
Зошит Англ мова СОЗ 3 курс 2 семестр
.pdf
Activity 8. Make a group of the words similar in meaning from the list below.
Наприклад: A. to perform, to exercise, to carry out; B. a man, a person, a human being
Verbs: to turn on, to provide, to type, to accept, to help, to learn, to observe, to call, to tell, to keep, to feed, to solve, to relate, to switch off, to communicate, to receive, to supply, to switch on, to assist, to print, to study, to input, to turn off, to decide, to store, to say, to name, to watch.
Nouns: work, machine, fundamentals, display, application, capabilities, job, storage, screen, state, basics, use, concept, specialist, journal, character, memory, idea, expert, magazine, position, symbol, command, data, solution, device, instruction, powers, information, decision.
Adjectives: basic, tiny, common, small, main, significant, routine, general, remarkable, uninterested, intricate, important, wonderful, complex, little.
Adverbs: rapidly, probably, instantaneously, in a moment, quickly, perhaps.
Activity 9. Match the definition with the correct spelling word.
1. computer |
11. bit |
2. mouse |
12. data base |
3. memory |
13. chip |
4. hardware |
14. file |
5. input |
15. Internet |
6. software |
16. e-mail |
7. output |
17. printer |
8. disk |
18. monitor |
9. processor |
19. cursors |
10. menu |
20. virus |
a)information or instructions put into a computer;
b)device that prints, especially one operated by a computer;
c)the basic unit of information in an electronic computer, equivalent to a choice between two possibilities, such as "yes" or "no";
d)an electronic machine that can store, recall, or process information;
e)information put out by or delivered by a computer;
f)an extremely large computer network, including many smaller networks of university, government, business, and private computers, linked by telephone lines;
61
g)a movable mark on a computer display screen, indicating the point at which the displayed data may be altered or processed, or at which new data may be inserted;
h)system of storing information in a computer on magnetic tape, etc.; storage;
i)a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, which holds an integrated circuit;
j)the central processing unit of a computer, especially the part of this unit in which data are examined, compared, changed, etc.
Activity 10. Using words from the list, fill in the blanks with the correct answers:
tapes |
computer(s) |
information |
skill |
operator(s) |
instructions |
paper |
printers |
upper level |
build |
machine |
engineers |
design |
reports |
responsibility |
memory |
training |
programmer(s) |
1.A computer is a _____________________ that stores ____________________ for later use and processes that ____________________ on demand.
2.A computer worker's main __________________ is to make sure _____________________ can be processed on the ______________________ when the customer needs it.
3.Those who ____________________ and ________________________ new computers are
_______________________ .
4.Most people working with computers are either ____________________ or ______________ .
5.A computer _____________________ is the one who actually runs a ____________________ .
6.The operator is kept busy telling the machine to prepare ______________________ , changing
___________________ in the ________________, and new computers are ________________ .
7.The computer ______________ is the person who tells the ____________________ how work.
8.Computer programmers take more ___________________ and need more ________________
than computer operators.
9.As an educational minimum, any ________________________ worker should be an
_________________ graduate.
10.A programmer must continue to be updated on new __________________________ and
_______________ .
Анотація (annotation) (від лат. annotatio — примітка) — коротка характеристика друкованого чи рукописного тексту.
Анотації за своїм змістом та кінцевим призначенням можуть бути:
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________;
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________.
За обсягом анотації поділяються на:
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________;
62
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________.
Для наших цілей найбільш цікаві загальні анотації газетних та журнальних статей. Вони можуть бути короткими (декілька фраз) та більш розгорнутими, але і в цьому разі вони подають у стислій формі лише найголовніші висновки та положення документів. В анотації вказують лише суттєві ознаки змісту статті, тобто такі, що дають змогу виявити його новизну та практичне значення, вирізнити його серед інших, близьких за тематикою та призначенням. При написанні анотації не варто переказувати зміст статті (висновки, рекомендації, фактичний матеріал). Слід звести до мінімуму використання складних зворотів, особових та вказівних займенників. Обсяг анотації не повинен перевищувати 600 друкованих знаків.
Анотація містить:
•________________________________________________________________________;
•________________________________________________________________________;
•________________________________________________________________________;
•________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Резюме (abstract, summary) — короткий виклад найважливіших фактів (питань, проблем, досліджень), які обговорюються у статті, засоби їх вирішення (реалізації), результати досліджень, підсумки, зроблені на базі цих досліджень, і рекомендації щодо застосування того чи іншого методу (одержаних даних тощо).
Як правило, термін “abstract” застосовується, коли резюме подається до статті, а термін “summary” — коли резюме подається після статті.
Використовують такі фрази:
The text / article under review ...(gives us a sort of information about...)
∙The article deals with the problem ...
The subject of the text is...
At the beginning (of the text) the author describes... (dwells on ...; explains...; touches upon...; analyses...; comments ...; characterizes ...; underlines ...; reveals...; gives account of...)
The article begins with the description of..,, a review of..., the analysis of...
•The article opens with ...
Then (after that, further on, next) the author passes on to ...,
•gives a detailed (thorough) analysis (description), goes on to say that ...
To finish with, the author describes ...
•At the end of the article the author draws the conclusion that ...;
•the author sums it all up (by saying...)
•In conclusion the author...
63
Activity 11. Read the text, make annotations in English, give the title of the text.
As it is well known, a computer cannot perform or complete any useful work unless it is able to communicate with its external environment. All data and instructions enter and leave the central processing unit through primary storage. Input-output devices are needed to link primary storage to the environment, which is external to the computer system. So input devices are used to enter data into primary storage. Output units accept data from primary storage to provide users with information or to record the data on a secondary storage device. Some devices are used for both the input and output functions.
The data with which these devices work may or may not be in a form that humans can understand. For example the data that a data entry operator keys into the memory of a computer by typing on a keyboard are readable by humans. However, the data that tell a computer about the performance of an automobile engine are not in a form that humans can read. They are electrical signals from an analog sensor. Similarly, output may be on a printed page, which humans can read easily, or upon some other medium where the data are not visible, such as on magnetic tape or disk.
As we know, all of the data flow from input to final output is managed by the control unit in the CPU. Regardless of the nature of the I/O devices, special processors called I/O interfaces are required to convert the input data to the internal codes used by the computer and to convert internal codes to a format which is usable by the output device.
Home task: _______________________________________________________________________
64

Заняття 11.
Тема Дієприкметник. Утворення дієприкметників. Значення та вживання дієприкметника теперішнього часу. CPU
Дієприкметник (The Participle) —
це неособова форма дієслова, що має властивості дієслова, прикметника і прислівника.
Дієприкметник теперішнього часу Present Participle або
Participle І
Present Participle утворюється за допомогою закінчення ing, яке додається до інфінітива дієслова без частки to.
Present Participle відповідає українському дієприкметнику активного стану теперішнього часу та дієприслівнику недоконаного виду:
resting—відпочиваючий, відпочиваючи
Дієприкметник минулого часу Past Participle або Participle II
Past Participle правильних дієслів утворюється за допомогою закінчення - ed, що додається до інфінітива без частки to:
To askasked
Past Participle перехідних дієслів відповідає українському пасивному дієприкметнику минулого часу:
dressed одягнутий made зроблений
Participle I is used in the function of:
1. Adverbial modifier of time (обставина часу): Walking home she didn't hurry.
When walking home she didn't hurry. Ідучи додому, вона не поспішала. While walking home she didn't hurry.
2. Adverbial modifier of cause (обставина причини):
Knowing the way she walked quickly. |
Знаючи дорогу, вона йшла швидко |
Not knowing the way she didn't hurry. |
Не знаючи дороги, вона не поспішала. |
Being busy she couldn't speak to me. |
Будучи зайнята, вона не могла поговорити зі мною. |
3. Adverbial modifier of manner (обставина способу дії). He stood at the window thinking about his future.
Він стояв біля вікна, думаючи про своє майбутнє.
Participle I in the function of attribute and adverbial modifier:
|
I saw her smiling face in the |
Я побачив у вікні її обличчя, яке |
Attribute |
window. |
посміхалося. |
|
In the window I saw her face |
У вікні я побачив її лице, що |
|
65 |
|
|
smiling at us. |
|
посміхалося нам. |
|
|
She said these words, smiling at |
Вона сказала ці слова, |
|
|
Adverbial modifier |
me. |
|
посміхаючись мені. |
|
|
Smiling happily she hurried to the |
Радісно посміхаючись, вона |
|
|
|
door. |
|
поспішила до дверей. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Participle II in the function of attribute: |
|||
|
|
|||
The discussed question is important. |
Питання, яке обговорюється, дуже |
|||
The written letter is on the table. |
важливе. |
|||
|
|
Написаний лист лежить на столі. |
||
|
|
|||
The question discussed by the students is very |
Питання, що обговорюється студентами, |
|||
important. |
дуже важливе. |
|||
The letter written by Mary is on the table. |
Лист, написаний Мері, лежить на столі. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 1. Translate into English.
Запитаний - запитуючий (питаючи); початий -починаючий (починаючи); запрошений – запрошуючий (запрошуючи); даний - даючий (даючи); залишений - залишаючий (залишаючи);
побачений – той, що бачить (бачивши); показаний - показуючий (показуючи); взятий - беручий (беручи); забуваючий (забуваючи);
знайдений – той, що знаходить (знаходячи);
Activity 2. Замініть підрядні означальні речення дієприкметниковими зворотами.
1.All the people who live in this house are students.
2.The woman who is speaking now is our secretary.
3.The apparatus that stands on the table in the corner of the laboratory is quite new.
4.The young man who helps the professor in his experiments studies at an evening school for laboratory workers.
5.People who take books from the library must return them in time.
6.There are many pupils in our class who take part in all kinds of extracurricular activities.
66

|
Форми дієприкметника |
|
||
Теперішнього часу |
Минулого часу |
|
Перфектна Пасивного і активного стану. |
|
Present Participle |
Past Participle |
Perfect Participle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Форма |
Перехідні дієслова |
Неперехідні дієслова |
||
дієприкметника |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Active Voice |
|
Passive Voice |
Active Voice |
Present Participle |
asking |
|
being asked |
going |
Past Participle |
|
|
asked |
gone |
|
|
|
|
|
Perfect Participle |
having asked |
|
having been asked |
having gone |
|
|
|
|
|
Present Participle не має певного часового значення і виражає різні часові відношення залежно від контексту і значення дієслова, від якого утворено дієприкметник.
a) Present Participle вживається для позначення дії, одночасної з дією, вираженою дієсловом-присудком речення. Залежно від часу дієслова-присудка Present Participle може відноситись до теперішнього, минулого або майбутнього часу:
Reading English books I write out new words.
Читаючи англійські книжки, я виписую нові слова.
Reading English books I wrote out new words.
Читаючи англійські книжки, я виписував нові слова.
Reading English books I'll write out new words.
Читаючи англійські книжки, я виписуватиму нові слова.
У першому з цих речень reading відноситься до теперішнього часу, в другому — до минулого, а в третьому — до майбутнього.
67

б) Present Participle може виражати дію, що відноситься до теперішнього часу, незалежно від часу дії, вираженої дієсловом-присудком речення:
The students working in our village came from Kiev.
Студенти, що працюють у нашому селі, прибули з Києва
Хоч дієслово-присудок цього речення стоїть у минулому часі, Present Participle виражає дію, що відноситься до теперішнього часу.
в) Present Participle Indefinite може вживатися безвідносно до якогось часу:
The bisector is a straight line dividing an angle into two equal parts.
Бісектриса —це пряма лінія, що поділяє кут на дві рівні частини.
г) Present Participle - може виражати дію, що передує дії, вираженій присудком, якщо обидві дії відбуваються безпосередньо одна за одною. У такому значенні часто трапляється Present Participle дієслів to enter входити; to open відчиняти; to close закривати; to arrive
прибуватиi; to seeбачити; to hear чути та ін.
Entering his room, he went quickly to the other door.
УВІЙШОВШИ в свою кімнату, він швидко пішов до інших дверей.
Dressing myself as quickly as I could I went for a walk.
Одягнувшись якомога швидше, я пішов на прогулянку.
У такому разі Present Participle перекладається на українську мову дієприслівником доконаного виду.
Вживання Present Participle
Participle виражає дію, що передує дії, вираженій дієсловомPerfect Participle відповідає українському дієприслівнику доконаного
said this, they stopped speaking.
це, вони припинили розмову. given her word, she ought to keep it.
слово, вона мусить дотримувати його.
Active вживається тоді, коли іменник або займенник, до якого позначає суб'єкт вираженої ним дії:
she walked back to the house.
Плачучи, вона повернулася в будинок.
Having opened my window, I went downstairs.
Відчинивши вікно, я зійшла вниз.
68

Present Participle Passive вживається тоді, коли іменник або займенник, до якого він відноситься, позначає об'єкт вираженої ним дії:
Being invited to an evening-party she couldn't go to the theatre.
Оскільки її запросили на вечір, вона не могла піти в театр.
Having been packed, the parcel was taken to the postoffice.
Після того як посилку запакували, її віднесли на пошту.
Activity 3. Read and translate the text.
Parts of a computer
A computer is an electronic machine that accepts, processes, stores and outputs information. A typical computer consists of two parts: hardware and software.
Hardware is any electronic or mechanical part of, the computer system that you can see or touch.
Software is a set of instructions, called a program, which tells a computer what to do. There are three basic hardware sections.
1.The CPU is the heart of the computer, a microprocessor chip which processes data and coordinates the activities of all the other units.
2.The main memory holds the instructions and data which are being processed by the CPU. It has two main sections: RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read only memory).
3.Peripherals are the physical units attached to the computer. They include:
Input devices, which let us enter data and commands e.g. the keyboard and the mouse.
Output devices, which let us extract the results (e.g. the monitor and the printer). Storage devices, which are used to store information permanently (e.g. hard disks and DVD-RW drives).
Disk drives are used to read and write data on disks.
69
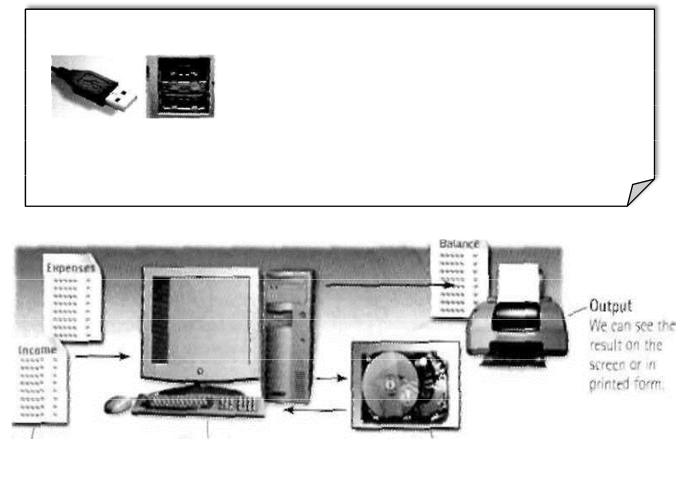
At the back of a computer there arc ports into which we can plug external devices
(e.g. a scanner, a modem, etc.). They allow communication between the computer and the devices.
USB connector USB ports
Input |
Processing |
Storage |
We enter data with a |
The data is manipulated according |
We keep data and programs in memory |
keyboard, a webcam, etc. |
to program instructions. |
systems where they are available for |
|
|
processing. |
Activity 4. Look at the computer essentials. Read these quotations and say which computer essential they refer to.
1.Accelerate your digital lifestyle by choosing a Pentium at 4.3 GHz.
2.Right-click to display a context-sensitive menu.
3.You will see vivid, detailed images on a 17" display.
4.This will produce high-quality output, with sharp text and impressive graphics.
5.Use it when you want to let the grandparents watch the new baby sleeping."
6.Press any key to continue.
Activity 5. Match the terms with their definitions. |
|
|
|
||||
1. |
CD/DVD drive |
a. any socket into which a peripheral device may be connected |
|||||
2. |
speaker |
b. device used to produce voice output and play back music |
|||||
3. |
modem |
c. mechanism that reads and/or writes to optical discs |
|||||
4. |
port |
d. device that converts data so that it can travel over the Internet |
|||||
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 6. Complete the diagram and sentences below.
1.Computer_____________________ is the visible or audible result of data processing – information that can be read, printed or heard by the user.
70
