
- •ANSYS Fluent Tutorial Guide
- •Table of Contents
- •Using This Manual
- •1. What’s In This Manual
- •2. How To Use This Manual
- •2.1. For the Beginner
- •2.2. For the Experienced User
- •3. Typographical Conventions Used In This Manual
- •Chapter 1: Fluid Flow in an Exhaust Manifold
- •1.1. Introduction
- •1.2. Prerequisites
- •1.3. Problem Description
- •1.4. Setup and Solution
- •1.4.1. Preparation
- •1.4.2. Meshing Workflow
- •1.4.3. General Settings
- •1.4.4. Solver Settings
- •1.4.5. Models
- •1.4.6. Materials
- •1.4.7. Cell Zone Conditions
- •1.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •1.4.9. Solution
- •1.4.10. Postprocessing
- •1.5. Summary
- •Chapter 2: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
- •2.1. Introduction
- •2.2. Prerequisites
- •2.3. Problem Description
- •2.4. Setup and Solution
- •2.4.1. Preparation
- •2.4.2. Launching ANSYS Fluent
- •2.4.3. Reading the Mesh
- •2.4.4. Setting Up Domain
- •2.4.5. Setting Up Physics
- •2.4.6. Solving
- •2.4.7. Displaying the Preliminary Solution
- •2.4.8. Adapting the Mesh
- •2.5. Summary
- •Chapter 3: Postprocessing
- •3.1. Introduction
- •3.2. Prerequisites
- •3.3. Problem Description
- •3.4. Setup and Solution
- •3.4.1. Preparation
- •3.4.2. Reading the Mesh
- •3.4.3. Manipulating the Mesh in the Viewer
- •3.4.4. Adding Lights
- •3.4.5. Creating Isosurfaces
- •3.4.6. Generating Contours
- •3.4.7. Generating Velocity Vectors
- •3.4.8. Creating an Animation
- •3.4.9. Displaying Pathlines
- •3.4.10. Creating a Scene With Vectors and Contours
- •3.4.11. Advanced Overlay of Pathlines on a Scene
- •3.4.12. Creating Exploded Views
- •3.4.13. Animating the Display of Results in Successive Streamwise Planes
- •3.4.14. Generating XY Plots
- •3.4.15. Creating Annotation
- •3.4.16. Saving Picture Files
- •3.4.17. Generating Volume Integral Reports
- •3.5. Summary
- •Chapter 4: Modeling Periodic Flow and Heat Transfer
- •4.1. Introduction
- •4.2. Prerequisites
- •4.3. Problem Description
- •4.4. Setup and Solution
- •4.4.1. Preparation
- •4.4.2. Mesh
- •4.4.3. General Settings
- •4.4.4. Models
- •4.4.5. Materials
- •4.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •4.4.7. Periodic Conditions
- •4.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •4.4.9. Solution
- •4.4.10. Postprocessing
- •4.5. Summary
- •4.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 5: Modeling External Compressible Flow
- •5.1. Introduction
- •5.2. Prerequisites
- •5.3. Problem Description
- •5.4. Setup and Solution
- •5.4.1. Preparation
- •5.4.2. Mesh
- •5.4.3. Solver
- •5.4.4. Models
- •5.4.5. Materials
- •5.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •5.4.7. Operating Conditions
- •5.4.8. Solution
- •5.4.9. Postprocessing
- •5.5. Summary
- •5.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 6: Modeling Transient Compressible Flow
- •6.1. Introduction
- •6.2. Prerequisites
- •6.3. Problem Description
- •6.4. Setup and Solution
- •6.4.1. Preparation
- •6.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •6.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •6.4.4. Models
- •6.4.5. Materials
- •6.4.6. Operating Conditions
- •6.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •6.4.8. Solution: Steady Flow
- •6.4.9. Enabling Time Dependence and Setting Transient Conditions
- •6.4.10. Specifying Solution Parameters for Transient Flow and Solving
- •6.4.11. Saving and Postprocessing Time-Dependent Data Sets
- •6.5. Summary
- •6.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 7: Modeling Flow Through Porous Media
- •7.1. Introduction
- •7.2. Prerequisites
- •7.3. Problem Description
- •7.4. Setup and Solution
- •7.4.1. Preparation
- •7.4.2. Mesh
- •7.4.3. General Settings
- •7.4.4. Models
- •7.4.5. Materials
- •7.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •7.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •7.4.8. Solution
- •7.4.9. Postprocessing
- •7.5. Summary
- •7.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 8: Modeling Radiation and Natural Convection
- •8.1. Introduction
- •8.2. Prerequisites
- •8.3. Problem Description
- •8.4. Setup and Solution
- •8.4.1. Preparation
- •8.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •8.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •8.4.4. Models
- •8.4.5. Defining the Materials
- •8.4.6. Operating Conditions
- •8.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •8.4.8. Obtaining the Solution
- •8.4.9. Postprocessing
- •8.4.10. Comparing the Contour Plots after Varying Radiating Surfaces
- •8.4.11. S2S Definition, Solution, and Postprocessing with Partial Enclosure
- •8.5. Summary
- •8.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 9: Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame
- •9.1. Introduction
- •9.2. Prerequisites
- •9.3. Problem Description
- •9.4. Setup and Solution
- •9.4.1. Preparation
- •9.4.2. Mesh
- •9.4.3. General Settings
- •9.4.4. Models
- •9.4.5. Materials
- •9.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •9.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •9.4.8. Solution Using the Standard k- ε Model
- •9.4.9. Postprocessing for the Standard k- ε Solution
- •9.4.10. Solution Using the RNG k- ε Model
- •9.4.11. Postprocessing for the RNG k- ε Solution
- •9.5. Summary
- •9.6. Further Improvements
- •9.7. References
- •Chapter 10: Using Multiple Reference Frames
- •10.1. Introduction
- •10.2. Prerequisites
- •10.3. Problem Description
- •10.4. Setup and Solution
- •10.4.1. Preparation
- •10.4.2. Mesh
- •10.4.3. Models
- •10.4.4. Materials
- •10.4.5. Cell Zone Conditions
- •10.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •10.4.7. Solution
- •10.4.8. Postprocessing
- •10.5. Summary
- •10.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 11: Using Sliding Meshes
- •11.1. Introduction
- •11.2. Prerequisites
- •11.3. Problem Description
- •11.4. Setup and Solution
- •11.4.1. Preparation
- •11.4.2. Mesh
- •11.4.3. General Settings
- •11.4.4. Models
- •11.4.5. Materials
- •11.4.6. Cell Zone Conditions
- •11.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •11.4.8. Operating Conditions
- •11.4.9. Mesh Interfaces
- •11.4.10. Solution
- •11.4.11. Postprocessing
- •11.5. Summary
- •11.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 12: Using Overset and Dynamic Meshes
- •12.1. Prerequisites
- •12.2. Problem Description
- •12.3. Preparation
- •12.4. Mesh
- •12.5. Overset Interface Creation
- •12.6. Steady-State Case Setup
- •12.6.1. General Settings
- •12.6.2. Models
- •12.6.3. Materials
- •12.6.4. Operating Conditions
- •12.6.5. Boundary Conditions
- •12.6.6. Reference Values
- •12.6.7. Solution
- •12.7. Unsteady Setup
- •12.7.1. General Settings
- •12.7.2. Compile the UDF
- •12.7.3. Dynamic Mesh Settings
- •12.7.4. Report Generation for Unsteady Case
- •12.7.5. Run Calculations for Unsteady Case
- •12.7.6. Overset Solution Checking
- •12.7.7. Postprocessing
- •12.7.8. Diagnosing an Overset Case
- •12.8. Summary
- •Chapter 13: Modeling Species Transport and Gaseous Combustion
- •13.1. Introduction
- •13.2. Prerequisites
- •13.3. Problem Description
- •13.4. Background
- •13.5. Setup and Solution
- •13.5.1. Preparation
- •13.5.2. Mesh
- •13.5.3. General Settings
- •13.5.4. Models
- •13.5.5. Materials
- •13.5.6. Boundary Conditions
- •13.5.7. Initial Reaction Solution
- •13.5.8. Postprocessing
- •13.5.9. NOx Prediction
- •13.6. Summary
- •13.7. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 14: Using the Eddy Dissipation and Steady Diffusion Flamelet Combustion Models
- •14.1. Introduction
- •14.2. Prerequisites
- •14.3. Problem Description
- •14.4. Setup and Solution
- •14.4.1. Preparation
- •14.4.2. Mesh
- •14.4.3. Solver Settings
- •14.4.4. Models
- •14.4.5. Boundary Conditions
- •14.4.6. Solution
- •14.4.7. Postprocessing for the Eddy-Dissipation Solution
- •14.5. Steady Diffusion Flamelet Model Setup and Solution
- •14.5.1. Models
- •14.5.2. Boundary Conditions
- •14.5.3. Solution
- •14.5.4. Postprocessing for the Steady Diffusion Flamelet Solution
- •14.6. Summary
- •Chapter 15: Modeling Surface Chemistry
- •15.1. Introduction
- •15.2. Prerequisites
- •15.3. Problem Description
- •15.4. Setup and Solution
- •15.4.1. Preparation
- •15.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •15.4.3. Solver and Analysis Type
- •15.4.4. Specifying the Models
- •15.4.5. Defining Materials and Properties
- •15.4.6. Specifying Boundary Conditions
- •15.4.7. Setting the Operating Conditions
- •15.4.8. Simulating Non-Reacting Flow
- •15.4.9. Simulating Reacting Flow
- •15.4.10. Postprocessing the Solution Results
- •15.5. Summary
- •15.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 16: Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
- •16.1. Introduction
- •16.2. Prerequisites
- •16.3. Problem Description
- •16.4. Setup and Solution
- •16.4.1. Preparation
- •16.4.2. Mesh
- •16.4.3. Solver
- •16.4.4. Models
- •16.4.5. Materials
- •16.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •16.4.7. Initial Solution Without Droplets
- •16.4.8. Creating a Spray Injection
- •16.4.9. Solution
- •16.4.10. Postprocessing
- •16.5. Summary
- •16.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 17: Using the VOF Model
- •17.1. Introduction
- •17.2. Prerequisites
- •17.3. Problem Description
- •17.4. Setup and Solution
- •17.4.1. Preparation
- •17.4.2. Reading and Manipulating the Mesh
- •17.4.3. General Settings
- •17.4.4. Models
- •17.4.5. Materials
- •17.4.6. Phases
- •17.4.7. Operating Conditions
- •17.4.8. User-Defined Function (UDF)
- •17.4.9. Boundary Conditions
- •17.4.10. Solution
- •17.4.11. Postprocessing
- •17.5. Summary
- •17.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 18: Modeling Cavitation
- •18.1. Introduction
- •18.2. Prerequisites
- •18.3. Problem Description
- •18.4. Setup and Solution
- •18.4.1. Preparation
- •18.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •18.4.3. Solver Settings
- •18.4.4. Models
- •18.4.5. Materials
- •18.4.6. Phases
- •18.4.7. Boundary Conditions
- •18.4.8. Operating Conditions
- •18.4.9. Solution
- •18.4.10. Postprocessing
- •18.5. Summary
- •18.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 19: Using the Multiphase Models
- •19.1. Introduction
- •19.2. Prerequisites
- •19.3. Problem Description
- •19.4. Setup and Solution
- •19.4.1. Preparation
- •19.4.2. Mesh
- •19.4.3. Solver Settings
- •19.4.4. Models
- •19.4.5. Materials
- •19.4.6. Phases
- •19.4.7. Cell Zone Conditions
- •19.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •19.4.9. Solution
- •19.4.10. Postprocessing
- •19.5. Summary
- •Chapter 20: Modeling Solidification
- •20.1. Introduction
- •20.2. Prerequisites
- •20.3. Problem Description
- •20.4. Setup and Solution
- •20.4.1. Preparation
- •20.4.2. Reading and Checking the Mesh
- •20.4.3. Specifying Solver and Analysis Type
- •20.4.4. Specifying the Models
- •20.4.5. Defining Materials
- •20.4.6. Setting the Cell Zone Conditions
- •20.4.7. Setting the Boundary Conditions
- •20.4.8. Solution: Steady Conduction
- •20.5. Summary
- •20.6. Further Improvements
- •Chapter 21: Using the Eulerian Granular Multiphase Model with Heat Transfer
- •21.1. Introduction
- •21.2. Prerequisites
- •21.3. Problem Description
- •21.4. Setup and Solution
- •21.4.1. Preparation
- •21.4.2. Mesh
- •21.4.3. Solver Settings
- •21.4.4. Models
- •21.4.6. Materials
- •21.4.7. Phases
- •21.4.8. Boundary Conditions
- •21.4.9. Solution
- •21.4.10. Postprocessing
- •21.5. Summary
- •21.6. Further Improvements
- •21.7. References
- •22.1. Introduction
- •22.2. Prerequisites
- •22.3. Problem Description
- •22.4. Setup and Solution
- •22.4.1. Preparation
- •22.4.2. Structural Model
- •22.4.3. Materials
- •22.4.4. Cell Zone Conditions
- •22.4.5. Boundary Conditions
- •22.4.6. Solution
- •22.4.7. Postprocessing
- •22.5. Summary
- •23.1. Introduction
- •23.2. Prerequisites
- •23.3. Problem Description
- •23.4. Setup and Solution
- •23.4.1. Preparation
- •23.4.2. Solver and Analysis Type
- •23.4.3. Structural Model
- •23.4.4. Materials
- •23.4.5. Cell Zone Conditions
- •23.4.6. Boundary Conditions
- •23.4.7. Dynamic Mesh Zones
- •23.4.8. Solution Animations
- •23.4.9. Solution
- •23.4.10. Postprocessing
- •23.5. Summary
- •Chapter 24: Using the Adjoint Solver – 2D Laminar Flow Past a Cylinder
- •24.1. Introduction
- •24.2. Prerequisites
- •24.3. Problem Description
- •24.4. Setup and Solution
- •24.4.1. Step 1: Preparation
- •24.4.2. Step 2: Define Observables
- •24.4.3. Step 3: Compute the Drag Sensitivity
- •24.4.4. Step 4: Postprocess and Export Drag Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.1. Boundary Condition Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.2. Momentum Source Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.3. Shape Sensitivity
- •24.4.4.4. Exporting Drag Sensitivity Data
- •24.4.5. Step 5: Compute Lift Sensitivity
- •24.4.6. Step 6: Modify the Shape
- •24.5. Summary
- •25.1. Introduction
- •25.2. Prerequisites
- •25.3. Problem Description
- •25.4. Setup and Solution
- •25.4.1. Preparation
- •25.4.2. Reading and Scaling the Mesh
- •25.4.3. Loading the MSMD battery Add-on
- •25.4.4. NTGK Battery Model Setup
- •25.4.4.1. Specifying Solver and Models
- •25.4.4.2. Defining New Materials for Cell and Tabs
- •25.4.4.3. Defining Cell Zone Conditions
- •25.4.4.4. Defining Boundary Conditions
- •25.4.4.5. Specifying Solution Settings
- •25.4.4.6. Obtaining Solution
- •25.4.5. Postprocessing
- •25.4.6. Simulating the Battery Pulse Discharge Using the ECM Model
- •25.4.7. Using the Reduced Order Method (ROM)
- •25.4.8. External and Internal Short-Circuit Treatment
- •25.4.8.1. Setting up and Solving a Short-Circuit Problem
- •25.4.8.2. Postprocessing
- •25.5. Summary
- •25.6. Appendix
- •25.7. References
- •26.1. Introduction
- •26.2. Prerequisites
- •26.3. Problem Description
- •26.4. Setup and Solution
- •26.4.1. Preparation
- •26.4.2. Reading and Scaling the Mesh
- •26.4.3. Loading the MSMD battery Add-on
- •26.4.4. Battery Model Setup
- •26.4.4.1. Specifying Solver and Models
- •26.4.4.2. Defining New Materials
- •26.4.4.3. Defining Cell Zone Conditions
- •26.4.4.4. Defining Boundary Conditions
- •26.4.4.5. Specifying Solution Settings
- •26.4.4.6. Obtaining Solution
- •26.4.5. Postprocessing
- •26.5. Summary
- •Chapter 27: In-Flight Icing Tutorial Using Fluent Icing
- •27.1. Fluent Airflow on the NACA0012 Airfoil
- •27.2. Flow Solution on the Rough NACA0012 Airfoil
- •27.3. Droplet Impingement on the NACA0012
- •27.3.1. Monodispersed Calculation
- •27.3.2. Langmuir-D Distribution
- •27.3.3. Post-Processing Using Quick-View
- •27.4. Fluent Icing Ice Accretion on the NACA0012
- •27.5. Postprocessing an Ice Accretion Solution Using CFD-Post Macros
- •27.6. Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement
- •27.7. Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement – Postprocessing Using CFD-Post
vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement
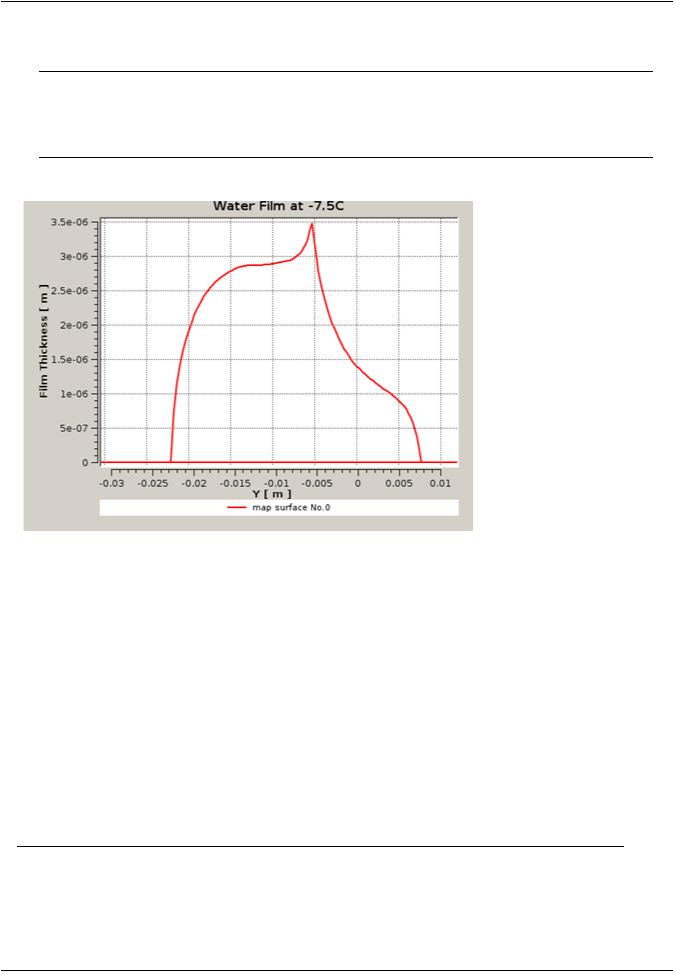
16.Leave the other default settings unchanged and click Calculate to update the 2D plot in the ChartViewer. The figure below shows the output of the macro.
Note
Users are invited to modify the input parameter of 2D-Plot (with) → Y-Axis to view different fields of the ICE3D solution.
Figure 27.26: 2D-Plot in CFD-Post, Water Film Distribution
27.6. Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement
As ice grows, the geometric profile of the contaminated airfoil changes which changes the flow of air and water droplets around it. The quasi-steady multishot approach allows simulation of realistic and accurate ice shapes. In this approach, the total time of ice accretion is divided into smaller steady-state intervals (shots), where the mesh used to calculate the airflow, the droplet impingement, and the ice accretion is updated at the end of each shot to account for the ice shape produced at each shot.
In the current version of Fluent Icing, multishot runs are done using automatic mesh displacement, where the ice surface is used to displace the contaminated walls and consequently the volume mesh around these walls. This process keeps the number of nodes and elements constant. As the ice shape grows, the total area covered by the boundary wall mesh increases which changes the size and the aspect ratio of the elements near the ice. This may result in a less than optimal grid spacing if the initial (undeformed) mesh is not fine enough. For complex ice shapes, manual remeshing maybe required in order to continue the multishot process when using automatic mesh displacement.
Note
FENSAP-ICE is able to utilize automatic remeshing in addition to the classic mesh deformation when simulating multi-shot icing. Remeshing of the iced surface refines and reorganizes the mesh topology on and around the ice, leading to more stable and ac-
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
925 |

vk.com/club152685050In-F ight Icing Tutorial Using| vk.Fluentcom/id446425943Icing
curate air and droplet solutions for the next shot. Negative volume elements that often form with large mesh deformations are also avoided with remeshing. These options are not yet supported by Fluent Icing. For more information regarding automatic remeshing, consult Automated Sequences and Multishot Icing Calculations within the FENSAP-ICE User Manual
1.Launch Fluent Icing from your working directory, FLUENT_ICING_NACA0012.
2.Go to File → Preferences…. Select Icing on the left hand-side of the Preferences window. Assign a number of CPUs, 2 to 4 CPUs, next to Default Fluent CPU and set Default work folder to the location of your working directory.
3.Go to File → Open case…. Browse to and select the file naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C.cas, created in Fluent Icing Ice Accretion on the NACA0012 (p. 912). In this tutorial, you will simulate 3 quasi-steady shots using the same in-flight icing conditions of the naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C.cas.
4.A message window will ask you to launch Fluent, click Yes. A new simulation tree appears under naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C.cas(loaded) in the Outline View window. All airflow, droplet and ice conditions and solutions previously configured and computed in the previous simulation are automatically imported under that .CAS.
5.Go to Set-up → Ice and its Properties window and check Beading under Model. Beading is the roughness model of the Ice component. At the end of each shot, Beading will produce a roughness distribution that is used by the airflow solver (Fluent or FENSAP (beta)) during the next shot. This approach removes any arbitrary specification of roughness value and removes empiricism in the specification of roughness. The first shot always needs some initial roughness, 0.5 mm in Flow Solution on the Rough NACA0012 Air-
foil (p. 892), since Ice is not run a priori. However, the remaining shots will use the distribution obtained from the beading model.
Note
Alternatively, the initial shots could be conducted over small time intervals where the surface roughness can be allowed to grow from 0 to a reasonable level, removing the need to specify an initial roughness value. For internal flows, it is not recommended to start with a non-zero initial roughness instead. Roughness should be allowed to build progressively using shorter icing shots.
6.Click on Solve and, in its Properties window, under Multi-shot:
•Set Number of shots to 3
•Check Save files at each shot to examine the steady-state solutions at the end of each shot.
7.Under Solve → Ice,
•In Time, change the Total time of ice accretion [s] from 420 to 140 which corresponds to 1/3rd of the total time.
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
926 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |

vk.com/club152685050 | vk.com/id446425943Multi-Shot Ice Accretion with Automatic Mesh Displacement
• In Output, check Run grid displacement to update the grid at the end of each shot.
Note
As the grid quality may deteriorate after each shot, it might be necessary to change several settings in Solve to improve the robustness and convergence of these simulations. In this manner, the number of iterations can be increased for Airflow and Particles and the CFL number can be lowered in the case of Particles.
8.Right-click Ice under Solve and choose Reset to erase the solution of the previous one shot simulation.
9.Go to File → Save Case as …, and name it naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C_multi. All multishot solutions will start with this name followed by the shot number and a suffix that describes the nature of the output file.
10.Launch the multishot calculation by right-clicking Solve and then by selecting Run multishot.
11.Once all the computations are complete, go to Ribbon menu and select View. In Quick-view, click Ice cover → Multishot ice cover - Viewmerical to see the final ice shape of the multishot calculation.
Figure 27.27: 3-Shots Ice Shape at -7.5 C
12.Compare the ice shape of the multishot run to that of the single shot run while the Viewmerical window that displays the multi-shot ice shape is up.
13.In the Objects panel, rename this object by double-clicking on its original name in the Object window and enter -7.5C, 3 shots in the window Rename dataset.
14.Click on the  button located at the right corner of the Object panel. A window appears to load a pair of files, a grid file and its solution file.
button located at the right corner of the Object panel. A window appears to load a pair of files, a grid file and its solution file.
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
|
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
927 |
vk.com/club152685050In-F ight Icing Tutorial Using| vk.Fluentcom/id446425943Icing
15.Click on the  folder icon of Grid file and select the naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C.ice.grid file located inside your working directory.
folder icon of Grid file and select the naca0012_rough_mvd_m7p5C.ice.grid file located inside your working directory.
16.Press the Load button. A new data set is added to the Object panel. Rename this dataset by double-clicking on its original name and enter -7.5C, 1 shot in the window Rename dataset.
17.Click the lock icon at the lower right of the data set list in the Objects window.
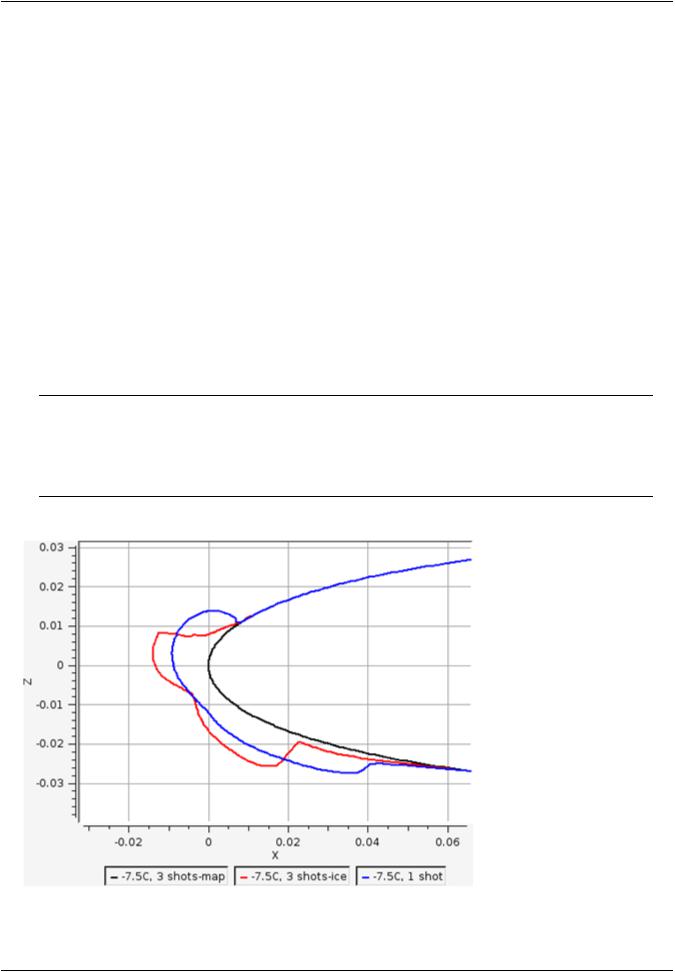
18.Go to the Query panel and activate the 2D plot. Set the Mode to Geometry and Cutting plane to Z. Set the horizontal axis to X. The three curves showing NACA0012 and the ice shapes should be visible. Change the curve colors and thickness using the Curve Settings in the cube menu located at the top right. You can also draw a zoom box by Shift + left-click.
Note
The multishot simulation produces an upper horn that is more pronounced due to higher water droplet catch area and higher heat fluxes with increase in curvature. The lower part of the ice is also thicker where the roughness has grown beyond the initial 0.5mm to about 1mm (average), which causes the water film to freeze sooner and show less runback compared to the single shot solution.
Note
The curves that have the -map suffix refer to the original surface and the curves that have the -ice suffix refer to the final iced surface (at 420 s).
Figure 27.28: Ice Shapes at -7.5 C, Obtained Using One Shot and Three Shots Computations
|
Release 2019 R1 - © ANSYS,Inc.All rights reserved.- Contains proprietary and confidential information |
928 |
of ANSYS, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates. |
