
english
.docxMass Media
No doubt, is an important part of our life. People from different walks of life have become nowadays listeners, readers, viewers. Or in other words, reading newspapers and magazines, watching TV, listening to the news on the radio are our main means of getting information in all its variety. Newspapers with their enormous circulation report different kinds of news. They carry articles which cover the latest international and national events. Now people buy newspapers also for the radio and TV programs which they publish. There are special newspapers which gave a full coverage of commercial, financial and publish affairs. There are newspapers and magazines for young people. They give a wide coverage of news, events and reports on education, sports, cultural life, entertainment, and fashion. There are a lot of advertising programs now, sensation material, too. They represent the views of today’s youth. Radio broadcasts are valued mainly for their music programs (Europa plus). TV, radio, press reflect the present day life. Their information may vary from social and economic crises, conflicts, wars, disasters, earthquakes, to diplomatic visits, negotiations, from terrorism, corruption, to pollution problems, strikes, and social movements. Much information is published concerning official governmental decisions.
Mechanical engineering as a future profession.
Engineering as said in the English-English dictionary is 1. The practical application of scientific knowledge in the design, building and control of machines, roads, bridges, electrical apparatus, chemicals; 2. The work, science or profession of an engineer. The primary types of engineering are chemical, civil, electrical, industrial, and mechanical.We will study thoroughly mechanical engineering. Mechanical engineering is the application of physical principles to the creation of useful devices, objects and machines.Mechanical engineers use principles such as heat, force, and the conservation of mass and energy to analyze static and dynamic physical systems, in contributing to the design of things such as automobiles, aircraft, and other vehicles, heating and cooling systems, household appliances, industrial equipment and machinery, weapons systems, etc. Fundamental subjects of mechanical engineering include: dynamics, statics, strength of materials, hydraulics, kinematics, and applied thermodynamics. Mechanical engineers should understand and be able to apply concepts from the chemistry and electrical engineering fields.Engineers in this field design, test, build, and operate machinery of all types; theyalso work on a variety of manufactured goods and certain kinds of structures.
Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of physics which describes motion with respect to speed, time and distance, the nature of the particle or object whose motion is under study being not specified. So, in kinematics we concern ourselves primarily with three physical quantities: 1) the distance between two positions; 2) speed, i.e. how fast a continuous change positions takes place; 3) the time it takes to get from one position (point, location) to another. Kinematics is not concerned with either the mass of a moving particle or forces producing change of speed.
Motion
is defined in physics as continuous change of position. We describe
motion from one position to another in terms of the distance moved
and the time it takes to go from one position to another. We describe
speed as amount of change of position per unit time, the amount of
position being measured in units of length (distance). Generally, the
word “per” indicates division, the mathematical definition of
speed being х=d/t – or in other words speed is the distance
travelled per unit time. The speedometer reads instantaneous velocity
of a car in mph (miles per hour).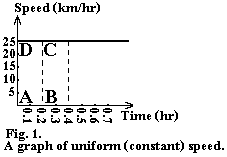
Constant velocity. A car moving with constant velocity, the distance travelled is directly proportional to the time. For constant velocity х, S=х*t, where S is the distance covered in time t. We may study particular motions by analyzing their graphs. Fig. 1 is an example of a speed-time graph. It shows us values of speed plotted against (vs) values of time. Of the three quantities involved in any study of motion, the speed-time graph relates to two directly.
Applied mechanics
Applied mechanics is a branch of the physical sciences and the practical application of mechanics. Applied mechanics examines the response of bodies (solids and fluids) or systems of bodies to external forces. Some examples of mechanical systems include the flow of a liquid under pressure, the fracture of a solid from an applied force, or the vibration of an ear in response to sound. A practitioner of the discipline is known as a mechanician.
Applied mechanics, as its name suggests, bridges the gap between physical theory and its application to technology. As such, applied mechanics is used in many fields of engineering, especially mechanical engineering. In this context, it is commonly referred to as engineering mechanics. Much of modern engineering mechanics is based on Isaac Newton's laws of motion while the modern practice of their application can be traced back to Stephen Timoshenko, who is said to be the father of modern engineering mechanics.
The greatest mathematicians
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) Nationality: German, American Famous For: E=m*c2 Albert Einstein excelled in mathematics early in his childhood. He liked to study math on his own. He was once quoted as saying, “I never failed in mathematics…before I was fifteen I had mastered differential integral calculus.”
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Nationality: English Famous For:Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy The book of Sir Isaac Newton,Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy, became the catalyst to understanding mechanics. He is also the person credited for the development of the binomial theorem.
Pythagoras (c. 570 – c. 495 BC) Nationality: Greek Famous For: Pythagorean theorem Pythagoras is best known in mathematics for the Pythagorean Theorem.
Georg Cantor (1845-1918) Nationality: German Famous For: Inventor of set theory One of the basic theories in mathematics is the set theory, thanks to the work of Georg Cantor. He helped define the importance of the “one-to-one correspondence” principle as well as introduce cardinal and ordinal numbers.
Euclid
Known as the Father of Geometry, Euclid is popularly recognized for his magnum opus, Elements. It is perhaps one of his greatest contributions in the field of Mathematics as it is still in use in the 20th century. Unluckily, less is written about his biography even until his death. He is also known for his logical proofs to several conjections and theorems. Today, Euclid has only five surviving works as his other five works were lost as time passed by. His works mostly revolved around the Number theory and Geometry.
