
- •Velocity of a body depends on time by the following form . What is the unit of the coefficient [b]?
- •If the electric field is uniform and makes an angle θ with the normal to a surface of area a, the electric flux through the surface is:
- •If two or more capacitors are connected in series, the equivalent capacitance of the series combination is given by:
- •If a wire coil has 10 turns and carries 500 mA of current, what is the magnetomotive force in ampere-turns?
- •If the cross-sectional area of a magnetic field increases, but the flux remains the same, the flux density
- •If the steel disk in a crankshaft position sensor has stopped with the tab in the magnet's air gap, the induced voltage
- •If vector b is added to vector a, which two of the following choices must be true in order for the resultant vector to be equal to zero?
- •In inelastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In elastic collision between the two bodies __________.
- •In rotational motion, the quantity, which plays the same role as the inertial mass in linear motion, is called ___________.
- •If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 ω, what is the current in the wire?
- •If a loop in a basic dc generator suddenly begins rotating at a faster speed, the induced voltage
If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 ω, what is the current in the wire?
2.2 A
An electric heater is constructed by applying a potential difference of 120 V to a Nichrome wire that has a total resistance of 8.00 Ω. Find the current carried by the wire.
15 A
An electric heater is constructed by applying a potential difference of 120 V to a Nichrome wire that has a total resistance of 8.00 Ω. Find the power rating of the heater.
1.8 kW
A battery has an emf of 12.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.05 Ω. Its terminals are connected to a load resistance of 3.00 Ω. Find the terminal voltage of the battery.
11.8 V
Calculate the power delivered to the load resistor, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 A, the load resistance is 3.00 Ω.
46.3 W
Calculate the power delivered to the internal resistance of the battery, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 A, the internal resistance of 0.05 Ω.
0.772 W
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b.

12 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points b and c.

2 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and c.

14 Ω
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I1.

I1=6.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a andb. Find the current I2.
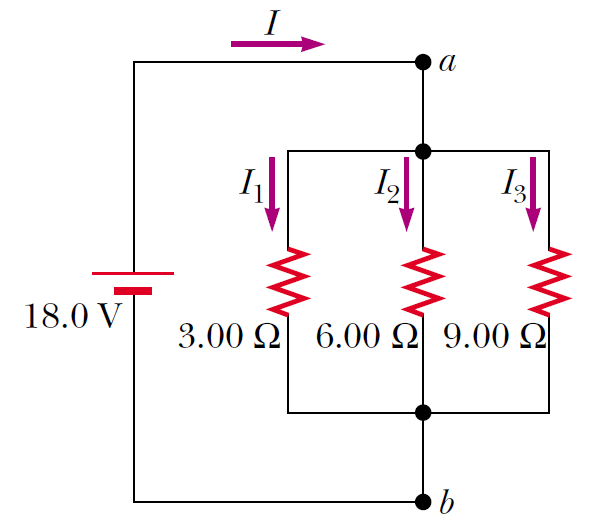
I1=3.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I3.

I1=2.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the power delivered to resistor R1.

P1=108 W
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit.

Req=1.64 Ω
A single-loop circuit contains two resistors and two batteries, as shown in Figure. (Neglect the internal resistances of the batteries.) Find the current in the circuit.

I=-0.33 A
A segment of steel railroad track has a length of 30.000 m when the temperature is 0.0°C. What is its length when the temperature is 40.0°C? (Average linear expansion coefficient for steel is α=11* 10-6 °C-1).
30.013 m.
An ideal gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3 at 20°C and 100 Pa. Find the number of moles of gas in the container (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K).
4.11 * 10-6 mol
The concrete sections of a certain superhighway are designed to have a length of 25.0 m. The sections are poured and cured at 10.0°C. What minimum spacing should the engineer leave between the sections to eliminate buckling if the concrete is to reach a temperature of 50.0°C? (Average linear expansion coefficient for concrete is α=12* 10-6 °C-1).
1.20 cm
Just 9.00 g of water is placed in a 2.00-L pressure cooker and heated to 500°C. What is the pressure inside the container? (Molar mass of water M(H2O) = 18 g/mol, universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K ).
1.61 MPa
The temperature of a silver bar rises by 10.0°C when it absorbs 1.23 J of energy by heat. The mass of the bar is 525 g. Determine the specific heat of silver.
234 J/kg . °C
A 50.0-g sample of copper is at 25.0°C. If 1 200 J of energy is added to it by heat, what is the final temperature of the copper? (Specific heat of copper c= 387 J/kg . °C).
87°C
Determine the work done on a fluid that expands from i to f as indicated in Figure.

-12 MJ
A gas is taken through the cyclic process described in Figure. Find the net energy transferred to the system by heat during one complete cycle.

12 kJ
An ideal gas initially at 300 K undergoes an isobaric expansion at 2.50 kPa. If the volume increases from 1.00 m3 to and 12.5 kJ is transferred to the gas by heat, what is the change in its internal energy?
7.5 kJ
A glass window pane has an area of 3.00 m2 and a thickness of 0.600 cm. If the temperature difference between its faces is 25.0°C, what is the rate of energy transfer by conduction through the window? (Thermal conductivity of glass k= 0.8 W/m* °C)
10 kW
A cylinder contains a mixture of helium and argon gas in equilibrium at 150°C. What is the average kinetic energy for each type of gas molecule? (Boltzmann constant kB= 1.38* 10-23 J/K).
8.76* 10-21J
Calculate the change in internal energy of 3.00 mol of helium gas when its temperature is increased by 2.00 K (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K ).
74.8 J
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What is the final pressure of the gas?
1.39 atm
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. What are the initial and final temperatures? (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K, 1 atm= 1.013* 105 Pa )
365 K, 253 K
A 2.00-mol sample of a diatomic ideal gas expands slowly and adiabatically from a pressure of 5.00 atm and a volume of 12.0 L to a final volume of 30.0 L. Find Q, ΔEint, and W (Universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K).
0 J, -4.66 kJ, - 4.66 kJ
A heat engine takes in 360 J of energy from a hot reservoir and performs 25.0 J of work in each cycle. Find the efficiency of the engine.
6.94 %
A heat engine performs 200 J of work in each cycle and has an efficiency of 30.0%. For each cycle, how much energy is (a) taken in and (b) expelled by heat?
667 J, 467 J
A particular heat engine has a useful power output of 5.00 kW and an efficiency of 25.0%. The engine expels 8 000 J of exhaust energy in each cycle. Find the energy taken in during each cycle
10.7 kJ
The unit for permeability is
Wb/At × m
What is the magnetomotive force in a 75-turn coil of wire when there are 4 A of current through it?
300 At
The direction of a magnetic field within a magnet is
from south to north
When the north poles of two bar magnets are brought close together, there will be
a force of repulsion
The ability of a material to remain magnetized after removal of the magnetizing force is known as
retentivity
The voltage induced across a certain coil is 200 mV. A 120
 resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current is
resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current is
1.7 mA
The induced voltage across a stationary conductor in a stationary magnetic field is
zero
When a solenoid is activated, the force that moves the plunger is
an electromagnetic field
What is the magnetomotive force (mmf) of a wire with 8 turns carrying three amperes of current?
24 At
