
- •1.The subject-matter of lexicology and its main problems
- •2.English vocabulary as a system
- •3. The classification of the English vocabulary
- •Idiographic groups
- •4.Moderrn methods of lexicological research
- •5.Etymological composition of the English Word- Stock
- •6.Causes and ways of borrowing into English. Etymological doublets.
- •7. Mechanism of borrowing
- •1)True loan words
- •3) Semantic loans
- •8. Criteria and assimilation of borrowings
- •9. International Words. Translator’s false friends. Culturally oriented words. Popular (false) etymology
- •10. The morpheme. Its types of meaning. The allomorph
- •11. Ic method. Morphemic and word-formation analysis
- •Ic method
- •12. Affixation. The classification of affixes. Semi-affixes. Hybrids.
- •13. Productivity of word-formation means. Conversion. Main types oа semantic relations between the members of a conversion pair.
- •14. Composition. Structural and semantic types of compounds. Compound words and word combinations.
- •15. Shortening(clipping, abbreviation, blending)
- •16. Minor Types of Modern Word-Building.
- •17.Word-meaning as a controversial linguistic problem
- •18. Types of word meaning
- •19. Polysemy. Meaning and context. Types of context.
- •20. The fundamentals of the componential analysis
- •21. Semantic change. Linguistic & extra-linguistic causes
- •22. Linguistic metaphor and metonymy. Types of semantic change
- •23. Definitions and criteria of synonyms. Main sources of synonymy. Synonymic dominant versus generic term.
- •24. The classification of synonyms.
- •25.Euphemisms as a specific type of synonyms
- •26. Antonyms: definition and criteria. The classification of antonyms.
- •27. Definition and sources of homonymy
- •28.The classification of homonyms
- •29. Phraseological units versus free word-groups.
- •30. Classification of phraseological units
- •31. Proverbs, familiar quotation and clichés
- •32. Standard English and local varieties of the English Language on the British Isles.
- •34. Functional varieties of the English vocabulary
- •35. Lexicography. Main lexicographical problems.
- •36. Types of dictionaries. The arrangement of entries in a dictionary.
17.Word-meaning as a controversial linguistic problem
What Is "Meaning"?
Generally speaking, meaning can be more or less described as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated, in this way endowing the word with the ability of denoting real objects, qualities, actions and abstract notions. The complex and somewhat mysterious relationships between referent (object, etc. denoted by the word), concept and word are traditionally represented by the following triangle:
Thought or Reference
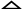
Symbol Referent
By the "symbol" here is meant the word; thought or reference is concept. The dotted line suggests that there is no immediate relation between word and referent: it is established only through the concept.
The mechanism by which concepts (i. e. mental phenomena) are converted into words (i. e. linguistic phenomena) and the reverse process by which a heard or a printed word is converted into a kind of mental picture are not yet understood or described.
The branch of linguistics which specialises in the study of meaning is called semantics. As with many terms, the term "semantics" is ambiguous for it can stand, as well, for the expressive aspect of language in general and for the meaning of one particular word in all its varied aspects and nuances (i.e. the semantics of a word = the meaning(s) of a word).
The modern approach to semantics is based on the assumption that the inner form of the word (i. e. its meaning) presents a structure which is called the semantic structure of the word. The referential approach seeks to formulate the essence of meaning by establishing the difference between ws. & the thing or concept they denote. According to this approach there are 3 components completly close with meaning but not identical with: the sound form of a linguistic sign; the concept underlying the second form; the actual referent; the relation between this comp. Are traditionally represented by the tryangle which underlies the symentic system of all the linguistis of this school.- the symantic triangle of Ogdan & Richards.
The sound form of the linguistic side[dˆv] is connected with the concept of the bird, which it denotes and through it with the referent that is with the actual bird. Te SF is not identical with its meaning. There is no inherent connectionmeaning being closely connected with the concept is not identical with it. Concept is the thought of the object that singles out its essential features. The difference between eaning & concept can be easely observed by comparing synonyms denoting practically the same thing.
To distinguish the meaning from the referent we should remember that meaning is the unit of ling. The referent denotad object is beyond the domain of ling. We can denote one object by more than 1 w. Of a differ. Meaning. The meaning shouldn’t be identified with any of 3 points of this triangle. However it’s closely connected with it. The main feature of the referential approach is te idea that meaning is connected with the referent
Functional approach studies the function of a w. In speech and is much more concerned with how meaning works. According to this approach the meaning may be studied through its relations to other ling units. As the distribution of 2 w. is different we conclude that these w. belonging to different classes of w/ have dif. Meanings. It follows that in the functional approach semantic investigation is confiened.
