
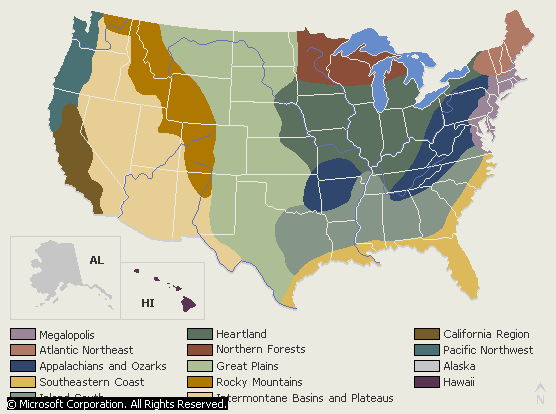
Here: Inland South (covered) Intermountain (Am. Spelling)
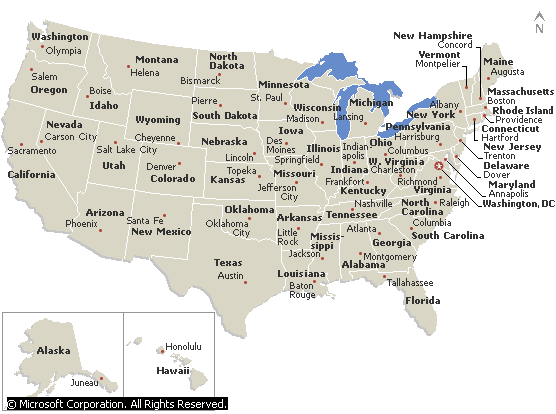
Regions of the United States
The northeast
The Northeast includes the states of New England and the Middle Atlantic region, the nation’s most densely populated area. From the north, the states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania. Together with Virginia in the south, they comprise the oldest settlement areas in the United States. Historic sites dating back to colonial times dot the region. Farming and fishing are significant, but industry, manufacturing and commerce are the most important economic activities.
With its high population density concentrated mainly in cities near the coast like Boston, New York and Philadelphia, much of the Northeast remains rural. Small towns and picturesque villages are spread throughout the region. The largest area of unspoiled nature – mountains, lakes and forests – remind the visitor that it was largely all wilderness only a little over two centuries ago.
The Northeast is one of the most historic areas of the country. The roots of democracy in the United States stretch back to the Mayflower Compact, an agreement drawn up in 1620 by colonists from England. Called “Pilgrims”, they founded Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts. Under the provisions (rules, regulations) of the Compact they decreed “just and equal laws” for all. The Declaration of Independence, enacted in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1776, proclaimed that “all men are created equal”, and signaled the break of the American colonies from the British rule. The Constitution, with its later Bill of Rights, was adopted in Philadelphia in 1787 and has served as the basic law of the United States ever since. The tradition of American ingenuity and resourcefulness first developed in this section of the country where people from different cultures and backgrounds came together to establish a new nation. The simple side of life in the Northeast is hard work and small pleasures.
Megalopolis
The region known as Megalopolis is a heavily populated area extending more than 800 km (500 mi) along a northeast-southwest axis from southern Maine to southern Virginia. Although it encompasses only 130,000 sq km (50,000 sq mi), or about 1 percent of the continent, Megalopolis held some 45 million people in the late 1990s, the second largest population of any U.S. region. It contains the world's greatest concentration of urban areas. Three characteristics define Megalopolis as a distinct region: high population density, major urban centers growing toward one another, and a large demand for primary goods that are brought in from other regions.
the Atlantic Northeast
In great contrast to the highly urbanized character of Megalopolis, the Atlantic Northeast is mainly rural in character. It includes the less-populated, less-developed parts of northern New England and upper New York state. The southern boundary of this region skirts the northern edge of Megalopolis just north of the urbanized areas of Portland, Maine, the Merrimack Valley in New Hampshire, the small cities of western Massachusetts, and the Mohawk Valley of New York. On the west and north, the region is bounded by Canada. The Atlantic Ocean forms the eastern boundary. The Atlantic Northeast is a land of bare rock, thin soils, rugged coastlines, swift streams, and slow-growing forests. Because of its location away from the highly populated and economically active urban core, this region developed its own unique way of life characterized by a high degree of self-reliance. Often families live in the same community for generations. Many communities celebrate local holidays that date to colonial times. In addition, unlike more urbanized regions of the nation, the presence of the forest and the sea continue to have a direct influence on people's lives. In rural areas, the house of the nearest neighbor is often beyond sight and sound, while the most dramatic presence is that of undeveloped natural environment.
THE SOUTHEAST (& APPALACHIA)
The history and traditions of the South (historically – South, regionally – Southeast) have created a sense of strong regional loyalty in Americans from the Southern states. For almost a century following the Civil War, which divided North and South over the issue of slavery, the region was economically depressed. Today, although agriculture – the plantation crops of tobacco, sugar cane and cotton – is still very important, an industrial boom has made the "New South" one of the fastest growing regions of the United States.
The first permanent settlement was the Jamestown Colony in Virginia in 1607. By 1733, Maryland, North and South Carolina, and Georgia had been established as English settlements. The South continued to expand in the 19th and 20th centuries, but not at the same pace as the Northeast, and there are fewer areas of high population density. Besides those mentioned, the Southern States include Delaware, Kentucky, Tennessee, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Arkansas. The port cities of Baltimore on the Chesapeake Bay in Maryland and New Orleans at the mouth of the Mississippi River in Louisiana are two of the largest cities in the South.
There are two main groups of Southerners: those descended from white English, Irish and Scottish colonists and immigrants, and those descended from the vast numbers of black Africans who were brought in as slaves to work on the plantations. The exploitation of slave labor created a Southern life style for the white owners that left a tradition of “graciousness".
The Appalachian Mountains – a part of the southeast region - were formed nearly 230 million years ago and are the oldest mountains in North America. The chain extends from Canada to central Alabama. Where it runs through Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, North Carolina, and Tennessee, although geographically part of the South, it also forms a distinct region of its own: Appalachia. Here the mountains are separated by ridges into valleys and sections called "gaps" or "hollows." Mining and lumbering are important economic activities of the area. Agriculture in the mountains is largely subsistence farming: small crops for home consumption and sale. The great scenic beauty of the mountains attracts many tourists to recreational areas and national parks.
The people are as rugged as the mountains. The southern Appalachians were settled by Scottish and English-immigrants from Virginia in the 18th century. While the rest of the settlers pushed westward, the highlanders stayed put in their mountain hollows, preserving a unique cultural heritage and distinct folk traditions. The songs, dances, crafts, even the speech forms of the people from Appalachia can be traced directly to those brought across the Atlantic by their colonial ancestors. Jesse Stuart, an American writer, wrote that these people – his people – remain among the holdouts (уклонение от чего-л.; стремление остаться в стороне; тот, кто отказывается/ уклоняется от участия в чем-л.) against an American mass culture.
