
- •2. Data, Information, knowledge
- •Flat file database model is a database that stores data in a plain text file. Each line of the text file holds one record, with fields separated by delimiters, such as commas or tabs.
- •Advantages
- •For every record in a child table (the “many” side), one and only one matching record must be in the parent table (the “one” side).
- •12. Designing the database
- •Specifying Field Data Types
- •Sorting records
- •Sorting by two or more fields
- •19. Filtering
- •22. Filters and Queries
- •Adding Selection Criteria
- •23. Performing Calculations in a Query
- •Using Aggregate calculations (Totals) in a Query
- •24. Parameter queries
- •25. Update queries
- •26.Make-table query
- •27. Three ways to arrange information for display or distribution
- •28. Record source can be
- •Creating Simple Forms with the Form Wizard
- •32. Creating a form in design view
- •33. The list of properties depends on current selection.
- •The easiest way to create an input mask is to use the Input Mask Wizard.
- •41. You can specify customized responses to user actions, such as clicking a button, opening a form, or selecting an option in an option group.
- •Events are grouped into eight categories, depending on the effects of the event. For example, some events relate to the data, others to filters, and still others to keyboard actions.
- •Associating the Macro with a Report Event
- •Some PivotTable Terms
- •Item – an element in a field.
- •To create a one-dimensional PivotTable that shows the data field details, you do the following:
- •Creating a PivotChart Report
1. Data as a vital asset
In this Information Age we are surrounded by mountains of data.
The ultimate role of a database management system is to implement controls and provide maintenance to data files using data security to ensure integrity of data.
Even more, data and information created from data are now considered vital enterprise assets, data and information are the lifeblood of the 21st century economy.
Money and people have long been considered to be enterprise assets. Assets are resources with recognized value under the control of an individual or organization. Enterprise assets help achieve the goals of the enterprise, and therefore need to be thoughtfully managed. The capture and use of such assets are carefully controlled, and investments in these assets are effectively leveraged to achieve enterprise objectives.
2. Data, Information, knowledge
Data is the representation of facts as text, numbers, graphics, images, sound or video. the foundation of information, knowledge, and ultimately, wisdom and informed action.
BUT! Data can be inaccurate, incomplete, out of date, and misunderstood.
On a practical level, we speak about information that must be of the highest quality – data that is available, relevant, complete, accurate, consistent, timely, usable, meaningful, and understood.
Technically, data is the plural form of the Latin word datum, meaning "a fact." However, people commonly use the term as a singular thing. Facts are captured, stored, and expressed as data.
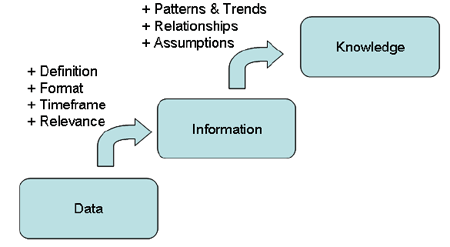
Information is data in context. Without context, data is meaningless; we create meaningful information by interpreting the context around data. This context includes:
The business meaning of data elements and related terms.
The format in which the data is presented.
The timeframe represented by the data.
The relevance of the data to a given usage.
3. A database is an organized collection of related information used for a specific purpose, such as keeping track of ongoing work order activities or maintaining a library.
Data Base Management SystemDBMS is a set of computer programs that controls the creation, maintenance, and use of a database.
4.
databases can be
Classified by function and database model
I. Function
Analytic(al)
Operational
II. Database model
Flat file
Hierarchical
Network
Relational

Analytical DatabasesThis data is meant for commercial usage. All such databases outside the organisation which are of use and limited access are together called external database
In its day to day operation, an organisation generates a huge amount of data. Think of things such as inventory management, purchases, transactions and financials. All this data is collected in a database which is often known by several names such as operational/ production database, subject-area database (SADB) or transaction databases.
An operational database is usually hugely important to organisations as they include the customer database, personal database and inventory database i.e. the details of how much of a product the company has as well as information on the customers who buy them. The data stored in operational databases can be changed and manipulated depending on what the company requires.
5. DATABASE MODELS.
Essentially a data model is a "description" of both a container for data and a methodology for storing and retrieving data from that container. Actually, there isn't really a data model "thing". Data models are abstractions, oftentimes mathematical algorithms and concepts. You cannot really touch a data model. But nevertheless, they are very useful. The analysis and design of data models has been the cornerstone of the evolution of databases. As models have advanced so has database efficiency.
Flat file database model is a database that stores data in a plain text file. Each line of the text file holds one record, with fields separated by delimiters, such as commas or tabs.
Hierarchical database model
Perhaps the most intuitive way to visualize this type of relationship is by visualizing an upside down tree of data. In this tree, a single table acts as the "root" of the database from which other tables "branch" out.
Relationships in such a system are thought of in terms of children and parents such that a child may only have one parent but a parent can have multiple children. Parents and children are tied together by links called "pointers"
The hierarchical structure is used primarily today for storing geographic information and file systems.
6.
6. Network database model
The Network model solves the problem of data redundancy by representing relationships in terms of sets (множества) rather than hierarchy.
The network model is very similar to the hierarchical model actually. In fact, the hierarchical model is a subset of the network model. However, instead of using a single-parent tree hierarchy, the network model uses set theory to provide a tree-like hierarchy with the exception that child tables were allowed to have more than one parent. This allowed the network model to support many-to-many relationships.
7. Relational database model
Of course in the 80's the "Relational Database Model" became the rage. The Relational Model developed out of the work done by Dr. E. F. Codd at IBM in the late 1960s who was looking for ways to solve the problems with the existing models. At the core of the relational model is the concept of a table (also called a relation) in which all data is stored. Each table is made up of records (horizontal rows also known as tuples) and fields (vertical columns also known as attributes).
It is important to note that how or where the tables of data are stored makes no difference. Each table can be identified by a unique name and that name can be used by the database to find the table behind the scenes. As a user, all you need to know is the table name in order to use it. You do not need to worry about the complexities of how the data is stored on the hard drive.
This is quite a bit different from the hierarchical and network models in which the user had to have an understanding of how the data was structured within the database in order to retrieve, insert, update, or delete records from the database.
