
Infrared waves
Thermographic
image of a hand that shows to
of
a hand (how much infrared radiation is given .off the surface).
Infrared waves are used for many things such as:
T
 hermography
hermographyNight vision

Tracking


Infrared port
Communications

Heating
Meteorology
Astronomy
The most common uses of IR waves are remote controls and infrared motion alarms. IM Alarms are made using passive infrared sensor which is an electronic sensor that measures infrared light radiating from objects in its field of view.
Dangers
The danger to people from too much infrared radiation is very simple - overheating.
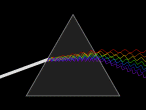 Light
Light
Beam
of light being dispersed by a prism.
W

 e
use light to see things! As the Sun sends so much light towards our
planet, we've evolved to make use of those particular wavelengths in
order to sense our environment. Light waves can also be made using a
laser. This works differently to a light bulb, and produces
"coherent" light. Lasers are used in Compact Disc & DVD
players, where the light is reflected from the tiny pits in the disc,
and the pattern is detected and translated into sound or data. Lasers
are also used in laser printers, and in aircraft weapon aiming
systems.
e
use light to see things! As the Sun sends so much light towards our
planet, we've evolved to make use of those particular wavelengths in
order to sense our environment. Light waves can also be made using a
laser. This works differently to a light bulb, and produces
"coherent" light. Lasers are used in Compact Disc & DVD
players, where the light is reflected from the tiny pits in the disc,
and the pattern is detected and translated into sound or data. Lasers
are also used in laser printers, and in aircraft weapon aiming
systems.
Dangers
Too much light can damage the retina in your eye. This can happen when you look at something very bright, such as the Sun. Although the damage can heal, if it's too bad it'll be permanent.
 Ultraviolet
waves
Ultraviolet
waves
UV waves are called like that because the spectrum consists of electromagnetic waves with frequencies higher than those that humans identify as the color violet. These frequencies are invisible to humans, but visible to a number of insects and birds.
“Black
light” lamps

UV has a has a wide range of applications. People use UV for:
Getting a sun tan
Detecting forged banknotes
Killing microbes

luminescent characteristics on banknotes
Sterilization of products
Revealing of invisible ink

You can also mention that your clothes sometimes starting to glow in black light. That’s happening because substances in washing powder "fluoresce" when UV light strikes them - they absorb the UV and then re-radiate the energy at a longer wavelength.
Clothes
glowing under backlight
Dangers
Large doses of UV can damage the retina in your eyes, so it's important to check that your sunglasses will block UV light. Large doses of UV cause sunburn and even skin cancer.
 X-Rays
X-Rays
An
example of radiograph

Because of x-rays’ ability to pass through surfaces, they widely used in medicine to see inside people. The pictures got using x-rays are called “radiographs”.
X-Ray Machine
 -rays
are also used in airport security checks, to see inside your luggage.
They are also used by astronomers - many objects in the universe emit
X-rays, which we can detect using suitable radio telescopes.
-rays
are also used in airport security checks, to see inside your luggage.
They are also used by astronomers - many objects in the universe emit
X-rays, which we can detect using suitable radio telescopes.
Dangers
X-ray
scanner in airports
G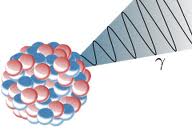 amma
Rays
amma
Rays
Emission
of a gamma ray from an atomic nucleus

Because Gamma rays can kill living cells, they are used to kill cancer cells without having to resort to difficult surgery. This is called "Radiotherapy". Gamma rays are used for killing microbes and sterilization of food this is known as "irradiated" food, so that it will keep fresh for longer. Gamma rays are also used to sterilize medical equipment. Moreover gamma rays are used in astronomy.
The
Moon as seen by the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory
Dangers
Gamma rays cause cell damage and can cause a variety of cancers. They cause mutations in growing tissues, so unborn babies are especially vulnerable.

Bibliography
Used sources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetic_radiation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio_waves
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microwave
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infrared_radiation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visible_spectrum
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultraviolet_radiation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_ray
http://www.darvill.clara.net/emag/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetic_spectrum
http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-electromagnetic-radiation.htm
