
- •Міністерство освіти і науки україни
- •Методичні рекомендації
- •Unit 1 lesson 1 niels bohr (1885-1962)
- •Lesson 2 l’VIV university of today
- •Lesson 3 history of education
- •Unit 2 lesson 1 systems of measurement
- •Lesson 2 mechanics
- •Lesson 3 number systems
- •Lesson 4 radiation
- •Lesson 5 fibre optics and communication
- •Unit 3 lesson 1 electronics helps man
- •Lesson 2 automatic plants in industry
- •Lesson 3 the automatic control systems
- •Lesson 4 computers in our life
- •Lesson 5 man and machines
- •Unit 4 lesson 1 what is automation?
- •Lesson 2 logical circuit elements
- •Lesson 3
- •Information systems in control engineering
- •Lesson 4
- •Lesson 5 sensors
- •Самостійна та індивідуальна робота студентів
- •6. Рейтингова система оцінювання набутих студентом знань і вмінь
- •Відповідність підсумкових семестрових рейтингових оцінок у балах
- •7. Контроль знань студентів денної форми навчання
- •7.1. Контроль знань студентів денної форми навчання
Lesson 5 fibre optics and communication
Key terms: fibre optics, optical signals, ultrapure glass fibre, total internal reflection, light pipe, image, transparent, light signal transmission, glass fibre technology, jamming, signal leaking
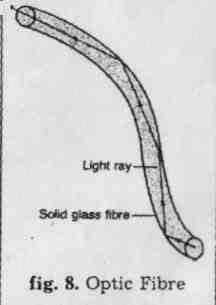
1. Fibre optics is the transmission of optical signals through strands of ultrapure glass fibre the thickness of human hair. The main principle of fibre optics is total internal reflection through a curved fibre. Special plastic and glass fibres a few micrometers in diameter have recently been developed to transmit light from one place to another. A bundle of these fibres is called a light pipe. Light can be transmitted through a light pipe for several kilometres with little loss in intensity. Light pipes can be used to illuminate inaccessible places, to transmit telephone calls and other modulated signals, and to carry out internal examination of the body. The finer the fibres and the greater their number, the clearer and more detailed the image being transmitted.
2. The idea of using light to transmit information is not new. In 4880, Alexander Graham Bell invented a «photophone» that used a narrow sunbeam to transmit voices over a short distance. He said, «I have heard articulate speech produced by sunlight! I have heard a ray of the sun laugh and cough and sing!» However, Bell's other invention, the telephone, was considered more promising at the time and the photophone was set aside. Light sign al transmission has become practical today due to advantages in laser and glass fibre technology.
3. Optical fibres have several advantages over traditional telephone cable. Glass fibres deliver a clean signal because they are immune to electrical interference, jamming and signal leaking. They also prevent eavesdropping. As well, glass fibres carry more information per square centimetre of cross-sectional area than do copper telephone cables. Twelve hair-thin optical fibres, inside a protective sheathing, can carry 48,000 two-way phone calls at the same time. Transmitting this number electrically would require a bulky coaxial cable the thickness of a man's arm.
4. Fibre optics can integrate two separate industries - telephone and cable television. Unlike electrical signals on a cable, light waves can pass right through one another without affecting each other. As a result, many kinds of information can be sent simultaneously along a single fibre. Because both telephone and television signals can be sent on the same fibre, we may ябоп not need two separate cable systems.
5. To transmit across the Atlantic Ocean, American and European telecommunications administrations have plans to install the first Trans-Atlantic fibre optic cable. This cable will handle 560 million bits of information each second. This is equivalent to 40,000 simultaneous conversations taking place along the same line.
6. Compared to traditional telephone cable, fibre optic cable is cheaper, more reliable, and can transmit not only voice, but data and visual images as well. Who knows — you too may be using this modern medium soon.
Exercise 1. Find the synonyms to the following words in the text:
1. super clean (1) 6. conventional (3)
2. complete (adj.), entire (1) 7. wire (3)
3. leakage (1) 8. to stop (3)
4. unavailable (1) 9. demand (3, 4)
5. distinct (2) 10. big, clumsy (3).
Exercise 2. Make up the word-combinations:
traditional sunbeam
optical sheathing
light pipe
narrow industries
protective cable
separate image
visual signal.
Exercise 3. Say if the statements are true or false:
1. Transmitting light through a light pipe avoids signal leaking.
2. As light waves do not interfere in fibres, much information can be sent along a single fibre at the same time.
3. Glass fibres deliver a clean signal, because they are not affected by signal leaking.
4. It is impossible to transmit across the oceans.
5. Traditional telephone cable can transmit voices, data, visual images.
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences:
1. The main principle of fibre optics is…
a). refraction of light
b). reflection of light
c). transmission of light
2. Light pipes cannot be used to…
a). illuminate in accessible places
b). transmit telephone calls
c). heat houses
3. 12- hair- thin optical fibres can carry at the same time…
a). 40000 two- way telephone calls
b). 56 million two- way telephone calls
c). 48000 two- way telephone calls
4. Glass fibres deliver a clean signal, because…
a). they transmit light with little loss in intensity
b). they are not subjected to electrical interference
c). they transmit optical signals through strands of ultrapure glass
5. Fibre optic cable can transmit…
a). audial images and data
b). visual images and voice
c). audio/video images and data
Exercise 5. Answer the following questions:
1. What purposes can light pipes be used for?
2. Is Bell’s phrase,, I have heard a ray of the Sun, laugh, cough and sing” refered to the invention of a ,, photophone” or a telephone?
3. What are the advantages of optical fibres over traditional telephone cables?
4. Thanks to what can many kinds of information be sent simultaneously along a single fibre?
5. What is the main property of optical fibres?
Exercise 6. Put a tick (v) or a cross (x):
Optic fibres… telephone cables…
v x 1. integrate two industries
2. deliver a clean signal
3. cannot send a lot of information at the same time.
4. prevent eaves dropping
5. can carry 48000 two- way phone calls
6. can transmit voice, data, visual signals
7. are cheap and reliable
8. are bulky.
Exercise 7. Define fibre optics, a light pipe.
Exercise 8. Describe the main principle of fibre optics.
Exercise 9. Explain why we may soon not need to separate cable systems.
Exercise 10. Compare traditional telephone cables with fibre optic ones.
Exercise 11. Prove that the finer the fibres and the greater their number, the clearer and more detailed the image being transmitted.
Exercise 12. Discuss the text according to the points:
1. Application of a light pipe.
2. Bell’s inventions.
3. Advantages of optical fibres over traditional cables.
4. Properties of optical fibres.
Notes:
1. strand – пасмо, нитка
2. curve – крива
3. bundle – вузол
4. beam – пучок
5. immune – стійкий
6. interference – накладення, перешкода, інтерференція
7. jamming – затискання
8. leaking – витік
9. eavesdropping підслуховування
10. sheathing – оболонка
11. coaxial - коаксіальний ( співпадаючий)
