
- •1 Alkanes
- •1.1 Nomenclature of Alkanes
- •1.2 Physical Properties of Alkanes
- •1.3 Preparation of Alkanes
- •Industrially Preparation
- •1.4 Reactions of Alkanes
- •3. Chain termination
- •1.5 Cycloalkanes
- •1.6 Nomenclature of Cycloalkanes
- •1.7 Isomerization of Cycloalkanes
- •1.8 Reactions of Cycloalkanes
- •2 Alkenes
- •2.1 Nomenclature of Alkenes
- •2.2 Physical Properties of Alkenes
- •2.3 Preparation of Alkenes
- •2.4 Reactions of Alkenes
1.5 Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n, where n is any integer.
They contain rings of carbon atoms.
Rotation is greatly reduced in cycloalkanes.
1.6 Nomenclature of Cycloalkanes
Naming substituted cycloalkanes
Count the number of carbon atoms in the ring and the number in the largest substituent. If the number of carbon atoms in the ring is equal to or greater than the number in the largest substituent, the compound is named as an alkyl-substituted cycloalkane. If the number of carbon atoms in the largest substituent is greater than the number in the ring, the compound is named as an cycloalkyl–substituted alkane.
e.g.
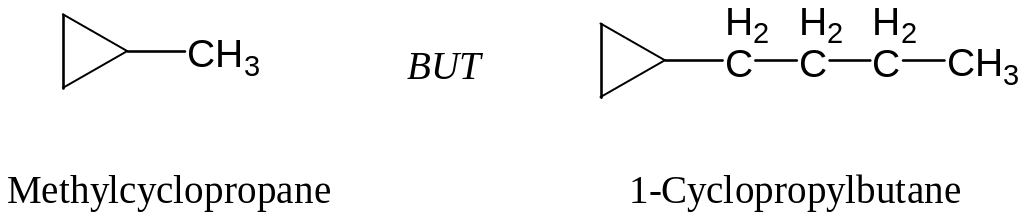
For alkyl-substituted cycloalkane, start at a point of attachmentand number the substituents on the ring so as to arrive at the lowestsum
e.g.

When two or more different alkyl groups are present, number them by alphabetical priority:
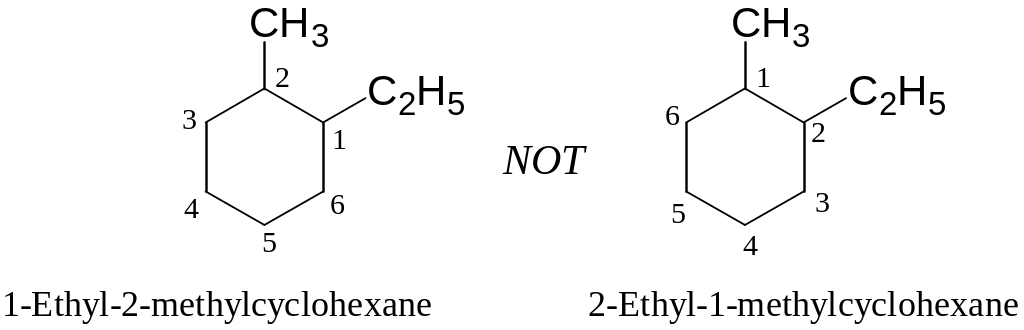
Halogens, if present, are treated exactly like alkyl groups:
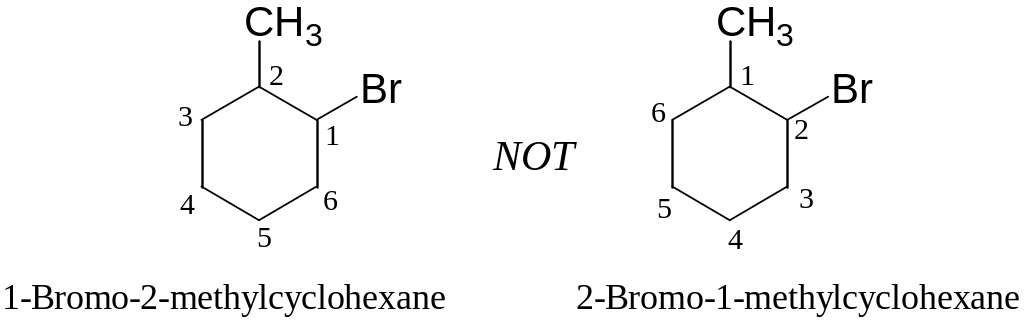
Examples:
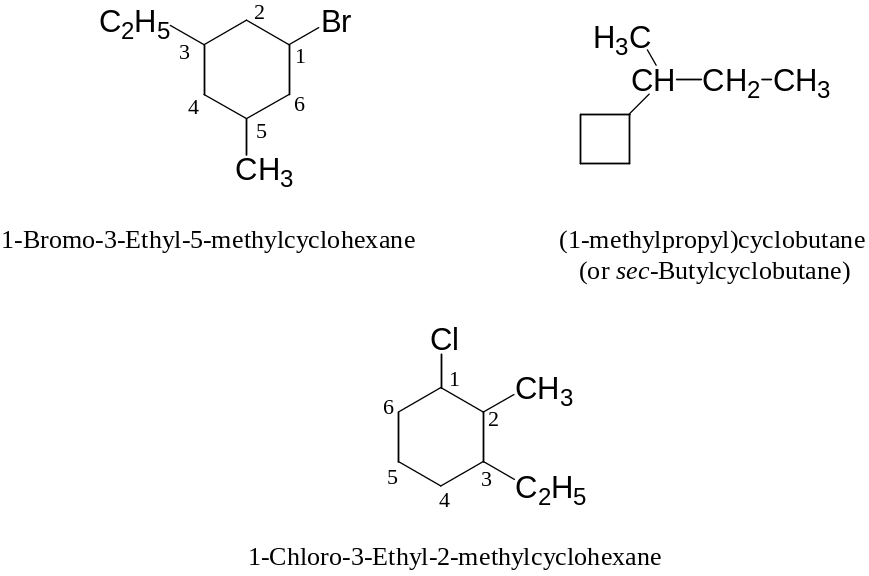
1.7 Isomerization of Cycloalkanes
Disubstituted cycloalkanes can therefore exist as cis-trans isomers (stereoisomers). The cis isomer has both substituents on the same side of the ring. The trans isomer has substituents on opposite side of the ring.

1.8 Reactions of Cycloalkanes
Like alkanes, cycloalkenes undergo Free Radical Substitution Reaction:

Cycloalkenes, wich have three or four carbon atoms in ring, undergo addition reactions with breaking ring (there is high tension between bonds in the ring) :

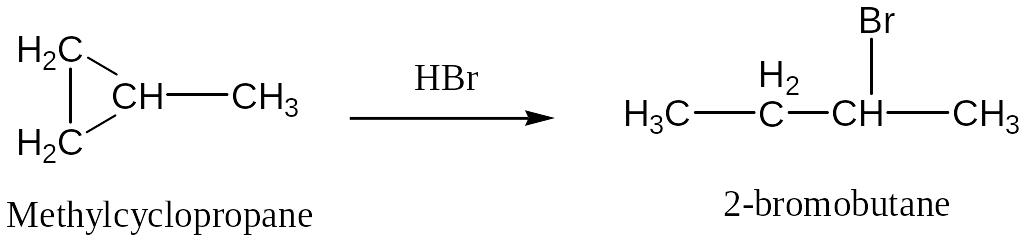
In the addition of HX to an alkyl-substituted cycloalkane, the halogen atom adds to the carbon atom of the ring carbon-carbon bond that already has the lesser number of hydrogen atoms. (Markownikoff’s rule )
2 Alkenes
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n, that contain double bond. Because they contain fewer hydrogen than related alkanes, alkene are often referred to as unsaturated.
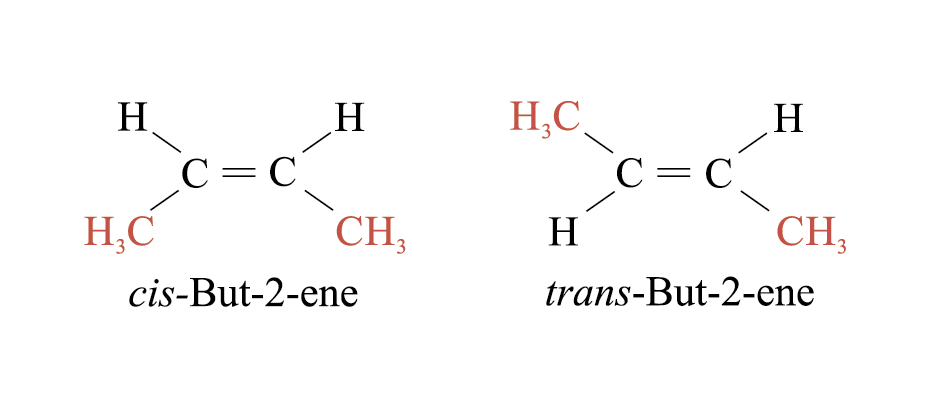
Alkenes show geometrical isomerism
2.1 Nomenclature of Alkenes
1. Determine the stem name by selecting the longest possible straight chain containing the C = C double bond and use the ending ‘-ene’
2. Number the parent chain so as to include both carbon atoms of the double bond, and begin numbering with the end of the chain nearer the C = C double bond
3. Designate the position of the C = C double bond by using the number of the first atom of the double bond
4. Designate the positions of the substituents by using the numbers obtained by application of rule 2
Examples:

Naming Cycloalkenes
Cycloalkenes are named in a similar way, but because there is no chain end to begin from, we number the cycloalkenes so that the doublebond is between C1 and C2 and so that the first substituent has as low a number as possible.
Note that it’s not necessary to include the position of the double bond in the name because it is always between C1 and C2

