
English fo MP student book
.pdf
UNIT 3
CRIMINAL INVESTIGATIONS
Before you read the text, discuss with a partner the steps undertaken by the police in detecting and solving a crime
What is the role of the police as a law-enforcement agency? What other law-enforcement agencies do you know?
Which departments of the police service deal directly with crime detection and apprehension of criminals?
What is the act that governs the activity of the police in UK? What are the arresting procedures in UK?
Who can press or drop charges? Who can try and sentence a criminal?
Principles of Police Investigations
How closely are the essential principles of investigations related to Human Rights? What are the consequences of the non-observance of these principles?
What are the causes of abuse in police work?
# Exercise 1
Read the following text, complete it by putting in appropriate prepositions and discuss the issues involved.
The Principles of Police Investigations.
THE CRIME SCENE
Processing a crime scene includes the application (1) … diligent and careful methods by investigators (2) … recognise, identify, preserve and collect facts and items of evidentiary value that may assist (3)… reconstructing that which actually occurred. It is (4) … the utmost importance to the success of any investigation that the investigating officer makes no errors
(5)… the crime scene or (6) … follow-up investigations. Also, the first officer (7)… the scene must avoid diminishing or destroying potential clues which may eventually lead (8) … the apprehension of the criminal.
Though the police are expected to investigate crime, a basic function (9) …the police is noninvestigative, that is to keep the peace and protect the people.
# Exercise 2
Interviews ands Interrogations
In investigations, the interviewing of witnesses, victims and suspects, personal searches, searches of vehicles and premises, the interception of correspondence and communications, the police are
55

English for Modern Policing
guided by a series of fundamental principles, as shown below. Complete the text with the appropriate word from the box
compelled |
presumed |
treated |
subjected |
prohibited |
conducted |
exercised |
permitted |
eexerted |
|
-everyone has the right to security of the person
-everyone has the right to a fair trial
-everyone is to be (1) ____________ innocent until proven guilty in a fair trial
-no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence
-no one shall be (2) _____________ to unlawful attacks on his honour or reputation
-no pressure, physical or mental, shall be (3)____________ on the suspects, witnesses or victims in attempting to obtain information
-torture and other inhuman or degrading treatment is absolutely (4) ___________
-victims and witnesses are to be (5)_________with compassion and consideration
-confidentiality and care in the handling of sensitive information are to be
(6)____________ at all times
-no one shall be (7)________________ to confess or to testify against himself
-investigatory activities shall be (8)____________ only lawfully and with due cause
-neither arbitrary, nor unduly intrusive investigatory activities shall be (9)______
Reading text Operation ‘Magician’
Discuss these issues with a partner before reading the text.
How and where can a police officer gather information on a case? Who does he speak to?
What are the steps an investigating officer takes immediately after discovering a crime? How important is crime prevention?
What is the situation in Romania?
What can the police do in order to deter crime?
How can the police raise public awareness on every person’s role in detecting, reporting and deterring crime? What concrete steps can they take?
How cost-effective can crime prevention be compared to crime investigations? How important are standardised policies, practices and procedures in police work? Do these limit the liberty of police officers in their work or do they help them?
Read the text Operation Magician
How the Flying Squad foiled the world's biggest ever robbery
Intelligence
In summer 2000 the Metropolitan Police Flying Squad developed intelligence that pointed to a major armed robbery plot. Its location was unclear, but police knew the identities of some of the robbers. They also knew the gang was highly organised and would probably be armed.
56

UNIT 3 – Criminal Investigations
Over a period of months detectives worked tirelessly to develop the intelligence picture. A major surveillance operation was launched, using officers from the Met’s Directorate of Intelligence. Within weeks, police were sure they knew the venue of the robbery – The Millennium Dome in Greenwich. The exact target within the Dome was not yet clear.
Discuss: How big a risk were the police taking at this point?
Surveillance
On 1 September 2000 three of the suspects, William Cockram, Raymond Betson and Aldo Ciarocchi were seen at the venue filming with a camcorder and studying the plans of the Dome. Over the coming weeks the surveillance continued, and further members of the gang were identified and some of the men were spotted testing a speedboat in a harbour in Kent. Detectives thought the gang might use the boat as a getaway. The robbery was getting close.
Discuss: What practical steps should the police already have been taking?
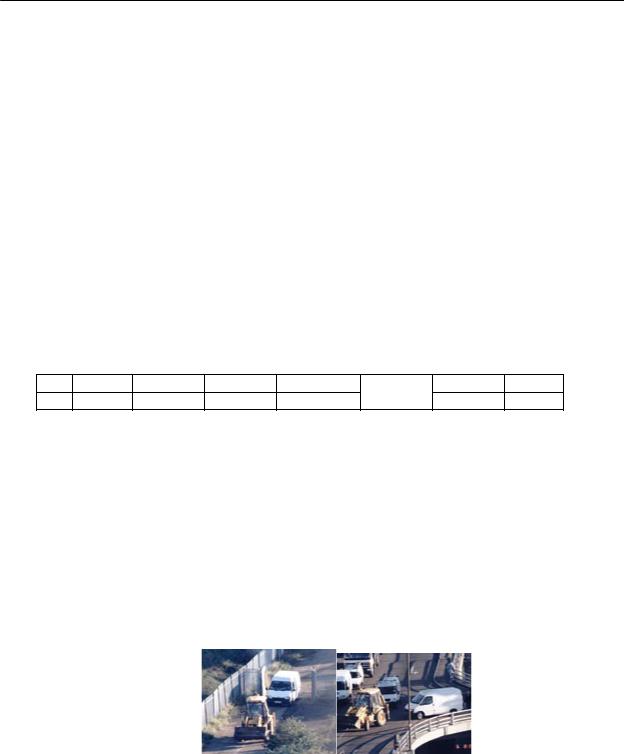
The JCB Mechanical Digger
By early October police inquiries had identified another venue linked to the robbery – The Old Coal Yard in Whitehart Road, Plumstead. The detectives observed gang members with a yellow mechanical digger, registration L245 AJU. The digger had been reported stolen some months earlier and would clearly have some role to play in the robbery.
Discuss: JCBs (yellow construction/digging vehicles) had been used before in a new version of the “smash and grab” raid known as “ram raids” What precautions should the police have taken?
The River
Police could not be sure when or indeed exactly how the robbery would take place On a number of days in October the gang looked as if they were about to commit the offence. On three separate days they towed a speedboat to Greenwich and placed it in the river opposite the Dome. Other activity on those days tended to indicate that the robbery was close – but strangely it didn’t materialise. Detectives were sure that there was more to this than merely a loss of nerve on the robbers’ part. They analysed the times and days of the aborted attempts and found that they had something in common – the tide. On each of the days when the robbery was aborted the tide was at its highest possible level. This was vital to the robbers’ escape, since the boat could only be launched on the north side of the Thames when the water was high. Through studying the patterns of the tide, police were able to predict the optimum times for the robbery to take place. One of these days was 7 November 2001
Discuss: Speedboat .. river.. possible mooring and launching locations.. tides.. a very obvious deduction and conclusion by the police ?
¾ Activity 1 |
The Day of the Robbery |
Match the two parts of the sentences to complete the text.
1)At 3 a.m. on 7 November 2001, approximately 200 officers involved in Operation Magician...
2)They were prepared for a tactical operation which had been months...
3)Public safety was the prime consideration and officers had plans....
57
English for Modern Policing
4)Amongst those present were 40 specialist firearms officers....
5)Others were sent into the Dome in disguise....
6)Surveillance officers disguised as Dome employees...
7)A further 60 armed Flying Squad officers were stationed around the Thames....
Officers also moved to a number of observation points between the Old Coal Yard in Plumstead and the Dome.
8)The Dome’s CCTV room was turned into a police control room...
A.gathered at the Dome for a dawn briefing
B.dressed as cleaners they concealed their guns in black plastic bags and rubbish bins.
C.to ensure that the robbers could be arrested quickly and safely at any given stage during the incident.
D.from where Det. Supt. Jon Shatford ran the whole operation.
E.and 20 on the river itself.
F.who would be hidden behind a secret wall within the Dome and in other places.
G.in planning and providing contingencies for many different outcomes.
H.also patrolled the area.
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
A
Discuss: If you had been a gang member would YOU have been keeping surveillance on the Dome?
Timetable of events on the morning of 7 November 2001
7:26 A white Transit van registration N770 AHE was seen towing the red and white speedboat along West Ferry Rd on the Isle of Dogs. The passenger was later identified as Kevin Meredith.
8:11 White Ford Transit van, registration number C673 COR, drove into the Old Coal Yard in Plumstead. The JCB was parked there.
8:39 A red and white speedboat was seen travelling east along the Thames towards the Dome. The driver, later identified as Kevin Meredith, then crossed the river into Bow Creek where he tied the boat up and waited.
8:43
The JCB and van drove out of the Yard towards Plumstead. The JCB driver – later identified as Betsonwas wearing a fluorescent waistcoat. The JCB traveled towards Greenwich, turning right into Anchor and Hope Lane. At this point the white van was lost. The driver was not identified and the vehicle has never been recovered.
58

UNIT 3 – Criminal Investigations
9:07
9:33
9:35
9:36
9:37
9:37
The JCB travelled along Bugsby Way towards the Dome. It turned left beneath the A102 Blackwall Tunnel Approach and parked out of sight. Police believe that this is where Ciarocchi, Cockram and Robert Adams got into the JC into the JCB alongside Betson. The gang had modified the cabin to fit four passengers people.
The JCB turned left into Ordnance Crescent towards the Dome. It stopped in Drawdock Road, just short of the Dome’s perimeter fence.
The JCB crashed through a gap in the fence, flattening a metal bollard as it went. It headed towards Gate 4 of the Dome.
The JCB rammed open the double locked gates at Gate 4 and moved into the grounds of the Dome.
The speedboat crossed the Thames toward the Dome from Bow Creek. It got into position at Millennium Pier where it waited for the robbers.
The JCB crashed through the side of the Millennium Dome and careered towards the Money Zone. It braked quickly outside the diamond exhibition, and Adams, Ciarrocchi and Cockram jumped down from the cabin.
All three were wearing gasmasks and body-armour. Adams and Cockram entered the vault while Ciarrocchi kept watch outside.
Inside the vault, Cockram dashed to the cabinet containing the 777-carat Millennium Star diamond. He fired into the glass with a loaded Hilti gun. Adams then set about smashing the cabinet with a sledgehammer. Having broken the glass he started on the second cabinet - where the De Beers Millennium Diamonds were displayed: eleven rare blue stones and the 777 carat flawless Millennium Star. Worth over £200 million, the diamonds are second in value only to the Crown Jewels.
At this point Det Supt Jon Shatford gave the order to arrest the suspects.
Outside the vault Ciarrocchi was still keeping watch. As armed officers approached him, he threw a grenade in their direction - which exploded into a ball of blue smoke. Ciarrocchi was quickly overpowered and arrested. When searched he was found to be carrying further grenades, a firework and ammonia.
59

English for Modern Policing
The arrests and after
Damage in the vault
With the suspects outside the vault safely detained, armed officers moved towards the vault itself. Distraction devices were thrown inside as officers entered and overpowered the pair. As they handcuffed Adams they noticed a strong smell of ammonia and discovered that both he and Cockram were carrying bottles of the substance.
Betson, who remained inside the JCB was also swiftly arrested and handcuffed.
Armour and ammonia
Meanwhile officers on the river moved in to arrest Meredith. Armed officers deployed on three boats left their hiding places and moved towards Millennium Pier. They quickly cut off his escape route, and arrested him. Meredith was carrying a large quantity of petrol – which police believe would have been used to set fire to the boat after the robbery.
A sixth man was arrested on the north side of the river Thames at the Lower Lea Crossing. He was parked in the White Ford Transit van (N770 AHE) which was seen towing the speedboat earlier that morning.
The robbers were taken to different police stations in South East London for questioning. On 8 November, the following day, they were charged.
Conviction and Sentence
# Exercise 3
Listen to the text and complete the notes
On 18 February 2002 at the Old Bailey, Adams, Ciarrocchi, Cockram and Betson were convicted of conspiracy to rob and Meredith was convicted of (1)………………….. Betson and Cockram were each jailed for (2)…………………... Adams and Ciarrocchi were each jailed for 15 years and Meredith was jailed for 5 years.
A sixth man involved in the robbery plot was jailed at the Old Bailey on Wednesday 20 February. Lee Wenham, aged 33, was sentenced to four years in jail (3)…………………. to
60

UNIT 3 – Criminal Investigations
conspiracy to steal. (4)………………………….. he was sentenced to nine years after pleading guilty to an attempted robbery which took place at Aylesford, in Kent, in June 2000.
Proceedings (5) ………………………….. against another man, 59-year-old James Wenham, who had been charged with conspiracy to rob in relation to the raid on the Dome.
# Exercise 4
Comprehension check. Complete the statements with the correct answer:
1)The police operation was
a)poor and superficial
b)massive and meticulous
c)obstructed by local politicians
d)detected by the gang at an early stage
2)‘Magician’ was the codename of the
a)police operation
b)intervention strategy
c)robbers’ plot
d)gang leader
3)The gang was supposed to be
a)badly organised and unarmed
b)well organised and armed
c)a group of criminals unknown to each other
d)former security officers at the Dome
4)The getaway of the gang was
a)a white van
b)a mechanical digger
c)a speedboat
d)a tunnel through the vault
5)The day of the robbery was connected to
a)an eclipse of the sun
b)the position of the stars
c)the phases of the moon
d)Atlantic high tides
6)The police ensured that the arrest would go
a)calculating a high risk to the public
b)quickly although riskily
c)spectacularly to set an example
d)rapidly with minimal risk to the public
7)The plan of the robbery
a)was known from the very beginning
b)had to be carefully figured out
c)had been instigated by police “agent provocateurs”
d)was based on a previous foiled plan
8)The prime consideration of the police was
a)their own safety
b)the apprehension of the robbers
c)the guarding of the diamonds
d)public safety
e)ensuring long prison sentences for the gang leaders
61

English for Modern Policing
9)The police operations’ room was
a)the ground floor of the police headquarters
b)the Dome’s CCTV room
c)The Old Coal Yard in Whitehart Road, Plumstead
d)The Old White Hart public house
10)Amongst the 200 officers involved in Operation ‘Magician’ there were
a)DVU and Internal Affairs officers
b)CPT and Fraud Squad officers
c)Flying Squad and Specialist Firearms officers
d)VAT and National Lottery protection officers
¾ Activity 2
With a partner, try to retell the story in your own words.
Look in the papers or on the Internet for other such operations. Do they involve reactive or proactive approaches?
Homework activity: Give a written account of a real police operation that you know about from Romania. This should be described in about 150 words.
Caution in UK:
‘You do not have to say anything. But it may harm your defence if you do not mention, during questioning, something which you later rely on in court. Anything you do say may be given in evidence’.
Caution in US: ‘Anything you say can and will be used against you in a court of law’
¾ Activity 3
Try to classify the following actions according to the person who performs them. Sometimes more than one answer is possible. There may also be a natural sequence or “chronology” related to some actions.
WORK IN GROUPS! Use the following abbreviations.
Investigating Officer = (IO) |
Victim=(V) |
Witness= (W) |
|
|||
Offender= (O) |
(CPS) = Crown Prosecution Service |
|
||||
|
|
Court = (C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investigating |
Victim |
Witness |
Offender |
CPS |
|
Court |
Officer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GROUP 1
to detect a crime, to report a crime, to commit a crime, to catch a criminal, to arrest a suspect, to interrogate, to make a confession, to break the law, to put an APB on a criminal, to take into custody, to browse a mug-shot book, to gather evidence, to prosecute, to send to prison, to
62
UNIT 3 – Criminal Investigations
handcuff a suspect, to commit to trial, to send to court, to take a statement, to give a statement, to release on parole, to release on probation, to plead guilty,
GROUP 2
to charge, to execute a search warrant, to press charges, to drop charges, to issue an warrant, to be on call, to perpetrate a crime, to conduct a crime scene examination, to report for duty, to follow a lead, to shadow a suspect, to apprehend a criminal, to be served with a subpoena, to admit an offence, to perform a ballistics match, to resort to the polygraph, to conceal facts, to combat crime, to conduct an interview, to exercise their right to silence, to elicit information from a suspect, to deny involvement, to establish the identity of a suspect
GROUP 3
to withhold information, to request legal advice, to locate a crime, to check an alibi, to do the fingerprints’ match, to handle exhibits and evidence, to obtain a confession, to record an interview, to prove an offence, to caution a suspect, to conspire with, to view an identification parade, to accuse, to carry out an intimate search, to detain a suspect, to witness an offence, to have the power to stop and search, to be assigned to a case, to be put on a case,
GROUP 4
to question a suspect, to pass sentence, to be under subpoena, to do a positive ID on somebody, to violate the law, to find guilty on all counts, to find guilty as charged, to bring charges against, to invalidate a confession, to dismiss a case, to hear a case, to disclose evidence, to arrest in anticipation of violent behaviour, to reach a verdict, to return a verdict, to sign a restraining order, to institute criminal proceedings, to testify,
to arrest on suspicion of murder
¾ Activity 4 Word Association
Each of these four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are to do with police matters. What are the missing link words?
1. intimate |
|
body |
house-to-house |
vehicle |
underwater |
|
|
|
2. investigating |
duty |
arresting |
custody |
|
crime prevention |
63
|
|
English for Modern Policing |
|
|
|
3. |
first-time |
juvenile |
|
repeat |
habitual |
4. |
detention |
search |
|
arrest |
eviction |
5. |
open-and-shut |
hit-and-run |
murder |
unsolved |
|
¾ Activity 5 What’s in a Name?
When a criminal is caught by the police he is first (a)(an) ……..…….., then (a)(an)
…………….., after that (a)(an)……………, probably both the ……………… and the …….. when he is in court, after sentencing he is a frequently (a)(an) …………!
Choose from the following and put them in the right order:
arrestee, detainee, convict, suspect, accused, defendant, chargee.
Are there any other possible stages (with names!) for a criminal?
Grammar focus
Modal verbs can also express possibility- may, could or might for greater doubt to replace phrases such as ‘it is possible’, ‘maybe’, ‘perhaps’, ‘it is likely’ etc; probability or deductions - must to replace phrases such as ‘it is probable, it is almost certain, I am sure, etc. and impossibility - can’t or couldn’t to replace phrases such as ‘it is impossible that’, ‘it is unlikely that’.
64
