
- •Учебное пособие по английскому языку
- •International monetary fund
- •Who Makes Decisions at the imf?
- •Where Does the imf Get Its Money?
- •Vocabulary
- •Suggested activities
- •V erb Noun
- •What is the world bank?
- •Vocabulary
- •Suggested activities
- •V erb noun To organize - organization
- •Unit III. The european bank for reconstruction and development
- •Treasury department
- •Vocabulary
- •Suggested activities
- •Unit IV. Economic and monetary union (emu)
- •Stage One of emu
- •Stage Two of emu
- •Stage Three of emu
- •Vocabulary
- •Unit V. The european central bank
- •Map of euro area
- •Issuance
- •The Governing Council consists of :
- •Responsibilities of the Governing Council:
- •Meetings and decisions
- •Vocabulary
- •Задания для программированного опроса
- •III. Find pairs of synonyms:
- •IV. Find pairs of opposites:
- •V. Supply the appropriate prepositions:
- •VI. Supply the proper tense and voice forms:
Unit V. The european central bank
The ECB was established on 1 June 1998 and is based in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Its main task is to maintain price stability and to conduct a single monetary policy across the euro area. It pursues this objective in cooperation with the national central banks. Together, the ECB and the national central banks from the euro area are known as the Eurosystem. The euro became the common currency of more than 300 million Europeans on 1 January 1999.
This was the final step in the world´s largest ever monetary changeover. The successful development of the euro contributes to a Europe in which people, services, capital and goods can move freely.
The banknotes and coins first went into circulation on 1 January 2002. Today, euro banknotes and coins are legal tender in 12 of the 25 European Union (EU) Member States. These 12 countries form the euro area.
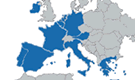
Map of euro area
 Participating
countries
Participating
countries
Participants: 12 countries in the European Union (EU) are currently participating in the single currency. They are: Belgium, Germany, Greece, Spain, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Austria, Portugal and Finland.
Non-participants: Cyprus, Denmark, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia, Sweden and the United Kingdom are members of the EU but are not currently participating in the single currency. Denmark is a member of the Exchange Rate Mechanism II (ERM II). This means that the Danish krone is linked to the euro, but the exchange rate is not fixed.
Issuance
Legally, both the ECB and the national central banks of the participating countries have the right to issue euro banknotes. In practice, only the national central banks physically issue and withdraw euro banknotes (as well as coins). The ECB does not have a cash office and is not involved in any cash operations. The legal issuers of euro coins are the participating countries.
Stocks and circulation
The ECB closely monitors the stocks of euro banknotes and coins. Potential shortages of banknotes in one country can be compensated for by surplus stocks from a national central bank in another country. Any major changes in demand can be met by drawing from an additional strategic reserve.
Objectives and tasks
The primary objective of the ESCB is to maintain price stability.
The basic tasks are:
the definition and implementation of monetary policy for the euro area;
the conduct of foreign exchange operations;
the holding and management of the official foreign reserves of the euro area countries (portfolio management).
the promotion of the smooth operation of payment systems.
The Governing Council consists of :
the six members of the Executive Board, plus
the governors of all the national central banks (NCBs) from the 12 euro area countries.
Responsibilities of the Governing Council:
to adopt the guidelines and take the decisions necessary to ensure the performance of the tasks entrusted to the Eurosystem;
to formulate monetary policy for the euro area. This includes decisions relating to monetary objectives, key interest rates, the supply of reserves in the Eurosystem, and the establishment of guidelines for the implementation of those decisions.
