. Paint application by spray is the most popular method in industry.
*Substrate is a substance or layer that underlies something, or on which some process occurs. (1 600 п.зн.)
Переведите предложения [...]0 письменно.
Закончите предложения по темам.
Foam is a substance...
Open cell structured foams...
Closed cell foams...
More recently synthetic foam has been used...
It is usually used as part of a structural insulated panel where the foam...
Paint is any liquid, liquefiable, or mastic composition...
Pigments are granular solids incorporated into...
Fillers are a special type of pigment that serves...
Binder is the actual...
As a solid, the paint is applied...
TEXT F
Переведите интернациональные слова.
ceramic, stick, calcium, silicate, press, mix, consistency, hydraulic, tunnel, organic, start, accurate, method, cable, wall, perforation, quartz, colourant, hydrate, autoclave, uniform, atmosphere, reflect, origin, correct, absorption.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
masonry construction — конструкция из каменной кладки;
shale — глинистый сланец, сланцеватая глина;
soft slate — мягкий сланец;
calcium silicate — силикат кальция;
quarried stone — бутовый/рваный камень;
shrinkage — усадка/усушка, усадочная деформация;
steel mould — мульда, (литейная) форма;
tunnel kiln — туннельная печь для обжига/сушки;
extruded brick — кирпич, изготовленный на ленточном прессе;
wall of wires — резательный аппарат, отрезной станок;
perforation — перфорирование, выдавливание;
crushed flint — дроблённая галька, кремень;
mineral colourant— минеральный краситель;
firing temperature — температура обжига;
surface texture — текстура/фактура поверхности;
thermal and moisture movement — характеристики (кирпича) при
воздействии температур и влаги.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Brick Part One
A brick is a block of ceramic material used in masonry construc- - tion with various kinds of mortar to stick the items together. Brick has been widely used for building purposes throughout human history, and is being largely used nowadays.
[Bricks may be made from clay, shale, soft slate, calcium silicate, concrete, or shaped from quarried stone.]0 Clay is the most common material, with modern clay bricks formed in one of three processes — soft mud, dry press, or extruded.
The soft mud method is the most common, as it is the most economical. [It starts with the raw clay in a mix with 25-30% sand to reduce shrinkage.]0 The clay is first ground and mixed with water to the desired consistency. The clay is then pressed into steel moulds with a hydraulic press. The shaped clay is then fired ('burned'') at 900- 1000°C to achieve strength.
In modem brickwork this is usually done in a fired tunnel kiln, in which the bricks move slowly through the kiln on conveyors, rails, or kiln cars. The bricks often are added lime, ash, and organic matter to speed the burning.
The dry press method is similar to mud brick but starts with a much thicker clay mix, so it forms more accurate, sharper-edged bricks. The greater force in pressing and the longer burn make this method more expensive.
With extruded bricks the clay is mixed with 10-15% water (stiff extrusion) or 20-25% water (soft extrusion). [This is forced through a die to create a long cable of material of the proper width and depth.]0 The material is then cut into bricks of the desired length by a wall of wires. [Most structural bricks are made by this method, as hard dense bricks result, and holes or other perforations can be produced by the die.]° The introduction of holes reduces the needed volume of clay through the whole process, with the reduction in cost as well. The bricks are lighter and easier to handle, and have thermal properties different from solid bricks. The cut bricks are hardened by drying for between 20 and 40 hours at 50-150°C before being fired. (1 700 п.зн.)
Part Two
[The raw materials for calcium silicate bricks include lime mixed with quartz, crushed flint or crushed siliceous rock together with mineral colourants.]° The materials are mixed and left until the lime is completely hydrated. The mixture is then pressed into moulds and cured in an autoclave* for two or three hours to speed the chemical hardening. The finished bricks are very accurate and uniform and can be made in a variety of colours, white is common.
[The fired colour of clay bricks is influenced by the chemical and mineral content of raw materials, the firing temperature, and the atmosphere in the kiln.]° Calcium silicate bricks have a wider range of shades and colours, depending on the colourants used. The names of bricks may reflect their origin and colour.
Bricks may also be classified as solid (less than 25% perforations by volume on one of the longer faces), perforated (containing a pattern of small holes through the brick removing no more than 25% of the volume), cellular (containing a pattern of holes removing more than 20% of the volume, but closed on one face), or hollow (containing a pattern of large holes removing more than 25% of the brick's volume).
[The correct brick for a job can be picked from a choice of colour, surface texture, density, weight, absorption and pore structure, thermal characteristics, thermal and moisture movement, and fire resistance.]0
* Autoclave is a strong, heated container used for chemical reactions and other processes using high pressures and temperatures. (1 300 п.зн.)
4. Переведите предложения письменно.
Ответьте на вопросы.
What are bricks composed of?
What processes of brick formation do you know?
Which of the production methods is the most economical?
How are extruded bricks made?
How is calcium silicate bricks processed?
What does the colour of the bricks depend on?
How can be bricks classified due to the perforations produced?
Закончите предложения.
Bricks may be made from...
The soft mud method is...
The dry press method is similar to ...
Extruded bricks are made from...
The raw materials for calcium silicate bricks include...
The fired colour of clay bricks is influenced by...
Bricks may also be classified as...
Ответьте на вопрос:
What should be taken into consideration while selecting a necessary type of bricks for construction?
Переведите текст устно. То sum up
Modern building is a huge industry, and the use of building materials is typically segmented into specific trades, such as carpentry, plumbing, roofing, insulation work, etc. The manufacture of building materials as well as production and harvesting of raw materials for building purposes is on a world large scale (often being a primary governmental and trade key point between nations). Environmental concerns are becoming a major world topic considering the availability and sustainability of certain materials, and the extraction of such large quantities needed for the human habitat. (500 п.зн.)
Передайте содержание текста в трёх предложениях.
♦ Подготовьте презентацию по теме 'Building Materials'.
Словарь к Разделу IV
absorption — абсорбция, поглощение;
additive — добавка, присадка, примесь;
aggregate — агрегат, заполнитель;
amorphous solid — аморфное твёрдое тело;
anhydrous powder substance — безводное порошкообразное вещество;
aqueduct — акведук, мост-водовод;
artificial — искусственный, синтетический;
availability — наличие, доступность, возможность использования;
• bar — брус, балка;
beam — балка, брус, прогон;
bedrock deposit — месторождение/залежь материковой породы;
belt conveyor — ленточный конвейер/транспортёр;
to bind (bound) — связываться, схватываться, затвердевать;
binder — связующее вещество;
blast furnace slag — печной доменный шлак;
blasting method — метод наружных зарядов;
bonding — соединение, сцепление;
bottom ash — шлак, зольный остаток;
breakwater — волнорез, мол;
brick — кирпич;
brittle — ломкий, хрупкий;
bubble — пузырёк (воздуха или газа);
bulletproof— пуленепробиваемый;
cable — зд. лента;
calcium silicate — силикат кальция;
capital-intensive — капиталоёмкий, дорогостоящий;
carbon steel — углеродистая сталь;
carpentry — плотничье дело;
to cast — лить, отливать;
to categorize — распределять по категориям, классифицировать;
cell—ячейка;
cellular material — ячеистый материал;
cementitious — цементирующий, вяжущий;
charcoal — древесный уголь;
chemical admixture — химическая добавка;
chemical composition — химический состав;
clay — глина;
cleavable — колкий, легко раскалываемый;
clinker — клинкер, спекшийся материал;
coarse — крупный, крупнозернистый;
colourant— краситель, красящее вещество;
to come along — сопровождать, идти;
commonly — обычно, как правило;
competent — походящий, достаточный;
composite material — композиционный материал, композит;
compressive stress — напряжение на сжатие;
concern — проблема, вопрос, требующий решения;
concrete delivery truck — машина для доставки бетона;
to conserve resources — сберегать ресурсы;
consistency — консистенция, степень плотности;
construction purpose — цель строительства;
content — содержание, состав;
to convert — трансформировать, превращать;
core — ядро, стержень;
corrosion — коррозия, окисление, ржавчина;
to counteract— противодействовать;
to crush — давить, дробить, толочь;
crushed flint — дроблённая галька, кремень;
to cure — отверждаться;
curtain wall — ненесущая (наружная) стена;
to deliver — доставлять, развозить;
demolition — разборка, снос (здания);
die — штамп, матрица;
to dismantle — разбирать, демонтировать;
to distribute — распределять, рассредоточивать;
dome— величественное здание;
dominant— господствующий, основной, доминирующий;
to dry — сушить, высушивать;
dry press — пресс полусухого прессования;
earth-moving equipment — оборудование для землеройных работ;
to eliminate — устранять, исключать;
emittance — излучательная способность;
to employ — употреблять, применять, использовать;
to entrain — захватывать (воздух, жидкость);
eventually — в конечном счёте, в итоге;
to expand— расширяться, увеличиваться (в размерах);
expensive — дорогой, дорогостоящий;
extender — наполнитель, добавка;
external insulation — внешняя/наружная изоляция;
external surface соvering — облицовка;
to extinguish fire — тушить пожар;
extraction — добывание, извлечение;
to extrude — прессовать, штамповать;
extruded brick — кирпич, изготовленный на ленточном прессе;
extrusion — прессование выдавливанием;
facade — фасад (здания);
fiber — волокно;
fibrous plant — волокнистое растение;
filler— наполнитель (минеральный порошок);
film — пленка, тонкий слой;
fine aggregate — мелкий заполнитель;
finish — отделка, отделочное покрытие;
fire resistance — огнестойкость;
firing temperature — температура обжига;
flexible — гибкий, податливый, эластичный;
flint— кремень, тонкозернистая кремнистая порода;
to fluctuate — быть неустойчивым, меняться, колебаться;
fly ash — летучая зола, зольная пыль;
frame — рама, каркас;
framework — рамная конструкция, каркас
functional extension — функциональный ряд;
fusion — плавка, плавление;
to gain — добывать, зарабатывать, добиваться;
gaseous — газообразный, газовый;
glass transition temperature — температура стеклования;
glass wool — стекловата;
gloss — глянец, лоск;
to glue — клеить, приклеивать;
granular solid — зернистое, гранулированное вещество;
to grind (ground) — измельчать, молоть, дробить, растирать;
harbour— гавань, порт;
hardening — отвердевание, затвердевание;
to harvest — собирать урожай, делать заготовки;
hematite — гематит, красный железняк;
hiding pigment — пигмент с хорошей укрывистостыо;
high-strength low alloy steel — высокопрочная низколегированная сталь;
hollow — пустой, полый;
horn — рог;
to hydrate — гидратизировать, гидратировать;
hydration — гидратация, гидратирование;
hydraulic render — гидравлический (затвердевающий в воде) нижний слой штукатурки;
to impart adhesion —- придавать свойство прилипания;
imperviousness — непроницаемость, водонепроницаемость;
to improve performance — улучшать характеристики;
improved insulation — улучшенные изоляционные свойства;
industrial setting — промышленная установка;
inert material — инертный (неактивный) материал;
insulator — диэлектрик, изоляционный материал;
interconnected — взаимосвязанный, соединённый;
iron — железо, чёрный металл (железо, сталь, чугун);
ironwork — изделие из железа, металлическая конструкция;
key point — стратегически важный, ключевой пункт, ориентир;
to last — длиться, сохраняться, выдерживать;
layer — слой, пласт, прослойка;
leather — кожа (выделанная);
lime — известь;
liquefiable— плавкий, растворимый, разжижаемый;
load bearing element — несущий элемент (конструкции);
lumber — пиломатериал;
major — более важный, значительный, главный;
malleability — ковкость, тягучесть, податливость;
manganese oxide — оксид марганца;
manufactured aggregate — промышленный/фабричный заполнитель;
marble — мрамор;
masonry cladding — плакирование, обшивка с помощью каменной кладки;
masonry construction — конструкция из каменной кладки;
mass concrete structure — конструкция из монолитного бетона;
mastic — мастичный, вязкий;
to melt — таять, плавиться, растапливаться, растворяться;
metal alloy — металлический сплав;
mineral colourant — минеральный краситель;
mixture— смесь, смешивание;
mortar— известковый, строительный раствор;
network — сеть, сетка;
obtainable — достижимый, доступный;
ochre — охра;
opaque film — непрозрачная плёнка;
to optimize — оптимизировать;
optionally — необязательно, по выбору;
partial replacement — частичная замена;
particulate material — зернистый материал;
paste — паста, мастика, густотёртая краска;
pebble — булыжник, галька, мелкий щебень;
perforation — перфорирование, выдавливание;
perlite — перлит, вулканическое стекло;
petroleum — нефть;
pigment — пигмент, краситель;
plain concrete mix — обычная бетонная смесь;
plaster — штукатурка;
plastic material — пластмасса, пластичный материал;
plumbing — водопроводное дело, слесарные работы;
pollutant — загрязняющее вещество, агент;
роrе — пора;
to pour — лить, наливать;
pozzolana — пуццолан, вулканический туф;
predictable — предвидимый, прогнозируемый;
predominant material— преобладающий материал;
prestressed — предварительно напряжённый;
to process — подвергать процессу, обрабатывать;
profile — сортовой прокат, стальной профиль;
pros and cons — (лат.) доводы за и против;
pumice — пемза, пористый вулканический материал;
quarried stone — бутовый/рваный камень;
quarry — каменоломня, открытая разработка, карьер;
quartz — кварц (эталонный твёрдый минерал);
quenched steel — закалённая (при быстром охлаждении) сталь;
raw material prices — цены на сырьё;
readily — легко, без труда;
recycled — повторно используемый;
to reduce weight — уменьшать вес;
to refine — очищать (от примесей);
to reinforce — укреплять, усиливать, армировать;
to release toxic fumes — испускать токсичный дым/испарения;
render — трёхслойная штукатурка;
resistance to smth — сопротивляемость чему-либо;
roofing — кровельные работы;
rough — грубый, неровный;
to sag down — провисать, прогибаться; sand — песок, формовочная смесь;
to sandwich — помещать посередине, вставлять, втискивать;
sedimentary — осадочный;
shale — глинистый сланец, сланцеватая глина;
shrinkage — усадка/усушка, усадочная деформация;
silicate — силикат, соль кремниевой кислоты;
siliceous rock — горная порода, содержащая кремний;
silicon — кремний;
similar — подобный, схожий;
slab — плита, панель перекрытия, пол (бетонный); slag — шлак;
soft mud — пластичная керамическая масса;
soft slate — мягкий сланец;
to soften — размягчать, смягчать;
to solidify — твердеть, затвердевать, густеть, застывать;
source — источник, начало, происхождение;
to span (over) — охватывать, простираться, перекрывать;
specialty aggregate — специализированный заполнитель;
steel mould — мульда, (литейная) форма;
to stick (stuck) — липнуть, приклеиваться;
stove — печь, сушильная печь, сушильная камера;
structural building material — конструктивный строительный материал;
structural framework — несущий каркас, каркасная конструкция;
structural integrity — конструктивная целостность;
stucco — наружная штукатурка, штукатурный раствор для наружных работ;
to be subjected to — подвергаться (воздействию, влиянию);
suitable — подходящий, соответствующий, годный;
superior — лучший, более совершенный, превосходящий;
surface texture — текстура/фактура поверхности;
survival — выживаемость, выживание, жизнеспособность;
to tailor — приспосабливать, подгонять, пригонять;
talc — тальк;
tempered steel — закалённая/отпущенная сталь;
tendon — преднапряжённая арматура, арматурная прядь/пучок;
tensile stress — растягивающее напряжение;
thermal and moisture movement — характеристики (кирпича) при воздействии температур и влаги;
thermal expansion — тепловое расширение;
thermosetting polymer — термореактивный полимер;
to thicken — сгущать, наращивать (толщину), загустевать;
toughness — вязкость, ударная вязкость, тягучесть, плотность;
trade — занятие, ремесло, профессия;
transparent — прозрачный, просвечивающий, светопроницаемый;
transportation ease — лёгкость/простота транспортировки;
to trap bubbles — удерживать/задерживать пузырьки;
to treat — подвергать обработке, обрабатывать, очищать;
tunnel kiln — туннельная печь для обжига/сушки;
twig — прут;
uniform — единообразный, одинаковый;
uniform properties — неизменные/постоянные свойства;
variety — разнообразие, ряд, множество;
to vary proportions — менять пропорции;
vermiculite — вермикулит (минерал, используемый в составе композитных строительных материалов);
versatility — универсальность, гибкость;
vice versa — (лат.) наоборот, обратно, противоположно;
void — пустота, пора, полость, карман;
wall of wires — резательный аппарат, отрезной станок;
to weaken — ослаблять обеднять, разупрочнять;
to weld — сваривать(ся), сцепляться;
widespread use — широкое использование.
Раздел V
ENERGY AND ITS SOURCES TEXT A
Переведите интернациональные слова.
dilemma, deficiency, generator, rotation, hydropower, biomass, focus, heliostat, utilize, parabolic, absorb, hydroelectricity, extraction, productive, comfortable, engine, mechanical, transportation, uranium.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
to generate energy -— вырабатывать/производить энергию;
renewable — восстановимый, возобновляемый;
fossil fuel — ископаемое топливо;
combustion — горение, возгорание, сжигание;
to run out— кончаться, иссякать;
to expel— исключать, изгонять;
by-product— побочный/промежуточный продукт;
replenishment — повторное наполнение, пополнение;
steam — пар;
to harness water — обуздывать/покорять воду;
to channel water— направлять в русло, проводить через канал.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Types of Energy
| [Modern civilization is put in dilemma of possible energy lack and everyday necessity to satisfy growing material and cultural needs.]0 Energy is generated from both non-renewable and renewable sources.
[Non-renewable energy includes three major types of fossil fuels — coal, oil and natural gas — deposited in the earth over millions of years. Since fossil fuels require a simple combustion to produce power, they are rather cheap. However, fossil fuels are consumed much more rapidly than they can be replaced. It means, one day we shall run out of fuel reserves.]0
Wood once expelled by coal and gas has been the solitary source of energy for centuries. Nowadays both gas and oil are closely connected with technological progress and standards of living.
[Uranium is one of the most perspective sources of energy for it doesn't emit CO2 causing global warming and climate changes.]0 Nuclear power generation has by-product wastes: tremendous emission of radioactive products and heat.
[Renewable sources of energy are very attractive because of their quick replenishment.]0 They are five: hydropower, solar, wind, bio- mass, and geothermal* energy.
The most popular way to utilize solar energy is thermal systems. Large centralized solar plants are known as 'power towers' with small rotating mirrors the top of towers to focus heat and turn water into steam for industrial purposes.
Hydropower generates electricity with no GHG effect. Since the supply of hydropower is water, hydropower stations are to be close to a water resource.
Mechanical energy depends on directing, harnessing or channeling water.
[To make daily life comfortable, productive and pleasant highly developed societies consume vast amounts of energy for heating, cooking, transportation, manufacturing, and entertainment.]0 The choices of how to make and use energy impacts greatly the environ-
ment and human lives.
means earth and 'thermal' is concerned with or caused by heat. (1 700 п.зн.)
4. Определите части речи, обращая внимание на суффиксы. Переведите.
generate, generated, generating, generation, generative, generator;
consume, consumable, consumer, consumership, consumption, consumptive (demand);
produce, producer, producible, product, production, productive, productiveness, productivity;
origin, original, originality, originally, originate, originating, origination, originative, originator;
concentrate, concentrated, concentration, concentrative, concentrator, concentric, concentrical, concentrically, concentricity;
absorb, absorbability, absorbable, absorbency, absorbent, absorber, absorbing;
combustion, comburent, combustible*, combustibility, combus- tibleness;
develop, developable, developer, development, developmental;
feasibility, (in)feasible, feasibleness, feasibly.
*A word combustible (from Lat. comburere) means:
capable of taking fire and burning, inflammable;
easily excited, quick.
Расположите предложения согласно логике изложения.
1. People have practically limited supplies of coal, oil, and natural gas which cannot be replaced. 2. It is a good idea to use the power of wind and ocean tides to generate electricity. 3. On the whole, there are many ways to produce energy without using up natural non-renewable resources and damaging the environment. 4. Firstly, we should make more use of solar power. 5. It is high time to start doing as much as possible to protect the Earth. 6. The sooner we initiate wide usage of alternative energy sources, the better. 7. If we fitted solar panels to the roofs of our houses, we would have a very cheap way of heating water for domestic purposes.
Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на сказуемое.
The supplies of coal, natural gas and oil are known to have been limited.
One of the simplest and most economical ways to utilize solar energy is solar thermal systems.
Nuclear energy is considered to be the key energy problem solution.
There should be certain alternative power sources to be discovered as actual solutions of energy shortage problem.
Since the supply of hydropower is water, hydroelectric power stations are to be close to natural water bodies.
Hydropower is reputed to generate electricity with no greenhouse effect.
Дайте определение терминов.
(A) renewable resources; (В) non-renewable resources; (С) replenishment; (D) by-product; (E) solitary source
Переведите письменно.
Provided, it is perfectly premeditated and maintained, a hydroelectric power source is comparatively cheap, safe, and reliable, being green oriented, with low escape risk, and demanding no fuel at all. As an alternative it has been proved much more perspective than both nuclear and wind power. Routine monitoring is required to anticipate virtual catastrophes and undertake all necessary remedial actions before real failure occurs. (370 п.зн.)
TEXT В
Переведите интернациональные слова.
geothermal, migration, laboratory, globe, alternative, generation, accumulate, nuclear, production, uranium, accident, turbine, control, statistics, radioactivity, actual, chance, serious,, potential, opposition, advocate, safe, percentage.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
to face a challenge — столкнуться со сложной задачей/проблемой;
to assess — оценивать, определять;
benefit — выгода, польза, преимущество;
alternative sources of energy — альтернативные источники энергии;
devastating potential out of control -— неконтролируемый разрушительный потенциал; fission — деление, расщепление;
harmful gases emission — выделение вредных газов;
greenhouse effect — парниковый эффект;
disadvantage — неудобство, помеха, вред;
storage — хранение;
reprocessing — переработка, вторичная обработка;
to accumulate radioactive wastes — накапливать радиоактивные
отходы;
urgent — срочный, безотлагательный, необходимый;
feasible — реальный, выполнимый, осуществимый.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
The idea to get energy from sunlight, wind, rain, geothermal water or ocean tides has migrated from laboratories into every house, especially in the countries faced with multiple energy-related challenges of today. To assess the benefits of alternative sources of energy it is necessary to know what they are alternative to.
About 17% of the world's electricity is generated at nuclear power stations, the percentage varying from country to country. After some accidents a lot of people strongly oppose nuclear energy use because of its colossal devastating potential out of control.
Any nuclear power plant generates electricity through the fission followed by a release of huge amount of heat, actually generated by a particular quantity of nuclear fuel, which is million times larger than the heat generated by burning the same amount of coal or oil. It is the water steam which makes turbines spin and generate electricity. The final step is identical at all power plants. The only difference is fuel to be used: coal, oil, or something else.
The obvious benefit of nuclear energy is the low cost of produced electricity. Statistics says the average production cost is 1.87% per kWh*.
The advocates of nuclear energy reiterate there is no harmful gases emission causing greenhouse effect. Hence, nuclear energy is much cleaner and eco-friendlier than coal, oil, or gas.
That the nuclear stations are extremely complicated systems and require a huge amount of money is one of disadvantages. Another highly debatable issue is long-term programs for storage or reprocessing. Nobody wants to accumulate radioactive wastes. Since the majority of available storage areas are almost filled, the question where to store dangerous wastes is urgent
Despite the fact that nuclear power is the most economically feasible, people still have to work hard to make it really safe. However, it
there is a chance to find alternative sources of energy with lesser | risks, it is our duty to find and use them wherever it is possible.
*kW is a written abbreviation of kilowatt; kWh stands for kilowatt hour. (1 750 п.зн.)
4. Соедините части, чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
Greenhouse (A) is the process of splitting an atom to produce effect large amounts of energy.
Fission (B) is an amount of gas or other substances that a
machine or factory produces and sends into the air.
Energy (C) is the gradual warming of the air surrounding
the Earth as a result of heat being trapped by pollution.
To be alter- (D) is the amount of something that a factory, com- native pany, machine etc. can produce or deal with.
Emission (E) is a substance such as coal, gas or oil that can be
burnt to produce heat of energy.
Capacity (F) is the power that is used to provide heat, drive
machines etc.
Fuel (G) is a layer of a mineral, metal, coal etc. that is
left in soil or rocks through a natural process.
Deposit (H) is the act of keeping or putting something in a
special place while it is not being used.
Reprocess (I) is a gas, especially carbon dioxide or methane
that is thought to trap heat above the Earth and cause the greenhouse effect.
Storage (G) is something that can be used instead of another
one.
GHG (K) is to treat a waste substance so that it can be
used again.
5. Закончите предложения.
Any nuclear power plant generates...
To assess the benefits of alternative sources of energy...
A lot of people strongly oppose...
The idea to get energy from...
The obvious advantages of nuclear energy are...
As for certain disadvantages of...
Nowadays our duty is...
Восстановите предложения по фрагментам.
... multiple energy-related challenges of today...
...the world's electricity production percentage...
...both advocate and strongly oppose ...
...no emission of harmful gases...
...dangerous radioactive wastes...
...the most economically feasible sources of energy...
...if there is a chance to find...
Переведите, обращая внимание на порядок слов.
The water steam makes the huge turbine spin and generate electricity. It is the water steam which makes the huge turbine spin and generate electricity.
The only difference is coal and oil to be used. The difference is only coal and oil to be used.
People still have to work hard to make life really safe. To make life reallу safe people still have to work hard. People have to work hard to make life still.
Сформулируйте главную идею текста и дайте ему название.
Прокомментируйте.
'Europeans had lived in the midst of vast forests throughout the earlier medieval centuries. After 1250 AD they became so skilled at deforesta- tion that by 1500 AD they were running short of wood for healing and cooking... By 1500 AD Europe was on the edge of a fuel arid nutritional* disaster, which was saved in the 16th century only by the burning of soft coal and the cultivation of potatoes and maize'.(Norman F. Cantor, historian)
*Nutrition is the process of giving or getting the right kind of food for good health and growth. (440 п.зн.)
TEXT С
1. Переведите интернациональные слова.
tradition, motivation, aspect, emission, effect, flora, fauna, atom, destructive, solar, percent, panel, absorb, silicon, constant, separate, kinetic, automobile, generator, atmosphere, resource.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
to diminish — убывать, уменьшаться;
devastating — опустошительный, разрушительный;
consequences — последствия;
ozone depletion — истончение/уменьшение озонового слоя;
irreversible — необратимый;
destructive effect— разрушительный эффект/влияние;
to implement — выполнять, осуществлять;
flora and fauna — флора и фауна;
affordable — возможный, допустимый, по средствам;
combustion — горение, возгорание, сжигание;
to suffer — страдать, испытывать, претерпевать;
to adapt— приспосабливать, прилаживать.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания. Alternative Energy Sources
[A traditional fuel problem as a great development impulse is that natural resources of fossil fuels are rapidly diminishing.]0
Another aspect is the devastating effect on the environment. [Humanity has already faced serious negative consequences of thoughtless use of non-renewable natural resources: global warming and ozone depletion caused by the vast emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) as well as air, water and soil pollution are only several examples of irreversible changes and destructive environmental effects.]0
People seem to have realized their mistakes, new sources of energy being developed and implemented around the world. [Modern alternative energy sources are renewable, eco-friendly, and safe not only for humans but for flora and fauna as well.]0
Solar power is captured by solar panels which change sunlight into electrical energy. Being renewable the very energy costs nothing but isn't constant. It can be reaped only during daytime and only fifty percent of it can be converted into electricity.
Wind is perfect because of its kinetic energy. Wind energy harvesters work easily and can be set up anywhere. The source of energy is
clean and renewable with no greenhouse gas contribution but comparatively slow.
Water has been generating energy for ages. Hydroelectricity generated by damming rivers and is quite affordable.
Hydrogen is eco-friendly and much safer than petrol. Electric current is passed through water to separate hydrogen from oxygen. The resulting gas (hydrogen) is then stored in pressurized tanks.
Geothermal energy is produced by thermal water heated naturally under the earth to generate steam which runs turbines.
Bio-fuel is produced from plants (ethanol) or animals (methane from animal excrement). The process used for obtaining bio-fuel is usually combustion. It is completely renewable.
[The best way to help our suffering planet is to adapt to the alternative energy sources, they being limitless and ecologically clean.]0
(1 660 п.зн.)
4. Выберите значение, в котором данное слово употреблено в тексте.
to realize
а) представлять себе; b) понимать; с) реализовать;
осуществлять; е) получать прибыль.
face
а) лицо; b) внешний вид; с) циферблат; d) облицовка; е) сталкиваться (с проблемой). emission
а) выделение (тепла); b) излучение (света); с) испускание, распространение (запаха, лучей); d) эмиссия (денежной массы);
опубликование.
effect
а) результат, следствие;b) цель, намерение; с) действие, влияb;
эффект, впечатление; е) осуществлятиf) производительность, полезный эффект; g) заключать, оформлять сделку.
development
а) развитие, рост, совершенствованиe; b) изложение, раскрытие; с) результат (развития); е) обрабатываемый участок земли;
предприятие; f) застройка; g) мелиорация.
potential
а) мощный; b) возможный, скрытый, потенциальный; с) потенциал; d) потенциальная возможность; е) напряжение.
Из приведенных слов составьте предложения.
non-renewable, include, types, fossil fuels, coal, of, energy, oil, and, natural gas.
to produce, rivers, and, hydro-electricity, waterfalls, can, darns,
be used.
renewable, two, main, of energy, categories, and, can, sources, be split into, non-renewable.
nuclear energy, does not put, carbon dioxide, into, the best one, is, because, it, the atmosphere.
old times, the wind, since, to have, controlled, energy, people, effectively, are known.
to generate, fossil fuels, easy, are, relatively cheap, and, electricity.
solar, efficient, very, quickly, economic, power, are, technologies, and, developed.
the most, solar, popular, renewable, sources, of energy, bio- mass, popular, are, hydropower/water, and geothermal systems, wind.
sunlight, don't decrease, wind, are, replenished, and, and, geothermal heat, naturally, rain.
Переведите письменно.
Having considered significant air pollution, irreversible climate changes, considerable deforestation, flooding in river systems, etc. and especially unaffordable prices of non-renewable energy, we have to look at alternative energy sources more carefully.
Global warming and ozone depletion caused by the huge emissions of GHG as well as air, water and soil pollution are only several examples of permanent changes and negative ecological effects.
People seem to have realized their actual mistakes, new ecological sources of energy being developed and implemented around the world these days.
Modern alternative energy sources are proved to be renewable, eco-friendly, and harmless not only for humans but biota as well.
The best way to help our suffering world is to adapt to the alternative energy sources, they being limitless and ecologically safe.
Дополните предложения подходящим вариантом.
Humanity has already faced ...
the challenge of alternative energy sources development.
serious negative consequences of thoughtless use of natural non-renewable resources.
only several examples of irreversible changes in the environment.
People have realized ...
the necessity to adapt to the alternative energy sources, they being limitless and ecological.
the natural resources of fossil fuels are quickly diminishing.
their great mistakes in careless treatment of natural nonrenewable resources.
Modern alternative energy sources ...
are affordable.
are renewable, cheap and harmless not only for humans but for flora and fauna as well.
have destructive effects on the environment.
Предложите все «за» и «против» (pros and cons) по вопросу использования альтернативной энергии.
Information-to-Swallow Milestones in Energy Application
1861 — August Mouchout invented the first steam engine powered by the Sun.
1839 — William Grove invented the first hydrogen fuel cell.
1888 — Charles Brush built the first windmill to generate electricity.
1892 — The first world's heating system was built in Idaho, where geothermal energy was used to heat the buildings.
1904 — Larderello Fields (Italy) built the first plant to convert geothermal heat into energy.
1908 — Henry Ford built the first mass-produced vehicle Ford T Model running on ethanol.
1930 — The first sludge digestion technology was developed in Russia, biogas having been burned to generate heat energy and electricity.
1936 — The world's largest Hoover Dam was built in Colorado.
1953 — The first solar cell generating electricity was made at Bell Laboratories.
1958 — The first solar powered satellite was launched in the USA.
1981-1990 — Over 17,000 wind machines were built in California.
2006 — The largest offshore wind turbine Repower generating 5 megawatt of electricity was installed in the North Sea.
2006 — Geothermal power plant was built in Alaska to generate electricity from geothermal waters with the record low temperature of 57° C.
2007 — Ford Fusion Hydrogen 999 reached the record speed of over 207mph.
— The two-seat sun-powered airplane Sky Spark reached the record speed of 250km/h.
— 1,100 houses in Holland get electricity after the biomass (dairy manure) special treatment.
— A patent for thermal pumps using the heat from municipal wastewater for heating the sewage pumping station is obtained at the Lyubertsy Wastewater Treatment Plant.
(1 340 п.зн.)
❖ Подготовьте презентацию наиболее важных событий в области использования энергии в России и за рубежом с учётом новейших строительных технологий.
Словарь к Разделу V
accident — несчастный случай, авария;
to accumulate radioactive wastes — накапливать радиоактивные отходы;
to adapt — приспосабливать, прилаживать;
advocate — защитник, сторонник;
affordable — возможный, допустимый, по средствам;
alternative sources of energy — альтернативные источники энергии;
to assess — оценивать, определять;
attractive — привлекательный, заманчивый;
average — средний, нормальный, обычный;
benefit — выгода, польза, преимущество;
by-product — побочный/промежуточный продукт;
to capture — захватывать;
to channel water — направлять в русло, проводить через канал;
cheap — дешёвый, недорогой;
combustion — горение, возгорание, сжигание;
comparatively — сравнительно, относительно;
complicated system — сложная, запутанная система;
consequences — последствия;
constant — постоянный, неизменный;
to consume — тратить, расходовать, потреблять;
contribution — вклад, ценные достижения;
dairy manure — навоз с молочной фермы;
damming river — река, перегороженная плотиной;
to deposit — отлагаться, осаждаться;
destructive — разрушительный, пагубный, деструктивный;
destructive effect — разрушительный эффект/влияние;
devastating potential out of control — неконтролируемый разрушительный потенциал;
development impulse — толчок для развития;
dilemma — дилемма, необходимость выбора;
to diminish — убывать, уменьшаться;
disadvantage —- неудобство, помеха, вред;
eco-friendly — безвредный для окружающей среды;
electric current — электрический ток;
to emit — испускать, выделять;
to expel — исключать;
to face a challenge — столкнуться со сложной задачей/проблемой;
feasible — реальный, выполнимый, осуществимый;
fission — деление, расщепление;
flora and fauna — флора и фауна;
to focus — собирать, сосредоточивать;
fossil fuel — ископаемое топливо;
to generate energy — вырабатывать/производить энергию;
geothermal water — вода геотермальных источников;
global warming — глобальное потепление; greenhouse effect — парниковый эффект;
harmful gases emission — выделение вредных газов;
to harness water— обуздывать/покорять воду;
to implement — выполнять, осуществлять;
irreversible — необратимый;
lack — недостаток, нужда, отсутствие;
to launch — запускать (спутник, ракету);
limitless — безграничный, бесконечный;
mirror — зеркало;
negative — отрицательный, негативный;
nuclear power station — атомная электростанция;
ocean tides — океанские приливы и отливы;
offshore — находящийся в море, на некотором расстоянии от берега;
to oppose — быть против, возражать;
ozone depletion — истончение/уменьшение озонового слоя;
petrol — бензин, газолин, моторное топливо, нефть;
pressurized tank — резервуар, находящийся под давлением;
to reach — достигать, доходить;
to reap — собирать урожай, пожинать плоды;
to reiterate — вновь подтверждать, повторять;
renewable — восстановимый, возобновляемый;
replenishment — повторное наполнение, пополнение;
reprocessing — переработка, вторичная обработка;
to run out— кончаться, иссякать;
safe — безопасный, не связанный с риском;
satellite — сателлит, спутник;
sludge digestion — перегнивание ила;
solitary — единичный, исключительный;
steam — пар;
storage — хранение;
storage area — место хранения;
to suffer — страдать, испытывать, претерпевать;
tremendous — огромный, потрясающий;
uranium — уран;
urgent — срочный, безотлагательный, необходимый;
to utilize — утилизировать, расходовать, употреблять;
vast amount — огромное количество;
wastewater treatment plant — станция водоочистки;
wind energy harvester — ветрогенератор, ветряк;
windmill — ветряная мельница.
Раздел VI
THE BUILDING INFRASTRUCTURE
TEXT A
Переведите интернациональные слова.
automatic, communication, ventilation, conditioning, control, public, address, system, elevator, escalator, security, signal, master, antenna, minimize, intercommunication, telephone, television, transportation.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
power equipment — энергетическое оборудование/оснащение;
closed-circuit television — замкнутая телевизионная система, сис- тема кабельного телевидения;
public address system — система оповещения населения;
security — безопасность, обеспечение безопасности;
alarm — тревога, сигнал тревоги, аварийная сигнализация;
circuit— цепь, схема;
communication system — система связи, система коммуникаций;
remote control system — система дистанционного управления, система телеуправления;
fire automatic detection — автоматизированное обнаружение/ выявление пожара;
conduit — кабельный канал;
fire alarm installation — система пожарной сигнализации;
loudspeaker system — акустическая система;
master antenna — коллективная антенна;
amplifier — усилитель.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
The Building Infrastructure
The universal uses of power equipment, vertical transportation systems such as elevators, escalators, and stairways; telephone, television and closed-circuit television; public address systems; environmental- control systems (heating, ventilating, air-conditioning, lighting, and acoustical systems,); security and alarm systems have led to a huge
quantity of wiring to be installed. (The power, water supply, and waste disposal systems should be also mentioned). [Circuits that transmit information or control other circuits can be classified as communication systems;]0 remote control systems arc technologically feasible as well.
Alarm systems cover security, fire automatic detection and fire alarm. All fire protective signal systems are separated into non-power limited and power-limited.
Required conduits with a wire inside must be foreseen to compose all final connections for telephoning.
Modern constructions provide master antennas and loudspeaker systems in buildings up to 20 storeys high, the amplifiers being often located on the roofs.
[Heating, conditioning, cooling, ventilation, lighting, and sound control are possible all year round, since 1970s all these processes having been computerized to optimize the use and minimize energy consumption wastes.]0 (1 100 п.зн.)
4. Соедините части, чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
Heating (A) is the system of communication that is
used to have a conversation with someone in another place.
Ventilation (B) is a system for making a room or a build
ing warm.
Amplifier (C) is the process to let fresh air into the a
room, building etc.
Cooling (D) is the process by which people exchange
information or express their thoughts and feelings.
Closed circuit tel- (E) is a group of related parts that work to- evision gether as a whole for the process by which
people exchange information.
Lighting (F) is a wire , rod etc. used for receiving radio
and television signals.
7 . Alarm (G) is the system to keep the temperature in a
building, engine, machine etc.
Communication (H) is a system in which cameras send pic
tures to television sets used in buildings to protect them from crime.
Television (I) is a system that makes the air in buildings,
rooms etc colder, or the machine that does it.
Communication (J) is a bell or other signals to warn everyone systems about something bad or dangerous that is already happening.
Consumption (K) is to give illumination to a place.
Air-conditioning (L) is a piece of electrical equipment to make
sound louder giving more information.
Antenna (M) is the amount of used electricity, energy,
oil etc.
Закончите предложения.
The general uses of power equipment and transportation systems have led to ...
Alarm systems cover...
All fire protective signal systems are...
Circuits to spread information or control other circuits are classified...
Modern constructions provide...
Environmental-control systems such as...
Since 1970s...
Восстановите предложения по фрагментам.
...a great number of wiring is to be...
...telephone, television as well as closed-circuit television...
...are classified as communication systems...
...security, fire automatic detection and fire alarm systems...
...empty conduits with a wire inside are to...
...are possible all year round...
...all the processes are programmed in order to...
Переведите, обращая внимание на порядок слов.
My neighbour has installed the alarm system recently.
My neighbour has the alarm system installed recently.
My neighbour installed the alarm system yesterday.
It was yesterday when the alarm system was installed.
It was the alarm system that was installed yesterday.
It was my neighbour who installed the alarm system yesterday.
Кратко перескажите текст. TEXT В
Выпишите интернациональные слова (не менее 12).
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
air conditioning — кондиционирование воздуха; to accomplish — совершать, достигать;
heat-activated equipment — оборудование, активизирующееся в результате нагрева;
dehumidification — осушение (воздуха), удаление избытка влаги;
corner convenience store — магазин шаговой доступности;
air contribution — забор воздуха;
low-rise apartment — малоэтажное жильё;
condominium — квартира в доме-совладении;
vapour compression — сжатие пара;
viable— жизнеспособный;
condenser — холодильник, конденсатор;
expansion device — расширительное (дросселирующее) устройство; evaporator— испаритель, выпариватель; absorption — всасывание, впитывание, абсорбция; refrigerant — хладагент.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
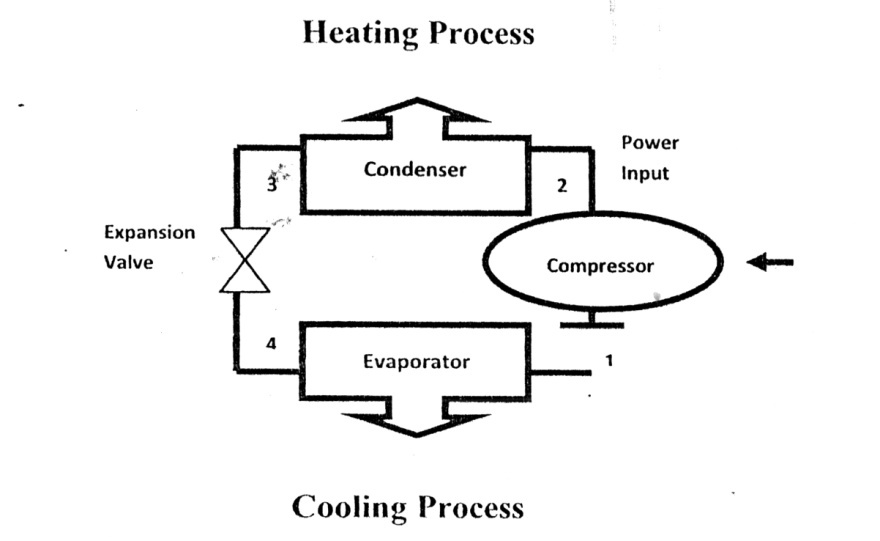
Air Conditioning Systems
[Air conditioning has rapidly grown from a luxury to a standard facility in most residential and commercial buildings and is usually accomplished with the use of mechanical or heat-activated equipment.]0 In most applications, the air conditioner is to provide either cooling or dehumidification to maintain comfort in the building.
Commercial buildings range from large high-rise buildings to the corner convenience stores with a great variety of equipment. [For larger buildings the air conditioning equipment is apart from a total system design including piping, air contribution, and cooling systems.]0
The residential building sector is dominated by single family houses and low-rise apartments or condominiums, the cooling equipment applied in such building coming in standard 'packages'.
[Most systems utilize the vapour compression cycle to produce desired cooling and dehumidification.]0 The first patent on mechanically driven refrigeration system was granted in London in 1834. It was Jacob Perkins who is the invention patentee. The first viable commercial system was produced in 1857 by James Harrison and D. Siebe.
[The four basic components in every compression refrigeration system are; the compressor, condenser. expansion device, and evaporator.]0
There are less common methods to cool buildings: by absorption cycle and evaporative cooling. With the vapour compression cycle, a working fluid (called refrigerant) evaporates and condenses at suitable pressures.
(1250 п.зн.)
Закончите предложения в соответствии с содержанием.
Air conditioning has grown to a standard facility and is usually...
The air conditioner is to make...
The air conditioning equipment includes...
The majority systems use the vapour compression cycle to...
It was Jacob Perkins who obtained.
In 1857 the first acceptable...
The absorption cycle and evaporative cooling...
The refrigerant is...
In every compression refrigeration system there are...
Восстановите предложения по фрагментам.
...from a luxury to a standard facility ...
...in most residential and commercial buildings...
... standard package...
...in London in 1834... ■ ...the first viable commercial system was...
■ ...methods to produce cooling in buildings...
...the vapour compression cycle is to...
...a working fluid called...
...the four basic components...
Переведите предложения, обращая внимание на сказуемое.
Air conditioning has rapidly grown from a luxury to a standard facility in most residential and commercial buildings and is usually accomplished with the use of mechanical or heat-activated equipment.
In most applications, the air conditioner is to provide either cooling or dehumidification to maintain comfort in the building.
The residential building sector is dominated by single family houses and low-rise apartments or condominiums, the cooling equipment applied in such building coming in standard 'packages'.
The first viable commercial system was produced in 1857 by James Harrison and D. Siebe.
There are less popular ways to produce cooling in buildings: the absorption cycle and evaporative cooling.
Переведите предложения, определив группу подлежащего.
Commercial buildings range from large high-rise office buildings to the corner storehouses with a great variety of equipment.
Most systems utilize the vapour compression cycle to produce the desired cooling and dehumidification.
The first patent for mechanically driven refrigeration system was granted to Jacob Perkins in London in 1834.
With the vapour compression cycle, a working fluid, which is called the refrigerant, evaporates and condenses at suitable pressures.
The four basic components in every compression refrigeration system are the compressor, condenser, expansion device, and evaporator.
Определите части речи выделенных слов и перефразируйте предложения.
1. Located at the end of the main the vertical pipe drips condensate into return piping. 2. The main function of windows is to give light and ventilation. 3. A construction project is a complex net of con
tracts. 4. A new shopping complex with a modern split system is re- i ported to be building here. 5. When we heat water, it turns into steam.
Concrete is a poor conductor of heat; besides, it doesn't catch fire.
Being fueled by gas, wood, oil, or coal, boilers fire automatically.
Air elimination from the piping and radiators is a must for steam systems to work properly. 9. This material is highly popular because of its light weight and relatively low cost.
Опишите схему.
10 Предельно кратко и информативно расскажите:
о системах охлаждения;
хладагентах;
процессе охлаждения.
11 Переведите и используйте выделенные слова в своих предложениях.
This expert is a patentee for some well-known inventions. They train as civil engineers under a famous professor in this field.
New trainees will start next week.
A trainer is a person who trains people or animals for sport, work, etc, and a trainee is a person who is trained for a job.
to examine, examiner, examinee;
to employ, employer, employee;
to interview, interviewer, interviewee;
to oblige, obligor, obligee.
TEXT С
Переведите интернациональные слова.
absorb, circulate, condenser, contact, expansion, effect, energy, federal, international, regulations, standard, identify, limit, production, thermal, toxicity, toxic, ethane, methane, series.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
heat exchanger — теплообменник, радиатор отопления;
to reject — отвергать, отклонять;
refrigerant— холодильный агент, хладагент;
medium — способ, средство, среда;
residential-sized equipment— размер оборудования для жилых зданий;
chiller — охладитель, холодильная установка;
heat exchanger — теплообменник;
capacity — вместимость, возможность, мощность, производительность;
federal regulations — федеральные постановления/акты;
international agreements — международные соглашения;
restriction — ограничение, запрет;
toxicity — токсичность, ядовитость;
flammability — воспламеняемость;
airborne — переносимый по воздуху, воздушный;
exposure — подверженность воздействию.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
[The condenser is a heat exchanger used to reject heat from the refrigerant to a cooling medium.]0 The refrigerant enters the condenser and usually leaves it as a sub-cooled liquid. Typical cooling mediums used in condensers are air and water. Most residential-sized equipment uses air, while many larger chillers use water.
[The refrigerant is at a temperature below that of the medium (air or water) to be cooled. The refrigerant travels through a heat exchanger called the evaporator.]0 It absorbs energy from the air or water circulated through the evaporator. It is a direct expansion system if air is circulated through the evaporator. If water is circulated through
the evaporator, it is called a chiller. In either case the refrigerant does not make direct contact with air or water.
The kW of thermal cooling capacity produced by the air conditioner must not be confused with the amount of electrical power (also expressed in kW) required to produce the cooling effect.
Many of the refrigerants are nontoxic and nonflammable. However, recent federal regulations and international agreements have placed strong restrictions on the production and use of CFCs* and HCFCs**. It is HFCs*** that are now being used instead of them.
ASHRAE**** has a standard numbering system to identify refrigerants. Most of them are in the methane and ethane series. ASHRAE groups refrigerants by their toxicity and flammability. Toxicity is based on the upper safety limit for airborne exposure:
Group A is nonflammable and less toxic.
Group В is flammable and toxic.
*CFCs — chlorofluorocarbons are chemicals widely used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pumps. They deplete the ozone layer, and an International agreement to reduce their use was reached in the Montreal Protocol in 1987.
** HCFCs — hydrochlorofluorocarbons are enabling the phase-out of CFCs. They are energy-efficient, low-in-toxicity, cost effective and can be used safely.
***HFCs — hydrofluorocarbons are any of a class of partly chlorinated and flu- orinated hydrocarbons used as an alternative to chlorofluorocarbons in foam production, refrigeration, and other processes.
***ASHRAE— the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air- conditioning Engineers. (1 900 п.зн.)
4. Соедините части АВ, чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
А.
The condenser is a heat exchanger used to...
Typical cooling mediums in condensers...
If air is circulated through the evaporator...
If water is circulated through the evaporator...
5. The kW of thermal cooling capacity must not...
6. Toxicity is based...
7. Recent federal regulations have placed...
B.
...are air and water.
...reject heat from the refrigerant to a cooling medium.
...be confused with the electrical power amount to produce the cooling effect.
...it is called a chiller.
...restrictions on the production and use of CFCs and HCFCs.
...on the upper safety limit for airborne exposure
...it is a direct expansion system.
Ответьте на вопросы.
What is a condenser?
What is an evaporator?
What is a direct expansion system?
What is called a chiller?
What is toxicity based on?
Из приведенных слов и словосочетаний составьте предложения.
■come, unitary and portable AC systems, room air conditioners, in two forms;
not only to, the refrigerant works, cool, but, also, dehumidify it, in the room, the air;
■air conditioning technologies, innovation, in, continues,and,im- proving, indoor air quality, emphasizes on;
■a wet sponge, to draw, an evaporative cooler,is,outer air, through, soaked, with water;
for venting, portable, air conditioners, all refrigerated type, re- quire, exhaust hoses.
7. Переведите письменно.
In either case the refrigerant does not come into direct contact with air or water.
The kW of thermal cooling capacity must not confused with the amount of electrical power (also expressed in kW) required to produce the cooling effect.
Recent federal regulations and international agreements have placed strong restrictions on the production and use CFCs and HCFCs; it is HFCs that are being used instead of CFCs and HCFCs.
Дайте тексту название.
Письменно составьте аннотацию к тексту. TEXT D
Выпишите интернациональные слова (не менее 12).
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
split system — раздельная система отопления и вентиляции;
fan system — система вентиляции;
vent flue — вентиляционный канал;
trunk duct— воздуховод;
discharge chamber— камера выпуска;
exhaust fan — вытяжной вентилятор;
to facilitate — способствовать, облегчать;
foul flues—взвешенные частицы (в воздухе);
exhaust flue — вытяжка, вытяжной канал;
hot-blast system — система подачи горячего воздуха;
radiator — радиатор, батарея, излучатель;
heating coil — нагревательный элемент, калорифер;
discharge opening — выпускное отверстие;
heat loss — потеря тепла.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Ventilation Systems
[if a regular air supply is needed, mechanical moving air is the only adequate method.]0 The most popular one is a split or fan system for air ventilation at about room temperature. The split system is modified to buildings with ventilation for certain periods of the time (offices, school buildings, etc). The precise temperature is maintained by the radiators; the fan system is operated if ventilation is crucial.
[Ventilation is to remove air at a supplied rate, a system of vent flues being provided for the purpose.]0 The flues from the separate rooms joining together in a trunk duct go ahead to a common discharge at the roof. The attic can be used as a discharge chamber, the flues leading directly to it. An exhaust fan is installed to facilitate the
foul flues removal at a velocity from 1,200 to 1,500ft per minute. In three- or four-storey buildings where the friction in exhaust flues is significant, an exhaust fan is known advantageous.
[The hot-blast system is attractive in industrial buildings as a means of supplying fresh air to replace fumes or moisture from manufacturing processes.]0 This system is predominantly popular if there is no space for radiators. Since such buildings are not often divided into many rooms, the air is supplied at a constant temperature through a trunk ducts system, the heating coils being placed on the suction side of the fan discharged directly into main duct.
Discharge openings are made in columns on each floor. The trunk and branch ducts are to be well insulated for the heat losses from imperfectly insulated ducts are significant.
(1 300 п.зн.)
Из приведенных слов и словосочетаний составьте предложения.
air ventilation, a split, the most, is, method, popular, for, at room temperature, or fan system.
to remove, ventilation, is, the air, at the supplied rate, from, rooms, a system, for the purpose, of vent flue, being provided.
poised is, the hot-blast system, very, for, attractive, industrial buildings, as, supplying fresh air, a means of.
for steel construction, the ducts, buildings, from the columns, iron, are galvanized, and, roof trusses, or.
no space for, hot-blast system, is predominantly, popular, radiators, there is, if.
in, buildings, as, reinforced concrete, the hollow, are often used, the air ducts, columns.
be well insulated, because of, the trunk, and, branch ducts, possible, heat losses, should.
Устно переведите предложения, обращая внимание на многозначность слов.
a) An increase of temperature in the boiler means corresponding increase of pressure, b) It is a case of finding the mean between 'adhesion' and 'cohesion', c) The mean of 7, 9, and 14 is 10. d) He seems to be bad-mannered; I mean he never even says 'Good morn
ing' e) Determine the meanings of the words. f) The hot-blast system equipment was loaded by means of powerful cranes. g) It is imperative to improve the work of the means of transport and communication in the area.
a) The heat of the burning fuel is used for generating steam. b) After the engine had run for 48 hours, the results of the test were excellent. c) The split system cannot be set, for it has been damaged.
a) The wind force was disastrous. b) The enemy forces were destroyed. An atmospheric pressure forces the water upwards.
a) He had to mark and number cars anew, for they were too old, no identification marks or numbers could be seen on their sides. b) They went out through side exits.
a) Community population numbers 12,000. b) The number of gadgets to be repaired per day should be increased. c) She has written a number of articles for the local newspaper. d ) My telephone number is 123-45-67.
a) Students decided to better their English. b) A large-scale survey of all existing conditions is a decided advantage of urban planning. c) It is a decided change for the better. d) Better late than never (proverb).
a) The flat consists of three rooms. b) My friend rooms together with his brother. c) The boiler room is to have been equipped by the end of the month. d) There is enough room for a fan system. He is a big fan of this pop-group. e) Holland is a flat country. f) He lay flat on the floor. g) It is a wonderful theory but falls flat when put into practice.
6. Раскройте скобки.
Recently, some split systems (to modify) to buildings with ventilation for certain periods of the time.
The fixed room temperature usually (to keep) by radiators.
The attic sometimes (to use) as a discharge chamber; the flues (to lead) directly to it.
A new exhaust fan (to set up) to ease the removal of the foul flues at a proper velocity two months ago.
If buildings (not to divide) into many rooms, the air is known (to supply) at a constant temperature through a trunk ducts system.
As a rule, heating coils (to place) on the suction side of the fan discharged directly into main duct.
When heating equipment and trunk duct (to place) on the roof, they (to discharge) the air into the top of each column.
7. Кратко перескажите текст. TEXT E
Переведите интернациональные слова.
temperature, total, sum, balance, constant, radiation, convection, conduction, reserve, adequate, determine, transmission, wall, condition, prevailing, orientation, climatic, thermal, local.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
aptitude — способность, умение (выполнять работу); total heat losses — суммарные потери тепла; convection — конвекция, перенос теплоты; conduction — проводимость, теплопроводность; heating system — система отопления;
reserve capacity — резервная мощность/производительность; reasonable — рациональный, приемлемый, подходящий; heating capacity — нагревательная способность; laying out— проектирование, планирование; heat transmission — теплопередача, теплоотдача; building exposure— расположение/ориентация здания; thermal insulation — тепло-/термоизоляция; to be compatible (with) — быть совместимым с ч-л; humidity — влажность.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
[The aptitude to keep a definite temperature in a building when the temperature is lower depends on the amount of heat and the total heat losses.]0 When the temperature is at the desired point, the sum of added heat should balance the lost in order to maintain a constant temperature via radiation, convection and conduction.
The required amount of heat depends on the building materials, the contents of the building, and the outer temperature. [The heating system should have a reserve capacity adequate to bring the temperature
up to the desired point in a reasonable duration of time.]0 That schools or industrial buildings can be kept at lower temperatures during the night or period when unoccupied — is evident.
Since the heating capacity depends on the heat losses, the first step in a laying out is to determine possible losses. [The main losses are due to the heat transmission through the outer walls plus convection losses because of wind conditions and building exposure.]0 The prevailing winter wind is proved to add at least 15% of the total heat losses on the exposed sides.
A thorough survey of all conditions of the site including building orientation, lay of land, and underground waters together with the average rainfall should be paid particular attention to where environmental and climatic factors have a significant effect. Structural design, style, and thermal insulation are to be compatible with local climatic and weather conditions especially severe ones. [Tall buildings are not recommended in places with strong winds and humidity causing damage and excessive heat losses.]0 (1 340 п.зн.)
List of Heat Pump Types
A split system is an outdoor unit where both a compressor and an indoor unit with a fan are placed. It is a quite operation as only the fan is inside the house to circulate the warm air.
A hi-wall type is mounted on the wall. It is a very slim model with advanced features such as remote control, reverse cycle, sleep and digital timer and moisture removal.
A compact floor console is put on the floor 60cm high and 74cm wide. It is a powerful and noiseless model.
• A ducted system is an invisible solution to heat the whole house.
1.
valve
(n)
(a)
general
2.
viable
(adj)
(b)
tap
3.
common
(adj)
(c)
phase
4.
cycle
(n)
(d)
part
5.
suitable
(adj)
(e)
typical
6.
component
(n)
(f)
appropriate
7.
produce(v)
(g)
exploit
124
4. Подберите синонимы.
standard (adj) (h) feasible
utilize (v) (i) generate
expansion (n) (j) diversity
variety (n) (k) increase
Переведите предложения, определив группу сказуемого.
The aptitude to keep a definite temperature in a building when the temperature is lower depends on the amount of heat and the total heat losses.
More heat is to be added than to be lost via radiation, convection and conduction.
This amount of heat does depend on the heat of the building materials, the contents of the building, and the temperature increase.
The heating system should have a reserve capacity adequate to bring the temperature up to the desired point in a reasonable duration of time.
That schools or industrial buildings can be kept at lower temperatures during the night or period when unoccupied — is evident.
Since the heating capacity depends on the heat losses, the first step in laying out a system is to determine possible losses.
The main losses are due to the heat transmission through the outer walls plus convection losses because of wind conditions and building exposure.
The prevailing winter wind is proved to add at least 15% of the total heat losses on the exposed sides.
Structural design, style, and thermal insulation are to be compatible with local climatic and weather conditions, especially severe ones.
Соедините части, чтобы получить предложения.
Convection...
Conduction...
Radiator...
Layout...
Insulation...
...is a device used for heating, consisting of flat hollow
metal container fixed to a wall.
...is a way in which practical intention is arranged.
...is a material to protect pipes, buildings, etc.
...is the passage of electricity through wires, heat through
metal, etc.
.. .is the movement in gas or liquid caused by heat.
Закончите предложения.
The heating system is to bring...
The main heat losses are due to...
Since the heating capacity depends on...
The aptitude to keep a definite temperature in a building...
When the temperature is at the desired point...
A thorough survey of the site includes...
Structural design, style, and thermal insulation are to...
Tall buildings are not recommended...
To minimize excessive heat losses it is necessary...
Дайте тексту название.
Кратко перескажите текст.
TEXT F
1. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Keeping cool has been a human concern for millennia... The idea of air conditioning had started before a machine was made to produce the cooling effect. First attempts were made by a physician John Gorrie (1803-1855) in Florida. Dr. Gorrie was the very man to create an ice-making machine blowing air over a bucket of ice for cooling hospital rooms of patients suffering from malaria and yellow fever.
A close 'ancestor' to modern air conditioners was made in 1902 by an American engineer Willis Carrier. The machine called 'Apparatus for Treating Air' was built in New York. After that breakthrough, air conditioners began to bloom though they were large, awkward, expen- sive, and dangerous due to the toxic ammonia used as a coolant.
After World War II, first window unit air conditioners appeared. Today it is an invention that is almost impossible to live without.
(720 п.зн.)
Найдите в тексте эквиваленты:
врач, доктор медицины
получить развитие
научный прорыв
изобретение
кондиционер, устанавливаемый в оконном проеме
достичь желаемых результатов
хладагент процветать
прототип
страдать
из-за, по причине
громоздкий
Перефразируйте.
The idea of air conditioning had started before a machine was created to produce the cooling effect.
Dr. Gorrie was the very man to make first attempts to cool hospital spaces.
■A close 'ancestor' to modern air conditioners was made in 1902 by an American engineer Willis Carrier.
The era of air conditioners started at the beginning of the 20th century
Today it is an invention that is almost impossible to live without.
Определите главную идею и дайте тексту название.
Письменно составьте аннотацию к тексту.
Information-to-Swallow HVAC
[HVAC* is an abbreviation standing for the closely related functions of 'Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning' which is a technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort.]0 HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer.
Heating, ventilating, and air conditioning is based on inventions and discoveries made by Nikolay Lvov, Michael Faraday, Willis Car-
tier, Reuben Trane, James Joule, William Rankin, Sadie Carnot, and many others. The HVAC systems components development went hand-in-hand with the industrial revolution.
[The central functions of heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning are closely interrelated, providing thermal comfort, acceptable indoor air quality together with reasonable installation, operation, and main- tenance costs.]0 HVAC systems are to provide ventilation, reduce air infiltration, and maintain pressure relationships between spaces. Air delivery and removal is known as air distribution.
[Indoor air contaminants cause physiological changes in occupants and damage building materials, furnishings, and equipment for they may be thickly coated with some fumes from burning tobacco, fire- places, chimneys, and even candles.]0 As a result, it worsens human health affecting eyes, nose, throat and causing skin irritation, allergic response, difficulty in breathing, etc.
Data and calculation methods predicting all potential IAQ** problems should be seriously considered to avoid or, at least, minimize them.
*HVAC— Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning system end-to-end accuracy;
**IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
(HVAC&R/HVACR — Seating, Ventilating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration' HACR — 'Heating, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration')
(1 540 п.зн.)
❖ Подготовьте презентацию наиболее важных событий в области HVAC&R в России и за рубежом с учётом новейших строительных технологий.
Словарь к Разделу VI
absorption — всасывание, впитывание, абсорбция;
to accomplish — выполнять, совершенствовать;
acoustical — акустический, звуковой;
adequate — соответствующий, достаточный;
advanced features — улучшенные характеристики;
advantageous — выгодный, полезный;
air conditioning— кондиционирование воздуха;
air contribution — забор воздуха;
air delivery — подача воздуха;
air distribution — распределение воздуха;
air removal — удаление воздуха;
airborne — переносимый по воздуху, воздушный;
alarm — тревога, сигнал тревоги, аварийная сигнализация;
allergic response — аллергическая реакция, аллергия;
ammonia — аммиак;
amplifier — усилитель;
to be apart (from) — быть отдельно, врозь;
application — применение, использование;
aptitude — способность, умение (выполнять работу);
attic — мансарда, чердак;
automotive — автомеханический;
awkward — неуклюжий, неудобный;
to bloom — расцветать, быть в расцвете;
to blow — дуть, веять;
breakthrough — прорыв, переворот (в технике);
to bring up — увеличивать, поднимать, доводить;
bucket — ведро, бадья, ковш;
building exposure — расположение/ориентация здания;
candle — свеча;
capacity — мощность, производительность;
chiller — охладитель, холодильная установка;
chimney — дымоход, труба (дымовая или вытяжная);
circuit — цепь, схема;
to circulate — циркулировать, распространяться;
closed-circuit television — замкнутая телевизионная система, система кабельного телевидения;
column — зд. шахта, стойка;
communication system — система связи, система коммуникаций;
to be compatible (with) — быть совместимым с ч-л;
condenser — холодильник, конденсатор;
condominium — квартира в доме-совладении;
conduction— проводимость, теплопроводность;
conduit — кабельный канал;
connection — связь, соединение, контакт;
console — стойка, шкафчик;
convection — конвекция, перенос теплоты;
cooling — охлаждение, система охлаждения;
corner convenience store — магазин шаговой доступности;
crucial— ключевой, критический, решающий;
dehumidification — осушение (воздуха), удаление избытка влаги;
to deplete — уменьшать, истощать;
desired point — желаемый уровень;
digital timer — цифровой таймер;
discharge chamber — камера выпуска;
discharge opening — выпускное отверстие;
disposal— избавление, сброс, удаление;
duct — труба, трубопровод;
duration of time — период/продолжительность времени;
end-to-end— непрерывной цепью, впритык;
evaporator— испаритель, выпариватель;
excessive — чрезмерный;
exhaust fan — вытяжной вентилятор; >
exhaust flue— вытяжка, вытяжной канал;
expansion device — расширительное (дросселирующее) устройство;
expansion valve — расширительный клапан, вентиль;
exposed — открытый, незащищённый, уязвимый;
exposure — подверженность воздействию;
to facilitate — способствовать, облегчать;
facilities — аппаратура, оборудование, средства;
fan system — система вентиляции;
federal regulations — федеральные постановления/акты;
fire alarm installation — система пожарной сигнализации;
fire automatic detection — автоматизированное обнаружение/ выявление пожара;
flammability — воспламеняемость;
fluid — жидкость;
foam — пена;
to foresee— предвидеть;
foul flues — взвешенные частицы (в воздухе);
fume — дым, газы, испарение;
to grant — представлять;
heat exchanger — теплообменник, радиатор отопления;
heat loss — потеря тепла;
heat pump — тепловой насос;
heat transmission — теплопередача, теплоотдача;
heat-activated equipment — оборудование, активизирующееся
в результате нагрева;
heating capacity — нагревательная способность;
heating coil — нагревательный элемент, калорифер;
heating system — система отопления;
high-rise building — высотное здание;
hot-blast system — система подачи горячего воздуха;
humidity— влажность;
ice-making machine — ледогенератор;
to identify — устанавливать, определять;
imperfect — недостаточный, с изъяном;
instead of— вместо, взамен;
international agreements — международные соглашения;
invention patentee — владелец патента на открытие;
invisible — невидимый, скрытый;
laying out — проектирование, планирование;
loudspeaker system — акустическая система;
low-rise apartment — малоэтажное жильё;
luxury — роскошь, предмет роскоши;
to make contact —- вступать в контакт;
master antenna — коллективная антенна;
medium — способ, средство, среда;
moisture — влажность, сырость;
moisture removal — удаление влаги;
phase-out — постепенное сведение на нет, ликвидация;
power equipment — энергетическое оборудование/оснащение;
power input— входная мощность, силовой вход;
power-limited — с ограниченной энергетикой;
precise — точный, определённый;
pressure — давление, сжатие;
public address system — система оповещения населения;
radiator — радиатор, батарея, излучатель;
reasonable — рациональный, приемлемый, подходящий;
to reduce — понижать, сокращать, уменьшать;
refrigerant— холодильный агент, хладагент;
refrigeration system — система охлаждения, холодильная установка;
to reject — отвергать, отклонять, отводить (тепло);
remote — дистанционный, действующий на расстоянии;
remote control system — система дистанционного управления, система телеуправления;
to remove — удалять, устранять;
reserve capacity — резервная мощность/производительность;
residential-sized equipment — размер оборудования для жилых зданий;
restriction — ограничение, запрет;
reverse cycle heating system — система отопления с тепловым насосом;
security — безопасность, обеспечение безопасности;
severe — суровый (о климате);
sleep timer — таймер ночного режима;
split system — раздельная система отопления и вентиляции;
stairway — лестница;
suction side — сторона всасывания/впуска;
supplied rate — норма;
thermal insulation — тепло-/термоизоляция;
total heat losses — суммарные потери тепла;
toxicity — токсичность, ядовитость;
trunk — вентиляционная шахта, канал;
trunk duct — воздуховод;
universal use — повсеместное использование;
vapour compression — сжатие пара;
vent flue— вентиляционный канал;
via — посредством, с помощью;
viable — жизнеспособный;
waste — отходы, мусор;
wiring — электропроводка, монтаж электропроводки;
to worsen — ухудшать;
yellow fever — жёлтая лихорадка.
Раздел VII
SEWAGE TREATMENT AND WASTE MANAGEMENT TEXT A
Переведите интернациональные слова.
civilization, chemicals, storm, separation, sanitary, discussion, efficiency, domestic, specialized, filter, seasonality, disinfection, regulation, resource, jurisdiction, composition, mechanical, biological, industrial, commercial, technical.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
sewerage— канализация;
sewer— канализационная труба (коллектор);
sewage — сточные воды;
run-off— отходы, отбросы (промышленности);
pollutant — загрязняющий агент, загрязнитель;
contaminant — загрязняющее вещество, примесь;
domestic sewage — коммунально-бытовые сточные воды;
industrial wastewater— промышленные сточные воды;
residential wastewater — отходы коммунальной канализации;
institutional wastewater — сточные воды общественных предприятий;
waterway — водоспуск, водоотвод;
discharge сток (слив) сточных вод;
seasonality — сезонность, сезонные изменения;
street-flushing operation — поливка улиц;
backing-up — (гидр.) запруживание, затор;
treatment plant — станция по очистке, водоочистное сооружение; storm water — ливневые воды.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Sewerage*
[That the civilization increases, the social and technical progress have led to natural water resources composition changes, rivers, lakes and ground waters containing numerous pollutants of various origin — is obvious.]0
Sewage created by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial (ICI) establishments includes household waste liquid from
toilets, baths, laundry waste, showers, kitchens plus storm water run- off that is disposed via sewers. [Sewage must be removed promptly in order to avoid endangering people health passing through special treatment.]0 Sewage from residence is domestic sewage; the one from industrial processes is industrial waste.
[Sewerage systems are known to be combined sewers.]0 They can complicate and reduce the efficiency of treatment plants due to seasonality. Heavy storms contributing more flows than treatment plants can handle overwhelm the sewage system and cause its spill or overflow.
[As rainfall picks up various contaminants (soil particles, heavy metals, animal urine and feces, organic compounds, oil and grease), jurisdictions oblige to treat storm water discharging into waterways.]0 Retention basins, wetlands, filters and vortex separators to remove coarse solids are used for it. Sanitary sewers are smaller than storm ones, and backing-tip of raw sewage occurs if excessive storm water is allowed into sanitary sewer systems.
Sewage collection and treatment is under discussion of local, state and federal regulations and standards. Separation of household waste into 'grey' and 'black' water is in common all over the world but depends on local conditions. Thus, 'grey' water is permitted for watering plants, toilets and street-flushing operations.
[In spite of definite progress in abating water pollution, many enterprises still need both time and money to meet water quality standards; environmental regulations and general guidelines ensure acceptable discharge of wastewater effluent.]0
* 'Sewerage' can mean:
system of sewers;
removal of waste by sewer system;
sewage.
(1 750 п.зн.)
Выберите предложение, выражающее главную мысль текста.
Sewage is a type of wastewater and a potential source of pollution, especially in urban areas.
■The removal of sewage is accomplished by sewers which are a part of a sewerage system.
Sewage is a liquid waste containing some solids from households and industry.
Humanity is making progress in abating water pollution.
Sewage composed of different types of wastes is to be removed passing through treatment.
Соедините части AB, чтобы получить законченное высказывание.
А.
Sewage is the mixture of waste...
Sewer is a pipe or passage under the ground that carries...
Contaminant is...
Pollutant is a substance that makes air, water, soil, etc. dangerously...
Run-off is rain or...
Environment is air, water, and land...
Environmental regulations, guidelines and policies guarantee...
Endanger is to put someone or something...
Sewerage is the system by which waste material and water are carried...
B.
...away waste material and used water from houses and factories.
...a poisonous substance that makes something impure.
...away in sewers and then treated to stop it being harmful.
...from the human body and used water that is carried away from houses by sewers.
...acceptable discharge of wastewater effluent.
...other liquid that flows off the land into the rivers.
...in a dangerous situation where they can be hurt, damaged, or destroyed.
...dirty, and is caused by cars, factories, etc.
...in which people, animals, and plants live.
Переведите предложения, учитывая многозначность слов.
1). There have been significant computer developments during the last decade. 2). A piece of land was sold for development.
1). The chemical plant to be constructed here will be the largest in the country. 2). This kind of plants is preferable here to decorate exteriors of the building.
1). The material is known to be the most important component of concrete. 2). Have you got any concrete proposals as to what should be done?
1). The British Museum currently houses a library. 2). Prefabricated structures and precast elements are classified into two principal groups — for residential houses and industrial buildings.
1). The dam could not withstand the water pressure. 2). They must consider all necessary water conditions to suit a particular cement application. 3). Politeness is not his strong suit 4). They have been shown two suits; one is a set of a jacket with trousers, and a second includes a jacket with a skirt.
1). Industrial waste has found its way into the water supply. 2). It was a total waste of time and money. 3). To be unemployed is a real waste of talents.
1). The best treatment for a cold is to rest and drink lots of fluids. 2). This method of sewage treatment to be adopted will depend only on local conditions. 3). That fluid movements and gestures are graceful is evident.
1). To raise the issue means the problem should be discussed. 2). It is very difficult to take issue with current analyses. 3). A corporation will issue all employees with uniforms and badges.
1). The place had completely changed since we went there two years ago. 2). Since primary treatment is insufficient, other kinds of treatment are used. 3). Since you are unable to solve the problem, we'll have to ask somebody else to do it.
Кратко перескажите текст.
Переведите, определив группу сказуемого.
That the civilization increases, the social and technical progress have led to natural water resources composition changes, rivers, lakes and ground waters containing numerous pollutants of various origin — is obvious.
As rainfall travels over roofs and the ground, it does pick up various contaminants, i.e. soil particles, heavy metals, animal urine and feces, organic compounds, oil and grease.
Sewage created by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial establishments includes household waste liquid as well as storm water run-off that disposed via sewers must be promptly removed to avoid endangering the people health passing through special treatment methods.
Heavy storms contributing more flows than the treatment plant can handle overwhelm the sewage system and cause its spill or overflow.
Despite industry is making progress in abating water pollution, many companies still need much time to meet federal water quality standards.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Suffering from thirst, large cities have two main concerns in water. One is that there is an adequate water supply to meet demand for both household and industrial use. The other is the water quality.
In fact, only 2 percent of supplied public water is estimated to be potable and widely applicable for drinking and cooking. The largest part of household water is for bathrooms: 135 litres for a bath, eight litres a minute for a shower and up to 27 litres each time the toilet is flushed.
As for typical urban household, it consumes approximately 1,000 litres of water a day. Less than 3 percent of all available water all over the world is estimated fresh water. Most of it is out of human reach, for it is trapped as polar ice or deep ground waters. (620 п.зн.)
Подберите эквиваленты.
снабжение, поставка a) to be thirsty
потребность, спрос b) demand
испытывать жажду с) potable
захваченный d) to consume
потреблять, расходовать е) available
промывание струей f) trapped
годный для питья, питьевой g) supply
доступный, имеющийся в наличии h) flush
11. Дайте тексту название.
TEXT В
Переведите интернациональные слова.
float, physical, chemical, biological, filtration, pump, microorganism, separation, irrigation, agriculture, landscape, park, golf, court, ecology, concentration, prior, goal, recreation, urban, lagoon, recycling, municipal.
Запомните слова и словосочетании.
pretreatment— предварительная очистка;
primary treatment — первичная очистка;
secondary treatment — дополнительная очистка;
tertiary treatment — окончательная очистка;
clarifier— очистная установка, фильтр;
to be subjected to —подвергаться чему-либо;
decomposable — способный к разложению, разложимый;
habitat — среда обитания, естественная среда;
effluent polishing — доочистка, удаление остаточных примесей из
питьевой воды;
wastewater treatment plants — водоочистная станция, станция водоочистки;
potable— годный для питья, питьевой;
impact— воздействие, влияние;
recycling — утилизация, повторное использование, регенерация;
to dilute — разжижать, разбавлять, растворять.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания;
Sewage Treatment
Conventional sewage treatment involves at least four stages: pretreatment, primary, secondary and tertiary.
Pretreatment removes large particles such as trash, bits of cloth, tree limbs, leaves, other — before they can damage or clog pumps and skimmers of primary treatment clarifiers.
Primary treatment consists of temporarily holding the sewage in a quiescent basin where heavy solids settle to the bottom, oil, grease and lighter solids floating to the surface. The settled and floating materials are removed, and the liquid is subjected to secondary treatment.
Since primary treatment is insufficient, partly clarified sewage still containing decomposable substances is to undergo secondary treatment. Secondary treatment requires a separation process to remove microorganisms prior to discharge. Secondary treatment removes dissolved and suspended biological matter, which is performed by indigenous, water-born microorganisms, in a habitat.
Tertiary treatment is defined as anything more than both primary and secondary treatments. Wastewater treatment includes physical, chemical and biological processes. If disinfection is used, it is a final process known as effluent polishing.
[The treatment goal is to remove completely or to reduce significantly the concentration of all existing contaminants so that received water can suit its desired end-use without any adverse ecological impact.]0
[Highly treated effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plants is a reliable source of water for irrigation, industrial recycling and either non-potable or potable reuse.]0 If not reused, treated wastewater is commonly discharged into a water body (stream, river, bay, lagoon or wetland) and diluted. (1 460 п.зн.)
Ответьте на вопросы.
What stages does conventional sewage treatment involve?
What does primary treatment consist of?
What does secondary treatment require?
What is tertiary treatment?
What does pretreatment lead to?
What other wastewater treatments do you know?
Выберите ответ на вопрос ‘Why should sewage go through tertiary treatment?'
because more than one treatment process should be used at any plant to remove all existing contaminants or considerably reduce the concentration of such contaminants so the water becomes fit for its desired end-use.
because primary secondary treatment is not sufficient, and partly clarified sewage does contain many decomposable substances.
because secondary treatment requires a separation process to remove microorganisms.
Закончите предложения.
Treated water is sometimes disinfected...
After treatment wastewater is either reused or...
The object of all treatment processes is...
Highly treated wastewater effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plants...
If not reused, treated water...
Расположите предложения согласно логике изложения.
1. If it is sufficiently clean, it can also be used for groundwater recharge or agricultural purposes. 2. First, the solids are separated from the wastewater stream. 3. The final effluent can be discharged into a stream, river, bay, lagoon or wetland, or it can be used for the irrigation of a golf course, green way or park. 4. Finally, the biological solids are neutralized and disposed of or reused, and the treated water may be disinfected chemically or physically (for example by lagoons and micro-filtration). 5. The sewage treatment involves three stages, called primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. 6. Then, dissolved biological matter is progressively converted into a solid mass by means of indigenous, water-borne microorganisms.
Переведите письменно, обращая внимание на 'to'-формы.
Pretreatment removes substances to be easily collected from raw wastewater before they spoil or clog pumps and skimmers of primary treatment clarifiers.
Since primary treatment is not sufficient, partly clarified sewage, still containing decomposable substances, is to go through secondary treatment.
Secondary treatment requires a separation process to get rid of either present dissolve or suspended biological matters.
To remove completely or to decrease the concentration of all existing contaminants is an obligatory task of any treatment process.
Highly treated effluents are known to be a reliable source of water for agricultural and landscape irrigation, industrial recycling as well as non-potable or even potable reuse.
9. Прокомментируйте.
Water supply system is analogous to human circulatory system. Heart pumps blood via arteries, veins, and capillaries to bring oxygen to all parts of the body. Water pump delivers water via primary, secondary, and distributor water mains to supply water to all consumers.
(230 п.зн.)
TEXT С
Переведите интернациональные слова.
sanitary, variation, pathogenic microorganism, bacterial, population, temperature, conservation, demonstrate, mimic, toxic, monitoring, goal, regular, parameter, compound, final, total, ultraviolet, radiation, classification, socio-economic, protection, management.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
to affect smth — воздействовать, влиять;
living standards — уровень жизни;
dependability — надёжность;
received environment — обычные условия/среда проживания;
impurity— грязь, примесь; health hazard — вред здоровью;
final disposal— завершающий/конечный сброс сточных вод;
crucial — решающий, критический;
disease — болезнь, заболевание;
to have unpredictable impact— иметь непредсказуемые последствия;
biota — биота, флора и фауна определённой местности;
to take responsibility (for) — брать на себя ответственность;
to forbid — запрещать;
odour — запах, аромат;
turbidity — мутность;
demand — потребность, спрос.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания. Wastewater Treatment in the Received Environment
[Municipal wastewater from sanitary conveniences of residential and ICI facilities with groundwater and storm water affects climate,
living standards, dependability and quality of water supply, water conservation requirements, etc — i.e. it impacts received environment.]0 Wastewater contains organic materials, nutrients, pathogenic and toxic impurities which entail ecological and health hazards and is to be treated before final disposal. [The final goal of wastewater management is the protection of the environment in accordance with public health and socio-economic concerns.]0 Understanding of wastewater nature is crucial for selecting effective treatment technologies.
[Treatment processes mimic natural ones. Bacteria feed on organic contaminants notably changing environment. Many disease-causing microorganisms are reduced naturally by ultraviolet radiation (UV).]°
[Recent evidence has demonstrated that specific contaminants have an unpredictable adverse impact on the biota altering source, location, geological conditions, level depth, and seasonal changes, as well as domestic, agricultural and industrial activity.]0
An Environment Agency in any developed country takes a responsibility lor the water quality forbidding uncontrolled discharges; water pollution quality standard monitoring is regularly carried out.
Physical parameters include colour, odour, temperature, and turbidity. Insoluble contents such as solids, oil and grease also fall into this category.
Chemical parameters associated with organic contents include biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon ( TOC) and total oxygen demand (TOD).
There is an international classification of water purity:
Good quality, Class la means highest quality water.
Good quality, Class lb stands for lower quality water of the same use,
Fair quality, Class 2 needs treatment to make potable water.
Poor quality, Class 3 is moderately polluted water for industrial purposes.
Bad quality. Class 4 stands for grossly polluted water. (1 750 п.зн.)
4. Составьте план текста.
5. Из приведенных слов и словосочетаний составьте предложения.
effective technologies, is fundamental for, wastewater treatment plants, an understanding of the waste-water nature, to select.
in many countries, of wastewater, discharges, are forbidden, uncontrolled.
public health, of waste-water management is, the ultimate goal, the protection of the environment, in accordance with, and socioeconomic concerns.
generally, contains, untreated waste-water, high levels, nutrients, numerous, of organic material, pathogenic microorganisms, and toxic compounds, as well as.
of water, the quantity, since, also, it, diluent, discharged, sewage treatment works, is, taken into consideration, dilutes, from.
6. Расшифруйте аббревиатуру терминов, например: GHG is a short form of/ stands for/ means greenhouse gases.
a) BOD; h) COD); с) TOC; d) TOD; e) UV.
7. Выберите предложения, отражающие основное содержание текста.
Physical parameters of water include colour, odour, temperature, and turbidity.
Urban wastewater is the combination of fluid wastes originating in the sanitary conveniences of dwellings, commercial or industrial facilities and institutions.
There are five water quality groups of classification.
The ultimate goal of waste-water management is the environment protection in accordance with public health and socio-economic concerns.
Recent evidence has demonstrated an unpredictable adverse impact on the natural biota if the water is reused.
The wastewater nature is significant to select effective treatment technologies.
Uncontrolled discharges of wastewater are forbidden in many countries.
Переведите письменно.
Municipal wastewater is known to be the combination of water- carried wastes originating in the sanitary conveniences of dwellings, commercial or industrial facilities and institutions, in addition to groundwater, surface water and storm water with variations in water usage, which is affected by climate, community size, living standards, dependability and quality of water supply, water conservation requirements etc.
An urban water supply system cannot service its customers unless there is a continuous supply of water to meet domestic consumption needs in the broadest sense and water needs for structural fire protection.
Current proofs have shown that if the water is reused for drinking water, certain impurities in wastewater either hormones or synthetic materials are able to have an unpredictable impact on the natural biota and human beings as well.
Перескажите текст, пользуясь планом.
Прокомментируйте высказывание.
It isn`t pollution that's harming the environment. It`s impurities in our air and water that are doing it. (Dan Quayle)
TEXT D
Переведите интернациональные слова.
historically, absolutely, siphon, condition, urban, public, private, asphalt, reservoir, periodic, scale, line, toilet, natural, complex, intersection, architect, management, drainage, individual, cholera, population, irrigation.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
natural sewage disposal — естественный сброс сточных вод;
natural water body — естественный водоём;
drain — водосток, дренажная канава, система осушения;
cesspool — сточный колодец;
plumbing pipes — зд. сточные канавы;
leak — течь, протечка, утечка;
siphon conduit — сифонный трубопровод;
sanitary conditions — санитарно-гигиенические условия;
water management system — водохозяйственная система;
precipitation — выпадение осадков;
sludge — густая грязь;
cesspit — помойная/выгребная яма;
fouls — нечистоты.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Historical Highlights
[Historically, human settlements were close to water sources, and rivers doubled a form of natural sewage disposal for early sewage was directed to a natural water body.]0
The Indus architects designed sewage systems on a large scale. The drains were seven to ten feet wide at two feet below ground level with U-shaped bottoms. Designers installed cesspools with steps leading down tor periodic cleaning. By 2700BC cities had plumbing pipes with broad flanges to stop leaks.
The first sanitation siphon conduits were found in Greece, and they are still (about 3,000 years!) in good condition.
Rome and Istanbul ancient sewer systems are perfectly functioning, the pipes being rerouted to modern sewer treatment.
In 46 BC-400 AD Romans had a complex net of sewers out of hollow elm logs butted together.
[Overcrowded communities required more intricate sewerage to meet high-quality sanitary conditions with outdoor flushed toilets.]0 There were public and private baths in urban areas, a sophisticated water management system with numerous reservoirs having been established.
However, many past cities had no sewers relying on the nearest rivers and occasional precipitation to cleanse. Wastewater was running down the streets with stepping stones to keep pedestrians from dirt and sludge. The over-polluted communities became a constant source of water-borne diseases. In South Wales inhabitants discharged their sewage to cesspits causing the pavements to be flooded with fouls.
[Today, advanced drainage is a demand and humanity necessitates good water for drinking, supporting aquatic life, generating electric - power, irrigating crops, and recreation.]0 Thus, the need for perfect wastewater treatment cannot be overestimated. (1 460 п.зн.)
Выберите предложения, не выражающие главную идею текста.
Historically, early human habitations were built close to water resources.
The past architects designed sewage disposal systems on a large scale.
The first sanitation systems are still, after 3,000 years, in good condition.
Developed countries required intricate sewer systems to achieve ideal sanitary conditions in crowded communities.
The population growth became a constant source of water- borne diseases.
Modern humanity does necessitate good quality water.
The need for perfect wastewater treatment cannot be overemphasized.
Закончите предложения в соответствии с содержанием текста.
Being vital and unique water...
Early human habitations were...
Many past cities had no...
Ancient architects designed sewage disposal systems ...
To achieve better sanitary conditions early civilizations...
Modern community badly needs...
It is absolutely impossible to overestimate...
Переведите цепочки слов.
Introduction
Classification introduction
Methods classification introduction
Monitoring methods classification introduction
Quality monitoring methods classification introduction
Water quality monitoring methods classification introduction
Town water quality monitoring methods classification introduction
Data
Lack data
Promotion lack data
Production promotion lack data
Components production promotion lack data
System components production promotion lack data
Sanitation system components production promotion lack data
Benefits
Development benefits
Strategy development benefits
Reduction strategy development benefits
Threat reduction strategy development benefits
Pollution threat reduction strategy development benefits
Water pollution threat reduction strategy development benefits
Кратко перескажите текст.
Прокомментируйте.
Benefits for man are benefits for nature.
Information-to-Swallow (1) Reclaimed Water Use 1. Irrigation
Treated effluents can be used to irrigate crops or landscaped areas. The main consideration is the water quality and its suitability for plants. Another problem is public health and safety hazards from the potential presence of bacterial pathogens, parasites, and viruses.
Industrial use
Reclaimed water is ideal for industrial processes that do not require potable water. Industrial water contains evaporated cooling water, boiler-feed water, process water, and the around plant landscape maintenance water. Any reuse is associated with corrosion, biological growth, fouling and foaming. These problems are also encountered when fresh water is used, though. Boiler-feed water should be softened and demineralized.
Recreational use
Reclaimed water is widely used for basins, pools, ponds and lakes for swimming, fishing, boating, fountains, and fish farming. The greater the potential of human contact, the higher the treatment level required (coagulation, filtration, and disinfection).
Groundwater recharge of reclaimed wastewater is to lessen water table decline, protect groundwater in coastal aquifers against saltwater invasion, and store water.
It includes surface spreading in basins and direct injection into aquifers. The method improves the reclaimed water quality, for it percolates through soil, unsaturated zone, and aquifer. Direct injection involves the pumping of reclaimed water directly into an aquifer. The
only disadvantage to be mentioned is the groundwater contamination risk.
Potable reuse
Although extensive research is being conducted, there are many active constraints on the determination of appropriate water quality criteria. The direct potable use of reclaimed municipal wastewater is limited because of public rejection and health, safety and aesthetic concerns. (1 560 п.зн.)
Information-to-Swallow (2)
Wastewater Contaminants
Suspended solids (SS) lead to sludge deposits and anaerobic conditions when untreated wastewater is discharged to the aquatic environment.
Biodegradable organics are made up of proteins, carbohydrates and fats. If discharged into inland rivers, streams or lakes, they tend to deplete natural oxygen resources and cause septic conditions hazardous to aquatic species.
Pollutants, both organic and inorganic, are highly toxic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic.
Pathogenic organisms cause infectious diseases.
Refractory organics include surfactants, phenols and agricultural pesticides.
Heavy metals, usually added by commercial and industrial activities, are to be removed before wastewater reuse. Dissolved inorganic constituents such as calcium, sodium and sulfate must be removed as well.
(680 п.зн.)
❖ Подготовьте презентацию наиболее важных событий в области очистки и использования сточных вод в России и за рубежом с учётом новейших строительных технологий.
Словарь к Разделу VII
to abate — уменьшать, снижать;
adverse — неблагоприятный, вредный;
to affect smth — воздействовать, влиять;
anaerobic — анаэробный (протекающий без воздуха);
aquatic — водяной, водный;
aquatic environment — водная среда;
aquifer — водоносный слой/пласт/горизонт (почвы);
backing-up — (гидр.) запруживание, затор;
biodegradable — поддающийся биологическому разложению;
biota — биота, флора и фауна определённой местности;
boiler-feed water— вода для питания котлов;
to but — соединять встык, состыковывать;
carbohydrates — углеводы;
carcinogenic — канцерогенный, онкогенный;
cesspit — помойная/выгребная яма;
cesspool — сточный колодец;
clarifier — очистная установка, фильтр;
to cleanse — очищать, промывать;
to clog — засорять, забивать;
coagulation — коагуляция (свёртывание и осаждение взвешенных коллоидных веществ);
coastal — прибрежный, береговой;
combined — объединённый, совместный, комбинированный;
to complicate — затруднять, осложнять;
concern — проблема, забота;
constraint — ограничение, сдерживающий фактор;
contaminant — загрязняющее вещество, примесь;
crucial — решающий, критический;
decline — ухудшение, спад;
decomposable — способный к разложению, разложимый;
demand — потребность, спрос;
dependability — надёжность;
to dilute — разжижать, разбавлять, растворять;
discharge — сброс (слив) сточных вод;
disease — болезнь, заболевание;
disinfection — дезинфекция, обеззараживание;
dissolved — растворённый;
domestic sewage — коммунально-бытовые сточные воды;
to double -дублировать, замещать;
drain — водосток, дренажная канава, система осушения;
effluent — отвод сточных вод, сброс, сток;
effluent polishing — доочистка, удаление остаточных примесей из питьевой воды;
elm — вяз, ильм (дерево);
to encounter — сталкиваться;
endangering — создание угрозы, поставление в опасность;
estimated — примерный, предполагаемый, теоретический;
to evaporate — испарять, превращать в пар; '
excessive — избыточный;
feces — экскременты, фекалии;
final disposal — завершающий/конечный сброс сточных вод;
flange — утолщённый борт/закраина;
to float — зд. всплывать;
flushed — сливной, проливной;
to forbid — запрещать;
fouls — нечистоты;
grease — жир;
grossly — избыточно, чрезвычайно;
ground waters — грунтовые, подземные, подпочвенные воды;
guidelines — руководящие указания/установки/документы;
habitat — среда обитания, естественная среда;
to have unpredictable impact — иметь непредсказуемые последствия;
health hazard — вред здоровью;
hollow— пустой, полый;
household — хозяйственный, бытовой;
impact — воздействие, влияние;
impurity — грязь, примесь;
indigenous —- свойственный, присущий;
industrial wastewater— промышленные сточные воды;
injection — закачивание, вливание, вбрызгивание;
inland— внутренний, удалённый от моря;
insoluble — нерастворимый;
institutional wastewater — сточные воды общественных предприятий;
invasion — вторжение, проникновение, инвазия;
jurisdictions — органы власти;
lagoon — отстойник, отстойный пруд/бассейн;
laundry — прачечная;
to lead (led) — приводить, вести;
leak — течь, протечка, утечка;
limb — ветка, ветвь, сук;
living standards — уровень жизни;
log — бревно;
to mimic — имитировать, воспроизводить;
moderately — умеренно;
monitoring — мониторинг, слежение;
mutagenic — мутагенный, вызывающий мутации;
natural sewage disposal — естественный сброс сточных вод;
natural water body — естественный водоём;
nutrient — питательное вещество, зд. остатки пищи;
to oblige — обязывать, заставлять;
obvious — очевидный;
odour —- запах, аромат;
outdoor — находящийся вне помещения;
to overestimate — переоценивать;
overflow — переполнение;
to overwhelm — переполнять, заливать, выводить из строя;
to percolate — просачиваться, проникать сквозь, проходить;
pesticide — пестицид, ядохимикат;
phenol — фенол, карболовая кислота;
to pick up — подбирать, захватывать, увлекать с собой;
plumbing pipes — зд. сточные канавы;
polishing — доочистка, удаление остаточных примесей из питьевой воды;
pollutant— загрязняющий агент, загрязнитель;
potable — годный для питья, питьевой;
precipitation — выпадение осадков;
pretreatment— предварительная очистка;
primary treatment — первичная очистка;
process water — техническая вода;
promptly — быстро, немедленно, срочно;
quiescent basin — неподвижный, статический резервуар;
received environment -— обычные/существующие условия/среда проживания;
recharge — пополнение, подпитывание;
reclaimed — регенерируемый, восстановимый;
reclaimed water — оборотная вода;
recycling — утилизация, повторное использование, регенерация;
refractory organics — нерастворимые органические вещества;
rejection — неприятие, отторжение;
to reroute — перенаправлять, переподсоединять;
residential wastewater — отходы коммунальной канализации;
retention basin — водохранилище местного стока;
run-off — отходы, отбросы (промышленности);
sanitary conditions — санитарно-гигиенические условия;
sanitation — канализация;
seasonality — сезонность, сезонные изменения;
secondary treatment — дополнительная очистка;
separator — отделитель, сепаратор;
septic — септический, связанный с поражением гнилостными микробами;
sewage — сточные воды;
sewer — канализационная труба, коллектор;
sewerage — канализация;
shower — обильные атмосферные осадки, ливень;
siphon conduit — сифонный трубопровод;
skimmer — сепаратор, отделитель;
sludge — густая грязь;
sophisticated — продвинутый, сложный;
species — биологический вид/род;
spill — разливание;
spreading — распыление;
storm water — ливневые воды;
street-flushing operation — поливка улиц;
to be subjected to — подвергаться чему-либо;
surfactants — поверхностно-активные вещества;
suspended matter — взвесь;
to take responsibility (for) — брать на себя ответственность;
tertiary treatment — окончательная очистка;
thirst — жажда;
to trap — захватывать;
trash — cop, мусор, хлам;
treatment plant — станция по очистке, водоочистное сооружение;
turbidity — мутность;
to undergo — подвергаться ч-л;
unsaturated — ненасыщенный;
urine — моча;
vortex — водоворот;
wastewater treatment plants — водоочистная станция, станция водоочистки;
water management system — водохозяйственная система;
water resources composition — состав/структура водных ресурсов;
water table — уровень грунтовых вод;
waterway — водоспуск, водоотвод;
wetland— заболоченное место, сырой участок.
Раздел VIII fire resistance
TEXT A
Переведите интернациональные слова.
aspect, adequate, protection, affect, apparatus, detector, installation, legal, magnitude, code, nature, obligation, ordinary, construction, plan, occupant, prevent, material, provision, range, structural.
Запомните значения слов и словосочетаний.
defence защита;
to eliminate — устранять, исключать, ликвидировать;
combustibles — горючие вещества;
ignition — возгорание, воспламенение;
fire spread — распространение огня;
to meet requirements — следовать требованиям, соответствовать;
mandatory — обязательный, принудительный;
building code — строительные нормы и правила (СНиПы);
fire resistance — огнеупорность, огнестойкость;
magnitude— величина, размер;
fire load— наличие горючих материалов;
Btu (British thermal unit) — британская тепловая единица
(0,252ккал);
extinguishment— гашение/тушение (пожара);
extinguisher — огнетушитель; hose — шланг, пожарный рукав;
sprinkler — разбрызгиватель, пульверизатор, спринклер;
flammable — огнеопасный, легковоспламеняющийся;
live electrical equipment — подключённое электрооборудование.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Fire Protection
There are two aspects of fire protection: life safety and property defence, full property protection being incapable. [It is impossible to eliminate all potential ignition* sources and combustible materials to prevent fire spread so as to protect life and avoid property damage.]0
The first obligation of designers is to meet legal requirements of the mandatory building code.
In accordance with fire resistance requirements buildings are classified as:
Fire-resistive.
Protected non-combustible.
Unprotected non-combustible.
Heavy-timber.
Ordinary.
Wood-frame.
[The nature and potential magnitude of fire in buildings are direct- ly related to the amount and physical arrangement of combustibles.]0 A total amount of combustibles is called the fire load. Fire load is ex- pressed in psf**, with an assumed value of 7000 to 8000 Btu/lb.
All buildings should include provisions for prompt extinguishment of fires. [Devices and apparatus installed for this purpose are to account the nature and amount of combustible and smoke-producing materials.]0 Such apparatus range from small, hand-held extinguish- -
ers for small (ires to hoses attached to a large pressurized water
supply, and automatic sprinklers. Fire and smoke detectors and a protective signalling system to sound an alarm for occupants and call fire ; fighters are also advantageous.
Fire extinguishing methods have developed a classification of combustible materials:
Class A involves ordinary combustibles and is readily extin- guishable by water or cooling, or coating with a suitable applied chemical powder.
Class В involves flammable liquids where smothering and cool- ing agents are effective.
Class С considers live electrical equipment where the extinguishing agent should be non-conductive to cut off current flow, after which an electrically conductive agent is safely used.
Class D involves magnesium, sodium, and powered aluminum. Special powders and trained personnel are necessary to attack such fires.
*To ignite means to start burning or to make something burning. ** psf is a written abbreviation of pounds per square foot.
(1780 п.зн.)
4. Ответьте на вопросы.
What is called the fire load of the building?
What are two diverse aspects of fire protection?
What do you know about a classification of combustible materials?
In what way are buildings classified in accordance with fire resistance requirements?
What devices and apparatus are installed for prompt extinguishment of fires?
Определите части речи, обращая внимание на суффиксы. Переведите.
protect, protected, protecting, protection, protective, protector; ignite, igneous, ignescent, ignitable, ignitability, igniter, igniting, ignition;
extinguish, extinguishable, extinguished, extinguisher, extinguishment, extinguishing;
flame, flameless, flame-out, flame-proof, flaming, flamingly, flammable, flammeous, flamy;
press, pressed, presser, pressing, pressman, pressure, pressurize, pressurized;
conduct, conductive, conduction, conductivity, conductor, semiconductor, conductance, conductibility, conducting.
accord, accordance, accordant, according, accordingly, accorded, accordion.
Переведите устно, определив группу сказуемого.
It is impossible to eliminate all potential ignition sources and all combustible materials.
The first obligation of designers is to meet legal requirements.
Buildings should be planned to prevent the fire spread, to protect life and avoid property damage because of possible fire.
Installed devices and apparatus are to take into account the nature and amount of combustible and smoke-producing materials.
Any type of constructions affects fire-protection-system design through requirements to protect structural members as well as contents of buildings.
Измените предложения по образцу.
They claim that buildings are designed in accordance with the mandatory building codes.
Buildings are claimed to be designed in accordance with the mandatory building codes.
It is claimed that buildings are designed in accordance with the mandatory building codes.
All buildings in this district are reported to be equipped with prompt extinguishment of fires.
Everyone knows that the nature and potential magnitude of fire are related to the amount and physical arrangement of combustibles.
Предельно кратко и информативно расскажите:
о требованиях противопожарной безопасности;
классах горючих материалов;
способах пожаротушения.
TEXT В
Переведите интернациональные слова.
actual, attack, adequate, assembly, calculate, component, condition, detail, degradation, design, document, equivalent, effect, element, erosion, experiment, extensive, ingredient, monitor, panel, period, rating ,regular, separation, service, special, standard, transmission, test.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
fire resistance rating — степень огнестойкости;
calculation — расчёт, прогноз;
listing service — опись, статистические данные;
fire resistance property — огнестойкость;
lintel — перемычка (над проёмом окна или двери);
beam — балка, брус, перекладина;
finishing — обработка, отделка;
specimen — образец, экземпляр;
bearing — несущий, опорный;
heat transmission criteria — критерии теплопередачи;
structural collapse characteristics — параметры обрушения конструкции;
salvage — спасение имущества (при пожаре);
structural integrity — прочность конструкции;
to evaluate — оценивать, определять;
to sustain — выдерживать, справляться;
equivalent thickness — примерная толщина, плотность;
actual thickness — фактическая толщина, плотность;
solid unit— цельная деталь (конструкции);
grouted — залитый раствором, цементом;
required web dimensions — зд. первоначальные размеры конструкции.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания. Fire Resistance Rating
Flire resistance rating is determined by
calculation;
listing service;
testing.
[The calculation is based on researches establishing a connection between materials properties and fire resistance.]0
[The listing service concerns unit size, shape, mix design, ingredients, and even manufacture plants.]0
[The testing covers fire resistance rating of masonry assemblies (walls, columns, lintels, and beams); fire protection for steel columns, plaster and drywall finishing, and such components as clay or shale.]0
The method is not common because of time expenditures to build, cure, and test specimens.
The calculation covers
resistance to the transmission of high temperature through the wall assembly,
resistance to the passage of hot gases through the wall sufficient to ignite cotton waste,
load carrying capacity of load bearing walls, and
resistance to the impact, erosion, and cooling effects of a hose stream on the assembly after exposure to the standard fire.
[The fire Resistance, rating is governed by the heat transmission criteria and is preferable to structural collapse characteristics from the standpoint of life safety and salvage ability for firefighters.]0
Fire testing evaluates the ability to carry design loads and the structural integrity under test conditions. [Fire testing of concrete masonry beams and lintels evaluates the ability to sustain design loads under standard conditions by insuring that the temperature does not exceed 593°C during the rating period.]0
It is important to set up a relationship between the fire resistance and equivalent solid thickness if the same masonry amount in a hollow unit is equal to the actual thickness.
The equivalent thickness of a 100% solid unit or a solid grouted unit is identical to actual purposes. For partially grouted walls where unfilled cells are left empty, the equivalent thickness for the fire resistance rating purposes is that of an ungrouted unit.
Load bearing units are obtainable for 100% solid units, 75% hollow units meeting required web dimensions.
(1 730 п.зн.)
Подберите соответствия и переведите.
flammable (adj.) (А) 1) rapid combustion in which a substance burns, producing heat, light, and flame; 2) burning which causes destruction and is out of control
sprinkler (n) (B) easily set on fire
extinguish (v) (C) to make a fire or light stop burning or shin- ing
fire (n) (D) not damaged or affected by something
disaster (n) (E) to get away from dangerous situation that is
likely to harm you if you do not leave
escape (danger) (F) a sudden event such as flood, storm, or acci- (v) dent to cause great damage or suffering
evacuate (v) (G) the act of starting to burn, or making some
thing do it
ignition (n) (H) to empty a dangerous place by making all
people leave and sending them to a safe place
resistant (adj.) (I) a piece of equipment with holes that is on a ceiling and scatters water if there is a fire
Переведите цепочки существительных.
Inevitability
Legalization inevitability
Processes legalization inevitability
Control processes legalization inevitability
System control processes legalization inevitability
Protection system control processes legalization inevitability
Fire protection system control processes legalization inevitability
Assessment
Rating assessment
Period rating assessment
Resistance period rating assessment .
Fire resistance period rating assessment
Elements fire resistance period rating assessment
Masonry elements fire resistance period rating assessment
Concrete masonry elements fire resistance period rating assessment
Закончите предложения.
The fire resistance rating period of concrete masonry elements can be ...
The calculated method is based on ...
Fire testing of concrete masonry...
Load bearing units are commonly available to include .
The listing service ...
Extensive testing has established ...
The fire resistance rating of concrete masonry is ...
Расскажите о методах, определяющих огнестойкость:
calculation;
listing service;
testing;
Information-to-Swallow (1)
Расположите предложения согласно логике изложения.
1. The method became more effective about 5000 years ago. 2. The ancient people used lenses and mirrors for the purpose. 3. How and where man learnt to produce flame at will is unknown. 4. Maybe, it was made with wood or stone through friction. 5. Fire and water are good servants, but bad masters. 6. The control of fire was the first of humanity's 'know-how'. 7. To early man fire was a religious gift in the form of lightning, forest fires or burning lava. (370 п.зн.)
Дайте тексту название.
TEXT С
1. Переведите интернациональные слова.
model, test, element, component, assembly, guarantee, imitation, evacuation, analyze, architecture, parameter, laminate, practical situa- tion, elevate, limit, computer-processing, formula, calculation, rehabil- itation, total, protection, rating, period.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
building integrity — целостность здания;
severe fire conditions — сложные/жёсткие условия пожара;
to make escape — организовать спасение;
faultless model — точная модель/образец;
feasible— подходящий, годный, осуществимый;
to provide basic data — давать исходные/основные данные;
laminated timber beam — слоённый (клееный) деревянный брус;
steel stud wall — стена, обитая сталью;
concrete slab — бетонная плита;
to assess — оценивать, давать оценку;
building rehabilitation — восстановление здания;
concrete filling — бетонный заполнитель;
drywall — гипсокартон, стена сухой кладки (без раствора);
finish — отделка, покрытие, отделочная обработка.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания. Fire Resistance Analysis
[The fire resistance requirements and building codes ensure building integrity for a certain period of time under severe fire conditions and permit occupants' evacuation and firefighters' access.]0 A key principle is: anyone confronted by fire can turn away from it and make a safe escape.
To meet fire resistance requirements in building codes is to subject specimens to costly and time-consuming fire tests. Current developments have made it possible to analyze and predict fire resistance by faultless models. [Developed to imitate behaviour of beams, columns, floors and walls exposed to fire, such models are feasible under severe fire conditions.]0
Recent models have been programmed to provide basic data for reinforced-concrete columns, multi-layer concrete slabs, laminated timber beams and columns.
[There are numerous formulas either to analyze fire resistance of major building materials or to predict the fire resistance of insulated
steel beams and columns, unprotected steel, load-bearing steel stud walls, and solid and hollow concrete slabs.]0 All such formulas must involve calculations of each component of the assembly.
[These models are proved to determine fire resistance in many situations, particularly when testing is not feasible, such as in assessing installed building elements for the purpose of upgrading structural fire protection in a building rehabilitation ]0 In addition, testing is often not feasible because the assembly is too large for test facilities.
New models are to obtain total information about innovative materials (high-strength concrete under fire conditions, for example) or on new approaches in structural fire protection viz the use of concrete fillings in hollow steel columns to provide improved fire resistance.
If the cells of hollow masonry unit are filled with approved materials (such as sand, gravel, crushed stone, slag, pumice, scoria, shale, clay, slate, expanded fly-ash, cinders, perlite or vermiculite),* the equivalent thickness of the assembly is considered the same as the actual thickness.
Drywall, plaster or stucco finishes are added for architectural reasons and provide extra fire resistance as well.
The high-strength columns are able to bear a higher load than normal-strength concrete without notable damage, the limit of fire resistance period being 2 hours.
(1 980 п.зн.)
slag — stony waste matter separated from metals during the smelting or refining of ore.
Pumice — a very light and porous volcanic rock. Scoria — basaltic lava ejected from a volcano; slag.
Shale — a dark fine-grained laminated sedimentary rock; breaks easily into thin layers.
Slate — a fine-grained rock easily split into flat plates.
Fly ash — fine solid particles of ash carried into the air during combustion.
Cinder — the black pieces left after smth (wood or coal) has burned away; slag.
Perlite — a form of obsidian consisting of glassy globules.
Vermiculite — mineral, an alteration product of mica and other minerals.
(520 п.зн.)
От данных слов образуйте существительные.
dangerous, similar, possible, long, deep, wide, high, distant, real, true, young, satisfactory, comfortable, different, noisy, important, significant, safe, thick, structural, flexible, resistant, sandy, equip, strong, weak, deformed, feasible, innovative, hopeless.
Соедините части предложений (ABC), чтобы получить за- конченное высказывание.
A.
The lire-resistance requirements and building codes...
Current developments have made...
Recent models have been programmed...
Developed to imitate behavior of...
Drywall, plaster or stucco finishes are...
...it possible to analyze and predict fire resistance...
...beams, columns, floors and walls exposed to fire...
...added for architectural reasons, they...
...are to ensure building integrity for a certain period of time under...
...to provide basic data for reinforced-concrete columns, multilayer...
...providing extra fire resistance as well.
...concrete slabs, laminated-timber beams and columns.
...by faultless models.
...such models are feasible under severe fire conditions.
...severe fire conditions and permit occupants' evacuation and firefighters' access.
Объясните пословицы и поговорки.
"То play with fire ".
"Danger foreseen is half avoided
"Fire and water are good servants but bad masters
7. Разгадайте кроссворд.
ACROSS
a bell or other signal to warn people of fire (in two words);
to say that something will happen;
something that is not flammable;
danger;
to prevent something happening;
a large scale destruction, especially by fire;
t
 o
make a fire stop burning
o
make a fire stop burning
Information-to-Swallow (2)
Fire Resistance Studies
To predict and determine fire resistance of hollow steel columns a large number of validated mathematical models and new methods have been developing. Hollow steel columns are very efficient struc-
tural sections for resisting compression loads, but a substantial increase in load-bearing capacity and fire resistance can be achieved by filling them with concrete.
Recently, some types of filling — plain concrete, steel-fibre - reinforced concrete and bar-reinforced concrete — have been studied. However, experimental and theoretical studies on high-strength concrete and concrete-filled steel columns have not been completed yet. (550 п.зн.)
Information-to-Swallow (3)
HIPS*
Innovative fire-resistant coating materials HIPS (developed in Melbourne) are able to withstand temperatures of over 1000° C; current coatings and structures break down at between 150° C-250° C.
HIPS coatings contain an inorganic geo-polymer resin, and a few polymer additives. Geo-polymers are ceramic-like inorganic polymers with a potential to renovate the building industry.
They are not only fire-, blast- and acid-resistant; they are also strong, cast able, sprayable, extrudable, and almost limitless. The polymer additives in HIPS improve flexibility and waterproofing properties, and provide strong adhesion, which are important properties for a coating.
HIPS form thin fireproof coatings on timbers and metals, such as structural or galvanized steel. It can protect brickwork, either as thin costing or as a render put by spray equipment, rollers or brushes.
HIPS do not burn or produce heat, and do not release smoke or toxic chemicals at temperatures up to 1200° C.
* The abbreviation HIPS stands for hybrid inorganic polymer systems. (890 п.зн.)
❖ Подготовьте презентацию наиболее важных событий в области пожаротушения в России и за рубежом с учётом новейших строительных технологий.
Словарь к Разделу VIII
access — доступ;
to account — учитывать, брать в расчёт;
actual thickness — фактическая толщина, плотность;
adhesion — сцепление, схватывание;
alarm — тревога, сигнал тревоги;
alteration — изменение, разновидность;
apparatus — прибор, инструмент, аппаратура;
• applied— практический, прикладной, наложенный;
approved materials— материалы, разрешённые к применению;
arrangements— расположение;
to assess — оценивать, давать оценку;
assumed value — допускаемое значение;
at will — по (своему) желанию;
to attack — приниматься, браться;
beam — балка, брус, перекладина;
bearing — несущий, опорный;
blast— взрыв, ударная волна, напор (воды);
Btu (British thermal unit) — британская тепловая единица (0,252ккал);
building code — строительные нормы и правила (СНиПы);
building integrity — целостность здания;
building rehabilitation — восстановление здания;
by insuring — зд. при условии;
calculation — расчёт, прогноз;
castable — способный плотно заполнять форму;
clay — глина;
to coat — покрывать слоем ч-л;
combustibles — горючие вещества;
concrete filling — бетонный заполнитель;
concrete slab — бетонная плита;
cotton waste — ветошь, хлопковые отходы, пакля;
to cure — отверждать, схватывать(ся);
current flow — электрический ток;
defence — защита;
detector — прибор для обнаружения, детектор;
device — прибор, устройство, механизм;
drywall — гипсокартон, стена сухой кладки (без раствора);
to eliminate — устранять, исключать, ликвидировать;
equivalent thickness — примерная толщина, плотность;
to evaluate — оценивать, определять;
exposure — подвергание (воздействию);
extinguisher — огнетушитель;
extinguishment — гашение/тушение (пожара);
faultless model — точная модель/образец;
feasible — подходящий, годный, осуществимый;
finish — отделка, покрытие, отделочная обработка;
finishing — обработка, отделка;
fire| load — наличие горючих материалов;
fire resistance — огнеупорность, огнестойкость;
fire resistance property — огнестойкость;
fire resistance rating — степень огнестойкости;
fire spread — распространение огня;
firefighter — пожарный;
flammable — огнеопасный, легковоспламеняющийся;
friction — трение;
galvanized steel — оцинкованная сталь;
globule — шарик, капля, глобула;
govern — определять, обусловливать;
grouted — залитый раствором, цементом;
heat transmission criteria — критерии теплопередачи;
heavy-timber building — здание из массивных брёвен;
hollow unit — полая деталь (конструкции);
holocaust — жертвование, самопожертвование, уничтожение, истребление (Holocaust — геноцид евреев нацистами);
hose— шланг, пожарный рукав;
ignition — возгорание, воспламенение;
impact — удар, сильное воздействие;
innovative — новаторский, передовой, рационализаторский;
insulated — изолированный, защищенный, покрытый изоляцией;
jeopardy — опасность, риск;
laminated timber beam — слоённый (клееный) деревянный брус;
lens — линза, оптическое стекло;
lintel — перемычка (над проёмом окна или двери);
listing service — опись, статистические данные;
live electrical equipment — подключённое электрооборудование;
load carrying capacity — грузоподъёмность;
magnitude — величина, размер;
to make escape — организовать спасение;
mandatory — обязательный, принудительный;
manufacture plant — завод-изготовитель, производственное предприятие;
masonry assembly — каменная/кирпичная конструкция;
to meet requirements — следовать требованиям, соответствовать;
mica — слюда;
mix design — подбор состава (бетонной) смеси;
non-conductive — не проводящий ток;
notable — заметный, значительный;
obsidian — обсидиан, вулканическое стекло;
obtainable — достижимый, доступный;
ordinary — обычный, простой;
ore — руда;
plaster — штукатурка;
роrоus — пористый;
to predict— прогнозировать, предсказывать;
preferable — предпочтительный;
pressurized — находящийся под давлением;
prompt — срочный, быстрый, немедленный;
property — свойство, качество;
to provide basic data — давать исходные/основные данные;
provision — обеспечение, оборудование, оснащение;
refining — очистка, рафинирование (металла);
render— нижний слой штукатурки;
to renovate— модернизировать, перестраивать;
required web dimensions — зд. первоначальные размеры конcтрукции;
research — (научное) исследование, изучение;
safety — безопасность;
salvage — спасение имущества (при пожаре);
severe fire conditions — сложные/жёсткие условия пожара;
shale — глинистый сланец;
smelting — плавка, выплавление;
to smother — гасить, тушить, душить;
solid unit — цельная деталь (конструкции);
specimen — образец, экземпляр;
sprinkler — разбрызгиватель, пульверизатор, спринклер;
standpoint — позиция, точка зрения;
steel stud wall — стена, обитая сталью;
structural collapse characteristics — параметры обрушения конструкции;
structural integrity — прочность конструкции;
stucco — наружная штукатурка;
substantial— действительный, значительный, большой;
to sustain — выдерживать, справляться;
testing — испытание, исследование, апробирование;
time expenditures — временные затраты;
to turn away — обойти, избежать;
upgrading — модернизация, совершенствование;
validated — утверждённый;
to warn — предупреждать;
to withstand— выдерживать, противостоять;
wood-frame building — деревянное здание рамной конструкции.
Ключ (см. Кроссворд на стр. 173):1. fire alarm; 2. predict; 3. non-combustible; 4. jeopardy; 5. avoid; 6. holocaust; 7. extinguish
Раздел IX
HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING TEXT A
Переведите интернациональные слова.
dam, barrier, primary, function, natural, reservoir, tunnel, structure, navigation, irrigation, canal, hydraulic, engineering, project, potential, pressure, catastrophe, stability.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
dam — дамба, плотина;
to impound — запруживать (воду);
valley — долина; пойма (реки);
reservoir line — линия/уровень водохранилища;
stream channel — русло реки;
to flank — располагаться по обе стороны;
embankment — дамба, плотина, набережная;
harbour — гавань, порт;
canal— канал (искусственный), русло, канава;
hydraulic engineering project — гидротехническое сооружение;
virtual conditions — вероятные условия/обстоятельства;
seepage — течь, просачивание;
to divert — отводить, направлять в другую сторону;
cofferdam — перемычка, водонепроницаемая крепь;
tunnel — тоннель, труба.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Hydroengineering Objects
[Dam is a barrier to stop, control, and impound water flows. One of the best places for it is a narrow part of a deep river valley, the val- ley sides acting as natural walls. The primary function of the dam's structure is to fill the gap in the natural reservoir line left by the stream channel. The most economical arrangement is a masonry dam flanked by earth embankments.]0
Water supply systems are among the earliest mankind's attain- ments; all early civilizations were agricultural and depended on irriga- tion. Harbours and canals as well as numerous dams are the oldest
engineering achievements. Being grouped together such systems are known as hydraulic engineering projects.
[Since stability, strength, and reliability of hydroengineering objects are of obligatory construction demands, much preliminary work should be fulfilled (especially under diverse virtual conditions)]° to predict and avoid catastrophes:
Analysis of all potential stresses which huge structures can be subjected to (including earthquakes and seasonality);
Testing of the velocity and pressure of the water that is being blocked to keep away from seepage;
All flow characteristics of the dammed stream or river should be found out and taken into consideration.
Yet, it is necessary to survey whether the flow should be diverted or the dam is to be constructed with the cofferdams1. To divert rivers the following contemporary techniques can be used:
digging tunnels for the channel;
excavating a temporary channel for the river around the dam site.
*Cofferdam is a watertight enclosure pumped dry to permit construction work below the waterline.
(1 370 п.зн.)
4. Подберите варианты и переведите.
Hydraulics (A) is an area of land between two lines of hills or
mountains, usually with a river flowing through it.
Harbour (B) is a barrier to stop or control the flow of wa
ter.
Stream (C) is a wide wall of stones or earth built to keep
water in a river from flowing over its banks.
Valley (D) is a scientific study of the moving liquids use.
Dam (E) is a natural flow of water that moves across
the land and is narrower than a river.
Gap (F) is a space between two objects or two parts of
an object because something is missing.
Embankment (G) is an area of water next to the land where the
water is calm, so that ships are safe to be inside it.
Расположите предложения согласно логике изложения.
1. Masonry dams are to control swift-flowing streams in narrow valleys with apt rock for foundations (the Hoover Dam). 2. As for embankment dams they are really great mounds of earth across wide streams where the water flows rather slowly. 3, Before the era of Portland cement massive blocks of cut stone were commonly used. 4. Compact earth dams are to be built with crushed rock or sand (the Aswan High Dam). 5. There are two basic types of construction for dams — masonry and embankment. 6. To control water flows was one of the first of humanity's 'know-how'. 7. Today, masonry dams are constructed with reinforced concrete.
Определите части речи, обращая внимание па суффиксы.
excavate; excavation; excavator; excavating; excavated;
achieve; achievement; achievable;
obligatory; obligate; obligated; obligation; oblige; obligor; obligee; obliging; obligingly; obligingness;
differ; difference; different; differentia; differentiae; differential; differentiate; differentiation; differently;
season; seasonable; seasonably; seasonal; seasonality; seasoned; seasoning;
navigation; navigability; navigable; navigate; navigating; navi- gational; navigator; navy;
significance; insignificancy; significant; signification; significa- tive; signify; signified; signifier
Вставьте нужное слово (canal или channel).
The Suez was originally opened in 1869, closed in 1967
because of warfare in the area, and reopened in 1975.
One of the most important — building projects of recent
times was the St. Lawrence Seaway constructed jointly by the USA and Canada.
A is an artificial for water used for irrigation and navigation.
Most of the rivers and ports of Europe are connected by a net- |
work of intricate to carry a large proportion of the commerce of |
this highly industrialized region.
The Hoover Dam supplies water to city of Los Angeles, with
which it is connected by a series of , tunnels, and aqueducts
across deserts and mountains of the southwest United States.
There is the most efficient irrigation system in the region to water to the crops.
Great Britain, the largest island in the northwest of Europe, is separated from Ireland by the Irish Sea and from the Continent by the English ... ... and the Strait of Dover.
Письменно переведите фрагменты текста [...]0
Составьте аннотацию к тексту. TEXT В
Выпишите из текста интернациональные слова (не менее 12).
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
flood control— регулирование паводков;
hydroelectric power — гидроэлектроэнергия;
power station — электростанция;
navigation lock — судоходный шлюз;
spillway facility — водосбросное сооружение, водосливная плотина;
auxiliary structure — вспомогательное сооружение;
screen — фильтр, заграждение, решётка;
duct — канал, проток, трубопровод;
powerhouse— генераторная силовая станция, электростанция;
penstock — напорный трубопровод, затвор (гидротехнический);
masonry dam — плотина из каменной кладки;
embankment dam — земляная, каменно-набросная плотина;
gravity dam — гравитационная плотина (с обеспечением устойчивости действием собственного веса);
arch-gravity dam — гравитационная арочная плотина;
buttress dam — контрфорсная плотина (с использованием подпор/быков);
earthfill dam — земляная насыпная плотина;
rock-fill dam — каменно-набросная, каменная плотина.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Dams: Types and Structure
The most impressive hydraulic engineering achievements are the Aswan High Dam (Egypt), the Daniel-Johnson Dam and the Quebec Dam (Canada), the Glen Canyon Dam and the Hoover Dam (the USA), and the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River (China)
which is more than five times the size of the Hoover Dam. The tallest dam in the world is the 300-meter-high Nurek Dam (Tajikistan).
[A large reservoir formed by the dam is for flood control, industrial and domestic water supply improvement, water storage, irrigation, navigation, hydroelectric power (generating electricity) and recreational areas.]0 Yet, it can link a highway or roadway systems across.
[In order to complete such diverse tasks a hydropower development on the river is to include a power station, navigation locks, spillway facilities, canals and tunnels to discharge floods, and other auxiliary structures. ] 0
Some other openings are necessary if the dam is used for irrigation or generating electricity. For these purposes gates are built to release water through. Gates are equipped with screens not to pass floating objects. The ducts carrying water to turbines in a powerhouse are called penstocks. Some dams have fish ladders allowing fish in the river to travel past the dam to or from their breeding grounds.
The most popular dams are:
Masonry dam (built of some kind of masonry such as cut stone, concrete, etc).
Embankment dam (built with a fill of compacted earth, crushed rock, etc).
Gravity dam (in which water is held back by the weight of the structure).
Gravity-arch dam (a gravity dam curved in an arch or semicircle).
Buttress dam (a masonry dam which is strengthened by buttresses).
Earthfill dam (an embankment dam in which the principal material is compacted earth).
Rock-fill dam (an embankment dam in which the principal material is crushed rock that has been compacted). (1 630 п.зн.)
4. Ответьте на вопросы.
What is a dam? What is it used for?
What is a masonry dam?
What is embankment dam built with?
What is the difference between a masonry dam and an embankment dam?
What is a gravity dam?
What is a gravity-arch dam?
How is a buttress dam strengthened?
What is the difference between an earthfill dam and a rock-fill dam?
Расскажите о типах плотин.
Переведите, обращая внимание на 'to'-формы.
То solve different problems a hydropower development may consist of a power station, navigation locks, spillway facilities, canals and tunnels to discharge floods, and other auxiliary structures.
Some dams are equipped with fish ladders allowing fish in the river to travel past the dam to or from their breeding grounds.
Gates are built to release water through; gates equipped with screens prevent floating objects from passing.
List of Dam Types
i
Masonry dam, embankment dam, gravity dam, gravity-arch dam, buttress dam, bank protection dam, coast protection dam, boulder dam, cantilevered-type steel dam, concrete dam, earthfill dam, rock-fill dam, A-Frame dam, and others.
TEXT С
Переведите интернациональные слова.
engineering, geological, stability, peak, reservoir, human, compensation, population, relocation, archeological, cultural, toxic, affect, ecology, period, stable, contribute, seismic, traditional, tend, transmission, alternative.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
permeability — проницаемость, проходимость;
landslide — обвал, оползень;
slope stability — устойчивость откоса;
water table — уровень грунтовых вод;
peak flood flow — пик объёма стока паводка;
reservoir silting — заиление, заращивание водохранилища;
suspended sediments — взвешенные наносы;
to scour (out) — промывать, вымывать;
riverbed — речное русло;
riverbank — речной берег;
fossil fuel — ископаемое топливо;
vulnerable — уязвимый, восприимчивый;
glacial melting — таяние ледников.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Hydraulic Engineering Objects: the Pros and Cons
There are some very serious engineering and geological considera- tions about dams' construction:
permeability of the surrounding rock or soil;
earthquake faults;
landslides and slope stability;
water table;
peak flood flows;
reservoir silting;
environmental impacts on river fisheries, forests and wildlife;
impacts on human habitations;
compensation for land being flooded as well as population re- location;
loss of archeological or cultural matters underwater;
removal of toxic materials and buildings from the proposed re- servoir area.
[Reservoirs affect river ecology, whilst rivers below dams expe-
rience long periods of very stable flow conditions. Water containing suspended sediments scours out riverbeds and riverbanks. Large servoirs contribute to seismic activity of the region because of changes in water load and the height of the water table.]0
The impact on human society is also significant. Approximately 40-80 million people worldwide are known to have been displaced from their homes in the result of dam construction.
Hydroelectric plants are large-scale projects compared to tradition- al ones based on fossil fuels. New sites tend to be far from population centers and necessitate extensive power transmission lines. [Hydroe-
lectric generation is vulnerable due to seasonality, glacial melting ground and surface water levels. Additional expenses are possible during low water periods.]0
However, hydroelectric power is comparatively cheap and reliable, consuming no fuel and being ecological. As an alternative energy source it is cheaper than both nuclear and wind power.
(1 400 п.зн.)
Письменно переведите фрагменты текста[…]0
Ответьте на вопросы.
What should be taken into consideration before hydraulic engineering projects implementation?
How can reservoirs affect rivers ecology?
Why do reservoirs contribute to seismic activity of the region?
What makes hydroelectric generation vulnerable?
What are the main advantages of hydroelectricity use?
Расскажите об особенностях гидротехнического строительства.
TEXT D
Переведите интернациональные слова.
routine, deformation, catastrophic, structural, collapse, monitoring, functional, mechanism, virtual, problem, destruction, installation, identification.
Запомните слова и словосочетания.
dam failure — прорыв плотины, авария;
to breach — пробивать брешь, проламывать;
deformation monitoring — текущий контроль/наблюдение за целостностью (плотины);
remedial action — устранение неисправностей, ремонт;
structural collapse — разрушение сооружения;
rock grouting — напорное инъецирование раствора, цементирование трещин в плотине; cement slurry — цементный раствор;
fractured rock — зд. дефектная (покрытая трещинами) конструкция плотины;
installation containing dangerous forces — объект повышенной опасности;
massive destruction — массовое разрушение/уничтожение;
early warning system — система раннего предупреждения;
levee — (земляная) дамба, плотина, мол;
dike — (защитная) дамба, плотина, запруда, перемычка;
spillway design error — ошибка в проектировании/строительстве
водосбросных сооружений;
water level — горизонт вод;
filling — наполнение/заполнение (водохранилища);
poor surveying— недостаточная разведка/анализ;
poor maintenance — плохое содержание/техническое обслуживание;
outlet pipe — выпускная труба, водовыпуск.
3. Прочитайте текст и выполните задания. Dams Failures
[Dam failures are catastrophic if the structure is breached or dam- aged.]0 Routine deformation monitoring of seepage in and around
dams is necessary to anticipate virtual problems and permit all re-
quired remedial actions before actual structural collapse occurs.
Most dams are well-equipped with functional mechanisms for such
problems. [Another solution is rock grouting (pressure pumping Port- land cement slurry into fractured rock). ]°
During military operations a dam is considered 'an installation containing dangerous forces' due to the massive destruction of the civilians and the environment. Dams are protected by International Humanitarian Law (IHL). To ease the identification, a protective sign — three bright orange circles on the same axis — is defined by the rules of IHL.
Since 2007 early warning systems for levee /dike failures have been used. Destruction processes are monitored by an international group of companies and scientific institutions.
The main dam failure causes to be taken into consideration are:
spillway design error;
geological instability caused by changes to water levels during filling or poor surveying;
poor maintenance, especially of outlet pipes;
extreme rainfall;
human, computer or design error. (1 060 п.зн.)
4. Переведите цепочки слов.
Processes
Development processes
Strategy development processes
Testing strategy development processes
Model testing strategy development processes
Behavior model testing strategy development processes
Dam behaviour model testing strategy development processes
Standard dam behavior model testing strategy development processes
Observation
Law observation
Development law observation
Monitoring development law observation
Defect monitoring development law observation
Foundation defect monitoring development law observation
Dams foundation defect monitoring development law observation
Analyses
Work analyses
Agency work analyses
Control agency work analyses
Quality control agency work analyses
Production quality control agency work analyses
Structure production quality control agency work analyses
Concrete structure production quality control agency work analyses
Определите части речи, обращая внимание на суффиксы.
construct, construction, constructional, constructionist, constructive, constructivism, constructor; constructiveness;
stability, stabilization, stabilize, stabilized, stabilizer, stabilizing, stable;
invention, inventiveness, invent, inventor, inventive, inventively;
form, formal, formalism, formalist, formalistic, formality, formalize, formally, format, deformation;
human, inhumane, humanely, humaneness, humanity, human- made, humanism, humanist, humanistic, humanitarian, humanize, hu- mankind
Соедините части предложений (AB), чтобы получить за- конченное высказывание.
Dam failures are disastrous if...
It is obligatory to foresee any possible problems and permit all remedial actions...
Any dam is to be thought an 'installation containing dangerous forces' because of...
International Humanitarian Law (IHL)...
The destruction process is monitored by...
...the structure is breached or out of order.
...protects dam constructions all over the world.
...sensor networks from an international group of companies and scientific institutions.
...the colossal danger to the population and the environment.
...before actual structural collapse occurs.
Information-to-Swallow
Historical Highlights
A word 'dam' originates with Middle Dutch. 'Amsterdam' and 'Rotterdam' are noteworthy proofs for it. (The central square of Amsterdam is the Dam Square or simply the Dam).
The oldest dam in Spain has been in use for almost two millennia. The earliest dam in Jordan was built in 3000 ВС.
The Ancient Egyptian dam (102m long and 87m wide) was destroyed by heavy rain in 2800 ВС.
in Roman Empire first dams were 'to plan and organize engineering construction on a grand scale' to provide water supply during dry seasons; special water-proof hydraulic mortar and concrete were used. Roman engineers demonstrated a high degree of inventiveness. Numerous survived arch-gravity dams, arch dams, buttress dams, multiple arch buttress dams, embankment dams, masonry gravity dams, and first dam bridges (the Valerian Bridge in Iran) are historical evidenced of high-standard hydroengineering construction.
The oldest structure in South India (the 1st century AD) is still in use.
The earliest irrigation system in China (251 ВС) with an enormous irrigation reservoir (62 miles in circumference) still works properly.
The era of mega-dams was initiated after the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River in 1936.
( 1000 п.зн.)
7. Письменно составьте аннотацию текста об истории плотин.
❖ Подготовьте презентацию наиболее важных событий в области сооружения плотин в России и за рубежом с учётом новейших строительных технологий.
Словарь к Разделу IX
to anticipate — предвидеть, упреждать;
apt — подходящий, соответствующий;
arch-gravity dam — гравитационная арочная плотина;
attainments — знания, навыки;
auxiliary structure — вспомогательное сооружение;
below — ниже;
boulder dam — дамба/плотина из валунов;
to breach — пробивать брешь, проламывать;
breeding — размножение, разведение;
buttress dam — контрфорсная плотина (с использованием подпор/быков);
canal — канал (искусственный), русло, канава;
cantilevered — консольный, свисающий, заделанный одним концом;
cement slurry — цементный раствор;
circumference — окружность.
civilians — гражданское население;
cofferdam — перемычка, водонепроницаемая крепь;
to compact — сдавливать, спрессовывать;
to complete — выполнять, доводить до конца;
dam — дамба, плотина;
dam failure— прорыв плотины, авария;
dammed stream — запруженный поток;
deformation monitoring — текущий контроль/наблюдение за целостностью (плотины);
to dig (dug) — копать, рыть;
dike — (защитная) дамба, плотина, запруда, перемычка;
diverse — разнообразный, разный, многообразный;
to divert — отводить, направлять в другую сторону;
duct — канал, проток, трубопровод;
early warning system — система раннего предупреждения;
earthfill dam — земляная насыпная плотина;
embankment — дамба, плотина, набережная;
embankment dam — земляная, каменно-набросная плотина;
enclosure — ограда, ограждение;
enormous — огромный;
to equip — оснащать, снабжать, оборудовать;
expenses — расходы, издержки, затраты;
extensive — обладающий большой протяжённостью;
to fill a gap — заполнить промежуток, поставить преграду;
filling — наполнение/заполнение (водохранилища);
to find out — выяснять, обнаруживать;
to flank — располагаться по обе стороны;
to flood — затоплять, наполнять;
flood — подъём воды, переполнение, поток;
flood control — регулирование паводков;
fossil fuel — ископаемое топливо;
fractured rock — зд. дефектная (покрытая трещинами) конструкция плотины;
to fulfill — выполнять, осуществлять, совершать;
gate — зд. затвор;
glacial melting — таяние ледников;
grand scale — крупный/огромный масштаб;
gravity dam — гравитационная плотина (с обеспечением устойчивости действием собственного веса);
harbour -— гавань, порт;
hydraulic engineering project — гидротехническое сооружение;
hydroelectric power — гидроэлектроэнергия;
hydroengineering object — гидротехнический объект;
hydropower development — гидроэнергетическое строительство;
to impound — запруживать (воду);
improvement — улучшение, усовершенствование;
installation containing dangerous forces — объект повышенной опасности;
inventiveness — изобретательность, мастерство;
irrigation — полив, орошение;
to keep away from — избегать ч-л;
landslide — обвал, оползень;
levee — (земляная) дамба, плотина, мол;
to link — соединять, связывать, смыкать;
masonry dam — плотина из каменной кладки;
massive destruction — массовое разрушение/уничтожение;
to monitor— наблюдать, отслеживать, контролировать;
mound — насыпь, холм;
navigation — навигация, судоходство;
navigation lock — судоходный шлюз;
to necessitate — неизбежно влечь за собой, вызывать необхо- димость;
noteworthy proof— заслуживающее внимания доказательство;
obligatory — непременный, обязательный, обязывающий;
opening—канал, пролив, окно;
outlet pipe — выпускная труба, водовыпуск;
peak flood flow — пик объёма стока паводка;
penstock — напорный трубопровод, затвор (гидротехнический);
permeability — проницаемость, проходимость;
poor maintenance — плохое содержание/техническое обслу- живание;
poor surveying — недостаточная разведка/анализ;
power station — электростанция;
power transmission line — линия электропередачи, ЛЭП;
powerhouse — генераторная силовая станция, электростанция;
proposed reservoir area — предполагаемая площадь зеркала водохранилища;
to release—выпускать, пропускать;
reliability—надёжность;
remedial action — устранение неисправностей, ремонт;
reservoir — резервуар, бассейн, водохранилище;
reservoir line — линия/уровень водохранилища;
reservoir silting — заиление, заращивание водохранилища;
riverbank — речной берег;
Р.А. Шамёнова, С.А. Кулиш 1
СОВРЕМЕННОЕ СТРОИТЕЛЬСТВО 1
УЧЕБНОЕ ПОСОБИЕ ПО АНГЛИЙСКОМУ ЯЗЫКУ для строительных специальностей вузов 1
Urban Planning 8
Part Two 10
B. 11
6. Подберите подходящий обсудите предложения. 12
7. Ответьте на вопросы. 12
8. Соедините предложения, чтобы получить краткое содержание текста. 12
А. 44
C. 44
6. Сложите предложения, чтобы получить пересказ текста. 45
TEXT В 45
1. Переведите интернациональные слова. 45
А. 76
B. 76
А. 133
B. 133
A. 163
spillway design error — ошибка в проектировавнии/строительстве водосбросных сооружений;
spillway facility — водосбросное сооружение, водосливная плотина;
stable flow conditions — устойчивый режим потока;
stream channel — русло реки;
structural collapse — разрушение сооружения;
to be subjected to — подвергаться ч-л;
to survey — (тщательно) исследовать, изучать;
suspended sediments — взвешенные наносы;
temporary channel — временный канал;
tunnel — тоннель, труба;
valley — долина, пойма (реки);
virtual conditions — возможные/вероятные вия/обстоятельства;
vulnerable — уязвимый, восприимчивый;
water level — горизонт вод;
water had— гидродинамическая нагрузка;
water storage — водохранилище, водные запасы;
water table — уровень грунтовых вод;
water-proof— водоупорный, водонепроницаемый;
watertight — водонепроницаемый;
whilst — пока.
БИБЛИОГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ СПИСОК
Английский для технических вузов: учеб. изд. / С.Г.Дубровская, Д.Б.Дубина ; М.: АСВ, 2010.
Англо-русский, русско-английский словарь технических терминов по отоплению, вентиляции, охлаждению, кондиционированию, теплоснабжению и строительной теплофизике/ В.Д. Коркин, Ю.А. Табунщиков, М.М. Бродач ; М.: АВОК-ПРЕСС, 2001.
Англо-русский словарь по строительству и новым строительным технологиям / А.А. Поздняков, В.В. Быков. — 3-е изд., стереотип. М.: Русский язык; Медиа, 2008. Большой англо-русский словарь: в 2 т. / Под общ. руковод. И.Р. Гальперина. М.: Русский язык, 1979.
Мюллер В.К. Большой русско-английский и англо-русский словарь. М.: Эксмо, 2007.
Коноваленко Ж.Ф. Language оf Communication. Английский для успешной коммуникации. СПб.: КАРО 2009.
Мир городов. №5 (декабрь 2009/январь 2010).
Современный город: пособие по английскому языку для студентов строит, спец. вузов / Е.В. Горбунова, М.М. Гришина, Н.И. Иванова и др. М.: Высш.шк., 1986. Building & Construction Dictionary English-Russian/MtL/L&H Co. Copenhagen. Building Design and Construction Handbook, 6th ed., 2000.
Construction Site Work, Site Utilities, and Substructures Databook / Sidney M. Levy, Tech books, 2001.
A Guide to Site Planning and Landscape Construction. /Harvey M.Rubenstein, Chiche ster; Wiley, 1996.
Housing Finance Systems for Countries in Transition. Principles and Examples. /New York and Geneva, 2005.
Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English. /Edinburgh Gate, Harlow. Reuters, August 20,2010.
Suggestions to Promoters of Town Planning Schemes, Royal Institute of British Archi- tects, Journal 3rd ser. 18 (August 26, 1911).
Sustainable Landscape Construction: a Guide to Green Building Outdoor, J. William Thompson, Kim Sorvig, Island Press, 2007.
The Oxford-Duden Pictorial English Dictionary, Oxford University Press, 1991. The people's dictionary of the English language, Noah Webster, W. A. Wheeler. London: Bell and Daldy.
Time-saver Standards: Site Construction Details Manual. Nicholas T. Dines, Kyle D. Brown, New York; Bogota; McGraw-Hill, 1999.
Town Planning into the 21 th Century. Andrew Blowers and Bob Evans, London, 1997.
www.all-about-wastewater-treatment.com
http://inro.ox.ac.uk/bnc (British National Corpus)
www.csiro.au/news/HlPS-fireproof-coatings.htmlwww.library.cornell.edu
http://www .engineering.com/Hoover- Dam- Вypass.aspx
www.homeenglish.ru
http://www./HTML/TransporterBridge.html www. mosvodokanal .ru www.multitran.ru www.inventors.about.com
Приложение 1
СПИСОК УСЛОВНЫХ ОБОЗНАЧЕНИЙ И СОКРАЩЕНИЙ
AC system (air conditioning system) — система кондиционирования воздуха;
A.D. — Anno Domini (лат.) — новой эры, нашей эры;
ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers) — Американское общество инженеров по отоплению, холодильной технике и кондиционированию воздуха;
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) — Американское общество испытаний и материалов;
B.C. (Before Christ) — до нашей эры;
BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) — окисляемость, биохимическая потребность в кислороде (БПК);
Btu (British thermal unit) — Британская тепловая единица (БТЕ) — 0,252ккал);
С° (Centigrade) — по шкале Цельсия, стоградусный;
CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) -— хлорфторуглерод, фреон;
COD ( chemical oxygen demand) — химическая потребность в кислороде (ХПК);
e.g. (exempli gratia (лат.) — for example — например;
ctc. (et cetera (лат.) — и так далее;
F° (Fahrenheit) — по шкале Фаренгейта (0°C=32°F);
Fig. (figure) — рисунок, чертеж;
ft. (foot) — фут, мера длины (30,48см);
GHS (greenhouse gases) — парниковые газы;
HIPS (hybrid inorganic polymer system) — гибридная неорганическая полимерная смесь;
HVAC (heating, ventilating, and air conditioning) — отопление, вентиляция и кондиционирование воздуха (ОВКВ);
HVACR (heating, ventilating, air conditioning, and refrigeration) — отопление, вентиляция, кондиционирование и охлаждение воздуха (ОВКОВ);
IAQ (indoor air quality) — качество воздуха внутри помещения;
ICI (institutional, commercial, industrial wastewater) — сточные воды промышленных, коммерческих, общественных предприятий;
i.e. (id est (лат.) — that is — то есть;
IHL (International Humanitarian Law) — международное гуманитарное право;
in. (inch) — дюйм, мера длины (2,54см);
km/h (kilometres per hour) — километры в час;
kW (kilowatt) — киловатт (кВт);
kWh (kilowatt-hour) — киловатт-час (кВт/ч);
lb. (libra (лат.) — фунт (327,45г);
psi. (pounds per square inch) — фунты на квадратный дюйм;
Р.Т.О. (please, turn over) — см. на обороте;
SS (suspended solids) — взвешенные твёрдые частицы;
ТОС (total organic carbon) — общий органический углерод;
• TOD (total oxygen demand) — общая потребность в кислороде (ОПК);
UV (ultraviolet) — ультрафиолетовое излучение;
v.v. (vice versa) — наоборот, обратно, противоположно;
viz (videlicet (лат.) — а именно, то есть;
vs. (versus (лат.) против, относительно;
WTPD (World Town Planning Day) — Всемирный день городского планирования.
Приложение 2
QUESTIONNAIRE
Раздел I: urban (town) planning
What is urban planning used for?
How do you understand the notion 'urban renewal'?
Why should be a town planning scheme based on a large-scale survey?
How is, the information obtained from the surveys summarized?
What can make up the individuality of a town from an architect's point of view?
The closest attention should be focused on traffic facilities, shouldn't it? Why?
What can traffic do within urbanized areas unless properly managed?
Why is zoning so important in town planning?
What does successful urban planning consider?
How can urban planning 'take its cues' from nature?
How do you understand the notion 'sustainability' as regards town planning?
When was the Town-planning Code of the Russian Federation passed?
Where and when did the concept of the garden city arise?
How did the modernist city solve the problem of disorder, congestion and small scale?
Why did many cities subsidize housing blocks throughout the late 1940s and 1950s?
What is the most prominent example of an entire modernist city?
The initial plan of a city is quite necessary, isn't it? Why?
How do you understand the notion 'organic settlement'?
When did architectural and landscape complexes appear?
When did town planning appear as profession?
What key urban needs are to be considered in town planning?
When is World Town Planning Day celebrated?
When was the international organization for WTPD founded?
How can WTPD advance public and professional interest in planning?
Раздел II: buildings and their functions
What is a building?
How do buildings serve needs of society?
When was the first shelter for a human built?
How did the most ancient homes on the territory of Russia look like?
Who are considered to be the first builders known to mankind?
Buildings have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, haven't they?
Why did buildings become higher?
Give definition of a multi-storey building.
What is a 'structural height' in technical usage?
What buildings are called Mow-rise' ones?
How do you understand the notion 'internal infrastructure of a building'?
What are conveying systems to transport people in large buildings presented by?
What is the main objective of modern construction practice?
What is a 'real estate development'? . 15. Mow do industrialization and advancement in technology influence building types?
How can creative imagination help to form the beauty and grandeur of cities?
What main types of buildings do you know?
What is land use?
What three types of construction projects do you know?
What main factor creates the need for design professionals?
Explain the sentence "A construction project is a complex net of contracts."
What professionals may the project team include?
What must all buildings comply with?
Who are 'developers'?
Раздел III: construction site
How does human habitat expansion relate to construction?
What exact steps should be undertaken before any construction begins?
What methods of establishing a site for construction do you know?
What is the primary reason for choosing a site location?
What professionals practice site planning?
Why is a program development of the site required for the project implementation?
How can you explain the notion 'a site'? Give definition.
What does a site analysis help to understand? 9. What is a site inventory?
What components go into a site analysis?
What legal information can be obtained from the deed to the property?
How is the site inventory completed?
What is a site analysis to form?
What does synthesis, based on a land use plan, evolve from?
What must be done to all design details to obtain the best possible site design?
Why should be site investigation made concurrent with the formulation of program objectives?
What should sustainable design consider?
What is the designer's challenge in creating a site design?
What stage of the design process does site planning refer to?
What does this stage involve?
What does a program of the site deal with?
What is program development based on?
Why is this program a constant process of refinement?
What do precedence relations between activities signify?
What natural sequences exist for construction activities?
What does the choice of appropriate technology involve?
What is the civil/site engineer responsible for?
What activities does site preparation involve?
What can be ground contaminated with?
What recyclable materials do you know?
How do you understand the notion 'prescribed topography'?
How does importing-exporting soil add to cost of a project?
Why is it necessary to ensure a level base on the site?
Of what quality, you think, should soil be to erect an object on?
What determines location and utilization of all site elements?
What helps to meet established deadlines?
What requirements must be followed in oil, fuel, and chemicals storing?
What are bunds used for?
What are the rules of setting up generators at a site?
How must the plant storage and refueling areas be established?
Why is it vital to have an up-to-date drainage plan of the site?
Who is legally responsible for storing and transporting waste materials?
How can be a standard site clearance achieved?
What are initial points of any construction planning?
Why is the construction plan development a critical task in the management of construction?
How does development of construction plan differ from its formation?
What essential elements are to be considered to form a good construction plan?
Who has to imagine the construction object as given in the plans and detailed descriptions?
What consequent phases does any construction project go into?
What makes construction management an art?
Why is construction the most dangerous land-based work?
What are leading safety hazards and risks on site?
What should be done to minimize hazards and risks on site?
Раздел IV: building materials
What are building materials?
What main categories of building materials do you know?
Where are synthetic building materials made?
What building materials are used for?
Choice of building materials is almost unlimited, isn't it?
What factors determine the choice of materials?
What building material is the predominant one in this modern age?
What is concrete composed of?
What main concrete extensions do you know?
What's the composition of cement?
How is cement used in building industry?
What is aggregate?
What types of aggregate do you know?
What are chemical admixtures in production of concrete used for?
What main types of concrete do you know?
How can be the process of hydration described?
Why is it necessary to reinforce concrete with other materials?
How is air entrained into concrete structure eliminated?
Why is it preferable to use mass concrete structures in heavy construction?
What are advantages of ready concrete delivery to the site?
What purpose is prestressed concrete used for?
What are physical properties of concrete?
What is cement?
What are aggregates used for?
Where are aggregates taken from?
What was the composition of ancient Roman concrete?
Mow did the Romans use concrete?
Why did many ancient Roman structures survive to the present day?
Who made the first modern concrete? When?
Who invented the first true artificial cement? When?
How is metal used in construction?
What metal is the usual choice for metal structural building material?
What are standard commonly used structural steels?
What are physical properties of steel used in construction?
What should be done to prevent structural steel from weakening in the event of fire?
What are the main advantages of steel structures use?
What are the physical properties of glass and how is it obtained?
Where is glass used?
What are physical properties of plastics?
Where are plastics used?
What structure do foams have?
Where are foams used?
What are paints and how are they used?
What are pigments incorporated into the paint for?
Why are fillers used?
Why is it necessary to use a binder in paint composition?
What are paint application techniques?
What are bricks composed of?
What processes of brick formation do you know?
Which of the production methods is the most economical?
How are extruded bricks made?
How is calcium silicate bricks processed?
What does the colour of the bricks depend on?
How can be bricks classified due to the perforations produced?
What is a major world topic considering availability and sustainability of construction materials?
Раздел V: energy and its sources
What do we need energy for?
What are major types of fossil fuels?
What process do fossil fuels require to produce energy?
Why is uranium one of the most perspective sources of energy?
What renewable sources of energy do you know?
What sources of energy (both renewable and non-renewable) do you know? Give definition of the word 'renewable'.
Why does humanity need to look for alternative energy sources?
Why do people oppose nuclear energy use? Do you agree with these reasons?
Mow does a nuclear power plant work?
What are the main disadvantages of nuclear power production?
What are the main characteristics of modern alternative energy types?
What alternative sources of energy do you know?
Раздел VI: the building infrastructure
Why should be a huge amount of installations made within buildings?
What equipment should be installed in modern buildings?
What do communication systems serve to?
What makes our dwellings comfortable for living?
What is air conditioning?
Why is it necessary to install air conditioning systems in different building types?
How does type of building affect choice of air conditioning?
What cycle do most air conditioning systems utilize?
When was the first refrigeration system invented?
When appeared the first viable commercial refrigeration system?
What are the main components of any compression refrigeration system?
What are less common methods to cool buildings?
What is condenser used for?
What types of cooling mediums are there?
What purpose does refrigerant serve to within the system?
What is a heat exchanger?
How does air conditioner work?
What do we call 'direct expansion system'?
What types of refrigerants do you know?
How does toxicity influence the type of refrigerant identification?
What for are split systems used within buildings?
How does the system work?
Where and when is the use of split systems preferable?
Why should be all the trunks and ducts well insulated?
How is constant temperature maintained within a building?
What factors does the required amount of heat depend on?
What are the causes of the main heat losses?
What should be taken into consideration as regards heat losses before a building construction?
Who and when created the first ice-making machine?
When was the first 'ancestor' to modern air conditioner made?
When appeared the first window air conditioners?
What is HVAC?
What influenced the development of HVAC?
What is known as air distribution?
What is the aim of HVAC systems in general?
What IAQ problems do you know?
Раздел VII: sewage treatment and waste management
What does sewage consist of?
Why should be sewage removed promptly?
What are the dangers to sewage systems due to seasonality?
Why should be storm water treated before discharging it into waterways?
What is used for storm water treatment?
When does backing-up of raw sewage take place?
How do you understand the notion 'grey' and 'black' water?
What main water concerns do large cities have?
How much supplied public water is estimated to be potable?
How much household water is used per bath, shower, and toilet?
How much available fresh water do we have on the planet?
How many stages does conventional sewage treatment have?
What do you know about pretreatment?
What is primary treatment?
What does the secondary treatment require prior to discharge?
Which process is known as effluent polishing?
When is tertiary treatment used?
What is the wastewater treatment goal?
Where does treated wastewater go after treatment?
How does municipal wastewater impact received environment?
What defines selection of effective treatment technologies?
Why is it important to forbid uncontrolled wastewater discharges?
What physical parameters of water condition do you know?
What do chemical parameters include?
What classes of water purity do you know?
How did human settlements discharge their wastewater in the past?
Can you tell about Indus sewage systems?
Where are the first sanitation systems found?
What can you tell about Rome and Istanbul ancient sewer systems?
How did the Romans build their sewage systems?
What can you tell about sewage systems in Old England?
Where can be treated effluents used?
What is reclaimed water ideal for?
Where else is reclaimed water widely used?
How can ground water recharge lessen water table decline?
Why is direct potable use of reclaimed wastewater limited?
What wastewater contaminants do you know?
Раздел VIII: fire resistance
What main aspects of fire resistance do you know?
How are buildings classified according to fire resistance requirements?
What is known as Tire load' of the building?
What are devices and apparatus for prompt fire extinguishment to account?
How are combustible materials classified?
What does the word 'to ignite' mean?
What is fire resistance rating determined by?
How do you understand 'calculation' as regards fire resistance rating?
What does 'listing service' concern?
What does testing cover?
What is the fire resistance rating governed by?
What does fire testing evaluate?
What is 'equivalent solid thickness' as concerning fire resistance?
What is actual thickness?
Can you explain the notion 'solid grouted unit'?
What does the notion 'required web dimensions' cover?
What do the fire resistance requirements and building codes ensure?
What key principle is there in the case of fire?
How can be fire resistance analyzed and predicted?
How is basic data provided as regards fire resistance?
What must each formula of calculating fire resistance involve?
Why testing is not feasible sometimes?
How can be improved fire resistance obtained in hollow steel columns?
What means can provide extra fire resistance of bearing elements?
What is the time limit of fire resistance for the high-strength columns?
How can be a substantial increase in load-bearing capacity and fire resistance of hollow steel columns achieved?
What do you know about marvelous HIPS?
Where were HIPS developed?
What do polymer additives in HIPS improve?
Раздел IX: hydraulic engineering
What is a dam used for?
What is the most economical arrangement to fill the gap in the natural reservoir line?
Why are harbours, canals, and dams among the oldest engineering achievements of early civilizations?
How can be catastrophes of hydroengineering objects avoided?
What contemporary techniques are used to divert rivers?
What is a cofferdam?
What are the most impressive hydraulic engineering achievements?
What is a large reservoir formed by the dam intended for?
What does a hydropower development on the river include?
Why are gates built on a dam?
What are the most popular dams' types?
What considerations should be taken into account concerning dams' construction?
How do large reservoirs affect ecology of the region?
How does hydroengineering construction impact human society?
Why do hydroelectric object site tend to be far from population centres?
What affects hydroelectric generation?
Why do people construct hydroengineering objects in spite of all their complexity?
When are dam failures catastrophic?
What should be done to anticipate dam problems?
How can be dams' deformation eliminated?
Why is dam considered to be 'an installation containing dangerous forces'?
What are the main dam failure causes?
What does a word 'dam' originate with?
Which dam is the earliest one?
What main purpose were the first Roman dams used for?
What evidences of high-standard hydroengineering construction in Roman Empire do you know?
When was the era of mega-dams initiated?
Рекомендуемое распределение часов на работу с разделами:
I: 12+2+2 (16) V: 8+2+2(12)
И: 12+2+2(16) VI: 12+2+2(16)
III: 16+2+2(20) VII: 10+2+2(14)
IV: 14+2+2(18) VIII: 10+2+2 (14)
IX: 10+2+2(14) Примечание: 2 ч. — контроль; 2 ч. — презентация.
1
1
1
1 The Suez was originally opened in 1869, closed in 1967
because of warfare in the area, and reopened in 1975.
One of the most important — building projects of recent
times was the St. Lawrence Seaway constructed jointly by the USA and Canada.
A is an artificial for water used for irrigation and navigation.
Most of the rivers and ports of Europe are connected by a net- |
work of intricate to carry a large proportion of the commerce of |
this highly industrialized region.
The Hoover Dam supplies water to city of Los Angeles, with
which it is connected by a series of , tunnels, and aqueducts
across deserts and mountains of the southwest United States.
