
- •ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Guide
- •Table of Contents
- •Using This Manual
- •1. What’s In This Manual
- •2. How To Use This Manual
- •2.1. For the Beginner
- •2.2. For the Experienced User
- •3. Typographical Conventions Used In This Manual
- •Chapter 1: Fluid Flow in an Exhaust Manifold
- •1.1. Introduction
- •1.2. Prerequisites
- •1.3. Problem Description
- •1.4. Setup and Solution
- •1.4.1. Preparation
- •1.4.2. Meshing Workflow
- •1.4.3. General Settings
- •1.4.4. Solver Settings
- •1.4.5. Models
- •1.4.6. Materials
- •1.4.7. Cell Zone Conditions
- •1.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •1.4.9. Solution
- •1.4.10. Postprocessing
- •1.5. Summary
- •Chapter 2: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
- •2.1. Introduction
- •2.2. Prerequisites
- •2.3. Problem Description
- •2.4. Setup and Solution
- •2.4.1. Preparation
- •2.4.2. Launching ANSYS Fluent
- •2.4.3. Reading the Mesh
- •2.4.4. Setting Up Domain
- •2.4.5. Setting Up Physics
- •2.4.6. Solving
- •2.4.7. Displaying the Preliminary Solution
- •2.4.8. Adapting the Mesh
- •2.5. Summary
- •Chapter 3: Postprocessing
- •3.1. Introduction
- •3.2. Prerequisites
- •3.3. Problem Description
- •3.4. Setup and Solution
- •3.4.1. Preparation
- •3.4.2. Reading the Mesh
- •3.4.3. Manipulating the Mesh in the Viewer
- •3.4.4. Adding Lights
- •3.4.5. Creating Isosurfaces
- •3.4.6. Generating Contours
- •3.4.7. Generating Velocity Vectors
- •3.4.8. Creating an Animation
- •3.4.9. Displaying Pathlines
- •3.4.10. Creating a Scene With Vectors and Contours
- •3.4.11. Advanced Overlay of Pathlines on a Scene
- •3.4.12. Creating Exploded Views
- •3.4.13. Animating the Display of Results in Successive Streamwise Planes
- •3.4.14. Generating XY Plots
- •3.4.15. Creating Annotation
- •3.4.16. Saving Picture Files
- •3.4.17. Generating Volume Integral Reports
- •3.5. Summary
- •Chapter 4: Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer
- •4.1. Introduction
- •4.2. Prerequisites
- •4.3. Problem Description
- •4.4. Setup and Solution
- •4.4.1. Preparation
- •4.4.2. Mesh
- •4.4.3. General Settings
- •4.4.4. Models
- •4.4.5. Materials
- •4.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •4.4.7. Periodic Conditions
- •4.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •4.4.9. Solution
- •4.4.10. Postprocessing
- •4.5. Summary
- •4.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 5: Modeling External Compressible Flow
- •5.1. Introduction
- •5.2. Prerequisites
- •5.3. Problem Description
- •5.4. Setup and Solution
- •5.4.1. Preparation
- •5.4.2. Mesh
- •5.4.3. Solver
- •5.4.4. Models
- •5.4.5. Materials
- •5.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •5.4.7. Operating Conditions
- •5.4.8. Solution
- •5.4.9. Postprocessing
- •5.5. Summary
- •5.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 6: Modeling Transient Compressible Flow
- •6.1. Introduction
- •6.2. Prerequisites
- •6.3. Problem Description
- •6.4. Setup and Solution
- •6.4.1. Preparation
- •6.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •6.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •6.4.4. Models
- •6.4.5. Materials
- •6.4.6. Operating Conditions
- •6.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •6.4.8. Solution: Steady Flow
- •6.4.9. Enabling Time Dependence and Setting Transient Conditions
- •6.4.10. Specifying Solution Parameters for Transient Flow and Solving
- •6.4.11. Saving and Postprocessing Time-Dependent Data Sets
- •6.5. Summary
- •6.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 7: Modeling Flow Through Porous Media
- •7.1. Introduction
- •7.2. Prerequisites
- •7.3. Problem Description
- •7.4. Setup and Solution
- •7.4.1. Preparation
- •7.4.2. Mesh
- •7.4.3. General Settings
- •7.4.4. Models
- •7.4.5. Materials
- •7.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •7.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •7.4.8. Solution
- •7.4.9. Postprocessing
- •7.5. Summary
- •7.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 8: Modeling Radiation and Natural Convection
- •8.1. Introduction
- •8.2. Prerequisites
- •8.3. Problem Description
- •8.4. Setup and Solution
- •8.4.1. Preparation
- •8.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •8.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •8.4.4. Models
- •8.4.5. Defining the Materials
- •8.4.6. Operating Conditions
- •8.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •8.4.8. Obtaining the Solution
- •8.4.9. Postprocessing
- •8.4.10. Comparing the Contour Plots after Varying Radiating Surfaces
- •8.4.11. S2S Definition, Solution, and Postprocessing with Partial Enclosure
- •8.5. Summary
- •8.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 9: Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame
- •9.1. Introduction
- •9.2. Prerequisites
- •9.3. Problem Description
- •9.4. Setup and Solution
- •9.4.1. Preparation
- •9.4.2. Mesh
- •9.4.3. General Settings
- •9.4.4. Models
- •9.4.5. Materials
- •9.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •9.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •9.4.8. Solution Using the Standard k- ε Model
- •9.4.9. Postprocessing for the Standard k- ε Solution
- •9.4.10. Solution Using the RNG k- ε Model
- •9.4.11. Postprocessing for the RNG k- ε Solution
- •9.5. Summary
- •9.6. Further Improvements
- •9.7. References
- •Chapter 10: Using Multiple Reference Frames
- •10.1. Introduction
- •10.2. Prerequisites
- •10.3. Problem Description
- •10.4. Setup and Solution
- •10.4.1. Preparation
- •10.4.2. Mesh
- •10.4.3. Models
- •10.4.4. Materials
- •10.4.5. Cell Zone Conditions
- •10.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •10.4.7. Solution
- •10.4.8. Postprocessing
- •10.5. Summary
- •10.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 11: Using Sliding Meshes
- •11.1. Introduction
- •11.2. Prerequisites
- •11.3. Problem Description
- •11.4. Setup and Solution
- •11.4.1. Preparation
- •11.4.2. Mesh
- •11.4.3. General Settings
- •11.4.4. Models
- •11.4.5. Materials
- •11.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •11.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •11.4.8. Operating Conditions
- •11.4.9. Mesh Interfaces
- •11.4.10. Solution
- •11.4.11. Postprocessing
- •11.5. Summary
- •11.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 12: Using Overset and Dynamic Meshes
- •12.1. Prerequisites
- •12.2. Problem Description
- •12.3. Preparation
- •12.4. Mesh
- •12.5. Overset Interface Creation
- •12.6. Steady-State Case Setup
- •12.6.1. General Settings
- •12.6.2. Models
- •12.6.3. Materials
- •12.6.4. Operating Conditions
- •12.6.5. Boundary Conditions
- •12.6.6. Reference Values
- •12.6.7. Solution
- •12.7. Unsteady Setup
- •12.7.1. General Settings
- •12.7.2. Compile the UDF
- •12.7.3. Dynamic Mesh Settings
- •12.7.4. Report Generation for Unsteady Case
- •12.7.5. Run Calculations for Unsteady Case
- •12.7.6. Overset Solution Checking
- •12.7.7. Postprocessing
- •12.7.8. Diagnosing an Overset Case
- •12.8. Summary
- •Chapter 13: Modeling Species Transport and Gaseous Combustion
- •13.1. Introduction
- •13.2. Prerequisites
- •13.3. Problem Description
- •13.4. Background
- •13.5. Setup and Solution
- •13.5.1. Preparation
- •13.5.2. Mesh
- •13.5.3. General Settings
- •13.5.4. Models
- •13.5.5. Materials
- •13.5.6. Boundary Conditions
- •13.5.7. Initial Reaction Solution
- •13.5.8. Postprocessing
- •13.5.9. NOx Prediction
- •13.6. Summary
- •13.7. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 14: Using the Eddy Dissipation and Steady Diffusion Flamelet Combustion Models
- •14.1. Introduction
- •14.2. Prerequisites
- •14.3. Problem Description
- •14.4. Setup and Solution
- •14.4.1. Preparation
- •14.4.2. Mesh
- •14.4.3. Solver Settings
- •14.4.4. Models
- •14.4.5. Boundary Conditions
- •14.4.6. Solution
- •14.4.7. Postprocessing for the Eddy-Dissipation Solution
- •14.5. Steady Diffusion Flamelet Model Setup and Solution
- •14.5.1. Models
- •14.5.2. Boundary Conditions
- •14.5.3. Solution
- •14.5.4. Postprocessing for the Steady Diffusion Flamelet Solution
- •14.6. Summary
- •Chapter 15: Modeling Surface Chemistry
- •15.1. Introduction
- •15.2. Prerequisites
- •15.3. Problem Description
- •15.4. Setup and Solution
- •15.4.1. Preparation
- •15.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •15.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •15.4.4. Specifying the Models
- •15.4.5. Defining Materials and Properties
- •15.4.6. Specifying Boundary Conditions
- •15.4.7. Setting the Operating Conditions
- •15.4.8. Simulating Non-Reacting Flow
- •15.4.9. Simulating Reacting Flow
- •15.4.10. Postprocessing the Solution Results
- •15.5. Summary
- •15.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 16: Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
- •16.1. Introduction
- •16.2. Prerequisites
- •16.3. Problem Description
- •16.4. Setup and Solution
- •16.4.1. Preparation
- •16.4.2. Mesh
- •16.4.3. Solver
- •16.4.4. Models
- •16.4.5. Materials
- •16.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •16.4.7. Initial Solution Without Droplets
- •16.4.8. Creating a Spray Injection
- •16.4.9. Solution
- •16.4.10. Postprocessing
- •16.5. Summary
- •16.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 17: Using the VOF Model
- •17.1. Introduction
- •17.2. Prerequisites
- •17.3. Problem Description
- •17.4. Setup and Solution
- •17.4.1. Preparation
- •17.4.2. Reading and Manipulating the Mesh
- •17.4.3. General Settings
- •17.4.4. Models
- •17.4.5. Materials
- •17.4.6. Phases
- •17.4.7. Operating Conditions
- •17.4.8. User-Defined Function (UDF)
- •17.4.9. Boundary Conditions
- •17.4.10. Solution
- •17.4.11. Postprocessing
- •17.5. Summary
- •17.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 18: Modeling Cavitation
- •18.1. Introduction
- •18.2. Prerequisites
- •18.3. Problem Description
- •18.4. Setup and Solution
- •18.4.1. Preparation
- •18.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •18.4.3. Solver Settings
- •18.4.4. Models
- •18.4.5. Materials
- •18.4.6. Phases
- •18.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •18.4.8. Operating Conditions
- •18.4.9. Solution
- •18.4.10. Postprocessing
- •18.5. Summary
- •18.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 19: Using the Multiphase Models
- •19.1. Introduction
- •19.2. Prerequisites
- •19.3. Problem Description
- •19.4. Setup and Solution
- •19.4.1. Preparation
- •19.4.2. Mesh
- •19.4.3. Solver Settings
- •19.4.4. Models
- •19.4.5. Materials
- •19.4.6. Phases
- •19.4.7. Cell Zone Conditions
- •19.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •19.4.9. Solution
- •19.4.10. Postprocessing
- •19.5. Summary
- •Chapter 20: Modeling Solidification
- •20.1. Introduction
- •20.2. Prerequisites
- •20.3. Problem Description
- •20.4. Setup and Solution
- •20.4.1. Preparation
- •20.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •20.4.3. Specifying Solver and Analysis Type
- •20.4.4. Specifying the Models
- •20.4.5. Defining Materials
- •20.4.6. Setting the Cell Zone Conditions
- •20.4.7. Setting the Boundary Conditions
- •20.4.8. Solution: Steady Conduction
- •20.5. Summary
- •20.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 21: Using the Eulerian Granular Multiphase Model with Heat Transfer
- •21.1. Introduction
- •21.2. Prerequisites
- •21.3. Problem Description
- •21.4. Setup and Solution
- •21.4.1. Preparation
- •21.4.2. Mesh
- •21.4.3. Solver Settings
- •21.4.4. Models
- •21.4.6. Materials
- •21.4.7. Phases
- •21.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •21.4.9. Solution
- •21.4.10. Postprocessing
- •21.5. Summary
- •21.6. Further Improvements
- •21.7. References
- •22.1. Introduction
- •22.2. Prerequisites
- •22.3. Problem Description
- •22.4. Setup and Solution
- •22.4.1. Preparation
- •22.4.2. Structural Model
- •22.4.3. Materials
- •22.4.4. Cell Zone Conditions
- •22.4.5. Boundary Conditions
- •22.4.6. Solution
- •22.4.7. Postprocessing
- •22.5. Summary
- •23.1. Introduction
- •23.2. Prerequisites
- •23.3. Problem Description
- •23.4. Setup and Solution
- •23.4.1. Preparation
- •23.4.2. Solver and Analysis Type
- •23.4.3. Structural Model
- •23.4.4. Materials
- •23.4.5. Cell Zone Conditions
- •23.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •23.4.7. Dynamic Mesh Zones
- •23.4.8. Solution Animations
- •23.4.9. Solution
- •23.4.10. Postprocessing
- •23.5. Summary
- •Chapter 24: Using the Adjoint Solver – 2D Laminar Flow Past a Cylinder
- •24.1. Introduction
- •24.2. Prerequisites
- •24.3. Problem Description
- •24.4. Setup and Solution
- •24.4.1. Step 1: Preparation
- •24.4.2. Step 2: Define Observables
- •24.4.3. Step 3: Compute the Drag Sensitivity
- •24.4.4. Step 4: Postprocess and Export Drag Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.1. Boundary Condition Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.2. Momentum Source Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.3. Shape Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.4. Exporting Drag Sensitivity Data
- •24.4.5. Step 5: Compute Lift Sensitivity
- •24.4.6. Step 6: Modify the Shape
- •24.5. Summary
- •25.1. Introduction
- •25.2. Prerequisites
- •25.3. Problem Description
- •25.4. Setup and Solution
- •25.4.1. Preparation
- •25.4.2. Reading and Scaling the Mesh
- •25.4.3. Loading the MSMD battery Add-on
- •25.4.4. NTGK Battery Model Setup
- •25.4.4.1. Specifying Solver and Models
- •25.4.4.2. Defining New Materials for Cell and Tabs
- •25.4.4.3. Defining Cell Zone Conditions
- •25.4.4.4. Defining Boundary Conditions
- •25.4.4.5. Specifying Solution Settings
- •25.4.4.6. Obtaining Solution
- •25.4.5. Postprocessing
- •25.4.6. Simulating the Battery Pulse Discharge Using the ECM Model
- •25.4.7. Using the Reduced Order Method (ROM)
- •25.4.8. External and Internal Short-Circuit Treatment
- •25.4.8.1. Setting up and Solving a Short-Circuit Problem
- •25.4.8.2. Postprocessing
- •25.5. Summary
- •25.6. Appendix
- •25.7. References
- •26.1. Introduction
- •26.2. Prerequisites
- •26.3. Problem Description
- •26.4. Setup and Solution
- •26.4.1. Preparation
- •26.4.2. Reading and Scaling the Mesh
- •26.4.3. Loading the MSMD battery Add-on
- •26.4.4. Battery Model Setup
- •26.4.4.1. Specifying Solver and Models
- •26.4.4.2. Defining New Materials
- •26.4.4.3. Defining Cell Zone Conditions
- •26.4.4.4. Defining Boundary Conditions
- •26.4.4.5. Specifying Solution Settings
- •26.4.4.6. Obtaining Solution
- •26.4.5. Postprocessing
- •26.5. Summary
- •Chapter 27: In-Flight Icing Tutorial Using Fluent Icing
- •27.1. Fluent Airflow on the NACA0012 Airfoil
- •27.2. Flow Solution on the Rough NACA0012 Airfoil
- •27.3. Droplet Impingement on the NACA0012
- •27.3.1. Monodispersed Calculation
- •27.3.2. Langmuir-D Distribution
- •27.3.3. Post-Processing Using Quick-View
- •27.4. Fluent Icing Ice Accretion on the NACA0012
- •27.5. Postprocessing an Ice Accretion Solution Using CFD-Post Macros
- •27.6. Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement
- •27.7. Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement – Postprocessing Using CFD-Post
vk.com/club152685050Using Overset and Dynamic| vkMeshes.com/id446425943
12.7.8. Diagnosing an Overset Case
Once an overset interface is created, it is important to check and diagnose it. In this section you will learn about diagnosing an overset interface and about the different cells participating in the solution.
In overset meshing all meshes are categorized into five cell types:
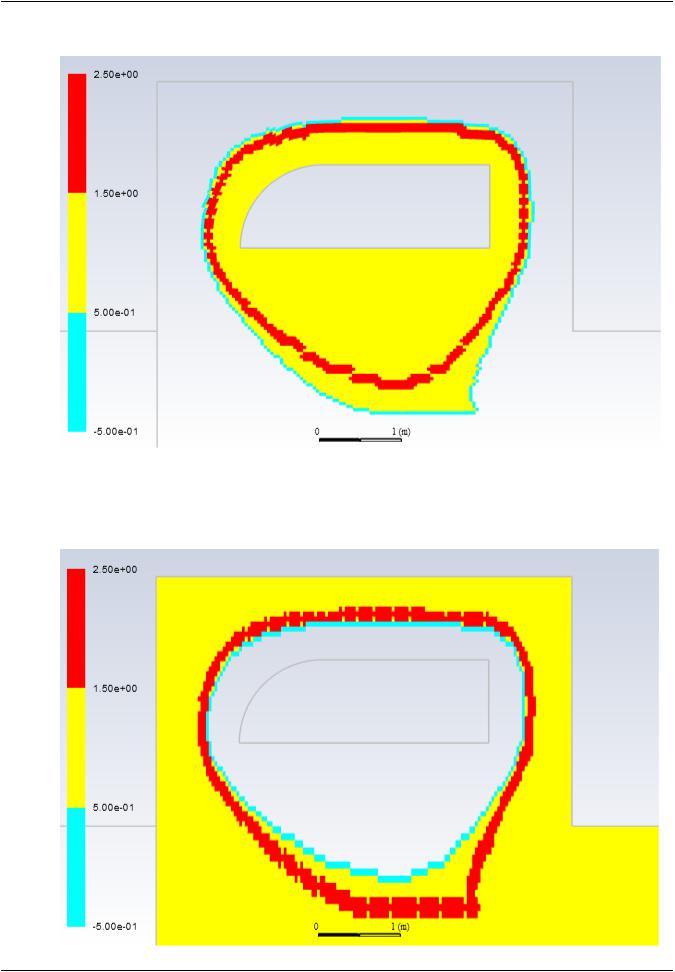
•Solve – (yellow in figures Figure 12.3: Cell Marking on component (p. 438) & Figure 12.4: Cell Marking on fluid-background (p. 438)) cells that take part in the solution.
•Donor – (marked red in figures Figure 12.3: Cell Marking on component (p. 438) & Figure 12.4: Cell Marking on fluid-background (p. 438)) provide information to corresponding cell zones.
•Receptor – (marked blue in figures Figure 12.3: Cell Marking on component (p. 438) & Figure 12.4: Cell Marking on fluid-background (p. 438)) receive information from donor cells in the corresponding cell zones.
•Dead – (marked in red in figures Figure 12.5: Dead Cells in the Component (p. 440)) deactivated cells located in regions of overlap between the background and component meshes, where multiple cells are present in the same exact location. Only one set of cells in a region is allowed to take part in the solution. Additionally, cells outside of the flow regime are marked as dead.
•Orphan – receptor cells that cannot find a corresponding donor cell. Although Fluent has intelligence to deal with orphan cells, their presence should be avoided to reduce the risk of solution inaccuracies and divergence.
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
434 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |

vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943 |
Unsteady Setup |
You can mark orphan cells using the TUI command:
define/overset-interfaces/mark-cells orphan no
This will show all of the orphan cells present in the case, unless you specify a particular zone. Marking orphan cells creates a register that you can display via the define/overset-interfaces/display- cells text command. The marked cells are in the overset-orphan-cells-r0 register.
In this case there are not any orphan cells, so nothing is displayed in the graphics window. If you mark solve cells or other cells types and display those registers, then it will appear in the graphics window.
If large number of orphan cells are generated in a case, then it is advisable to modify the mesh accordingly.
Different type of cells can also be displayed creating contours of Cell Info and displaying the Overset Cell Type for given surfaces.
Enable the following TUI command to include receptor cells in the contours display:
/define/overset-interfaces/options/render-receptor-cells? yes
The overset interface for this tutorial is created properly, but issues could arise during overset interface creation for geometries with complex topology. ANSYS Fluent provides options to diagnose issues and fix them. You can use the ‘debug hole cut’ option to understand more about flood filling of seed cells or leakage between overlapping boundaries. For detailed information on overset mesh diagnosis, refer to "Diagnosing Overset Interface Issues" in the Fluent User's Guide.
1.Start a new Fluent session, and read overset-pod-steady-state.cas.gz and overset-pod- steady-state.dat.gz.
 File → Read → Case & Data...
File → Read → Case & Data...
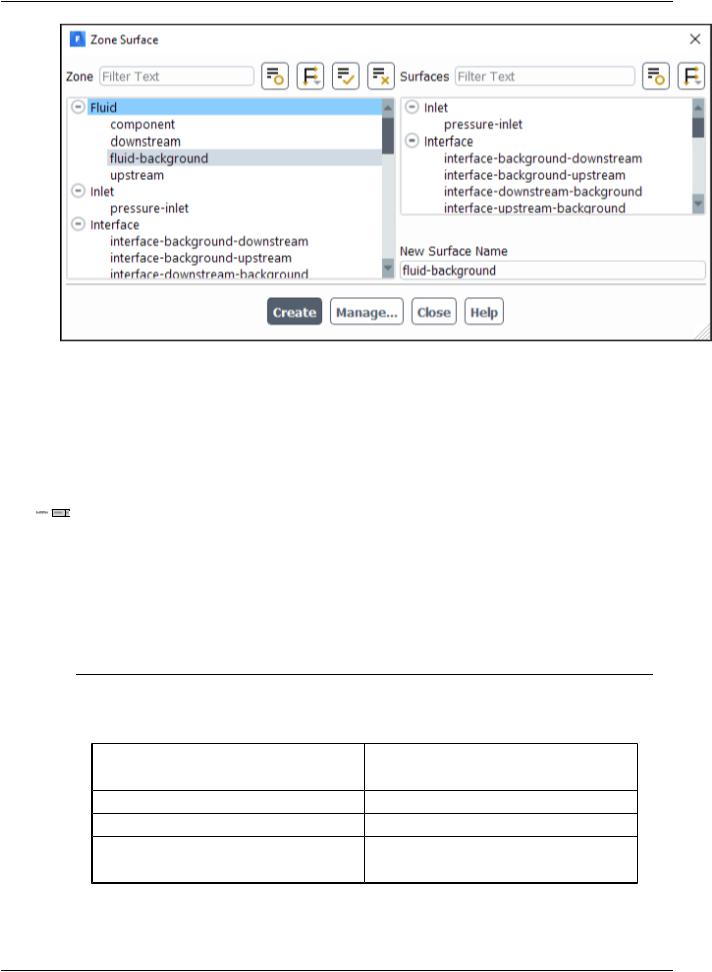
2.Create zone surfaces for component and fluid-background.
 Results → Surface → Create → Zone...
Results → Surface → Create → Zone...
a.Select component in the Zone list.
b.Retain component for New Surface Name and click Create.
c.Similarly, create a zone surface for fluid-background.
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
435 |
vk.com/club152685050Using Overset and Dynamic| vkMeshes.com/id446425943
d.Close the Zone Surface dialog box.
3.Enter the following TUI command in the console:/define/overset-interfaces/op- tions/render-receptor-cells? Yes
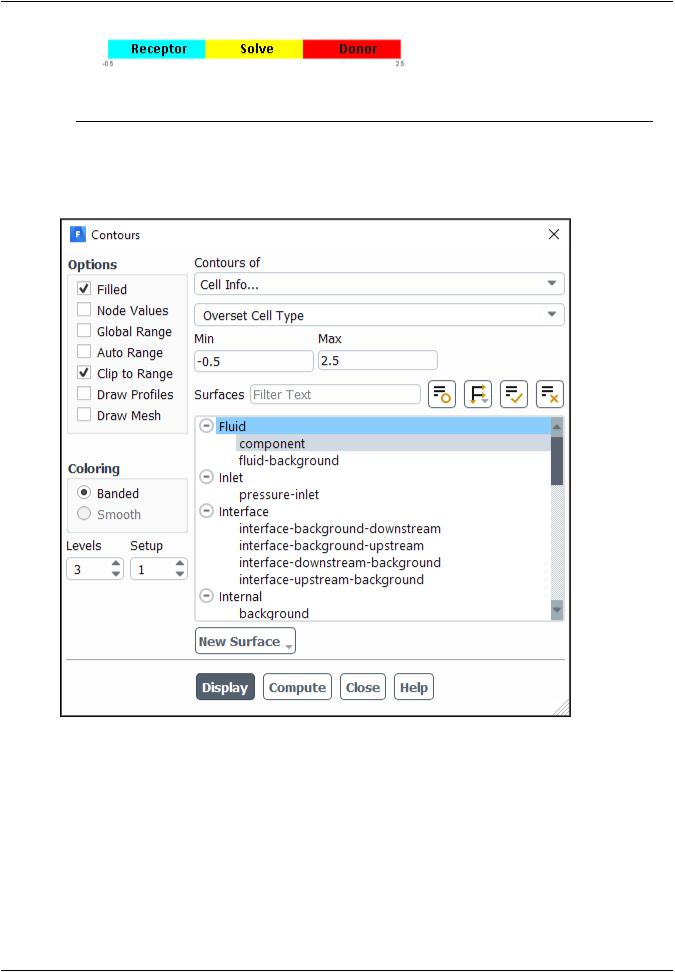
4.Display contours of the overset cell type on the surface you just created.
 Results → Graphics → Contours → Edit...
Results → Graphics → Contours → Edit...
a.Enable Filled and disable Autorange (which enables Clip to Range) in the Options group box.
b.Disable Node Values and Global Range in the Options group box.
c.Select Cell Info... and Overset Cell Type from the Contours of drop-down lists.
d.Enter -0.5 for Min and 2.5 for Max.
Note
Table 12.1: Meaning of Values |
|
Cell Type |
Integer Function Value |
Donor |
2 |
Solve |
1 |
Receptor |
0 |
Orphan |
-1 |
Dead |
-2 |
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
436 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943 |
Unsteady Setup |
Dead cells cannot be displayed in contours.
e.Enter 3 for Levels.
f.Select component from the list of Surfaces.
g.Click Display.
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
437 |
vk.com/club152685050Using Overset and Dynamic| vkMeshes.com/id446425943
Figure 12.3: Cell Marking on component
h.Repeat the process for fluid-background.
Figure 12.4: Cell Marking on fluid-background
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
438 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |

vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943 |
Unsteady Setup |
5.Marking and displaying dead cells.
a. Expand Cell Zones in the tree to check the id number.


 Setup → Cell Zone Conditions
Setup → Cell Zone Conditions
b.Mark dead cells in component with the following TUI command: define/overset-inter- faces/mark-cells dead yes 29
c.Mark dead cells in fluid-background with the following TUI command: /define/overset-in- terfaces/mark-cells dead yes 7
d.Display the dead cells by entering the define/overset-interfaces/display-cells text command in the console.
i.Enter 0 for the text command prompt to display the overset-dead-cells-component-r0 register (you can enter 0 instead of typing the full name of the register).
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
439 |

vk.com/club152685050Using Overset and Dynamic| vkMeshes.com/id446425943
Figure 12.5: Dead Cells in the Component
ii.Enter 1 for the text command prompt to display only the overset-dead-cells-fluid-background- r1 register.
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
440 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
