
- •Министерство образования и науки Российской Федерации Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования
- •Иваново 2012
- •153003, Иваново, ул. Рабфаковская, 34 Unit I. Size and dimention
- •Listening
- •Speaking
- •Information required
- •Reading
- •Writing
- •ProGolf
- •Omnibot – the electronic butler
- •Language translator
- •Listening
- •Reading
- •Speaking
- •Writing
- •Listening
- •Reading
- •Speaking
- •Writing
- •Listening
- •Speaking
- •Writing
- •Reading
- •It’s not just the hard hat, the gear and the glove
Reading
Part I
2.1. Study the vocabulary.
Pressure [´preʃǝ] – давление
What is the atmospheric pressure today?
Vessel [´ves(ǝ)l] – сосуд
The reactor pressure vessel is that part of the nuclear power plant, where heat
is produced from nuclear fission.
Heat [hi:t] – теплота
Heat is a form of energy.
Nuclear [´nju:klɪǝ] – ядерный
He studied nuclear physics at the University. Nuclear fuel is used in the reactor.
Fission [´fɪʃ(ǝ)n] – расщепление
To enrich [ɪn´rɪʧ] – обогащать
The enriched Uranium235 is necessary in the nuclear fission process.
Core [kͻ:] – ядро, центр
The core of the electromagnet is usually made of iron.
Assembly [ǝ´semblɪ] – блок, узел
Fuel assemblies contain the actual uranium.
To interrupt [ɪntǝ´rʌpt] – прекращать, прерывать
Nuclear fission is interrupted when reactor control elements are fully lowered.
Output [´aʊtpʊt] – производительность, мощность
The scientists tried to increase the output power of the generators.
To withdraw [wɪð´drɔ:] – извлекать, вынимать
The plant operates at a maximum output when the reactor control elements
are withdrawn.
To monitor [´mɔnɪtǝ] – отслеживать, наблюдать
The process of nuclear fission is monitored and controlled by the expert teams
in the central control rooms.
Circuit [´sɜ:kɪt] – контур; электрическая цепь
To separate [´sep(ǝ)reɪt] – отделять, разделять
To prevent [prɪ´vent] – мешать, препятствовать
To escape [ɪs´keɪp] – исчезать
The two water circuits are fully separated from each other, what prevents radiation from escaping and makes the process of steam generation quite safe.
Generator [´ʤen(ǝ)reɪtǝ] – генератор
A generator is one of the essential parts of any power plant which is used to generate electricity.
To drive [draɪv] – приводить в движение, вращать
Electricity is used to drive machinery. He drove me to the station.
To feed [fi:d] – питать, подавать
From the generator electricity is fed into the transformer.
Condenser [kǝn´densǝ] – конденсатор
Condenser is the part of the plant, where cooling water is used to transform the steam of the secondary circuit back to a liquid state.
Liquid [´lɪkwɪd] – жидкость
At what temperature does this liquid boil?
Voltage [´vɔltɪʤ] – напряжение
High voltage is dangerous. A transformer is used to step up and down
the voltage.
To pump [pʌmp] – накачивать
From a condenser water transformed from the steam of the secondary circuit is pumped back to the steam generator.
To discharge [dɪs´ʧa:ʤ] – выпускать; разряжать(ся)
When the battery operates it discharges. The stack is the part of a power plant where flue gases are discharged into.
Ore [ɔ:] – руда
After extraction uranium ore is crashed and nuclear fuel is fabricated.
To crash [kræʃ] – крошить, измельчать
In a coal crasher coal is crashed into a fine powder.
To extract [ɪk´strækt] – добывать
Coal is extracted from underground.
Fabrication [fæbrɪˊkeɪʃ(ǝ)n] – производство
The process of fuel fabrication is quite difficult.
Mine [maɪn] – шахта
The hardest work in mines is now performed by robots.
To transform [træns´fɔ:m] – превращать, преобразовывать
Is it possible to transform the electric current?
To reprocess [ri:prǝʊˊses] – перерабатывать
Eventually the spent fuel has to be reprocessed.
To use up [ju:z ʌp] – полностью использовать
In the reactor the nuclear fuel – Uranium235 – is fully used up.
To purify [ˊpjʊǝrɪfaɪ] – очищать
The water is carefully purified before use.
To turn [tɜ:n] – вращать, превращать
The motor turns electrical energy into mechanical energy. The turbines driven by the kinetic energy of the running water turn electric generators, which, in their turn, produce electric energy.
Steam [sti:m] – пар
Steam can be used to drive machinery. Steam is used to produce electricity.
Substance [´sʌbst(ǝ)ns] – вещество
Many chemical substances can be produced from coal.
Due to [dju: tǝ] – из-за, благодаря
We can watch TV due to electricity. Lomonosov was the first to state that heat phenomena were due to molecular motion.
Level [´lev(ǝ)l] – уровень
The city is 1,500 metres above the sea level.
To occur [ǝ´kɜ:] – случаться, происходить
The car accident occurred in the centre of the town. The process of heat generation from nuclear fission occurs in a reactor core.
Pellet [´pelɪt] – брикет, гранула
Rod [rɔd] – стержень
The nuclear fuel is made in the form of pellets. These pellets are then formed into rods.
2.2. Read the words correctly and give their Russian equivalents.
[´preʃǝ] [´fɪʃ(ǝ)n]
[ɪn´rɪʧ] [kǝn´densǝ]
[´nju:klɪǝ] [ǝ´semblɪ]
[wɪð´drɔ:] [ɪk´strækt]
[´sɜ:kɪt] [dɪs´ʧa:ʤ]
[´ʤen(ǝ)reɪtǝ] [´vɔltɪʤ]
[ri:prǝʊ´ses] [´lɪkwɪd]
[´pjʊǝrɪfaɪ] [´sʌbst(ǝ)ns]
[dju: tǝ] [ǝ´kɜ:]
[´pelɪt] [træns´fɔ:m]
2.3. Find the English equivalent to the Russian translation, given at the beginning of each line.
1. давление a) voltage; b) pressure; c) temperature; d) core
2. теплота a) level; b) steam; c) heat; d) vapour
3. расщепление a) fission; b) splitting; c) division; d) separation
ядерного топлива
4. обогащать a) to purify; b) to interrupt; c) to extract; d) to enrich
5. блок a) rod; b) pellet; c) assembly; d) ore
6. мощность a) input; b) output; c) liquid; d) circuit
7. наблюдать a) to control; b) to discharge; c) to monitor; d) to occur
8. вещество a) substance; b) phenomenon; c) team; d) heat
9. питать a) to pump; b) to reprocess; c) to feed; d) to escape
10. очищать a) to prevent; b) to purify; c) to use up; d) to turn
2.4. Match the pairs of synonyms.
A. transform B. turn
produce increase
occur input
due to convert
raise owing to
output generate
drive happen
2.5. Translate the following word-combinations into Russian.
pressurized water reactor fuel assemblies
fine powder operate at maximum output
opencast mining primary circuit
underground mining secondary circuit
fuel fabrication steam generator
nuclear fission process to drive the turbine
spent fuel voltage level
reactor pressure vessel liquid state
fissile reaction cooling tower
reactor core cooling water
2.6. Uranium is the basis of nuclear energy.
Put these sentences in the right order so that they describe the processes the uranium goes through.
Use the verbs in brackets in the correct form (Present Simple Passive).
a) After that, the uranium ore _____________ (to crush) into a fine powder.
b) First of all, uranium ______________ (to extract) from opencast or underground mining.
c) The next step is fuel fabrication. The nuclear fuel ____________________ (to transform) into pellets.
d) This “yellow cake” then __________ (to enrich) to increase the proportion of
uranium 235, which is essential in the nuclear fission process.
e) Finally, the spent fuel must _____________ (to reprocess) and ____________ (to store) long term underground.

f) Following that, they ______________ (to form) into rods and _____________ (to place) in the reactor pressure vessel.
g) In the reactor pressure vessel, heat _____________ (to produce) through a fissile reaction and eventually the uranium _____________ (to use up).
h) After crushing, the powder then _____________ (to purify); the substance at the end of this process ______________ (to call) “yellow cake”.
2.7. A guide is giving a group of visitors a tour of one of ELEC's nuclear power plants. Read the text on its operation and label the diagram.
Firstly I'd like to welcome you all. Today I’ll be showing you round one of our pressurized water reactors. I'll talk you through the basics using this diagram on the screen. If you look first at the left-hand side of the diagram, you can see the reactor pressure vessel which produces heat from nuclear fission. This occurs in the reactor core where the fuel assemblies are situated – they contain the actual uranium. Above these assemblies you can see the control elements. When these are fully lowered, nuclear fission is completely interrupted, the plant therefore operates at maximum output when they're withdrawn. All this is monitored and controlled by our expert teams in the central control rooms.
Now, it's important to realize that pressurized water reactors have two water circuits – the primary and secondary circuits, which are completely separated from each other. This prevents radiation from escaping, and so that's why they are relatively safe. In
the first circuit, water transports the heat produced by nuclear fission in a closed circuit to the steam generator, where the heat is then transferred to the secondary circuit. So in the steam generator, heat from the primary circuit turns water of the secondary circuit into steam. This steam, I'd like to stress again, is totally nonradioactive due to the separation of the circuits.
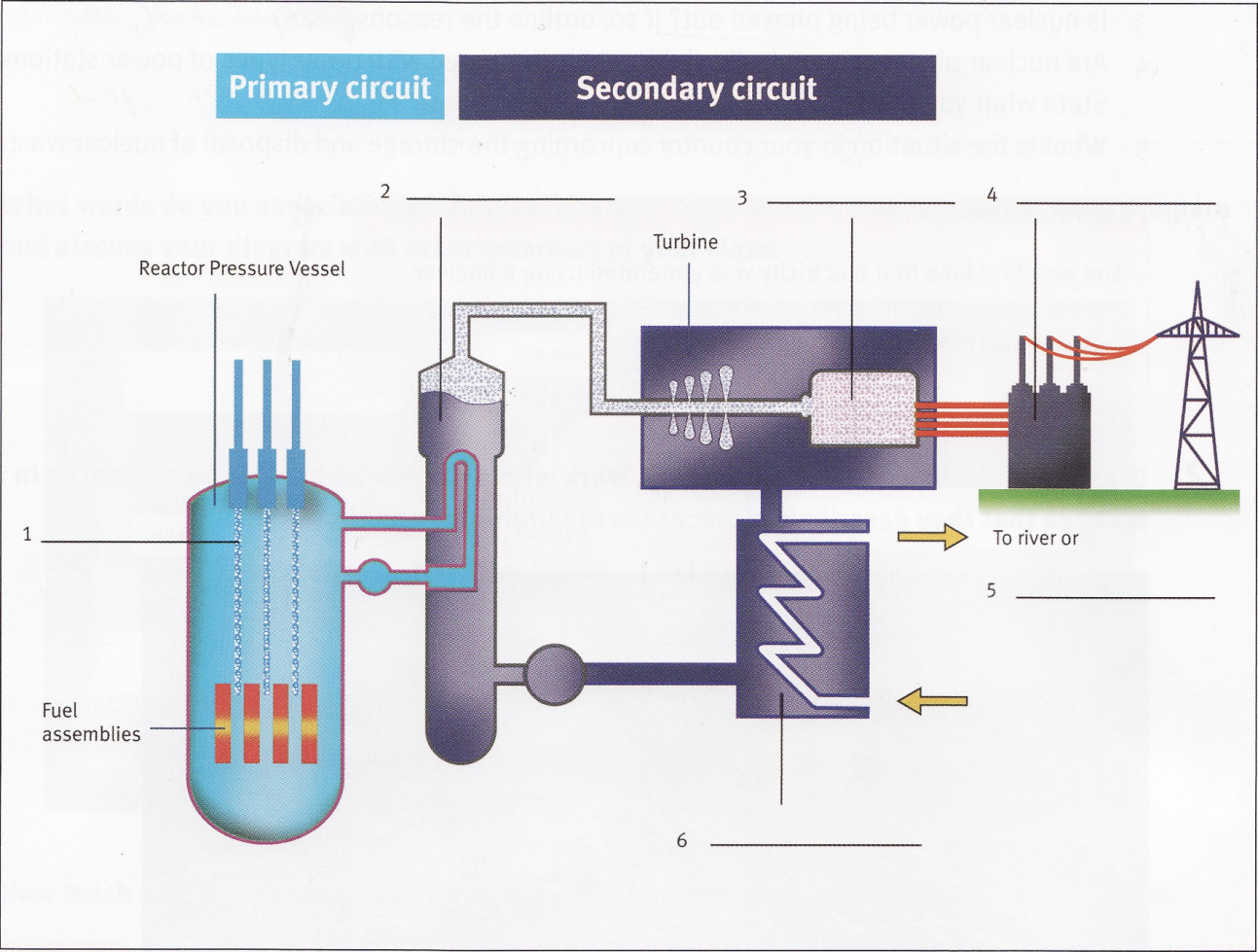
OK, so the steam produced in the steam generator passes to and drives the turbine. This is connected to the generator which actually produces the electricity. From there the electricity is fed into the transformers, which raise voltage levels to the required 380 kV. Now, if you look below the box with the turbine and the generator, you can see the condenser. In this part of the plant, cooling water is used to transform the steam of the secondary circuit back to a liquid state. In a sense the cooling water forms a third circuit, but we don't in fact call it that. Anyway, this cooling water in the condenser transforms the steam of the secondary circuit back to water, which is then pumped back to the steam generator. The cooling water on the other hand can be discharged back into the river which you saw nearby the plant, or it's fed into the cooling towers. This depends on the level of the water's temperature.
.Fill in the table with the necessary information from the text.
Part of the power station |
The purpose |
The function |
The reactor pressure vessel |
|
|
The primary circuit
|
|
|
The steam generator
|
|
|
The transformers
|
|
|
The condenser
|
|
|
Part II
2.1. Study the vocabulary.
1. Induction [ɪn´dʌkʃ(ǝ)n] – индукция; индукционный.
The principle of work of most metal detectors is based on electromagnetic induction. The induction coil is connected to the circuit in order to increase its inductance.
2. Field [fi:ld] – поле; область (науки, техники)
In autumn all the farmers work in the fields. In what field of science did Volta work?
Voltage [´vɔltɪʤ] – напряжение.
High voltage is dangerous. A transformer is used to step up and down the voltage.
Current [´kʌr(ǝ)nt] – ток.
All metals conduct the electric current. Where is the current used?
Coil [kɔɪl] – катушка.
Let us pass the current through the coil.
Wire [waɪǝ] – провод, проволока.
Wires are made of different metals.
To generate (generated) [´ʤen(ǝ)reɪt] – вырабатывать, производить.
Generators generate electrical energy.
8. To convert (converted) [´kɔn´vɜ:t] – превращать, преобразовывать.
Water can be converted into steam.
9. To drive (drove, driven) [draɪv] – приводить в движение, вращать.
Electrical current drives various machines at power plants.
10. To reverse (reversed) [rɪ´vɜ:s] – изменять на обратное, реверсировать.
If the resistance is reversed the current in the circuit is reversed too.
11.Target [´ta:gɪt] – цель.
What is the target object you want to find ?
To fade [feɪd] – ослабевать, постепенно исчезать.
It is not possible to switch the current off in the object; it has to fade naturally.
To amplify (amplified) [´æmplɪɪfaɪ] – увеличивать.
Can this voltage be amplified?
14. To detect (detected) [dɪ´tekt] – обнаруживать, открывать.
The fault was detected by the measuring instrument.
15. To cause [kɔ:z] – вызывать, являться причиной.
What caused the fire?
2.2. Read the following abbreviations and give their full forms.
AC, DC, V, MW, kWh, 317oF, 45oC, emf, mmf, e.g., etc.
2.3. Read the words correctly and give their Russian equivalents.
[´kɔn´vɜ:t] [waɪǝ]
[ɪn´dʌkʃ(ǝ)n] [´æmplɪɪfaɪ]
[´vɔltɪʤ] [´ʤen(ǝ)reɪt]
[´ta:gɪt] [feɪd]
[kɔ:z] [kɔɪl]
[´kʌr(ǝ)nt] [rɪ´vɜ:s]
.Translate the words and their derivatives into Russian.
Electrical – electricity – electrically – electrician; to drive – drive – driver; to generate – generator – generation – regeneration; magnetism – magnet – to magnetize – to demagnetize – magnetic; to indicate – indication – indicator – indicative; to cause – cause – causeless; to convert – conversion – converter; to reverse – reversal – reversible; switch – to switch on – to switch off.
.Translate the word combinations, given below into Russian.
Electronic metal detector pulse induction detector
Electromagnetic induction to cause currents to flow
Magnetic field target object
Electrical voltage/current to reactivate the search coil
Search coil to indicate with a sound
To reverse direction a flashing light
.Complete the puzzle to find out the synonym to the word-combination “a coil of wire”.
To change the direction of motion into opposite
To produce
A source of direct current (DC)
A current that flows in one direction
The flow of moving electrons
A device, used to turn on/off something
To find out
To transform
To move/to turn
A current that flows first in one direction and then in the opposite one
a





 1
1




 2
2


 3
3
4
 5
5

 6
6



 7
7

 8
8
 9
9
10
.Read the text below.
Use the verbs in brackets in the correct form (Present Simple Passive).
How a metal detector works
Electronic metal detectors use the principle of electromagnetic induction. This means that, if an object __________ (to place) in a changing magnetic field, an electrical voltage ____________ (to create) in that object. In a metal detector, an electrical current ____________ (to pass) through a coil of wire, called the search coil, to create a magnetic field. The DC from the battery ___________ (to
convert) into the AC needed to drive the coil with the help of an AC generator.
Since AC regularly reverses the direction, the necessary ever-changing magnetic field ___________ (to produce).
Currents _____________ (to generate) in a metal object that comes within the magnetic field by a process known as induction. When a current __________ (to induce) in a metal object (e.g., a buried coin), it in turn produces its own magnetic
fields. These magnetic fields are capable of inducing a small amount of electricity in the detector’s search coil itself.
The simplest kind of metal detector is the pulse induction type. A powerful current _____________ (to pass) from the battery through the search coil and then switched off. The pulse of magnetism causes currents to flow in any target objects below the ground. But, unlike the current in the search coil, the current in the object cannot ___________ (to switch off); it has to die away naturally. As it fades, the current in the object reactivates the search coil. This voltage ________ then _________ (to amplify) to indicate with a sound or a flashing light that an object has been found.
. Answer the questions.
1. What does the principle of electromagnetic induction mean?
2. How is a magnetic field created in a metal detector?
3. What device helps to transform DC into AC?
4. When is the changing magnetic field produced?
5. How are the currents generated in a metal object? Describe the process.
6. Why is the simplest metal detector called the “pulse induction detector”?
7. When is the search coil reactivated?
8. How can we learn that an object has been found?
. Fill in the scheme with the sentences given below to describe the work of a metal detector.
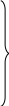











1. Current flows in an object underground.
2. Current in the object reactivates the search coil.
3. Current passes through the coil of wire.
4. A sound or a flashing light indicates the object found.
5. Current leaves the battery.
6. Current in an object fades.
7. Voltage increases.
8. Current is switched off.
