
- •1 Introduction
- •2 Nomenclature of Halogeno-compounds
- •3 Physical Properties of Halogeno-compounds
- •4 Preparation of Halogeno-compounds
- •5 Reactions of Halogeno-compounds
- •6 Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- •1. Sn2 reactions
- •2. Sn1 reactions
- •1. Experiment 1 : Comparison of the rates of hydrolysis of 1-chlorobutane, 1-bromobutane and 1-iodobutane
- •2. Experiment 2: Comparison of the rates of hydrolysis of primary, secondary and tertiary haloalkanes and halobenzene
- •7 Elimination Reactions
- •8 Uses of Halogeno-compounds
7 Elimination Reactions
Formation of Alkenes
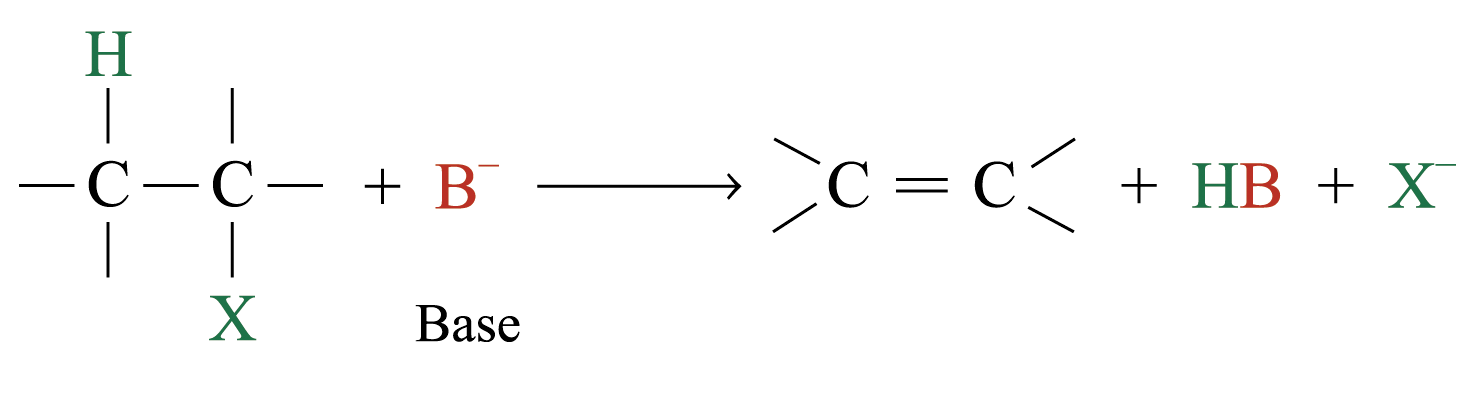
The elimination of HX from adjacent atoms of a haloalkane is widely used for synthesizing alkenes
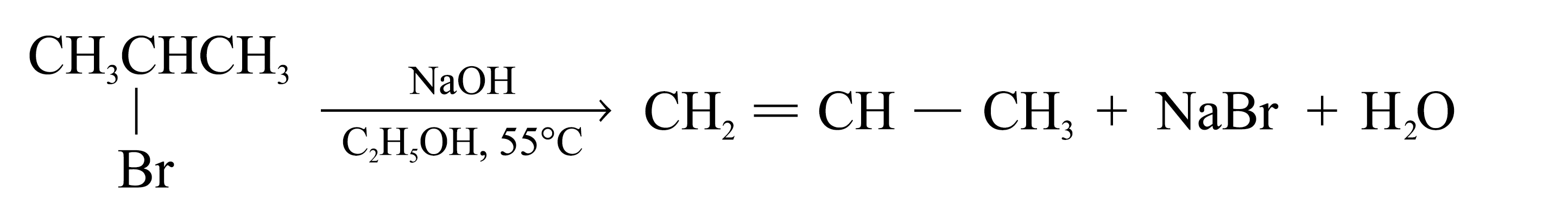
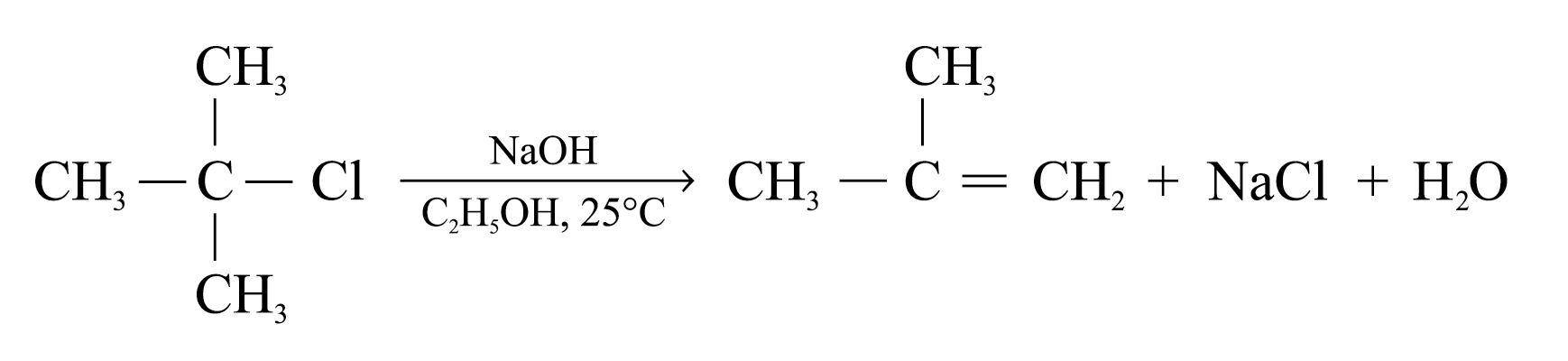
The elements of a hydrogen halide are eliminated from a haloalkane in this way, the reaction is called dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation of most haloalkanes yields more than one product
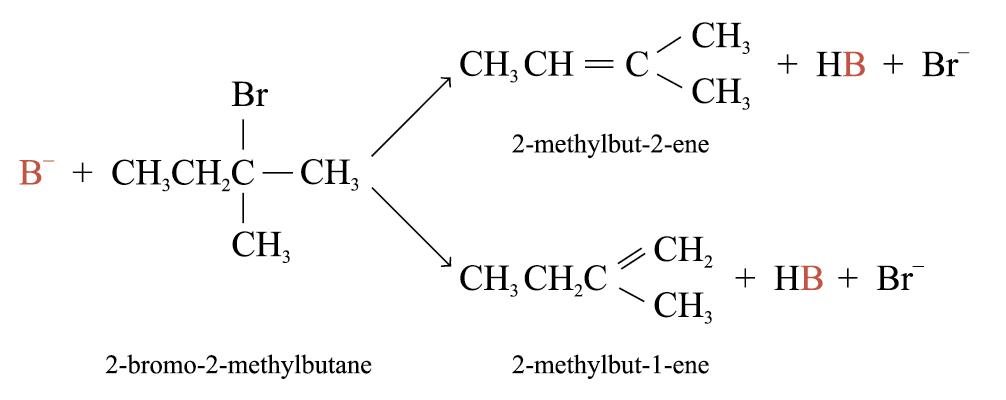
The major product will be the more stable alkene
The more stable alkene has the more highly substituted double bond
Elimination follows the Saytzeff’s rule when the elimination occurs to give the more highly substituted alkene as the major product
The stabilities of alkenes:

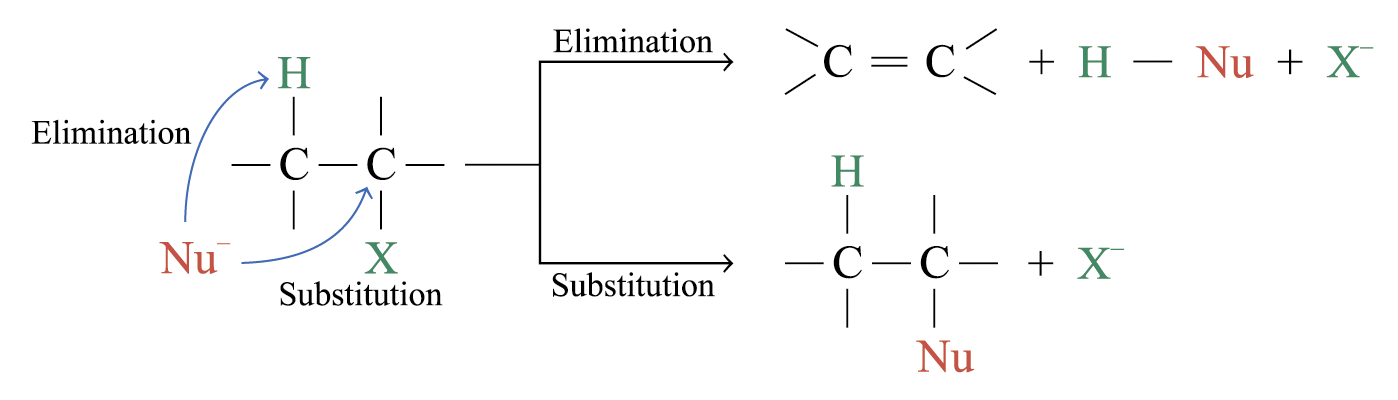
Elimination Versus Substitution
Nucleophiles are potential bases
Bases are potential nucleophiles
In SN2 pathway, elimination and nucleophilic substitution compete each other
Substitution is favoured when the substrate is primary alcohol and the base is hydroxide ion
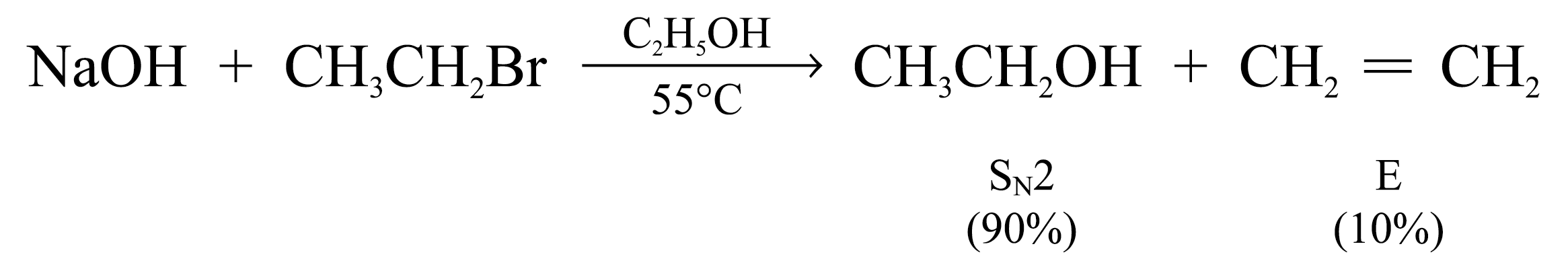
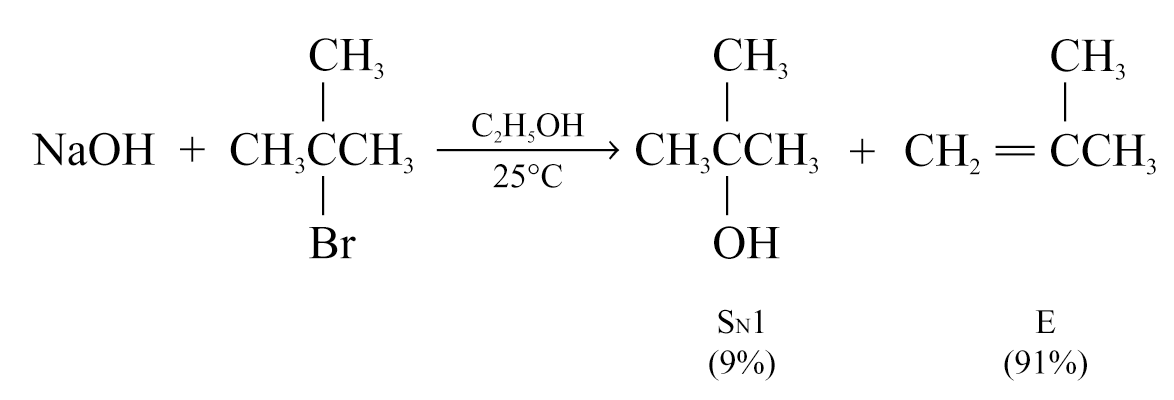
Elimination is favoured when the substrate is secondary alcohol

With tertiary haloalkanes, SN2 reactions cannot take place Þ Elimination is highly favoured especially at high temperatures Þ Substitution occurs through SN1 mechanism only
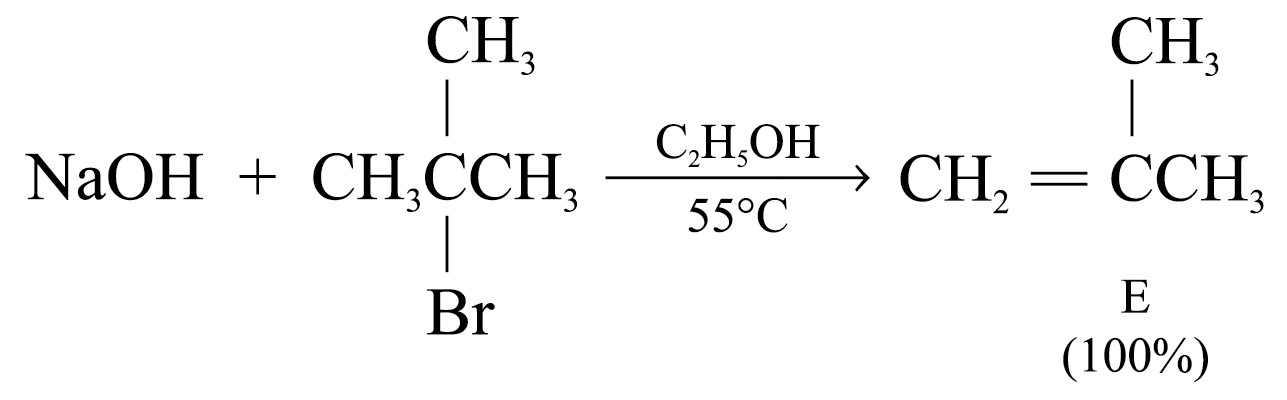
Eliminations will be favoured when using:
1. higher temperatures
2. strong sterically hindered bases (e.g. (CH3)3CO–)
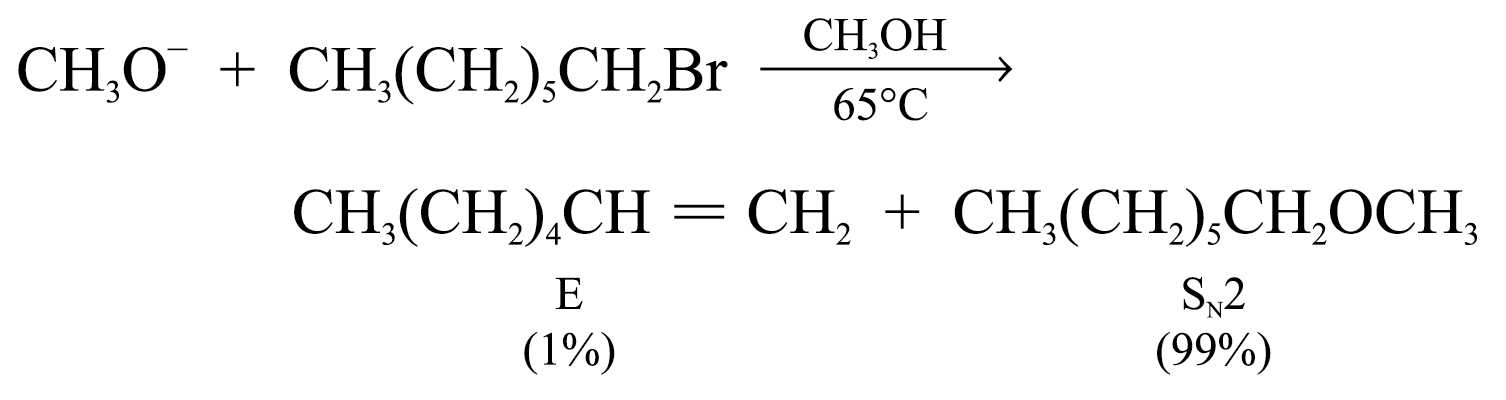
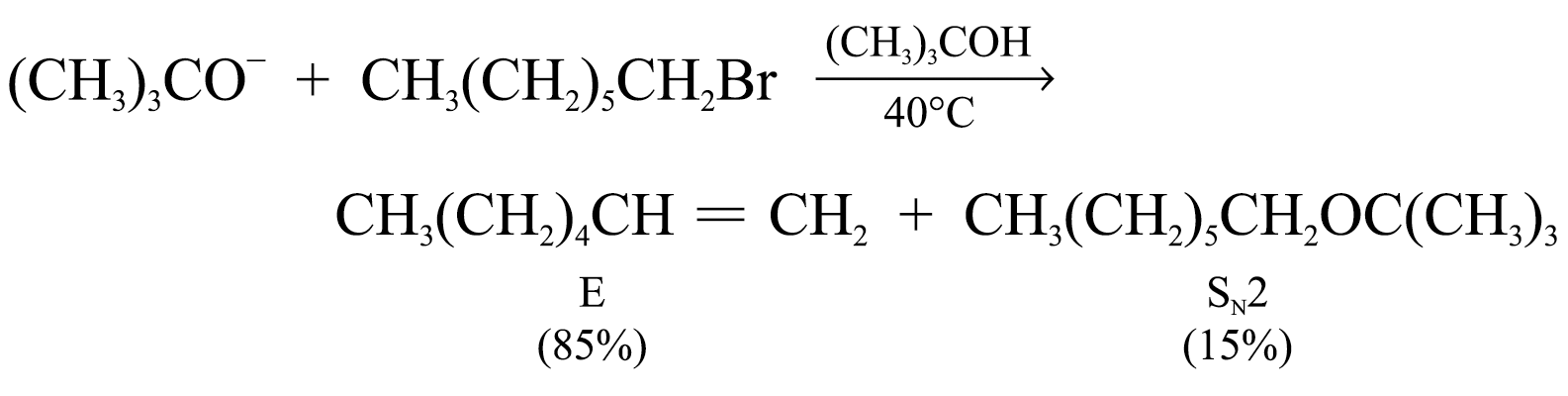
Summary of the reaction pathways for the substitution and elimination reactions of simple haloalkanes
CH3X Methyl |
RCH2X 1° |
R2CHX 2° |
R3CX 3° |
Gives SN2 reactions only |
Gives mainly SN2 and gives mainly E with a strong sterically hindered base (e.g. (CH3)3CO–) |
Gives mainly SN2 with a weak base (e.g. I–, CN–, RCO2–) and gives mainly E with a strong base (e.g. RO–) |
No SN2 reaction. In hydrolysis, gives SN1 or E. At low temperatures, SN1 is favoured. When a strong base (e.g. RO–) is used or at high temperatures, E predominates. |
Formation of Alkynes
Alkynes can be produced by dehydrohalogenation of dihaloalkanes
Two molecules of hydrogen halides are eliminated
e.g.
![]()
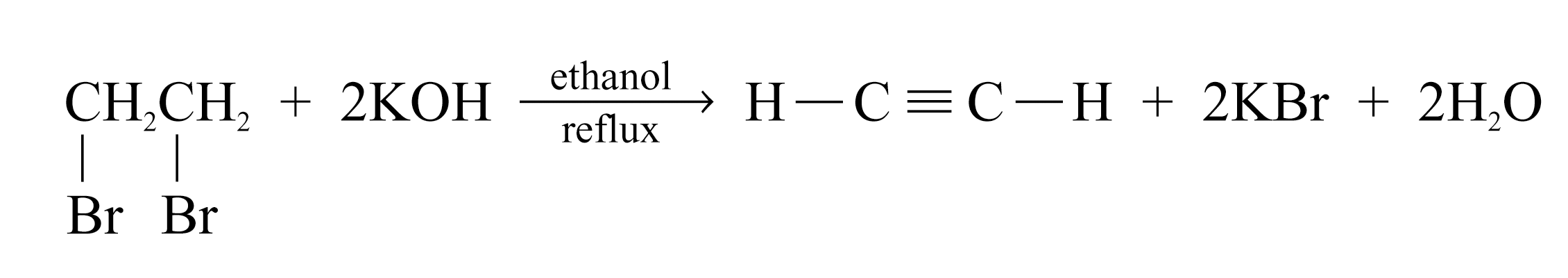
8 Uses of Halogeno-compounds
As Solvents in Dry-cleaning
Chlorinated hydrocarbons are good solvents for oil and greases Þ widely used in the dry-cleaning industry
e.g. trichloroethene, CCl2 = CHCl tetrachloroethene, CCl2 = CCl2
Properties that favour the use: 1. Relatively non-flammable
2. Volatile
3. Little or no structural effect on fabrics
As Raw Materials for Making Addition Polymers
Poly(chloroethene) (also known as PVC):
Produced by means of the addition polymerization of the chloroethene monomers in the presence of a peroxide catalyst
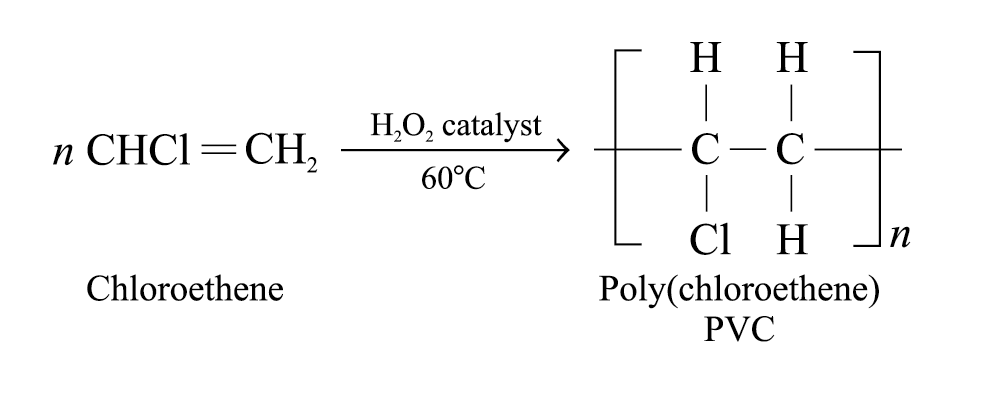
Polar C – Cl bond results in dipole-dipole interactions between polymer chains, making PVC hard and brittle and used to make pipes and bottles
PVC becomes flexible when plasticizer is added
Used to make shower curtains, raincoats, artificial leather, insulating coating of electrical wires
Poly(tetrafluoroethene) (PTFE, ‘Teflon’):
Produced through addition polymerization of the tetrafluoroethene monomers under high pressure and in the presence of catalyst
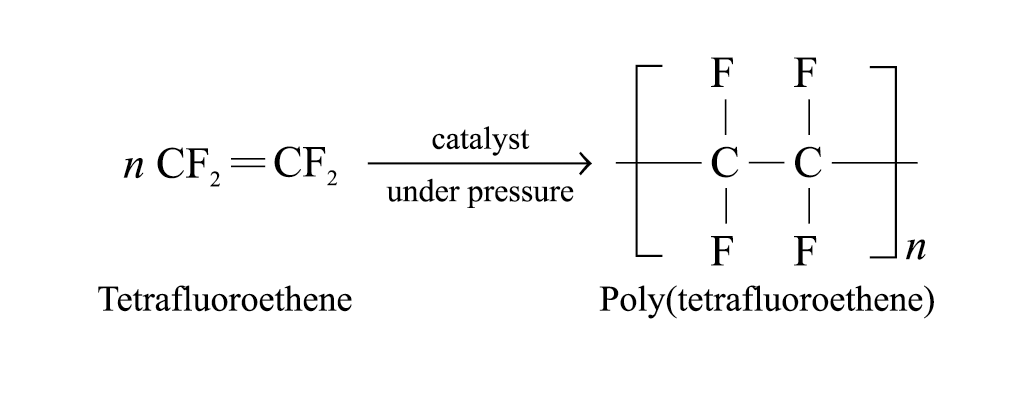
Teflon has a high melting point and is chemically inert
Used to make non-stick frying pans
Questions and problems
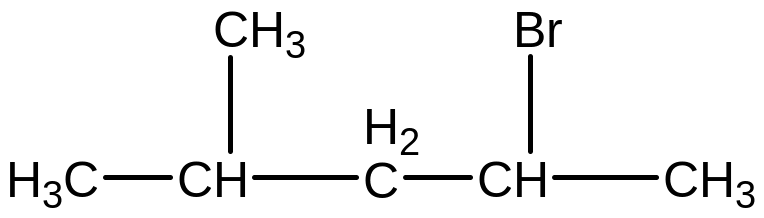
Give the name to the following compound:
Write the equations of butanol formation from 1-bromobutane.
What type of isomers are created while monochlorination of isobutane? What quantity (in percent) of each isomer is there in products of monochlorination if it is known that relative rate of replacement of one hohydrogen atom is changed in order: 10 >20 >30 such as 5,0 : 3,8 : 1.
Find out the structure of compound using the empirical formula and the products of chemical reactions: С4Н9Br, while hydrolysis 10 alcohol is created, while dehydrohalogenation with next hydrohalogenation 30 bromoalkane is created. Write the equations.
