
14-05-2015_19-15-42 / AНСМОВА_ПДРУЧНИК
.pdf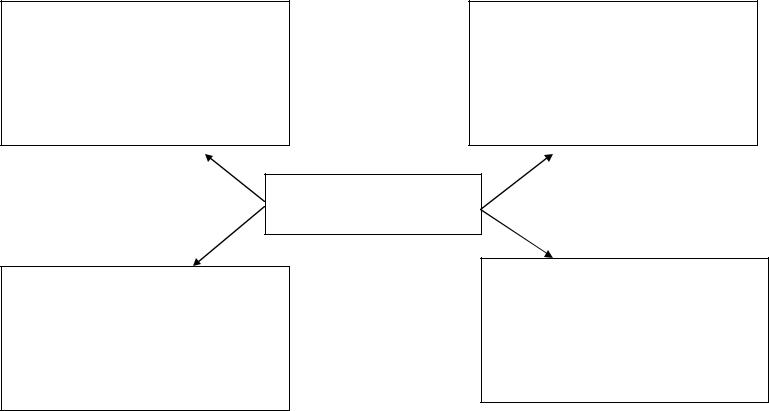
261
Appendix 4. Tables
The Subject Matter of Methods of Foreign Language Teaching
Why do we study/teach foreign/new languages ?
What are aims & objectives?
With the help of what do we teach?
What are teaching aids & materials?
Methods of FLT
What do we actually study/teach in educational process?
What is the content of the course?
How do we study/teach?
What approaches, methods, principles & techniques do we use in educational process?
Table 1 (to chapter 1.1)
262
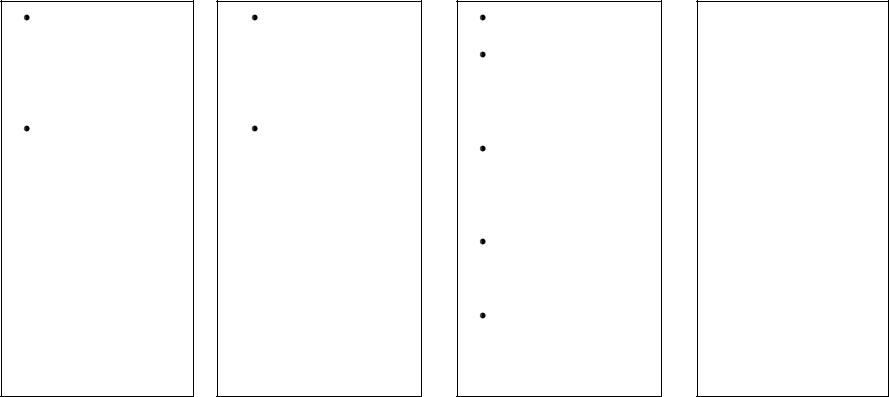
Aims & Objectives of Teaching English at School
Practical Aim |
|
Educational Aim |
|
Cultural Aim |
|
Developmental |
|
|
|
Aim |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of speech habits and skills on the level available for the target language intercourse;
Acquire a foreign language for the same purpose as the native language: to use it as a means of communication, gaining one more code for receiving and conveying information.
Deeper insight into the nature and functioning of language as social phenomenon;
Development of learner‘s intellect, memory, imaginative abilities, will power.
Table 2 (to chapter 1.1)
Promote cultural growth;
Educate culture of personal contacts and social intercourse accepted in a modern society;
Develop positive attitude to the target language and customs and traditions of the target culture;
Upbringing of such valuable traits as kindness, hard-working, tolerance and the like;
Develop collaborative skills.
Develop:
 Creative abilities of learners;
Creative abilities of learners;
 Critical-thinking skills;
Critical-thinking skills;
 Speech facilities (as phonetic and intonation hearing, imitation, logic, linguistic guessing etc.);
Speech facilities (as phonetic and intonation hearing, imitation, logic, linguistic guessing etc.);
 Provide problemsolving activities.
Provide problemsolving activities.

263
Content of Foreign Language Teaching
Components of Content
of FLT
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of |
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of |
|||
|
COMMUNICCATIVE COMPETENCE |
|
|
|
communicative skills |
|||||||
|
|
Includes three main branches |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Speech |
|
|
Language |
|
|
Sociocultural |
|
|
||||
|
||||||||||||
Spheres of intercourse, |
||||||||||||
competence |
|
|
competence |
|
|
competence |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
topics, situations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Listening |
|
|
Grammar |
|
|
Regional |
|
|
||||
Speaking |
|
|
Vocabulary |
|
|
|
studies |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Language material |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Reading |
|
|
Pronunciation |
|
|
Linguistics |
|
|
||||
Writing |
|
|
Spelling |
|
|
and regional |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
studies |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3 (to chapter 1.1)

264
Teaching aids & materials
Teaching aids |
|
Teaching materials |
|
|
|
Non-Mechanical
lantern flannel board magnet board blackboard
Mechanical |
Educational complex |
Audio-visual materials |
-Visual materials |
tape recorder |
|
Teacher's book |
|
video films, |
|
objects, |
CD player |
|
Pupil's/Student's book |
|
sound film |
|
flashcards, |
overhead projector |
|
Grammar/Reading |
|
loops, |
|
sentence cards, |
TV & radio equipment |
|
manuals |
|
films, |
|
wall-charts, |
video |
|
Work book/Activity |
|
computer software. |
|
posters, |
white interactive board |
|
book |
|
|
|
pictures, |
|
|
Text booklets |
|
|
|
photographs, |
|
|
Audio-visual materials |
|
|
|
albums, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
maps & plans, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
slides. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Audio materials
records,
discs, tapes
Table 4 (to chapter 1.1)

265
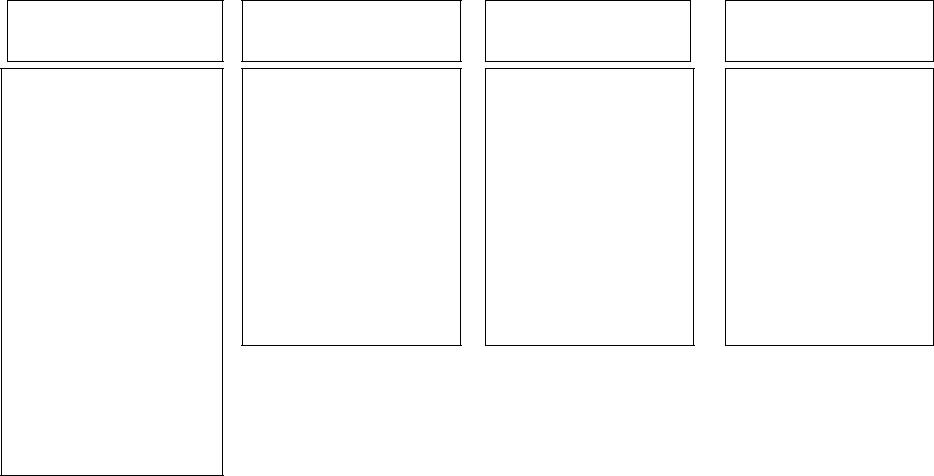
Nature of communicative competence
Common European |
National |
English Language |
Foreign Language |
Framework of |
Educational |
Programme for 12-year |
Programme for 12- |
Reference for |
Standard of |
Secondary School ( 2001) |
year Secondary |
Languages |
Foreign Languages |
|
School (2005) |
|
|
|
|
Linguistic competence |
Language |
Linguistic (speech) |
Linguistic (speech) |
|
competence; |
competence |
competence |
|
Speech |
|
|
|
competence. |
|
|
Pragmatic competence |
|
Discourse |
Pragmatic competence |
|
|
competence; |
|
|
|
Strategic competence. |
|
|
|
|
|
Sociolinguistic |
Sociocultural |
Sociocultural competence |
Sociolinguistic |
competence |
competence |
|
competence; |
|
|
|
|
Table 5 (to chapters 1.2; 2.3)
266
Communicative language competences of language learners/users
(according to CEF)
Linguistic competences |
|
|
Sociolinguistic |
|
|
Pragmatic competences |
|
|
|
|
competences |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lexical competence; |
|
|
Linguistic markers of social |
|
|
Discourse competences; |
|
Grammatical competence; |
|
|
relations; |
|
|
Functional competence. |
|
Semantic competence; |
|
|
Politeness conventions; |
|
|
|
|
Phonological competence; |
|
|
Expressions of folk wisdom; |
|
|
|
|
Orthographic competence; |
|
|
Register differences; |
|
|
|
|
Orthoepic competence. |
|
|
Dialect and accent. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 6 to chapter 2.3
267
General competences of language learners/users
(according to CEF)
Declarative
knowledge
Knowledge of the world Sociocultural knowledge:
Everyday living Living conditions Interpersonal relations
Values, beliefs and attitudes in relation to different social factors Body language
Social conventions Ritual behaviour
Intercultural awareness
Skills and know-how
Practical skills and know-how
Social skills Living skills Vocational and professional skills Leisure skills
Intercultural skills and know-how
‗Existential‟ competence
Attitudes
Motivations
Values
Beliefs
Cognitive styles Personality factors
Ability to learn
Language and communication awareness
General phonetic awareness and skills
Study skills
Heuristic skills
Table 7 to chapter 2.3
268
The Common Reference Levels: global scale
Proficient |
C2 |
Can understand with ease virtually everything heard or read. Can summarise information from different spoken and written |
User |
|
sources, reconstructing arguments and accounts in a coherent presentation. Can express him/herself spontaneously, very fluently |
|
|
and precisely, differentiating finer shades of meaning. |
|
|
|
|
C1 |
Can understand a wide range of demanding, longer texts, and recognise implicit meaning. Can express him/herself fluently and |
|
|
spontaneously without much obvious searching for expressions. Can use language flexibly and effectively for social, academic |
|
|
and professional purposes. Can produce clear, well-structured, detailed text on complex subjects, showing controlled use of |
|
|
organisational patterns and cohesive devices |
|
|
|
Independent |
B2 |
Can understand the main ideas of complex text on both concrete and abstract topics, including technical discussions in his/her |
User |
|
field of specialisation. Can interact with a degree of fluency and spontaneity that |
|
|
makes regular interaction with native speakers quite possible without strain for either party. Can produce clear, detailed text on a |
|
|
wide range of subjects and explain a viewpoint on a topical issue . |
|
|
|
|
B1 |
Can understand the main points of clear standard input on familiar matters regularly encountered in work, school, leisure, etc. |
|
|
Can deal with most situations likely to arise in an area where the language is spoken. Can produce simple connected text on |
|
|
topics which are familiar or of personal interest. Can describe experiences and events, dreams, hopes and ambitions and briefly |
|
|
give reasons and explanations for opinions and plans. |
|
|
|
Basic User |
A2 |
Can understand sentences and frequently used expressions related to areas of most immediate relevance (e.g. very basic personal |
|
|
and family information, shopping, local geography, employment). Can communicate in simple and routine tasks requiring a |
|
|
simple and direct exchange of information on familiar and routine matters. Can describe in simple terms aspects of his/her |
|
|
background, immediate environment and matters in areas of immediate need. |
|
|
Can understand and use familiar everyday expressions and very basic phrases aimed at the satisfaction of needs of a concrete |
|
A1 |
type. Can introduce him/herself and others and can ask and answer questions about personal |
|
|
details such as where he/she lives, people he/she knows and things he/she has. Can interact in a simple way provided the other |
|
|
person talks slowly and clearly and is prepared to help. |
Table 8 (to chapters 1.2; 2.3)

269
The Common Reference Levels.
Correlation with the Program of Teaching Foreign Languages in Ukraine
|
A |
|
|
B |
C |
|
Basic User |
|
Independent User |
Proficient User |
|
||
A1 |
A2 |
|
B1 |
B2 |
C1 |
C2 |
Breakthrough |
Waystage |
|
Threshold |
Vantage |
Effective Operational Proficiency Mastery |
|
|
|
A2+ |
B1+ |
B2+ |
|
|
|
Strong Waystage |
|
Strong Threshold |
Strong Vantage |
|
|
2-4 years of study |
5-9 years of study |
10-12 years of study |
|
|
||
Table 9 (to chapters 1.2; 2.3)

270
Basic theories of language and language learning
Basic theories
|
Basic theories |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic theories |
|
|
|
||
|
of language |
|
|
|
|
of language learning |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
behaviorism |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TBL |
|
|
structural |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cognitivism |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
functional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
language acquivisition |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
interactional |
|
|
|
theory |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
humanistic aspects |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of learning |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 10 (to chapter 1.4)
