
14-05-2015_19-15-42 / AНСМОВА_ПДРУЧНИК
.pdf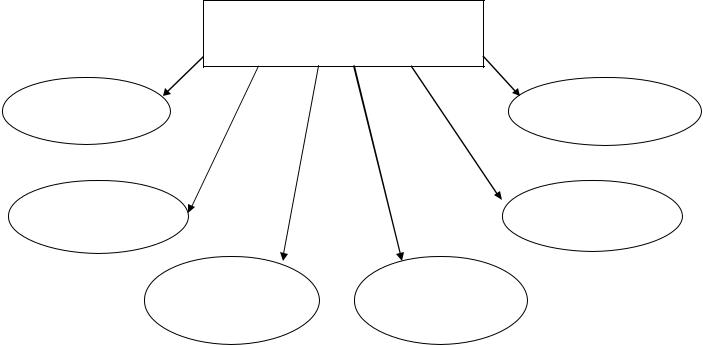
291
Teaching vocabulary
Criteria for vocabulary selection
Frequency |
Learnability |
Coverage |
Familiarity |
Ease or |
Learner‟s |
difficulty |
needs |
Table 31 (to chapter 3.3.)

292
Teaching vocabulary
Vocabulary structure
Real
Potential
Functional/Active/
Productive
Vocabulary
Receptive/
Passive/Recognition
Vocabulary
Table 32 (to chapter 3.3.)

293
|
|
Nature of lexical competence |
||||||||
|
Lexical competence is viewed as acquiring |
|||||||||
|
an appropriate quantity of lexical units, |
|||||||||
|
in other words, owning vocabulary, words. |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
components of owning |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
a word |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MEANING |
|
|
|
|
FORM |
|
||||
Denotation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Connotation |
|
|
|
|
phonology - |
|
|
|
||
Polysemy |
|
|
|
|
pronounciation |
|
|
|
||
Homonymy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Homophones |
|
|
|
|
orthography - spelling |
|
|
|
||
Synonymy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Antonymy |
|
|
|
|
morphology – |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
affixation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hyponymy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DISTRIBUTION
Collocation
Register
Style
Table 33 (to chapter 3.3.)
294
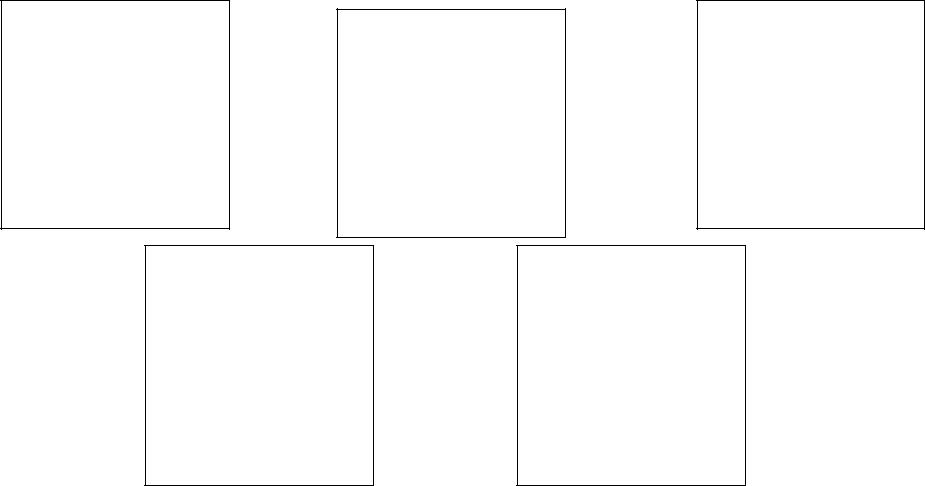
The stages of vocabulary acquisition
Learner |
Teacher |
1 PRESENTATION |
Furnishing explanations, presenting |
identification of concepts, i.e. learning |
words, getting learners to identify the |
what the word means |
concept correctly |
2 PRACTICE |
Teacher's activities to get learners to |
ASSIMILATION |
recognise and recall the words by means |
Learner's activities for the purpose of |
of different exercises |
retaining the word |
|
RETENTION |
Encouraging learners to review the words |
Performing different exercises to fix the |
using them again & again in various |
words in memory |
exercises |
3 PRODUCTION/APPLICATION |
|
Learner's activity in using the words in |
To stimulate learners to use the words |
the process of communication in |
properly to express their thoughts & |
different situations |
ideas |
Table 34 (to chapter 3.3.)

Bilingual/Translation
Word-translation
Polisemantic translation
L1 explanation
L1 definition
Phrase-translation
295
Ways of Presenting Vocabulary
Direct method techniques
Visual |
|
Verbal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Visual aids |
|
|
|
Context |
|
Objects; pictures; |
|
|
|
dictionaries |
|
photos; video |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
materials; realia |
|
Crosswords |
|
|
|
|
|
Matching; |
|
||
|
|
|
Body language |
|
definitions; |
Movements; |
|
examples |
gestures; facial |
|
|
|
|
|
expressions |
|
Word-building |
|
|
|
|
|
Synonyms; |
|
|
|
Pictograms |
|
|
|
antonyms; |
|
Tables; graphs; |
|
homonyms; |
mind-maps; |
|
homophones; |
matching |
|
hyponymic words |
|
|
|
Table 35 (to chapter 3.3.)
296
Teaching Pronunciation
Three Main Types of Pronunciation Lessons
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Integrated lessons, |
|
|
|
|
Remedial or |
|
|
|
|
Practice lessons, |
|
|||
|
in which |
|
|
|
|
reactive lessons, |
|
|
|
where a pronunciation |
|
||||
|
pronunciation forms |
|
|
|
where a pronunciation |
|
|
|
difficulty which arises |
|
|||||
|
an essential part of the |
|
|
|
difficulty which arises |
|
|
|
in class is dealt with |
|
|||||
|
language analysis and |
|
|
|
in class is dealt with |
|
|
|
there and then, in |
|
|||||
|
the planning process, |
|
|
|
there and then, in |
|
|
|
order to facilitate the |
|
|||||
|
and the language |
|
|
|
order to facilitate the |
|
|
|
successful |
|
|||||
|
presentation and |
|
|
|
successful |
|
|
|
achievement of |
|
|||||
|
practice within the |
|
|
|
achievement of |
|
|
|
classroom tasks. |
|
|||||
|
lesson. |
|
|
|
|
classroom tasks. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(According to Kelly G. How to Teach Pronunciation. – Harlow: Longman, 2000)
Table 36 (to chapter 3.4.)
297
Learner's Problems in Teaching English Pronunciation
discrimination of sounds
hearing the differences between phonemes which are not distinguished or used in L1 and between falling, rising and level, tones
intonation of sounds
learning to make right stresses, pauses and use appropriate patterns
articulation of sounds
learning to make the motor movements adequate to proper production of English sounds
integration of sounds
learning to assemble the phonemes of a connected discourse with the proper allophonic variations
automaticy of sounds
making correct production so habitual that if does not need to be attended to in the process of speaking
Table 37 (to chapter 3.4.)

298
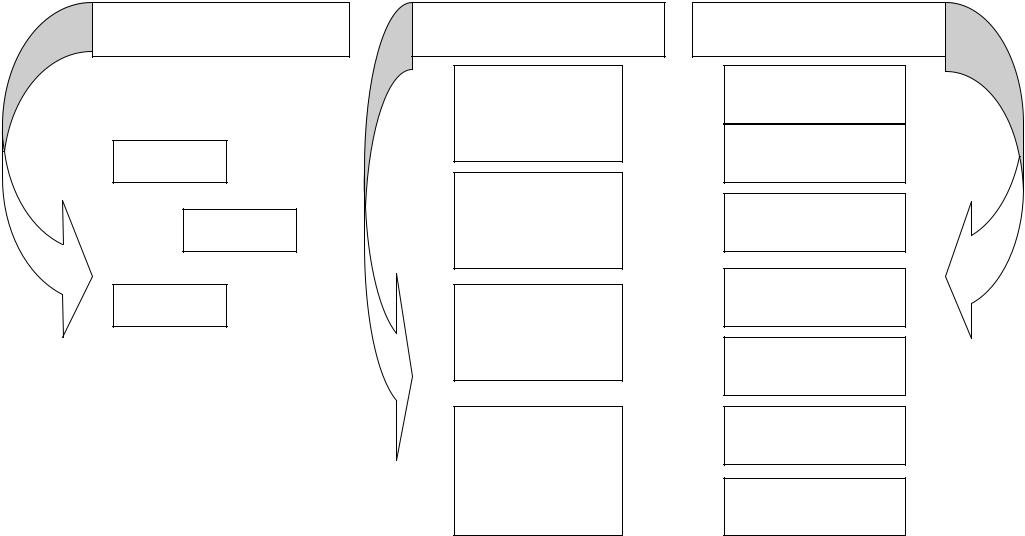
|
Teaching Pronunciation |
|
transaction |
Primary Communicative Goal |
interaction |
|
accessibility |
Main Criterion |
acceptability |
|
instrumental |
Motivation |
integrative |
transmission |
Communication seen as |
negotiation |
|
Table 38 (to chapter 3.4.)
299
Teaching Listening
A model of how the listening process works
echoic |
|
Short-term |
|
Long-term |
memory |
|
memory |
|
memory |
|
|
(STM) |
|
(LTM) |
|
|
|
|
|
'freezes' the message |
the messageis interpreted |
the message is stopped |
|
language drops out |
drops out if not used |
|
|
(discarded) |
Table 39 (to chapter 4.1.)
300
Learner's Difficulties in Listening Comprehension
Linguistic difficulties
Phonetics
Vocabulary
Grammar
Table 40 (to chapter 4.2.)
Content difficulties
Topic of communication;
Type of communication (description, narration);
Form of communication (dialogue, monologue);
Context plus learners' readiness (intellectual and situational)
to understand it
Conditions
Tiredness of listener
Times of presentation
Visual "props"
Recorded or alive presentation;
Speed of speech (tempo)
Speaker‘s voice
Background noise
