
- •Foreword
- •Preface to the Fourth Edition
- •Contents
- •Instructions for Use
- •Bones
- •Sutures, joints and ligaments
- •Muscles
- •Muscles, synovial bursae and sheaths
- •Digestive system
- •Digestive and respiratory system
- •Urogenital system
- •Peritoneum
- •Endocrine glands
- •Heart
- •Veins
- •Lymphatic system
- •Spinal cord
- •Cranial nerves
- •Autonomic nervous system
- •Sense organs
- •Skin and its appendages
- •General terms
- •References
- •Index

|
272 |
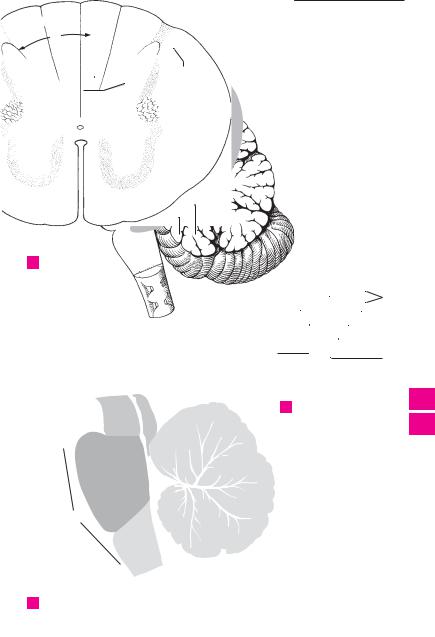
Spinal cord |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1 |
Cranial pia mater. Pia mater cranialis (en- |
14 |
Cervical enlargement. Intumescentia cervi- |
|||||||||||||
1 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
cephali). Delicate meninx bearing blood vessels |
|
calis. Enlargement of the spinal cord from C3 to |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
and covering the surface of the brain as well as |
|
T2 owing to the larger supply region for the |
|||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
extending into its sulci. |
|
|
|
|
arms. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
2 |
Tela choroidea of fourth ventricle. Tela 15 |
Lumbosacral |
enlargement. |
Intumescentia |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
choroidea ventriculi quarti. Thin membrane of |
|
lumbosacralis. Expansion of the spinal cord |
|||||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
pia mater and ependyma in lower part of roof |
|
from T9−10 to L1−2 caused by the greater |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
of fourth ventricle. It is attached laterally to the |
|
supply region for the lower limbs. D |
|
|
|||||||||||
4 |
|
|
tenia and exhibits lateral and median aper- |
16 |
Conus medullaris. Tapered termination of the |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
tures. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
spinal cord at the level of L1−2 where it be- |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
5 |
3 |
Choroid |
plexus |
of |
fourth |
ventricle. Plexus |
|
comes continuous with the filum terminale. D |
||||||||||
|
|
choroideus ventriculi quarti. Paired garland- |
17 |
Filum terminale (spinale). Thin terminal pro- |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
like, ependyma-covered villous projections |
|
longation of spinal cord attached inferiorly to |
|||||||||||||
6 |
|
|
which extend into both lateral apertures. B |
|
the posterior surface of the coccyx. D E |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
4 Tela choroidea |
of |
third |
ventricle. |
Tela |
18 |
Terminal ventricle. Ventriculus terminalis. En- |
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
7 |
|
|
choroidea ventriculi |
tertii. Thin, |
ependyma- |
|
largement of the central canal at the end of the |
|||||||||||
|
|
covered membrane of pia mater between right |
|
conus medullaris. E |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
and left teniae of thalamus. C |
|
|
19 |
Anterior median fissure. Fissura mediana |
|||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
5 |
Choroid plexus of third ventricle. Plexus |
|||||||||||||||||
|
anterior. Deep longitudinal fissure along the |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
choroideus ventricul tertii. Paired, highly |
|
anterior aspect of the spinal cord. F |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
9 |
|
|
vascularized villous formations projecting from |
20 |
Posterior |
median |
sulcus. Sulcus |
medianus |
||||||||||
|
|
the thin roof into the third ventricle and con- |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
posterior. Median longitudinal groove between |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
tinuing anteriorly through the interventricular |
|
the right and left posterior funiculi. F |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
10 |
|
|
foramina into the choroid plexuses of the |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
21 |
Posterior |
median |
septum. |
Septum |
medi- |
|||||||||||
|
6 |
lateral ventricles. C |
|
ventricle. Plexus |
|
anum posterius. |
Thickening |
of |
the |
sub- |
||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
11 |
Choroid |
plexus |
of |
lateral |
|
arachnoid connective tissue within the poste- |
||||||||||||
|
|
choroideus ventriculi lateralis. Villous, highly |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
rior median sulcus, less in the cervical region, |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
vascularized garland invaginated into |
the |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
more in the thoracic segment. F |
|
|
||||||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
lateral ventricle through the choroid fissure. It |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
22 |
Anterolateral |
sulcus. Sulcus |
anterolateralis. |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
extends from the interventricular foramen to |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Shallow furrow occasionally present at the exit |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
the inferior horn. C |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of the ventral root fibers. F |
|
|
|
|||||||
7 |
Choroid |
glomus. |
Glomus |
choroideum. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
23 Posterolateral sulcus. Sulcus posterolateralis. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Enlargement of the choroid plexus in the region |
|||||||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
Longitudinal groove external to the boundary |
||||||||||||||
|
|
of the collateral trigone at the root of the infe- |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
between the lateral and posterior funiculi. It |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
rior horn. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
marks the |
site |
of |
entry of the dorsal spinal |
||||||
15 |
|
8 Spinal pia mater. Pia mater spinalis. Vascu- |
|
nerve roots. F |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
larized |
connective tissue membrane firmly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
24 Posterior intermediate sulcus. Sulcus inter- |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
united to the surface of the spinal cord. A |
|
||||||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
|
medius posterior. Shallow longitudinal fissure |
|||||||||||||
9 |
Denticulate ligament. Lig. denticulatum. Fron- |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
on both sides of the median sulcus. Externally it |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
tally situated connective tissue membrane con- |
|
marks the boundary between the funiculi |
|||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
necting the spinal cord with the spinal dura |
|
gracilis and cuneatus. F |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
mater. It has bow shaped recesses at the level of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
the spinal nerve roots. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1810 Intermediate cervical septum. Septum cervicale intermedium. Connective tissue partition
19in the cervical segment of the spinal cord between the gracilis and cuneatus fasciculi extending from the pia mater to the depths of the
20posterior funiculus. A F
11 Internal filum terminale. Filum terminale in-
21ternum (piale). Filamentous, caudal extension of the spinal cord and pia mater contained in the external terminal ligament. D E
2212 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Systema nervosum centrale. It comprises the brain and spinal
23cord.
13SPINAL CORD. Medulla spinalis. Consists of the myelin-rich white matter and the myelin-poor
24gray matter. It extends from the caudal end of the medulla oblongata, near the exit of the first
25spinal nerves, to the beginning of the filum terminale at L1−2. A D
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Spinal cord 273
8
10 9
A Spinal meninges
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CChoroidal plexus of lateral ventricles
15
16
18
 11;17
11;17
 11;17
11;17
BRoof of thomboid fossa (fourth ventricle)
23 24 20
 10
10
 21
21
 19
19
22 
D |
Spinal cord |
E |
Lower termination |
F |
Cross section of spinal cord |
|
|
|
of spinal cord |
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
274 |
Spinal cord |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Funiculi of spinal cord. Funiculi medullae spi- |
14 |
White matter. Substantia alba. Consists of my- |
||||
1 |
|
1 |
|||||||
|
|
|
nalis. Three columns of white matter seg- |
|
elinated nerves and is organized into three |
||||
|
|
|
|
mented by the posterior and anterior horns and |
|
cords (funiculi) which contain the nerve path- |
|||
2 |
|
|
|
their root fibers. |
|
|
ways. A |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Anterior funiculus. Funiculus anterior. Con- |
15 |
Substantia gelatinosa centralis. A narrow zone |
||||
3 |
|
|
|
duction bundle located between the anterior |
|
around the central canal with processes from |
|||
|
|
|
median fissure and the anterior horn with its |
|
ependymal cells. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
4 |
|
|
|
root fibers. A |
|
16 |
GRAY COLUMNS. Columnae griseae. Three |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
3 |
Lateral funiculus. Funiculus lateralis. Conduc- |
|
ridge-like columns of gray matter. B |
|||||
|
|
|
|
tion bundle located lateral to the gray matter |
17 |
Anterior column. Columna anterior. It is com- |
|||
5 |
|
|
|
and between the posterior and anterior spinal |
|
prised predominantly of motor neurons (ante- |
|||
|
|
|
|
nerve roots. A |
|
|
rior horn cells). B |
||
6 |
|
4 |
Posterior funiculus. Funiculus posterior. Post- |
18 |
Anterior horn. Cornu anterius. Hook-shaped |
||||
|
|
|
erior column situated between the posterior |
|
structure seen in transverse section of the spi- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
horn with its root fibers and the posterior me- |
|
nal cord. D |
|
||
7 |
|
|
|
dian septum. A |
|
19 |
Anterolateral nucleus. Nucleus anterolater- |
||
|
|
|
5 Segments of spinal cord. Segmenta medullae |
|
alis. Situated anterolaterally in the anterior |
||||
8 |
|
|
|
spinalis. Here, the spinal cord segments are de- |
|
horn, it is localized in segments C4−8 and L2− |
|||
|
|
|
|
fined as regions where root fibers pass through |
|
S1 and innervates the muscles of the limbs. D |
|||
9 |
|
|
|
a specific intervertebral foramen. The boundar- |
20 |
Anteromedial |
nucleus. Nucleus anterome- |
||
|
|
|
ies are not determinable in the isolated spinal |
||||||
|
|
|
|
dialis. From its anteromedial position in the |
|||||
|
|
|
|
cord. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
anterior horn, it extends the entire length of the |
|||
10 |
|
6 |
Cervical segment. Segmenta cervicalia [1−8] = |
|
|||||
|
|
spinal cord. D |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
pars cervicalis. Eight cervical segments repre- |
21 |
Posterolateral nucleus. Nucleus posterolater- |
|||
|
|
|
|
sent the seven cervical vertebrae because the |
|||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
alis. It lies posterior to the anterolateral nucleus |
||||
|
|
|
root fibers of segments 1−7 exit above the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
in segments C5−T1 and L2−S2 and innervates |
|||||
|
|
|
|
vertebrae of the same number. Root fibers of |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
the muscles of the limbs. D |
||||
12 |
|
|
|
the 8th cervical segment, on the other hand, exit |
|
||||
|
|
|
22 |
Retroposterolateral nucleus. Nucleus retro- |
|||||
|
|
|
below C7. The cervical portion of the spinal |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
posterolateralis. It lies posterior to the post- |
||||
|
|
|
|
cord extends from the atlas to the middle of C7. |
|
||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
erolateral nucleus in segments C8−T1 and S1−3. |
||||
|
|
|
C |
|
|
||||
|
|
7 |
Thoracic segment. Segmenta thoracica [1−12] |
|
D |
|
|||
14 |
|
23 |
Posteromedial |
nucleus. Nucleus posterome- |
|||||
|
|
|
= pars thoracica. The 12 segments comprising |
|
dialis. From the vicinity of the white matter, it |
||||
|
|
|
|
this group extend from the middle of C7 to the |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
extends over segments T1−L3 and probably in- |
||||
15 |
|
|
|
middle of T11. C |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
nervates the trunk musculature. D |
||||
|
8 |
Lumbar segment. Segmental lumbaria [1−5] = |
|
||||||
|
|
24 |
Central nucleus. Nucleus centralis. A less |
||||||
|
|
|
|
pars lumbaris. Comprised of five segments; it |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
16 |
|
|
|
|
prominent group in several cervical and lumbar |
||||
|
|
|
extends from the middle of the body of T11 to |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
the upper border of the body of L1. C |
|
|
segments. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 Nucleus of accessory nerve. Nucleus nervi ac- |
||||
17 |
9 |
Sacral segment. Segmenta sacralia [1−5] |
= |
||||||
|
cessorii (nuc. accessorius). It lies in segments |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
pars sacralis. These five sacral segments |
lie |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
C1−6 in the area of the anterolateral nucleus |
||||
|
|
|
|
posterior to the body of L1. C |
|
|
|||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
and provides the root fibers of the spinal por- |
|||
10 |
Coccygeal segment. Segmenta coccygea [1−3] |
|
|||||||
|
tion of the accessory nerve. D |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
= pars coccygea. Three quite small segments. C |
26 |
Nucleus of phrenic nerve. Nucleus nervi |
|||
19 |
|
|
|
||||||
11 |
SPINAL CORD SECTIONS. Sectiones medullae |
||||||||
|
phrenici (nuc. phrenicus). It lies in the middle |
||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
spinalis. These serve mostly as a foundation for |
|
of the anterior horn and extends from seg- |
|||
|
|
|
description of the following parts. |
|
|
ments C4−C7. D |
|
||
12 Central canal. Canalis centralis. Obliterated re-
21mains of the embryonic neural tube lumen. It is usually located in the central intermediate substance (gray matter). A D
2213 Gray matter. Substantia grisea. In transverse section, it is seen as an H-shaped column
23(columna grisea = gray column) consisting primarily of multipolar ganglion cells and enclosed by white matter. Sections of the spinal
24cord reveal that the ”horns” (cornua) which correspond to the gray column S are charac-
25teristically different in the individual segments. A
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Spinal cord 275
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
||
13 |
|
|||
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spinal cord, schematic |
|
9 |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
16 |
17 |
|
|
14 |
B |
Gray matter of spinal cord, |
15 |
|
||
|
three-dimensional |
|
8 |
16 |
9
 10
10
26 (24) |
12 |
22 |
18 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
20 |
25 |
|||||
|
Segments of spinal cord |
|
Nuclei of spinal cord in anterior horn |
||||||
C |
D |
||||||||
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
|
276 |
Spinal cord |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Posterior column. Columna posterior. It is |
|
18 Anterior white commissure. Commissura alba |
||||||||
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
composed primarily of sensory neurons. B |
|
|
anterior. White matter with fibers crossing be- |
|||||||
|
|
|
2 Posterior horn. Cornu posterius. Hook-shaped |
|
|
tween the central intermediate gray matter and |
|||||||
2 |
|
|
|
|
the anterior median commissure. C |
||||||||
|
|
|
structure seen in transverse section of the spi- |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
nal cord. A |
|
|
|
|
18 a Posterior |
white |
commissure. |
Commissura |
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
Apex. Apical cap of posterior horn consisting of |
|
|
alba posterior. Individual fibers crossing into |
||||||
|
|
|
large nerve cells ventral to the substantia gelat- |
|
|
the posterior gray commissure. |
|
||||||
4 |
|
|
|
inosa. A C |
|
|
|
|
19 Anterior funiculus. Funiculus anterior. Mass of |
||||
|
|
4 |
Head. Caput. Thickened middle part of poste- |
|
|
white matter between anterior root fibers, |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
rior horn in the lower cervical and thoracic spi- |
|
|
anterior horn and anterior median fissure. A C |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
Anterior |
fasciculi |
proprii. Fasciculi proprii |
|||||
5 |
|
|
|
nal cord. A |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
5 Cervix. Thinner segment of posterior horn be- |
|
|
anteriores. Lying directly on the gray matter, |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
these bundles comprise longer |
and shorter |
|||||||
6 |
|
|
|
tween the head and base. A |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
fibers involved in connecting individual sem- |
|||||||
|
|
6 |
Base. Basis. Broadened attachment of the post- |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
gents of the spinal cord with one another. Re- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
erior horn to the middle part of the gray matter. |
|
|
|||||||
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
flex apparatus. C |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
Sulcomarginal fasciculus. Fasciculus sulcom- |
|||||
|
|
|
7 Substantia gelatinosa. Mobile, slightly glassy |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
arginalis. Fibers of the reflex apparatus located |
||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
substance above the apex of the posterior horn. |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
at the anterior median fissure. |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
It consists primarily of glia and small ganglion |
|
22 Anterior corticospinal (pyramidal) tract. Trac- |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
cells. A C |
|
|
|
|
|||||
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tus corticospinalis (pyramidalis) anterior. Un- |
||||
|
|
8 Secondary |
visceral |
substance. |
Substantia |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
crossed portion of pyramidal tract lateral to the |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
visceralis secundaria. Small field of autonomic |
|
|
anterior median fissure. C |
|
|||||
10 |
|
|
|
ganglion cells anterior to the central interme- |
|
23 |
Vestibulospinal tract. Tractus |
vestibulospi- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
diate substance. A |
|
|
|
|
nalis. Fibers in the anterior funiculus for im- |
||||
|
|
|
9 Lateral column. Columna lateralis. Gray matter |
|
|
||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
pulses from the vestibular organ. C |
||||||||
|
|
|
between the anterior and posterior horns. B |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
Reticulospinal tract. Tractus reticulospinalis. |
|||||||
|
|
|
10 Lateral horn. Cornu laterale. Lateral promi- |
|
|||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
Arising from the reticular formation of the |
||||||||
|
|
|
nence of gray matter. A |
|
|
|
brain stem, it forms a nondefinable tract in the |
||||||
|
|
|
11 |
Interomediolateral |
(autonomic) |
column. |
|
|
middle of the anterior funiculus and ends in the |
||||
13 |
|
|
|
Columna |
intermediolateralis (autonomica). |
|
|
anterior horn. C |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Structure seen as the lateral horn in transverse |
|
25 |
Anterior spinothalamic tract. Tractus sphino- |
||||||
14 |
|
|
|
section. It |
contains |
cells of the sympathetic |
|
|
thalamicus anterior. Fibers ascending to the |
||||
|
|
|
nervous system and extends from T1−L2. A B |
|
|
thalamus for pressure and tactile sensation. C |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
15 |
|
|
12 Central intermediate gray matter. Substantia |
|
26 |
Lateral funiculus. Funiculus lateralis. It lies be- |
|||||||
|
|
|
[grisea] intermedia centralis. Ganglion cells at |
|
|
tween the anterior and posterior horns together |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
the central canal. A C |
|
|
|
with their root fibers. A C |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
16 |
13 |
Lateral intermediate gray matter. Substantia |
|
27 |
Lateral fasciculi proprii. Fasciculi proprii later- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
[grisea] intermedia lateralis. Part of the sympa- |
|
|
ales. Shorter fibers on the gray matter for con- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
thetic nervous system in the lateral horn. It ex- |
|
|
nection with individual spinal cord segments. C |
||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
tends from T1−L2. A C |
|
|
28 |
Lateral corticospinal (pyramidal) tract. Trac- |
||||||
|
|
14 |
Thoracic column. Columna thoracica (nuc. |
|
|
tus corticospinalis [pyramidalis] lateralis. Sit- |
|||||||
18 |
|
|
|
thoracicus) [[Stilling-Clarke]]. It lies at the base |
|
|
uated in front of the posterior horn. It transmits |
||||||
|
|
|
|
of the posterior horn and usually extends from |
|
|
conscious motor impulses. C |
|
|||||
19 |
|
|
|
C8−L2. It belongs partly to the posterior |
|
29 |
Rubrospinal tract. Tractus |
rubrospinalis |
|||||
|
|
|
spinocerebellar tract. A C |
|
|
|
[[Monakow]]. It passes from the red nucleus to |
||||||
|
|
|
15 Sacral parasympathetic nuclei. Nuclei para- |
|
|
the anterior horn cells and lies in front of the |
|||||||
20 |
|
|
|
sympathici sacrales. Cells of the sacral para- |
|
|
lateral corticospinal tract. C |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
symphathetic nervous system in segments S2− |
|
30 |
Bulboreticulospinal tract. Tractus bulboreticu- |
||||||
21 |
|
|
|
4 situated between the anterior and posterior |
|
|
lospinalis. A tract the existence of which is con- |
||||||
|
|
|
horns. |
|
|
|
|
|
troversial in man. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
22 |
|
|
16 Reticular formation. Formatio reticularis. Net- |
|
31 |
Pontoreticulospinal tract. Tractus pontoreticu- |
|||||||
|
|
|
like mixture of gray and white matter in the |
|
|
lospinalis. Likewise, a controversial tract in man. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
angle between the lateral and posterior horns. |
|
32 Tectospinal tract. Tractus tectospinalis. Fibers |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
A C |
|
|
|
|
|||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in the anterolateral region of the anterior |
||||
|
|
16 a |
Anterior/posterior gray commissure. Com- |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
funiculus from the tectal lamina. They cross |
|||||||||
24 |
|
|
|
missura grisea anterior/posterior. Gray matter |
|
|
into the brain stem and terminate in the ante- |
||||||
|
|
|
situated in front of and behind the central |
|
|
rior horns. C |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
canal. C |
|
|
|
|
33 Olivospinal tract. Tractus olivospinalis. Present |
||||
25 |
|
17 |
WHITE MATTER. Substantia alba. It consists pri- |
|
|
only in the cervical cord, its fibers pass from the |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
marily of myelinated nerve fibers. |
|
|
|
olive region to the anterior root fibers. C |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Spinal cord 277
7 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
||||
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
26 |
|||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
8 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
||
1
A Cross section of spinal cord
9;11
B |
Columns of spinal cord |
28 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
16 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
29 |
|
|
|
16a |
12 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
33 |
|||
|
|
|
|
22 |
20 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C Cross section of spinal cord with tracts
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

278 Spinal cord, Brain
1 |
Spinotectal tract. Tractus spinotectalis. Its |
1 |
fibers arise from the posterior horn of the op- |
posite side, run in the lateral spinothalamic
2tract and end in the tectal lamina. A
2Spinothalamic tract. Tractus spinothalamicus. Lies in the lateral funiculus and arises primarily
3from the opposite side. Its fibers transmit pain and temperature sensations. A
4 3 Anterior spinocerebellar tract. Tractus spino-
|
cerebellaris anterior [[Gowers]]. It extends |
|
5 |
partly from the opposite side and transmits to |
|
the cerebellum information necessary for the |
||
|
||
|
coordination of movements concerning muscle |
6extension and limb position. A
|
4 Posterior spinocerebellar tract. Tractus spino- |
|
7 |
cerebellaris posterior [[Flechsig]]. Its fibers are |
|
uncrossed and function similar to those of the |
||
|
||
|
anterior spinocerebellar tract. A |
85 Dorsolateral tract. Tractus dorsolateralis [[Lissauer]]. Bundle of fine myelinated and nonmy-
9elinated fibers between the apex of the posterior horn and the surface. The fibers are short and some form lateral branches of posterior
10 root fibers. A
6 Spino-olivary tract. Tractus spino-olivaris
11[[Hellweg]]. Predominantly crossed fibers to the olive. They lie by the anterior root fibers together with the olivospinal tract. A
127 Spinoreticular tract. Tractus spinoreticularis. Its fibers lie beside the spino-olivary tract and
13end in the reticular substance of the medulla oblongata. A
8Posterior funiculus. Funiculus posterior. White
14 |
matter between the posterior horns. A |
|
9Posterior fasciculi proprii. Fasciculi proprii
15posteriores. They lie directly on the gray matter and unite individual spinal cord segments for
16coordinated activity.
Septomarginal fasciculus. Fasciculus septo-10
marginalis. Bundle of mostly descending fibers
17situated along the posterior median septum in the lower half of the thoracic spinal cord. A
1811 Interfascicular fasciculus. Fasciculus interfascicularis. Bundle of mostly descending fibers [comma tract of Schultze] located chiefly in the
19upper half of the thoracic spinal cord between the fasciculi gracilis and cuneatus. A
2012 Fasciculus gracilis [[Goll]]. Medial fasciculus that contains fibers from the lower half of the spinal cord which function in the transmission
21of tactile and proprioceptive sensory information. A
2213 Fasciculus cuneatus [[Burdach]]. It begins with the upper half of the thoracic cord an likewise contains fibers for transmission of tactile and
23proprioceptive impulses. A
14 BRAIN. Encephalon.
2415 BRAINSTEM. Truncus encephali. It extends from the medulla oblongata to the midbrain.
25According to some, the diencephalon and insula likewise belong to the brainstem.
16HINDBRAIN. Rhombencephalon. It includes the brain substance around the rhomboid fossa, thus the cerebellum, pons with dorsally attached substance and medulla oblongata. B
17MEDULLA OBLONGATA (BULBUS). Beginning at the lower margin of the pons, it extends up to the root fibers of C1. In the rhomboid fossa it arises from the medullary striae of the 4th ventricle. B
18Anterior median fissure. Fissura mediana anterior. Anterior groove continuous with that of the spinal cord. The pyramidal decussation crosses over it. C
19Pyramid. Pyramis [medullae oblongatae]. Longitudinal elevation of pyramidal tract fibers to the right and left of the anterior median fissure. It ends with the pyramidal decussation. C
20Pyramidal decussation. Decussatio pyramidum (dec. pyramidalis anterior motoria). 3−5 bundles of lateral pyramidal tract fibers crossing to the opposite side at the end of the medulla. C
21Anterolateral sulcus. Sulcus anterolateralis. Furrow lateral to the pyramid for transmission of the hypoglossal nerce. C
22Lateral funiculus. Funiculus lateralis. Continuation of the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord up to the olive. C
23Olive. Oliva. Bean-shaped prominence about 1.5 cm long between the roots of cranial nerves X and XII. it is produced by the nuclei lying beneath it. C
24Anterior external arcuate fibers. Fibrae arcuatae externae anteriores. Fibers from the arcuate nucleus coursing over the caudal end of the olive to the caudal cerebellar peduncle. Part of the pontocerebellar tract. C
25Retro-olivary sulcus. Sulcus retro-olivaris. Furrow behind the olive. C
26Retro-olivary area. Area retro-olivaris. Area behind the olive. C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
Spinal Cord, Brain 279
8 |
12 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
11 |
9 |
||
|
|
||
2
3
1
67
A Cross section of spinal cord
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
23 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
20 |
|
C Medulla oblongata from above
16
17
B Rhombencephalon
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
280 |
Brain |
|
|
||
|
|
1 |
Posterolateral sulcus. Sulcus posterolateralis. |
19 |
Internal arcuate fibers. Fibrae arcuatae inter- |
|
1 |
||||||
|
|
Furrow reaching up to the lateral recess of the |
|
nae. Fiber component of the medial lemniscus |
||
|
|
|
4th ventricle. Site of exit of cranial nerves IX, X |
|
arising from the nucleus of the posterior |
|
2 |
|
|
and XI. A |
|
funiculus. C |
|
|
2 |
Inferior cerebellar peduncle. Pedunculus cere- |
20 |
Decussation of medial lemniscus. Decussatio |
||
|
||||||
3 |
|
|
bellaris inferior. Inferior connection to the cere- |
|
lemniscorum medialium (d. sensoria). Formed |
|
|
|
bellum with fibers of the posterior spinocere- |
|
by fibers of nuclei gracilis ans cuneatus, second |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
bellar tract and olive. A |
|
order neurons of posterior funiculus. C D |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|||
3 |
Trigeminal tubercle (tuber cinereum). Tuber- |
21 |
Medial lemniscus. Lemniscus medialis. Con- |
|||
|
|
|
culum trigeminale. Low lateral elevation above |
|
tinuation of second order neuron of posterior |
|
5 |
|
|
the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. B |
|
funiculus after decussation of lemniscus [bul- |
|
|
4 |
Cuneate fasciculus. Fasciculus cuneatus. |
|
bothalamic tract]. D |
||
|
22 |
Tectospinal tract. Tractus tectospinalis. Decus- |
||||
6 |
|
|
Lateral part of posterior funiculus coming from |
|||
|
|
|
the upper half of the body. A |
|
sated connection between the quadrigeminal |
|
|
|
5 Cuneate tubercle. Tuberculum cuneatum. Ob- |
|
plate and the spinal cord. It lies between the fa- |
||
7 |
|
|
cial and trigeminal nuclei. D |
|||
|
|
long prominence at the end of the cuneate |
|
|||
|
|
|
23 |
Medial longitudinal fasciculus. Fasciculus |
||
|
|
|
fasciculus produced by the nucleus cuneatus. A |
|||
8 |
6 |
Fasciculus gracilis. Medial part of posterior |
|
longitudinalis medialis. Nerve fiber bundle for |
||
|
reciprocal connection to the motor nuclei of |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
funiculus coming from the lower half of the |
|
ocular muscles, as well as vestibular, accessory |
|
9 |
|
|
body. A |
|
and cervical muscle nuclei. C |
|
7Gracile tubercle (clava). Tuberculum gracile. 24 Posterior longitudinal fasciculus. Fasciculus
10 |
|
|
Oblong bulge over the nucleus gracilis. A |
|
longitudinalis posterior [[Schütz]]. Connection |
||
|
8 |
Posterior |
median sulcus. Sulcus |
medianus |
|
between the hypothalamus, III, VII, XII cranial |
|
|
|
nerve nuclei, nucleus ambiguus, tractus solitar- |
|||||
11 |
|
|
posterior. Posterior furrow continued from the |
|
|||
|
|
|
ius and tractus salvatorius in the floor of the |
||||
|
|
spinal cord and closed above by a medullary |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
rhomboid fossa. C |
|||
|
|
|
lamella (obex). A |
|
|
||
12 |
|
|
|
25 |
Spinal tract of trigeminal nerve. Tractus spi- |
||
9 |
Sections through the medulla oblongata. Sec- |
||||||
|
|
|
tiones medullae oblongatae. |
|
|
nalis nervi trigeminalis. Descending fibers of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
13 |
|
|
|
|
the trigeminal nerve for transmission of pain |
||
10 |
Pyramidal fasciculus (tract). Fasciculus py- |
|
|||||
|
and temperature stimuli. C D |
||||||
|
|
|
ramidalis. Nerve tract for the transmission of |
26 Spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve. Nucleus |
|||
14 |
|
|
impulses concerned with conscious move- |
||||
|
|
|
spinalis nervi trigeminalis. Continuous with the |
||||
|
|
|
ments. C D |
|
|
|
substantia gelatinosa in the spinal cord; this nu- |
|
11 |
Corticospinal fibers. Fibrae corticospinales. |
|
||||
15 |
|
cleus receives the fibers of the spinal tract of the |
|||||
|
|
Fibers from the precentral gyrus of the cortex to |
|
trigeminal nerve. C D |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord. |
27 |
Reticular formation (substance). Formatio |
||
16 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
12 |
Corticonuclear fibers. Fibrae corticonu- |
|
(substantia) reticularis. Cells lying scattered in |
||||
|
|
|
cleares. Fibers from the precentral gyrus of the |
|
the tegmentum in the vicinity of the vagus, ves- |
||
17 |
|
|
cortex to the motor nuclei of cranial nerves. |
|
tibular and facial nuclei with a regulatory effect |
||
|
|
13 |
Decussation of the pyramids. Decussatio py- |
|
on the muscles of the pharyngeal arch and other |
||
|
|
|
muscles of the body. It extends cranially and |
||||
|
|
|
|||||
18 |
|
|
ramidum (dec. motoria). Fibers of the lateral py- |
|
|||
|
|
|
caudally. C |
||||
|
|
|
ramidal tract with 3−5 bundles crossing at the |
28 |
Inferior olivary nucleus. Nucleus olivaris infe- |
||
19 |
|
|
end of the medulla oblongata. B |
|
|||
|
14 |
Fasciculus |
gracilis. Medial part of |
posterior |
|
rior. Main olviary nucleus lying below the olive. |
|
|
|
|
It is shaped like a thick-walled pouch that opens |
||||
|
|
|
funiculus coming from the lower half of the |
|
|||
20 |
|
|
|
medially and is connected with the spinal cord |
|||
|
|
body. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
and cerebullum. C |
||
|
|
15 |
Nucleus gracilis. Nucleus of fasciculus gracilis |
29 |
Amiculum of the olive. Amiculum olivare. |
||
21 |
|
|
medial to cuneate nucleus. D |
|
|
Fibrous sheath that surrounds and contains af- |
|
|
|
16 |
Cuneate |
fasciculus. Fasciculus |
cuneatus. |
|
ferent and efferent fibers of the olivary nucleus. C |
22 |
|
|
Lateral part of posterior funiculus coming from |
30 |
Hilum of inferior olivary nucleus. Hilum nu- |
||
|
|
|
the upper half of the body. |
|
|
clei olivaris inferioris. Opening of the medially |
|
23 |
|
17 |
Cuneate nucleus. Nucleus cuneatus. Nucleus of |
|
oriented pouch-like olivary nucleus. C |
||
|
|
Medial accessory olivary nucleus. Nucleus |
|||||
|
|
|
fasciculus cuneatus lateral to the nucleus 31 |
||||
24 |
|
|
gracilis. D |
|
|
|
olivaris accessorius medialis. It is located in front |
|
18 |
Accessory cuneate nucleus. Nucleus cuneatus |
|
of the hilum of the olivary nucleus. C |
|||
|
|
|
accessorius. Gray matter lateral to the upper |
32 |
Posterior accessory olivary nucleus. Nucleus |
||
25 |
|
|
part of cuneate nucleus. Origin of external ar- |
|
olivaris accessorius posterior. It is situated be- |
||
|
|
|
cuate fibers which pass to the cerebellum. D |
|
tween the olive and reticular formation. C |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 281
2
7 5
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
A Rhomboid fossa
3
13
B Pons and medulla oblongata
26 |
20 |
24 |
23 |
|
27 |
|
|||||||
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29
10
C Section through medulla oblongata
18 17 15
25
26 
21 
 20
20
22
10
D Section through medulla oblongata
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
282 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Olivospinal tract. Tractus olivospinalis. Ex- |
16 |
Cochlear nuclei. Nuclei cochleares. Mass of |
||||
1 |
|
1 |
|||||||
|
|
|
trapyramidal tract limited to the cervical cord. |
|
nerve cells situated below the lateral recess of |
||||
|
|
|
|
It influences head and hand movements. D |
|
the 4th ventricle, where it may form a slight |
|||
2 |
|
2 |
Spino-olivary tract. Tractus spino-olivaris. |
|
elevation, the tuberculum acusticum. A |
||||
|
|
|
|
Tract that extends throughout the entire spinal |
17 |
Anterior cochlear nucleus. Nucleus cochlearis |
|||
3 |
|
|
|
cord and provides information for the olive, |
|
anterior. Its fibers pass to the opposite side pri- |
|||
|
|
|
partly for its own needs, partly for those of the |
|
marily via the trapezoid body and join the |
||||
4 |
|
|
|
cerebellum. D |
|
lateral lemniscus. A |
|
|
|
|
3 |
Olivocerebellar tract. Tractus olivocerebellaris. |
18 |
Posterior |
cochlear |
nucleus. |
Nucleus |
||
|
|
|
|
It passes through the inferior cerebellar |
|
cochlearis posterior. Its fibers pass mostly to |
|||
5 |
|
|
|
peduncle from the olive to the cerebellum. B |
|
the midline just beneath the floor of the rhom- |
|||
|
|
4 Inferior cerebellar peduncle. Pedunculus cere- |
|
boid fossa, where they penetrate deeply in |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
6 |
|
|
|
bellaris inferior. Inferior connection to the cere- |
|
order to join the trapezoid body. A |
|
||
|
|
|
bellum without a sharply defined boundary |
19 |
Commissural nucleus. Nucleus commissuralis. |
||||
|
|
|
|
from the middle cerebellar peduncle. It con- |
|
Little-known nucleus in the medulla oblongata. |
|||
7 |
|
|
|
tains fibers primarily from the spinocerebellar |
20 |
Nucleus |
ambiguus. |
Nucleus of |
origin for |
|
|
|
tract and olive. A B |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
cranial nerves IX and X as well as the cranial |
||||
|
|
5 |
Nucleus of hypoglossal nerve (hypoglossal |
|
|||||
8 |
|
|
portion of XI. It is located behind the olive. C D |
||||||
|
|
|
nucleus). Nucleus nerve hypoglossi (nucleus |
21 Inferior salivary nucleus. Nucleus salivarius in- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
hypoglossalis). It is located below the floor of |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
ferior. Autonomic nucleus for the parasympa- |
||||
9 |
|
|
|
the lower rhomboid fossa. C D |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
thetic fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve. A C |
|||||
|
|
6 Posterior paramedian nucleus. Nucleus para- |
|
||||||
|
|
|
22 Arcuate nucleus. Nucleus arcuati. Located in |
||||||
|
|
|
|
medianus posterior. Cell group in the vicinity of |
|||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
front of and medial to the pyramidal tract. This |
||||
|
|
|
the hypoglossal nucleus that communicate |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
group of nuclear cells gives origin to the exter- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
with the reticular formation. |
|
||||
11 |
|
7 |
|
nal arcuate fibers. It corresponds to caudally |
|||||
|
Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve (dorsal vagal |
|
|||||||
|
|
displaced pontine nuclei. B |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
nucleus). Nucleus dorsalis nervi vagi (nucleus |
23 Anterior external arcuate fibers. Fibrae ar- |
||||
|
|
|
|
vagalis dorsalis). Autonomic and sensory cell |
|||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
cuatae externae anteriores. Fibers from the ar- |
||||
|
|
|
group located lateral and caudal to the hypo- |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
cuate nucleus which |
pass externally around |
||||
|
|
|
|
glossal nucleus. C D |
|
||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
and transversely across the olive into the cere- |
||||
|
8 |
Nucleus intercalatus. Nuclear group of un- |
|
||||||
|
|
bellar peduncles. C |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
known function situated between the nucleus |
24 Posterior external arcuate fibers. Fibrae ar- |
||||
14 |
|
|
|
of the hypoglossal nerve and the dorsal nucleus |
|||||
|
|
|
|
cuatae externae posteriores. Fibers which pass |
|||||
|
|
|
of the vagus. C |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
uncrossed from the lateral part of the arcuate |
||||
|
|
|
9 Tractus solitarius. Taste fibers of cranial nerves |
|
|||||
15 |
|
|
|
nucleus to the inferior cerebellar peduncle. |
|||||
|
|
|
V, VII, IX and X for the nucleus of the tractus |
|
They replace the posterior spinocerebellar tract |
||||
|
|
|
|
solitarius. C |
|
for the region above C8. The thoracic nucleus is |
|||
16 |
|
10 |
Nucleus solitarius. Row of cells for the tractus |
|
absent here. D |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
solitarius extending from the middle of the |
25 |
Raphe of medulla oblongata. Raphe medullae |
|||
|
|
|
|
rhomboid fossa to the decussation of the py- |
|||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
oblongatae. Median line in the decussation of |
||||
|
|
|
ramids. C |
|
the lemniscus. C |
|
|
||
|
|
11 Nucleus parasolitarius. Dispersed cells ven- |
26 |
Nuclei raphae. Cells of the reticular structure |
|||||
|
|||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
trolateral to the nucleus solitarius with no |
|||||
|
|
|
|
located near the median plane. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
known function. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
12 |
Vestibular nuclei. Nuclei vestibulares. Four ter- |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
minal nuclei of the vestibular division. They |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
have projections to the spinal cord, cerebellum |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and medial longitudinal fasciculus. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
Inferior vestibular nucleus. Nucleus vestibu- |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
21laris inferior. Oblong nuclear group lying laterally beneath the medial nucleus with projections to the cerebellum and medial longitudi-
22nal fasciculus. A
14 Medial vestibular nucleus. Nucleus vestibular
23medialis. Group of nuclei lateral to the limiting sulcus with fibers of origin for the medial longitudinal fasciculus of both sides. A
2415 Lateral vestibular nucleus. Nucleus vestibularis lateralis. Smaller group of nuclei located
25toward the lateral recess with projections to the anterior horn of the spinal cord. A
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 283
|
21 |
|
4 |
|
|
286.12 |
|
||
4 |
14 |
12 |
|
|
15 |
3 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
13 |
|
|
17 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclei of thombencephalon |
B Section through medulla oblongata |
||||||
A |
|||||||||
|
|
from behind |
10 |
7 |
8 |
5 |
|||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
25 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
280.26 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 
C Section through medulla oblongata
24 |
7 |
||
|
5 |
||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 |
2 |
|
|
D Section through medulla oblongata
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
284 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
METENCEPHALON. Part of the rhomben19 |
Medial |
longitudinal |
fasciculus. |
Fasciculus |
|||||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
cephalon consisting of the pons, cerebellum |
|
longitudinalis medialis. Tract that connects the |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
and tegmentum. |
|
|
nuclei of the ocular and neck muscles on one |
|||||
2 |
|
2 |
PONS. Located between the interpeduncular |
|
side and the vestibular organ on the other. C |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
fossa and pyramids. It consists mostly of cross- |
20 |
Posterior longitudinal |
fasciculus. Fasciculus |
|||||
3 |
|
|
|
ing fibers and cells of the cerebral, pontine and |
|
longitudinalis |
posterior [[Schütz]]. Reciprocal |
|||||
|
|
|
cerebellar tracts. A B |
|
|
connections between the hypothalamus and |
||||||
|
|
3 |
Bulbopontine (pontobulbar) |
sulcus. Sulcus |
|
the nuclei of cranial nerves III, V, VII, X; XII, the |
||||||
4 |
|
|
nucleus ambiguus, and the tractus solitarius |
|||||||||
|
|
|
bulbopontines. Limiting furrow between the |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
inferior margins of the medulla oblongata and |
|
and salivatorius in the mesencephalic central |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
gray region. C |
|
|
|||||
5 |
|
|
|
pons. Site of exit of cranial nerves VI, VII and |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
21 |
Medial lemniscus. Lemniscus medialis. De- |
||||||||
|
|
|
VIII. A |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
4 Basilar sulcus of pons. Sulcus basilaris. Median |
|
cusssating connection between the nuclei of |
|||||||
6 |
|
|
|
the posterior funiculus and the thalamus lo- |
||||||||
|
|
|
groove produced by the pyramidal tract fibers |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
situated to the right and left of the midline. It is |
|
cated mainly medially but also laterally. C |
||||||
|
|
|
|
22 Tectospinal (spinotectal) tract. Tractus tec- |
||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
occupied by the basilar artery. A C |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
tospinalis. It begins in the superior colliculus, |
||||||||
|
|
|
5 Middle (pontine) cerebellar peduncle. Pedun- |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
crosses the opposite side and then lies ventral |
||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
culus cerebellaris medius (pontinus). Thick |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
to the medial longitudinal fasciculus. It is con- |
||||||||
|
|
|
middle peduncle containing the pontocerebel- |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
cerned with optic reflexes. C |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
lar tract. A |
|
|
|
|||||
9 |
|
|
|
|
23 |
Reticular formation. Formatio reticularis. Lo- |
||||||
|
6 |
Pontocerebellar trigone. Trigonum pontocere- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
bellare. Clinically important angle between the |
|
cated in the posterior part of the pons; this long |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
group of cells is permeated by nerve fibers and |
|||||||
10 |
|
|
|
pons, medulla oblongata and cerebellum. A |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
continues anterosuperiorly and caudally. It is |
||||||||
|
|
7 SECTIONS OF PONS. Senctiones pontis. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
concerned with the integration of visceral and |
||||||||
11 |
|
8 |
Anterior (balisar) part of pons. Pars anterior |
|
muscular functions. C |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
(balisaris) pontis. Portion of pons consisting |
24 |
Spinal lemniscus. Lemniscus spinalis. Cranial |
||||||
12 |
|
|
|
mainly of fibers of the cerebropontocerebellar |
|
continuation of the lateral and anterior |
||||||
|
|
|
tract. C |
|
|
spinothalamic tracts. C |
|
|
||||
|
|
9 |
Longitudinal pontine fibers. Fibrae pontis |
25 |
Spinal tract of trigeminal nerve. Tractus spi- |
|||||||
13 |
|
|
|
longitudinales. Longitudinally |
coursing tracts |
|
nalis nervi trigeminalis. Trigeminal fibers de- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
of fibers described below. |
|
|
scending as far as C4 to join the nucleus of the |
|||||
14 |
|
10 |
Corticospinal fibers. Fibrae |
corticospinales. |
26 |
spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. B |
||||||
|
|
|
Part of the pyramidal tract passing into the spi- |
Spinal (inferior) nucleus of trigeminal nerve. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
nal cord. C |
|
|
Nucleus spinalis (inferior) nervi trigeminalis. |
|||||
|
11 |
Corticonuclear (corticobulbar) fibers. Fibrae |
|
Nucleus belonging to the spinal tract of the |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
corticonucleares. Fibers of the pyramidal tract |
|
trigeminal nerve. B |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
27 |
Pontine nucleus of trigeminal nerve. Nucleus |
|||||||
16 |
|
|
|
passing to the motor nuclei of cranial nerves. C |
||||||||
|
|
12 |
Corticoreticular fibers. Fibrae corticoreticu- |
|
pontinus nervi trigeminalis. Main nucleus of |
|||||||
|
|
|
trigeminal serving primarily for the sense of |
|||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
lares. Fibers passing from the cerebral cortex to |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
touch. B |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
the reticular formation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
Trigeminal |
lemniscus |
(trigeminothalamic |
||||
|
13 |
Corticopontine fibers. Fibrae corticopontinae. |
||||||||||
18 |
|
tract). Lemniscus trigeminalis (tractus trige- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
Fibers extending to the pontine nuclei from the |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
frontal, occipital and temporal lobes. C |
|
minothalamicus). Crossed fibers of the trigemi- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
nal nucleus extending to the thalamus. C |
|||||||
19 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
14 |
Transverse pontine fibers. Fibrae pontis trans- |
|
||||||||||
29 Mesencephalic tract of trigeminal nerve. Trac- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
versae. Transversely coursing fibers of the cere- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
tus mesencephalicus nervi trigeminalis (trac- |
|||||||
20 |
|
|
|
bropontocerebellar tract. C |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
tus mesencephalicus trigeminalis). Trigeminal |
|||||||
15 |
Pontocerebellar fibers. Fibrae pontocerebel- |
|
||||||||||
|
fibers for the nucleus of the trigeminal nerve |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
lares. Fibers of the pontocerebellar tract pass- |
|
tract located lateral to the cerebral aqueduct |
||||||
21 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
ing from the pons to the cerebellum. C |
|
and in the lateral part of the arch to the 4th ven- |
|||||||
|
16 |
Pontine nuclei. Nuclei pontis. Intercalary cells |
|
tricle. B C |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
of the cerebropontocerebellar tract situated in |
30 |
Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
the ventral part of the pons. C |
|
|
Nucleus |
mesencephalicus nervi |
trigeminalis |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
23 |
17 |
Posterior part of pons (tegmentum of pons). |
|
[nucleus mesencephalicus trigeminalis]. Upper |
||||||||
|
sensory nucleus extending to the area below |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Pars posterior pontis (tegmentum pontis). Part |
|
|||||||
24 |
|
|
|
of pons situated between the 4th ventricle and |
|
the tectal lamina. B |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
the transverse pontine fibers. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
18 Pontine raphe. Raphe pontis. Fibers from the
25trigeminal nucleus forming the midline of the pons. C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 285
|
|
|
29;30 |
|
|
|
286.1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
25;26 |
|
|
||
|
3 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Metencephalon |
|
|
|
B |
Nuclei of rhombencephalon |
||||||||
20 |
29 |
|
medial view |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|||
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
16 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
14 4
C Cross-section through pons
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
286 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve. Nucleus |
|
16 |
Posterior nucleus of trapezoid body. Nucleus |
||||||||||
1 |
|
1 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
motorius nervi trigeminalis [nucleus motorius |
|
|
corporis trapezoidei posterior. It lies behind the |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
trigeminalis]. It is located near the exit of the |
|
|
anterior nucleus. D |
|
|
|||||||
2 |
|
|
|
trigeminal nerve. A B |
|
|
|
|
17 |
Lateral lemniscus. Lemniscus lateralis. Ascend- |
||||||
|
|
|
2 Nucleus of abducens nerve. Nucleus nervi ab- |
|
|
ing continuation of the trapezoid body. Part of |
||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
ducentis |
[nucleus |
abducens]. |
It |
is |
found |
|
|
the hearing pathway. D |
|
|
||
|
|
|
beneath the facial colliculus. A B |
|
|
|
|
18 Nucleus of lateral lemniscus. Nuclei lemnisci |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
3 Nucleus of facial nerve. Nucleus nervi facialis |
|
||||||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
lateralis. Ganglion |
cells interspersed |
in the |
|||||||||
|
|
|
[nucleus facialis]. This motor nucleus lies later- |
|
|
lateral lemniscus. |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
ally below the nucleus of the abducens. A B |
|
19 Fourth ventricle. Ventriculus quartus. Dilata- |
||||||||||
|
4 |
Genu of facial nerve. Genu nervi facialis. Arch |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
tion of the lumen of the embryonic neural tube |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
formed by fibers of facial nerve below the facial |
|
|
in the rhombencephalon. D |
|
|
|||||||
6 |
|
|
|
colliculus and above the nucleus of the abdu- |
|
20 |
Rhomboid fossa. Fossa rhomboidea. Floor of |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
cens. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4th ventricle. A C |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
5 |
Superior salivary |
(salivatory) |
nucleus. Nu- |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
21 |
Lateral |
recess. |
Recessus |
lateralis. |
Lateral |
|||||||||
|
|
|
cleus salivarius superior. Autonomic nucleus |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
corner |
of the 4th |
ventricle |
ending with the |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
for the |
parasympathetic fibers |
of |
the |
facial |
|
|
||||||
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
lateral aperture. C D |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
nerve. It supplies preganglionic fibers for the |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
22 |
Median sulcus. Sulcus medianus. Median fur- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia. A |
|
|||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
row passing through the rhomboid fossa. C |
||||
|
6 |
Lacrimal nucleus. Nucleus lacrimalis. Auton- |
|
23 |
Medial eminence. Eminentia medialis. Oblong |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
omic cells lying beside the superior salivary nu- |
|
|
elevation located between the median sulcus |
|||||||||
|
|
|
cleus for the control of lacrimal secretion. A B |
|
|
and the sulcus limitans. C |
|
|
||||||||
11 |
|
7 |
Superior olivary nucleus. Nucleus olivaris su- |
|
24 |
Facial colliculus. Colliculus facialis. Promi- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
perioris. It lies lateral to the trapezoid body, |
|
|
nence above the medullary striae produced by |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
contains fibers from the cochlear nuclei and in- |
|
|
the genu of the facial nerve and the nucleus of |
|||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
tegrates hearing via the olivocochlear tract. D |
|
|
the abducens nerve. C |
|
|
|||||||
|
8 |
Olivocochlear tract. Tractus olivocochlearis. |
|
25 |
Limiting sulcus. Sulcus limitans. Shallow fur- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
Tract from the superior olivary nucleus to the |
|
|
row situated lateral to the medial eminence. C |
|||||||||
|
|
|
hair cells of the ear. |
|
|
|
|
26 |
Vestibular area. Area vestibularis. Field above |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
9 Vestibular nuclei. Nuclei vestibulares. Four ter- |
|
||||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
the vestibular nuclei and lateral to the limiting |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
minal nuclei of the vestibular division with |
|
|
sulcus at the beginning of the lateral recess. C |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
projections to the spinal cord, cerebellum and |
|
27 |
Superior fovea. Fovea superior. Pit situated |
|||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
medial longitudinal fasciculus. A B |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lateral to the facial colliculus. C |
|
||||||||
|
|
10 Medial vestibular |
nucleus. Nucleus vestibu- |
|
28 |
Locus ceruleus. Locus caeruleus. Elongated |
||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
laris medialis. Nucleus of nerve cells that lies |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
group of bluish cells located in the lateral wall |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
lateral to the sulcus limitans and gives attach- |
|
|
of the 4th ventricle and under it. C |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
ment to the medial longitudinal fasciculus of |
|
|
|
|||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
29 |
Inferior fovea. Fovea inferior. Pit at the apex of |
||||||||||
|
|
|
both sides. A D |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
11 Lateral vestibular nucleus. Nucleus vestibu- |
|
|
the trigone of the vagus nerve. C |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
18 |
|
|
30 |
Medullary striae. Striae medullares. Strongly |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
laris lateralis. Smaller nucleus of nerve cells sit- |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
uated near the lateral recess with projections to |
|
|
myelinated transverse nerve bundles from the |
|||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
the anterior horn of the spinal cord. A D |
|
|
|
arcuate nucleus to the cerebellum. C |
|
|||||||
|
12 |
Superior vestibular nucleus. Nucleus vestibu- |
|
31 |
Trigone of hypoglossal nerve. Trigonum |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
laris superior. Nucleus located above the lateral |
|
|
nervi hypoglossi (t. hypoglossale). Triangular |
|||||||||
|
|
|
nucleus with projections to the medial longi- |
|
|
bulge over the nucleus of the hypoglossal nerve |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tudinal fasciculus and cerebellum. A D |
|
|
|
located between the median sulcus and the sul- |
||||||||
21 |
|
13 |
Cochlear nuclei. Nuclei cochleares. Dorsal and |
|
|
cus limitans. C |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
ventral terminal nuclei of the cochlear division |
|
32 |
Funiculus separans. Transparent strip of |
|||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
of the vestibulocochlear nerve. Both lie below |
|
|
ependyma between the trigone of the vagus |
|||||||||
|
|
|
the lateral recess. A D |
|
|
|
|
|
nerve and the area postrema. C |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
23 |
|
14 |
Trapezoid body. Corpus trapezoideum. Mass of |
|
33 |
Trigone of vagus nerve. Trigonum nervi vagi |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
fibers arising from the cochlear nuclei that |
|
|
(t. vagale). Triangle over the dorsal nucleus of |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
forms part of the auditoy pathway. D |
|
|
|
the vagus nerve caudal to the trigone of hypo- |
||||||||
24 |
|
15 |
Anterior nucleus of trapezoid body. Nucleus |
|
|
glossal nerve. C |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
corporis trapezoidei anterior. Smaller nucleus |
|
34 |
Area postrema. A triangular field caudal to the |
|||||||||
25 |
|
|
|
situated posterolaterally in the trapezoid body. |
|
|
trigone of the vagus with highly vascularized, |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
glia-rich tissue. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 287
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
5 |
3 |
10 |
3 |
9 |
|
||||
6 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
282.13 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Rhomboid fossa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclei of rhombencephalon |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
||||||||||||
|
25 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
medial view |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
||
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
30 |
|
|
13 |
|
7 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
||||||||
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
C Rhomboid fossa D Cross section through rhomboid fossa 23 at level of lateral recess
24
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

288 Brain
1 |
1 Tegmen of fourth ventricle. Tegmen ventriculi |
quarti. Roof of 4th ventricle. A |
2 Superior medullary velum. Velum medullare
2superius. Lamina of white matter spread out be-
|
tween the right and left superior cerebellar |
3 |
peduncles. It is fused with the lingula of the cere- |
bellum. A |
3 Frenulum of superior medullary velum. Frenulum
4 |
|
veli medullaris superioris. Band-like ridge from |
|
|
|
the superior medullary velum to the tectal |
|
5 |
|
lamina. A |
|
4 |
Inferior medullary velum. Velum medullare in- |
||
|
|||
|
|
ferius. Plate of white matter in the upper part of |
|
6 |
|
||
|
the lower roof of the rhomboid fossa. It is fused |
||
|
|
with the peduncle of the flocculus and the |
|
|
|
||
|
|
nodulus of the cerebellum. A |
|
7 |
5 |
||
Tela choroidea of fourth ventricle [ventriculi |
|||
|
quarti]. Clear pia mater carrying the choroid
8plexus and stretched between the inferior medullary velum and tenia of the fourth ventricle. A
96 Choroid plexus of fourth ventricle. Plexus choroideus [ventriculi quarti]. Paired, garland-
10like ependyma-covered, highly vascularized tufted projection which extends into the two lateral apertures. A
117 Tenia of fourth ventricle. Taenia [ventriculi
|
quarti]. Ridge on lower portion of roof of rhom- |
12 |
boid fossa. A |
8Obex. Small bridge at lower end of rhomboid
13 |
fossa. A |
|
9Median aperture of fourth ventricle [foramen
of Magendie]. Apertura mediana [ventriculi
14quarti] [Magendie]. Unpaired opening directly above the obex for passage of cerebrospinal fluid.
15A
10 Lateral aperture of fourth ventricle [foramen of Luschka]. Apertura lateralis [ventriculi quarti]
16[[Luschkae]]. Opening for passage of cerebrospinal fluid located at the end of the right and left
17lateral recesses. A
11CEREBELLUM. It is located above the rhomboid fossa.
1812 Folia of cerebellum. Folia cerebelli. Delicate cerebellar convolutions (gyri) separated by fissures.
19B
13Cerebellar fissure. Fissura cerebelli. Deeply branched furrow located between two cerebellar
20 |
folia. B |
|
14 Vallecula. Deep median groove located inferiorly
21between the right and left halves of the cerebellum. It lodges the medulla oblongata. C
2215 Body of cerebellum. Corpus cerebelli. Entire
cerebellum except for the flocculonodular lobe.
16 Vermis of cerebellum. Vermis cerebelli. Phylo-
23 genetically older, unpaired segment of the cerebellum. B
24 17 Cerebellar hemisphere. Hemisphaerium cerebelli. Either of the two halves of the cerebellum. C
2518 Anterior lobe of cerebellum. Lobus anterior cerebelli. Region cranial to primary fissure. B D
19Lingula. Unpaired part of vermis fused with the superior medullary velum. It belongs to the archeocerebellum. C D
20Central lobule. Lobulus centralis. It lies over the lingula and is continuous on both sides with the ala of the central lobule. C D
21Culmen. Segment of vermis between the central lobule and primary fissure. B C D
22Ala of central lobule. Ala lobuli centralis. Lateral extension of central lobule for connection with the cerebellar hemispheres. B C D
23Quadrangular lobule. Lobulus quadrangularis (pars anterior). Part attaching laterally to the declive. B C D
24Primary fissure. Fissura prima. Identation between the quadrangular and simplex lobules. B D
25Posterior lobe of cerebellum. Lobus posterior cerebelli. Region located between the primary and dorsolateral fissures. D
26Declive. Part of vermis declining posteriorly from the culmen. B D
27Folium of vermis. Narrow midline connection between the left and right superior semilunar lobules. B D
28Tuber of vermis. Median connection between the right and left inferior semilunar lobules. B C D
29Pyramid of vermis. Pyramis vermis. Segment situated between the right and left biventral lobules. C D
30Secondary (postpyramidal) fissure. Fissura secunda. Fissure between the pyramid and uvula of the vermis. C D
31Uvula vermis. Part of the vermis lying between the cerebellar tonsils. C D
32Lobulus simplex (lobulus quadrangularis) (pars inferoposterior). Portion located between the quadrangular and superior semilunar lobules. B C D
33Superior semilunar lobule. Lobulus semilunaris superior. Part situated between the inferior semilunar lobule and lobulus simplex. B C D
34Horizontal fissure. Fissura horizontalis. Deep groove between the superior and caudal semilunar lobules. B C D
35Inferior semilunar lobule. Lobulus semilunaris inferior. Part of the cerebellum located between the superior semilunar and biventral lobules. B C D
36Gracile (paramedian lobule). Lobulus gracilis (l. paramedianus). It is located between the caudal semilunar and biventral lobules. D
37Biventral lobule. Lobulus biventer. It lies between the paramedian lobule and cerebellar tonsil. C D
38Tonsil of cerebellum. Tonsilla cerebelli. Small bean-shaped portion of the hemisphere lateral to the uvula. C D
39Posterolateral fissure. Fissura posterolateralis. Furrow separating the nodulus and flocculus on one side and the cerebellar tonsil and biventral lobe on the other. C D
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 289
1
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
22 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
||
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
24 |
18 |
26 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
A Roof of rhomboid fossa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
34 |
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cerebellum from above |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
||||||
17 |
20 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
19 |
22 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
31 |
|
35 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
29 38 |
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
||||
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
28 |
|
39 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
18 |
|
||||||
C |
Cerebellum from below |
|
23 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
21 |
|
24 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
27 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
28 |
25 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
29 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
39
D Cerebellum, schematic
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
2
3
4
5
6
7
32
8
339
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
34
21
22
23
24
25

|
290 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
1 Flocculonodular lobe. Lobus flocculonodularis. |
19 Hilum of dentate nucleus. Hilum nuclei dentati. |
||||||||
1 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Small archicerebellar portion of the cerebellum |
|
Opening of dentate nucleus from which |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
located caudal to the dorsolateral fissure. |
|
emerges most of the superior cerebellar |
||||||
2 |
|
2 |
Nodulus. Medial protuberance of the vermis |
|
peduncle. C |
|
||||||
|
20 |
Emboliform nucleus. Nucleus emboliformis. It |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
united with the flocculus by the peduncles. E |
||||||||
3 |
|
3 |
Flocculus. Claw-like portion of the cerebellum |
|
is found just in front of the hilum of the dentate |
|||||||
|
|
nucleus. C |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
between the inferior cerebellar peduncle and |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
21 |
Globose nucleus. Nucleus globosus. It lies me- |
|||||||
4 |
|
|
|
biventral lobule. E |
|
|
||||||
|
|
4 Peduncle of flocculus. Pedunculus floccularis. |
|
dial to the dentate nucleus. C |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
22 |
Fastigial nucleus. Nucleus fastigii. The most |
||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
Band of nerve fibers connecting the flocculus to |
||||||||
|
|
|
the nodulus. Part of it extends into the inferior |
|
medial of the deep cerebellar nuclei. C |
|||||||
6 |
|
|
|
medullary velum. E |
|
|
23 Cerebellar peduncles. Pedunculi cerebellares. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
5 |
Paraflocculus. In humans, a small insignificant |
|
Fibers that provide connections to and from the |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
part of the caudal lobe of the cerebellum that |
|
cerebellum. |
|
|||||
7 |
|
|
|
communicates with the flocculus. |
|
24 |
Inferior |
cerebellar peduncle |
(restiform |
|||
|
|
6 |
Archicerebellum. Archaeocerebellum. Phylo- |
|
body). Pedunculus cerebellaris inferior. Infe- |
|||||||
8 |
|
|
|
genetically the oldest part of the cerebellum; it |
|
rior connection to the cerebellum formed by |
||||||
|
|
|
|
fibers of the posterior spinocerebellar tract and |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
consists of the lingula and the flocculonodular |
|
|||||||
9 |
|
|
|
lobe. A |
|
|
|
|
olive. E F |
|
|
|
|
|
7 Paleocerebellum. An old part of the cerebel- |
25 Middle cerebellar peduncle (brachium pon- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
lum consisting of the central lobule, culmen, |
|
tis). Pedunculus cerebellaris medius (pon- |
||||||
10 |
|
|
|
pyramid, uvula, ala of the central lobule and |
|
tinus). Large peduncle containing fibers origi- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
quadrangular lobule. A |
|
|
|
nating from the pontocerebellar tract. E F |
||||
11 |
|
8 |
Neocerebellum. Phylogenetically young por- |
26 Superior |
cerebellar peduncle |
(brachium |
||||||
|
|
|
|
tion of the cerebellum; it comprises the declive, |
|
conjunctivum). Pedunculus cerebellaris su- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
perior. Superior, paired (right and left) connect- |
|||||||
12 |
|
|
|
folium, tuber, lobulus simplex, cranial and |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
ing fibers extending from the cerebellum to the |
||||||||
|
|
|
caudal semilunar lobules, paramedian lobule |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
and tonsil. A |
|
|
|
brain stem. The superior medullary velum ex- |
||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
tends between them. E F |
|
||||
|
9 |
CEREBELLAR SECTIONS. Sectiones cerebellares. |
|
|
||||||||
|
27 MIDBRAIN. Mesencephalon. It consists of cere- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Anatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum. |
||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
bral crura, tegmentum and quadrigeminal plate |
|||||||
|
10 |
Arbor vitae [cerebelli]. Treelike pattern of the |
|
|||||||||
|
|
(tectal lamina). |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
white matter seen in prepared sections of the |
28 Cerebral peduncle. Pedunculus cerebri (cere- |
|||||||
15 |
|
|
|
cerebellum. C |
|
|
|
bralis). It comprises the cerebral crura and the |
||||
|
11 |
Medullary body. Corpus medullare. White |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
tegmentum and extends up to cerebral aque- |
|||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
matter consisting of myelinated fibers. C |
|
duct. D |
|
|
||||
|
12 |
White laminae. Laminae albae. White matter |
29 Anterior part (cerebral crus, basis pedunculi). |
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
extending |
into the folia |
from the |
medullary |
|
Part anterior (crus cerebri). It consists of the |
|||
|
|
|
body. C |
|
|
|
|
previously mentioned cerebral crura. D |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
13 Cerebellar cortex. Cortex cerebellaris. Superfi- |
30 |
Part posterior. Posterior part of cerebral |
||||||||
18 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
cial gray matter of the cerebellum, about 1 mm |
|
peduncle or tegmentum. See p. 292.10 D |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
thick, that consists pirmarily of nerve cells. B C |
31 Oculomotor sulcus. Sulcus oculomotorius. Fur- |
|||||||
19 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
14 |
Molecular |
(plexiform) |
layer. |
Stratum |
|
row on the medial surface of the cerebral crus, |
||||||
|
|
|
|
moleculare (plexiforme). External cortical layer |
|
exit site of the oculomotor nerve. D |
||||||
20 |
|
|
|
rich in dendrites and axons, poor in cell bodies. |
32 |
Interpeduncular fossa. Fossa interpeduncu- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
The nuclei of the Purkinje cells are found at its |
|
laris. Fossa situated between the cerebral crura. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
border with the granular layer. |
|
|
||||||
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
15 |
Purkinje cell layer. Stratum neurium piri- |
33 |
Interpeduncular (posterior) perforated sub- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
formium. The layer in which the perikarya of |
|
stance. Substantia perforata interpeduncularis |
||||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
the Purkinje cells are located. B |
|
|
[posterior]. Perforated floor of interpeduncular |
||||||
|
16 |
Stratum granulosum. Internal nuclear layer |
|
fossa produced by openings for numerous ves- |
||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
containing numerous closely packed small |
|
sels. D |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
neurons. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2417 Nuclei of cerebellum. Nuclei cerebellaris.
18 Dentate nucleus. Nucleus dentatus. Large
25cerebellar nucleus located in the medullary body and resembling a folded pouch. C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 291
 6
6
7
8
7
6
A Cerebellum, schematic
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
20 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||




 19
19



 18
18
14
 15 13
15 13
16
B Layers of cerebellar cortex
30
28
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
29 |
32 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
||||
D Section through midbrain
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
10
10
C Horizontal section through cerebellum
26
25
24
26
25
2
24
3
E Cerebellum from below |
4 |
F Cerebellar peduncles |
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
292 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Basis pedunculi cerebri. Synonymous with |
|
18 |
Trigone of lemniscus. Trigonum lemnisci. Tri- |
||||||||||
1 |
|
1 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
anterior part of cerebral peduncle, the cerebral |
|
|
angular field located laterally between the tec- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
crus. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
tal lamina, superior cerebellar peduncle and |
|||||
2 |
|
2 |
Corticospinal |
fibers. Fibrae corticospinales. |
|
19 |
cerebral crus. A |
|
|
Pedunculus |
||||||
|
|
|
|
Fibers of the pyramidal tract leading into the |
|
Superior |
cerebellar |
peduncle. |
||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
spinal cord. B C |
|
|
|
|
cerebellaris superior. It transmits fibers mainly |
|||||||
|
3 |
Corticonuclear |
(corticobulbar) |
fibers. Fibrae |
|
|
from the dentate nucleus to the red nucleus |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
and thalamus. A |
|
|
|
|||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
corticonucleares. Pyramidal tract fibers for the |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
Mesencephalic (cerebral) aqueduct. Aquae- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
cranial nerve nuclei. B C |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
4 Corticopontine fibers. Fibrae corticopontinae. |
|
|
ductus mesencephali (cerebri). Narrow canal in |
||||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
|
the midbrain between the 3rd and 4th ventricle. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Fibers of the cerebropontocerebellar tract. |
|
|
B C D |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
5 |
Parietotemporopontine fibers. Fibrae parie- |
|
21 |
Sections through the mesencephalon. Sec- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
totemporopontinae. Fibers of the cerebropon- |
|
|
tiones mesencephalici. B C D |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
tine tract which originate from the parietal and |
|
22 |
Reticular |
formation |
(substance). Formatio |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
temporal lobes. They lie in the lateral part of |
|
|||||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
(substantia) reticularis. Mesencephalic portion |
||||||||||
|
|
|
the cerebral crus. B C |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of reticular formation extending up from the |
||||||||
|
|
6 |
Frontopontine |
fibers. Fibrae frontopontinae. |
|
|
||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
spinal cord. It lies around the cerebral aque- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
Fibers of the cerebropontine tract which arise |
|
|
duct, and its scattered ganglion cells function in |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
from the frontal lobes and occupy the medial |
|
|
the integration of muscular activities. B C D |
|||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
sixth of the cerebral crus. B C |
|
|
23 |
Corticoreticular fibers. Fibrae corticoreticu- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
7 Substantia nigra. Black nucleus lying on the |
|
|
lares. Nerve fibers extending from the cerebral |
||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
cerebral crus. Its name is derived from its con- |
|
|
motor cortex to the ganglion cells of the reticu- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
tent of numerous pigmented ganglion cells |
|
|
lar formation. |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
rendering it visible with the naked eye. B C |
|
24 |
Medial |
longitudinal |
|
fasciculus. |
Fasciculus |
|||||
|
8 |
Compact part. Pars compacta. Dense part of |
|
|
longitudinalis medialis. Fiber bundle with con- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
substantia nigra containing pigmented cells. |
|
|
nections to the ocular muscles, neck muscles |
|||||||||
12 |
|
9 |
Pars reticularis. Reticular (fibrous) part of sub- |
|
|
and vestibular nuclei for coordination of move- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
ments of the eyeball and head. B C D |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
stantia |
nigra. It contains |
disaggregated pig- |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
Posterior longitudinal |
fasciculus. Fasciculus |
|||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
mented fibers facing the cerebral crus. Its cells |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
longitudinalis posterior [[Schütz]]. Descending |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
are irregularly dispersed between the fibers of |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
and ascending fibers with projections to the |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
the cerebral crus. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
14 |
|
10 |
|
Tegmentum |
|
|
hypothalamus and cranial nerve nuclei III, V, |
|||||||||
|
Mesencephalic |
tegmentum. |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
VII, X, XII, as well as the nucleus ambiguus and |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
mesencephalicum. It extends from the sub- |
|
|
the tractus solitarius and salivatorius. D |
|||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
stantia nigra to an imaginary plane drawn |
|
26 |
Mesencephalic tract of trigeminal nerve. Trac- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
through the cerebral aqueduct. B C |
|
|
tus |
mesencephalicus |
nervi trigeminalis. |
|||||||
|
|
11 Central |
gray |
matter. |
Substantia grisea |
|
|
|||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
Trigeminal fibers to the nucleus of the tract of |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
centralis. Gray matter around the cerebral |
|
|
the trigeminal nerve located lateral to the cere- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
aqueduct. B C |
|
|
|
|
|
bral aqueduct and the 4th ventricle. D |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
||||||||
12 |
Mesencephalic tectum. Tectum mesencephali- |
|
Nucleus of mesencephalic tract of the trigemi- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cum. Part of the mesencephalon located dorsal |
|
|
nal nerve. Nucleus tractus mesencephalici |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
to the previously mentioned transverse plane |
|
|
nervi trigeminalis (n. mesencephalica trigemi- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
through the cerebral aqueduct. B C |
|
|
nalis). Upper sensory trigeminal nucleus ex- |
|||||||||
19 |
|
13 |
Tectal lamina (quadrigeminal plate). Lamina |
|
|
tending to below the tectal lamina. D |
||||||||||
|
|
28 |
Nucleus of oculomotor nerve. Nucleus nervi |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tectalis [[quadrigemina]]. A |
|
|
|
|||||||||
20 |
|
14 |
Inferior colliculus. Colliculus inferior. Inferior |
|
|
oculomotorii (nucleus oculomotorius). It is |
||||||||||
|
|
|
found in front of the cerebral aqueduct. B |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
hillock of quadrigeminal plate connected to the |
|
29 |
Accessory nucleus of oculomotor nerve. Nu- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
auditory pathway. A |
|
|
|
|||||||||
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cleus |
oculomotorius |
accessorius |
(autonomi- |
|||||
|
15 |
Superior colliculus. Colliculus superior. Super- |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
cus). A parasymathetic portion of oculomotor |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ior hillock of quadrigeminal plate connected to |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
nucleus. 96% supplies the ciliary muscle, the |
||||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
the visual pathway. A |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rest supplies sphincter pupillae muscle. |
|||||||||
|
|
16 |
Brachium of inferior colliculus. Brachium col- |
|
30 |
Nucleus of trochlear nerve. Nucleus nervi |
||||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
liculi inferioris. Connecting arm between the |
|
|
trochlearis (nucleus trochlearis). It is located in |
|||||||||
|
|
|
inferior colliculus and the medial geniculate |
|
|
the central gray matter caudal to the nucleus of |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
24 |
|
|
|
body. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
the oculomotor nerve. C |
|
||||
|
17 |
Brachium of superior colliculus. Brachium col- |
|
31 |
Interpeduncular nucleus. Nucleus inter- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
liculi superioris. Connecting arm between the |
|
|
peduncularis. Located in the floor of the inter- |
|||||||||
25 |
|
|
|
superior colliculus and the lateral geniculate |
|
|
peduncular fossa and has projections to the ol- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
body. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
factory tract. C |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 293
|
12 |
|
|
28 |
|
20 |
10 |
11 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
122
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
B |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
D |
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
Section through superior colliculus |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
7 |
|
|
|
2 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section through inferior colliculus |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
||||||||||
|
|
|
Midbrain and rhomboid fossa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
20 |
25 27 26 |
|||||||||||||
22
24
D Section through level of exit of trochlear nerve
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
294 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Interstitial nucleus of Cajal. Nucleus inter- |
14 |
Lemniscus medialis. Decussating connection |
|||||||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
stitialis [[Cajal]]. Group of cells located lateral to |
|
between nuclei of posterior funiculus and |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
the nucleus of the oculomotor nerve, from |
|
thalamus. B C D |
|
|
|
|||
2 |
|
|
|
which it is separated by the medial longitudinal |
15 Spinal lemniscus. Lemniscus spinalis. Segment |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
fasciculus. It contains fibers from the vestibular |
|
of spinothalamic tract lodging in the midbrain |
||||||
|
|
|
|
nuclei, globus pallidus and stratum griseum of |
|
|||||||
3 |
|
|
|
|
adjacent to the medial lemniscus. D |
|
||||||
|
|
|
the superior colliculus. B |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
16 Trigeminal lemniscus. Lemniscus trigeminalis. |
|||||||||
|
|
2 |
Tegmental nuclei. Nuclei tegmenti (tegmen- |
|||||||||
4 |
|
|
Crossing fiber tract between the sensory nuclei |
|||||||||
|
|
|
tales). Nuclei in the reticular formation dorsal |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
of the trigeminal and the thalamus. It also lies |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
to the trochlear nucleus and ventral to the me- |
|
in the vicinity of the medial lemniscus. |
||||||
5 |
|
|
|
dial longitudinal fasciculus. C |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
17 Mesencephalic tectum. Tectum mesencephali- |
|||||||||
|
|
3 Red nucleus. Nucleus ruber. Iron-rich nucleus |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cum. Part of midbrain located dorsal to the |
||||||||
6 |
|
|
|
between the substantia nigra and central gray |
|
above-mentioned plane through the cerebral |
||||||
|
|
|
matter with tributaries from the cerebral cor- |
|
aqueduct. B C |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
tex and thalamus. It is inserted in the tract from |
18 |
Tectal lamina. |
Lamina |
tectalis |
[[quad- |
|||
7 |
|
|
|
the cerebellum to the spinal cord. B |
|
rigemina]]. Quadrigeminal plate. A |
|
|||||
|
4 |
Parvicellular part. Pars parvocellularis. Group |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
19 Nucleus of inferior colliculus. Nucleus colliculi |
||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
of small cells forming the larger part of the red |
|
inferioris. Nucleus connecting the |
auditory |
|||||
|
|
|
nucleus and part of the rubrospinal tract. |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
tract with the extrapyramidal system. C |
|||||||
|
|
5 |
Magnocellular |
part. |
Pars magnocellularis. |
|
||||||
9 |
|
20 Brachium of inferior colliculus. Brachium col- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
Group of large cells occupying the caudal part |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
liculi inferioris. Connecting arm between the |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
of the red nucleus; most of its fibers enter the |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
inferior colliculus and medial geniculate body. |
|||||||
10 |
|
|
|
rubrospinal tract. |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
6 |
Endopeduncular nucleus. Nucleus en- |
21 Commissure of |
inferior colliculus. Commis- |
|||||||
11 |
|
|
|
dopeduncularis. Cell group located medially in |
|
sura colliculorum inferiorum. Connection be- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
the cerebral crus directly after the site where it |
|
tween the right and left inferior colliculi which |
||||||
12 |
|
|
|
enters the base of the brain. It probably inserts |
|
also receives fibers from the lateral lemniscus |
||||||
|
|
|
in the tract between the globus pallidus and re- |
|
of the opposite side. C |
|
|
|||||
13 |
|
|
|
ticular formation. |
|
22 Gray and white layers of superior colliculus. |
||||||
|
7 |
Decussations |
of |
tegmentum. Decussationes |
||||||||
|
|
Strata [grisea et alba] colliculi superioris. Gray |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tegmenti (tegmentales). Crossing of the ru- |
|
matter and white matter surrounding the su- |
||||||
14 |
|
|
|
brospinal, rubroreticular and tectospinal tracts. |
|
perior colliculus. B |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
23 Brachium of superior colliculus. Brachium col- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
8 Decussation of superior cerebellar peduncle. |
|||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
liculi superioris. Connection between the su- |
||||||||
|
|
|
Decussatio pedunculorum cerebellarium su- |
|
perior colliculus and lateral geniculate body. A |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
periorum. Crossing of the superior cerebellar |
24 Commissure of superior colliculus. Commis- |
|||||||
16 |
|
|
|
peduncle below the inferior colliculus and |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
sura colliculorum superiorum. Connection be- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
anterior to the medial longitudinal fasciculus. C |
|
tween the right and left superior colliculi. B |
||||||
|
|
|
9 Dentatorubral fibers. Fibrae dentatorubrales. |
|
||||||||
17 |
|
|
25 |
Decussation of |
trochlear |
nerve. Decussatio |
||||||
|
|
|
Component of the superior cerebellar peduncle |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
trochlearis (d. nervorum trochlearium). Fibers |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
which passes into the red nucleus. |
|
|||||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
of trochlear nerve crossing in the white matter. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
10 Rubrospinal |
tract. |
Tractus rubrospinalis |
|
D |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
[[Monakow]]. From its origin in front of the |
26 Central tegmental tract. Tractus tegmentalis |
|||||||
19 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
lateral pyramidal tract, this extrapyramidal |
|
centralis. Tract passing to the olive, thought to |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
tract passes from the red nucleus to the ante- |
|
partially arise from the thalamus. B D |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
20 |
|
|
|
rior horn cells. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11Tectobulbar tract. Tractus tectobulbaris. It extends from the posterior tegmental decussa-
21tion to the opposite side, anterior to the medial longitudinal fasciculus and then passes to the
22pontine nuclei, especially to the nuclei of the ocular muscles.
23 |
12 |
Tectospinal tract. Tractus tectospinalis. Ini- |
|
|
tially courses similar to the tectobulbar tract, |
|
|
then descends in the anterior funiculus of the |
24 |
|
spinal cord. |
13 Lateral lemniscus. Lemniscus lateralis. Partly
25crossing portion of auditory tract passing to the inferior colliculus. C D
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 295
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
26 |
|||||
20 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
3 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|||||||
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
C |
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section through midbrain |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
21 |
||||||
17
13
14 
2
10
8
C Section through midbrain
A Brain stem, dorsal view |
25 |
|
13
26
15
14 
D Section through midbrain
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
296 |
Brain |
|
|
|
||
|
|
1 |
FOREBRAIN. Prosencephalon. Terminal portion |
19 Subcommissural organ. Organum subcommis- |
|||
1 |
|||||||
|
|
of neural tube situated anterior to the anterior |
surale. Group of specialized ependymal cells |
||||
|
|
|
margin of the mesencephalon. It comprises the |
below the posterior commissure. They produce |
|||
2 |
|
|
telencephalon and diencephalon. |
|
Reissner’s fiber. B |
||
2 |
DIENCEPHALON. The part of the prosencephalon |
20 Dorsal thalamus. Thalamus dorsalis. Portion of |
|||||
|
|||||||
|
thalamus located cranial to the hypothalamic sul- |
||||||
|
|
|
that extends from the anterior margin of the |
||||
3 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
anterior colliculus to the interventricular fora- |
cus. |
||||
|
|
|
men. |
|
|
21 Interthalamic adhesion (massa intermedia). Ad- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
3 |
Epithalamus. It consists mainly of the habenulae, |
hesio interthalamica. Inconstant (70−85%) con- |
||||
nection between right and left thalami. B |
|||||||
|
|
their accessories and the epiphysis. |
|
||||
|
4 |
Habenula. |
Dorsal continuation of |
the stria |
22 Anterior tubercle of thalamus. Tuberculum an- |
||
5 |
terius thalamicum. Small protuberance dorsal to |
||||||
|
|
medullaris of the thalamus. A B |
|
||||
|
|
|
the anterior end of the thalamus above the ante- |
||||
|
5 |
Habenular |
sulcus. Sulcus habenuale |
(habenu- |
rior nucleus of the thalamus. A |
||
6laris). Shallow furrow between the habenular 23 Internal/external medullary laminae. Laminae
|
|
|
trigone and the pulvinar. A |
|
|
|
medullares interna/externa. Layers of white mat- |
|||
7 |
|
6 Trigone of habenula. Trigonum habenulae (t. |
|
ter located partly lateral to the thalamus and |
||||||
|
|
habenulare). Triangular field between the stria |
|
partly in it. They incompletely separate the in- |
||||||
|
|
|
medullaris of the thalamus and the habenula. The |
|
dividual thalamic nuclei. E |
|
||||
8 |
|
|
habenular nuclei lie beneath it. A |
|
24 |
Medullary stria of thalamus. Stria medullaris |
||||
|
|
7 Commissure of habenula. Commissura habenu- |
|
thalamica. Bundle located at the medial side of |
||||||
|
|
|
larum (habenularis). Fibers of the habenulae |
|
the thalamus below the thalamic tenia. It con- |
|||||
9 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
crossing over the midline. The decussation lies |
|
tinues dorsally into the habenula and receives |
||||||
|
|
|
superior to the pineal recess. B |
|
|
fibers from the fornix of the stria terminalis and |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
10 |
|
8 Posterior (epithalamic) commissure. Commis- |
|
the precommissural septum. A B |
||||||
|
25 |
Pulvinar. Posterior part of thalamus projecting |
||||||||
|
|
sura epithalamica (posterior). Commissure lo- |
||||||||
|
|
|
cated between the pineal recess and entrance |
|
freely. A |
|
|
|||
11 |
|
|
26 |
Metathalamus. Appendage of thalamus below |
||||||
|
|
into the cerebral aqueduct; its fibers cross from a |
||||||||
|
|
|
nearby area. B |
|
|
|
the pulvinar. A C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 Medial geniculate body. Corpus geniculatum |
|||||
12 |
9 |
Pineal gland (body), epiphysis. Corpus pineale |
||||||||
|
mediale. United with the inferior colliculus, it |
|||||||||
|
|
|
(glandula pinealis). Topographically speaking, it |
|
forms a part of the auditory pathway. A C |
|||||
|
|
|
lies free on the quadrigeminal plate and is sus- |
|
||||||
13 |
|
|
28 Lateral geniculate body. Corpus geniculatum |
|||||||
|
|
pended from the habenula withouth a functional |
||||||||
|
|
|
laterale. Connects |
with the |
superior colliculus |
|||||
|
|
|
connection. A B C |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
and visual cortex; it is the termination of most of |
||||
|
|
10 Sections of epithalamus. Sectiones epithalamici. |
|
|||||||
14 |
|
|
the fibers of the optic tract. A C |
|||||||
11 |
Medial and lateral habenular nuclei. Nuclei |
|
||||||||
|
29 |
Ventral thalamus (subthalamus). Thalamus |
||||||||
|
|
|
habenulares medialis et lateralis. Cell groups |
|
ventralis (subthalamus). Part of the diencephalon |
|||||
15 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
contained in the reflex tract of the rhinen- |
|
situated basally with respect to the hypothalamic |
||||||
|
|
|
cephalon. D |
|
|
|
sulcus. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
16 |
12 |
Habenulointerpeduncular |
tract. |
Tractus |
30 |
Hypothalamus. Basal part of the diencephalon. B |
||||
|
|
|
habenulointerpeduncularis. Connection between |
31 |
Preoptic area. Area preoptica. Area behind the |
|||||
|
|
|
habenulae and interpeduncular nucleus. D |
|
lamina terminalis and in front of the paraventric- |
|||||
17 |
|
|
|
|||||||
13 |
Commissure of habenula. Commissura habenu- |
|
ular nucleus, partly also in front of the supra- |
|||||||
|
|
|
larum (habenularis). See p. 7 A B |
|
|
optic nucleus. Its nuclei are probably inserted be- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
|
14 |
Pretectal area. Area pretectalis. Region extend- |
|
tween the olfactory tract and tuber cinereum. B |
|||||
|
32 |
Optic chiasma. Chiasma opticum. Decussation of |
||||||||
|
|
|
ing from in front of the upper margin of superior |
|
medial optic nerve fibers between the optic tract |
|||||
|
|
|
colliculus as far as the |
commissure |
of the |
|
||||
19 |
|
|
|
and nerve. B C |
|
|
||||
|
|
epithalamus. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
33 Optic tract. Tractus opticus. Superficial part of |
||||||
|
|
15 |
Pretectal nuclei. Nuclei pretectales. From their |
|||||||
|
|
|
the visual pathway between the optic chiasma |
|||||||
20 |
|
|
origin dorsolateral to the |
commissure |
of the |
|
||||
|
|
|
and lateral geniculate body visible at the base of |
|||||||
|
|
epithalamus, they extend as far as the superior |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
the brain. C |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
colliculus. They receive fibers from the occipital |
34 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Lateral root. Radix lateralis. Fibers of optic tract |
|||||||
21 |
|
|
lobe and the area in front of it, as well as the optic |
|||||||
|
|
|
which end in the lateral geniculate body or su- |
|||||||
|
|
|
tract and send fibers to the accessory nucleus of |
|
perior colliculus. C |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
the oculomotor nerve for the sphincter pupillae |
35 |
|
|
||||
22 |
|
|
Medial root. Radix medialis. C |
|||||||
|
|
muscle. |
|
|
||||||
|
|
16 |
Posterior (epithalamic) commissure. Commis- |
36 |
Mamillary body. |
Corpus |
mamillare. Paired, |
|||
|
|
|
round elevation on the floor of the diencephalon |
|||||||
23 |
|
|
sura epithalamica (posterior). See p. 8 B |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
connected with the thalamus and midbrain. B |
||||||
|
|
17 |
Pineal gland (body). Corpus pineale (glandula |
37 |
Tuber cinereum. Gray matter in the posterior |
|||||
24 |
|
|
pinealis). See p. 9 A B C |
|
|
|
wall of the infundibulum. B |
|
||
|
18 |
Subfornical organ. Organum subfornicale. Organ |
38 |
Infundibulum. Funnel-shaped passage to the |
||||||
|
|
|
in the interventricular foramen between right |
|
posterior lobe of the hypophysis. B |
|||||
25 |
|
|
and left fornix. It influences blood pressure and |
39 |
Neurohypophysis. Posterior lobe of hypophysis |
|||||
|
|
|
water excretion. B |
|
|
|
suspended by the infundibulum. B |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brain |
297 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
2 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
7;13 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
9 |
25 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
27 |
28 |
32 |
|
8;16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
26 |
38 37 36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
9
A Brain stem, dorsal view B Brain stem, sagittal section 10
11
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
33 |
34 |
28 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
14 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|||||||||
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Termination of optic tract |
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
||||||||||
C |
|
D |
Oblique section through midbrain |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
23 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Section through |
24 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
diencephalon
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
|
298 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Third ventricle. |
Ventriculus |
tertius. |
Dien- |
|
16 |
Anteromedial |
nucleus. |
Nucleus anterome- |
|||||
1 |
|
1 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
cephalic portion of the cerebral ventricular sys- |
|
|
dialis. Degenerating nuclear remains situated |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tem. It extends from the lamina terminalis to |
|
|
medial and inferior to the anteroventral nu- |
|||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
the beginning of the cerebral aqueduct. A C |
|
|
cleus. B |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
2 |
Hypothalamic sulcus. Sulcus hypothalamicus. |
|
17 |
Median nuclei of thalamus. Nuclei mediani |
||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
Furrow extending from the interventricular |
|
|
[thalami]. Collective term for the nuclei located |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
medial and for the most part directly inferior to |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
foramen to the entrance into the cerebral aque- |
|
|
||||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
duct. It separates the dorsal and ventral |
|
|
the ependyma. |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
thalami. A |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
Anterior/posterior |
paraventricular |
nuclei. |
||||
|
|
3 |
Interventricular foramen. Foramen inter- |
|
|
Nuclei |
paraventriculares |
anteriores/posteri- |
||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
ores. Cell groups in the wall of the third ven- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
ventriculare. Opening between the lateral ven- |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tricle and third ventricle behind the genu of the |
|
|
tricle with neuronal function (among others, |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
vasopressin, angiotensin II, renin). C D E |
||||||||||
6 |
|
|
|
fornix. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
4 |
Optic recess. Recessus opticus. Recess of third |
|
19 |
Rhomboidal nucleus. Nucleus rhomboidalis. It |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
often forms the interthalamic adhesion. D |
|||||||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
ventricle above the optic chiasm. A |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
Nucleus reuniens. Nucleus extending from the |
||||||||||
|
5 |
Recess of infundibulum. Recessus infundibuli |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
anterior |
end of |
the |
anterior tubercle to the |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
(infundibularis). |
Recess |
of third ventricle |
|
|
||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
middle of the interthalamic adhesion. It may be |
||||||||||
|
|
|
within the infundibulum. A |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
6 Pineal recess. Recessus pinealis. Recess of third |
|
|
concerned with the formation of the latter |
||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
|
when present. It is absent in 28% of males and |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
ventricle extending partially into the epiphysis. |
|
|
14% of females. D |
|
|
|
|||||||
10 |
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
20 a |
Paratenial nucleus of thalamus. Nucleus |
|||||
|
7 |
Supraspinal recess. Recessus |
supraspinalis. |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
parataenialis [thalami]. Located between the |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Recess between the roof of the third ventricle |
|
|
stria medullaris, tenia, anterodorsal and para- |
|||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
and the epiphysis. A |
|
|
|
|
|
ventricular nuclei of the thalamus; it is prob- |
||||||
|
|
8 Tela choroidea. Forms the thin, narrow roof of |
|
|
ably involved in the processing of |
olfactory |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
stimuli. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12 |
|
|
|
third ventricle and its choroid plexus. B C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
21 |
Medial nuclei of thalamus. Nuclei mediales |
|||||||||||
|
9 |
Tenia of thalamus. Taenia thalami. Lateral at- |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
[thalami]. Mass of nuclei medial to the internal |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tachment line of the upper wall of the third |
|
|
||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
medullary lamina with projections |
to other |
|||||||||
|
|
|
ventricle along |
the stria |
medullaris |
of the |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
thalamic nuclei and to the frontal lobe. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
thalamus. B C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
Dorsal |
medial |
nucleus. Nucleus |
medialis |
|||
|
10 |
Choroid plexus. Plexus |
choroideus. |
Paired, |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
dorsalis. Principal nucleus of this group. C D |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
highly vascularized villous infolding which |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
Internal/external medullary lamina. Lamina |
||||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
hangs down from the thin roof of the third ven- |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
tricle and is continuous anteriorly with the |
|
|
medullaris interna/externa. Layer of white |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
choroid plexus of the 4th ventricle via the inter- |
|
|
matter which, provided it is located internally, |
|||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
ventricular foramen. B C |
|
|
|
|
|
has Y-shaped sections and divides the thalamus |
||||||
|
|
11 Sections of thalamus and metathalamus. Sec- |
|
|
into anterior, medial and lateral regions. B |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
24 Reticular (intralaminar) nuclei of thalamus. |
|||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
tiones thalamici et metathalamici. See p. 409. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Nuclei reticulares (intralaminares thalami). Nu- |
|||||||||||
|
|
12 Reticular nucleus of thalamus. Nucleus reticu- |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
clei located in |
the |
medullary lamina. They |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
latus [thalami]. Thin layer lying mainly laterally |
|
|
||||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
correspond functionally to the reticular forma- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
along the thalamus between the posterior limb |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
tion and thus are integrating nuclei. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
of the internal capsule and external medullary |
|
|
|
|||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
Centromedian nucleus. Nucleus centromedi- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
lamina of the thalamus. It receives tributaries |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
from the entire cerebral cortex, globus pallidus |
|
|
anus. It is the largest nucleus of this group and |
|||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
and reticular formation of the brainstem and |
|
|
has projections to the corpus striatum, hy- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
gives off efferent fibers to the reticular forma- |
|
|
pothalamus, and other structures. E |
|
|||||||||
21 |
|
|
|
tion of the midbrain and thalamus. B |
|
|
26 |
Paracentral nucleus. Nucleus paracentralis. It |
||||||||
|
13 |
Anterior nuclei of thalamus. Nuclei anteriores |
|
|
lies in the internal medullary lamina lateral to |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
[thalami]. Cell group in the apex of the |
|
|
the centromedian nucleus. CD |
|
||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
thalamus. They receive fibers from the mamil- |
|
27 |
Parafascicular nucleus. Nucleus parafascicu- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
lothalamic tract and have projections to the |
|
|
laris. It lies medial to the occipital region of the |
|||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
cingulate gyrus. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
centromedian nucleus. E |
|
|
|||
|
14 |
Anterodorsal nucleus. Nucleus anterodorsalis |
|
28 |
Lateral central nucleus. Nucleus centralis |
|||||||||||
24 |
|
|
|
(anterosuperior). Narrow cell plate anterosupe- |
|
|
lateralis. It lies dorsolateral and medial to the |
|||||||||
|
|
|
riorly. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
centromedian nucleus. E |
|
|
||||
|
|
15 |
Anteroventral nucleus. Nucleus anter- |
|
29 |
Medial central nucleus. Nucleus centralis me- |
||||||||||
25 |
|
|
|
oventralis (anteroinferior). Main nucleus of the |
|
|
dialis. It lies at the lower medial end of the in- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
anterior nuclei. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ternal medullary lamina. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 299
3
16
4
5
2
7
A Diencephalon, sagittal section
15
8
16
9 

10
B Diencephalon, cross section
28
22
18 
19

20 
14
23
12
300.1
26
828
300.1
9 |
|
|
|
10 |
1 |
22 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C Diencephalon, cross section
300.11
28 
25
18 
27 
D Diencephalon, cross section |
E Diencephalon, cross section |
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
300 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Nuclei ventrolaterales [thalami]. Ventrolateral |
|
15 |
Lateral geniculate nucleus [ventral part]. Nu- |
|||||||||||||||
1 |
|
1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
nuclei, the group of nuclei lateral to the internal |
|
|
cleus corporis geniculati lateralis [pars |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
medullary lamina. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ventralis]. Small group of cells with fibers from |
||||||||||
2 |
|
2 |
Posterior lateral nucleus. Nucleus lateralis |
|
|
the retina: part of a light reflex tract. C |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
posterior. Portion of the lateral nucleus situated |
|
16 |
Medial geniculate nucleus [ventral part]. Nu- |
||||||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
between the pulvinar and dorsal lateral nu- |
|
|
cleus corporis geniculati medialis [pars |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
cleus with connections to the parietal lobe. A |
|
|
ventralis]. Possibly the true acoustic part of the |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
3 |
Dorsal lateral nucleus. Nucleus lateralis |
|
|
geniculate nucleus. C |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
4 |
|
|
17 |
Subthalamic nucleus. Nucleus subthalamicus |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
dorsalis. Anterosuperior portion of the lateral |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
nucleus with projections to the region of the |
|
|
[corpus Luysii]. It lies between the lower end of |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
the internal capsule and the zona incerta. Of |
|||||||||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
posterior cingulum segment and the lower part |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
clinical importance is its reciprocal connection |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
of the parietal lobe. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with the globus pallidus. B |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
4 |
Anterior ventral nucleus. Nucleus ventralis |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
6 |
|
|
18 |
Reticular nuclei of thalamus. Nuclei reticulares |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
anterior. Anterior portion of the ventral nucleus |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
with |
projections |
to the |
interlaminar |
nuclei, |
|
|
[thalami]. Disaggregated |
cell |
layer on |
the |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
lateral surface of the thalamus between the ex- |
|||||||||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
globus pallidus and dentate nucleus and recip- |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ternal medullary lamina and internal capsule. B |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
rocal connections to the precentral gyrus and |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
Zona incerta. Basal continuation of the reticu- |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
the area anterior to it. It plays a role in Parkin- |
|
||||||||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
son’s disease. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lar nucleus of the thalamus and other struc- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tures. It lies in the path of the globus pallidus to |
|||||||||||
|
|
5 |
Intermediate |
ventral |
nucleus. |
Nucleus |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
the tegmentum of the diencephalon. B |
|
||||||||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
ventralis intermedius. Portion of the ventral |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
Nuclear |
regions |
H, |
H1 |
and |
H2. Nuclei re- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
nucleus situated behind the anterior |
|
ventral |
|
|
gionum H, H1 and H2. Dispersed neurons in the |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
nucleus; it is a synaptic station connecting the |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
corresponding Forel’s fields. Field H lies medial |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
cerebellum, red nucleus and motor cortex. A |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
to the zona incerta and in front of the red nu- |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
6 |
Medial ventral nucleus. Nucleus ventralis me- |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cleus, H1 between the thalamus and zona in- |
|||||||||||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
dialis. Poorly demarcated nuclear region sit- |
|
|
certa, H2 between the zona incerta and sub- |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
uated anterior to the posterior ventral nuclei; |
|
|
thalamic nucleus. B |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
its function is unclear. A |
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
Thalamic |
tract |
and |
fasciculi. Tractus |
et |
||||||
|
7 |
Posterior ventral nuclei. Nuclei ventrales |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
fasciculi thalamici. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
posteriores. Collective term for the following |
|
22 |
Lateral lemniscus. Lemniscus lateralis. Audi- |
||||||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
two nuclei. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tory pathway passing into the medial genicu- |
||||||||
|
|
|
8 Posterolateral ventral nucleus. Nucleus ventralis |
|
|
late body. A |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
posterolateralis. The lateral part of the poste- |
|
23 |
Medial lemniscus. Lemniscus |
medialis. Con- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
rior ventral nucleus that receives the medial |
|
|
tinuation of the tract from the posterior |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
lemniscus and spinothalamic tract and relays |
|
|
funiculus radiating into the posterolateral ven- |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
their impulses to the postcentral gyrus via the |
|
|
tral nucleus. A |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
thalamocortical tract. A |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
Spinal lemniscus. Lemniscus spinalis. Pain |
||||||||||
16 |
|
9 |
Posteromedial ventral nucleus. Nucleus ventralis |
|
|
pathway extending into the posterolateral ven- |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
tral nucleus. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
posteromedialis. Part located between the cen- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tromedian and posterolateral nuclei. It receives |
|
25 |
Trigeminal lemniscus. Lemniscus trigeminalis. |
||||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
the trigeminal lemniscus. A |
|
|
|
|
|
Fibers of the sensory trigeminal nucleus. They |
||||||||||||
|
|
10 Posterior nuclei of thalamus. Nuclei posteri- |
|
|
pass into the posteromedial ventral nucleus. A |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
26 Brachium of inferior colliculus. Brachium col- |
||||||||||||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
ores [thalami]. Collective term for the following |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
liculi inferioris. Outwardly visible connection |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
three parts of the thalamus. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
19 |
|
11 |
Pulvinar nuclei. Nuclei pulvinares. Nuclei that |
|
|
between the inferior colliculus and the medial |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
geniculate body. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
occupy the posterior portion of the thalamus; |
|
27 |
Acoustic radiation. Radiatio acustica. Portion of |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
they begin at the habenulae, receive tributar- |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
auditory pathway extending from the medial |
|||||||||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
ies from the auditory and visual pathways as |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
geniculate body to the transverse temporal gyn. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
well |
as |
from |
other thalamic |
nuclei |
and are |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
It passes through the occipital part of the poste- |
|||||||||||||||
21 |
|
|
|
connected with the visual cortex, optic and |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
rior limb of the internal capsule. A |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
acoustic control centers, and other structures. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 Brachium of superior colliculus. Brachium col- |
|||||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
liculi superioris. Externally visible connection |
|||||||
|
12 |
Lateral |
geniculate nucleus |
[dorsal |
part]. |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
between the superior colliculus and the lateral |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Nucleus |
[corporis geniculati] |
lateralis [pars |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
geniculate body. Connection of the visual path- |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
dorsalis]. Part of the visual pathway. A |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
way with the extrapyramidal system. C |
|
||||||||||||
|
13 |
Medial geniculate nucleus [dorsal part]. Nu- |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
29 Optic radiation. Radiatio optica [[Gratiolet]]. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cleus |
[corporis |
geniculati] |
medialis |
[pars |
|
||||||||||||
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
Portion of the visual pathway emanating from |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
dorsalis]. Part of medial geniculate body con- |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
the lateral geniculate body. It passes through the |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
taining small cells. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
occipital part of the posterior limb of the inter- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
25 |
|
14 |
Sections of ventral thalamus. Sectiones |
|
|
nal capsule and around the posterior horn of the |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
thalami ventralis. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lateral ventricle to the area striata. A |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brain |
301 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
298.13 |
|
|
|
1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
298.21 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
||||
|
12 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
22 |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
Thalamic nuclei and pathways |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
A |
28 16 15 |
|
|
|
13 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
H1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
20 |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
H2 |
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
||||
|
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
B |
Subthalamic region |
|
|
|
C |
Geniculate body |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
302 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Anterior thalamic radiations. Raditiones 13 |
Sections of the hypothalamus. Sectiones hy- |
||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
thalamicae anteriores. Fibers of the anterior nu- |
|
pothalami. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
cleus passing to and from the cingulate gyrus |
14 |
Dorsal (posterior) hypothalamic region. Regio |
||||||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
and likewise reciprocal connections between |
|
(area) hypothalamica dorsalis. Area of the hy- |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
the lateral nucleus and frontal lobe. The fibers |
|
pothalamus next to the apex. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
run in the anterior limb of the internal capsule. A |
15 |
Nucleus of ansa lenticularis. Nucleus ansae |
||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
Central |
thalamic |
radiations. |
Radiationes |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
lenticularis. Groups of cells dispersed in the |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
thalamicae centrales. Reciprocal fibers passing |
|
ansa lenticularis. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
fan-like through the posterior limb of the inter- |
16 |
Anterior |
(ventral) region of |
hypothalamus. |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
nal capsule from the posterior lateral, anterior |
|
Regio hypothalamica anterior. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ventral, lateral ventral and posterior ventral nu- |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
17 |
Medial/lateral |
preoptic |
nucleus. |
Nucleus |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
clei to the preand postcentral gyri in addition |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
to the connecting fields of the cortex. A |
|
|
preopticus medialis/lateralis. Group of nuclei |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
located beneath the anterior commissure and |
||||||||||||||||
6 |
|
3 |
Posterior |
thalamic |
raditaions. |
Radiationes |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
along the lamina terminalis with projections to |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
thalamicae posteriores. They lie in the occipital |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
the |
stria terminalis, |
medial |
telencephalic |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
region of the posterior limb of the internal cap- |
|
|||||||||||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
|
fasciculus and medial thalamic nuclei. D |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
sule and contain fibers from the lateral genicu- |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
18 |
Supraoptic |
nucleus. |
Nucleus supraopticus. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
late body (optic radiation) and the pulvinar for |
|
Nucleus lying above the optic chiasm with neu- |
||||||||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
the occipital lobes and adjacent regions. A |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
rosecretory fibers (oxytocin and vasopressin) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
4 |
Dentatothalamic |
tract. |
Tractus |
denta- |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
projecting to the posterior pituitary. D |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tothalamicus. It arises from the cerebellum and |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
19 |
Paraventricular nuclei. Nuclei paraventricu- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
radiates into the thalamic fasciculus and to the |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
lateral ventral nucleus. C |
|
|
|
|
|
lares. Group |
of |
autonomic nuclei |
with neu- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rosecretory fibers (oxytocin and vasopressin) |
|||||||||||||
10 |
|
5 |
Thalamic fasciculus. Fasciculus thalamicus. It |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
projecting to the posterior lobe of the hypophy- |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
lies below the thalamus, next to and above the |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
sis. They lie superiorly near the base of the hy- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
zona incerta in field H1 and is composed of the |
|
|||||||||||||||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
pothalamic sulcus and behind the anterior hy- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
ventricular fasciculus, ansa |
lenticularis |
and |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pothalamic nucleus. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
fibers from the cerebellum. It is a conveyor of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
20 |
Anterior hypothalamic nucleus. Nucleus hy- |
|||||||||||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
impulses for the anterior ventral and lateral |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pothalamicus anterior. Located behind the pre- |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
ventral nuclei. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
6 |
Subthalamic fasciculus. Fasciculus subthalami- |
|
optic nucleus with projections to the hemi- |
|||||||||||||||||
13 |
|
|
spheres, stria terminalis and thalamus, its effer- |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
cus. Fiber bundle extending from the globus pal- |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ent fibers communicate with motor and auton- |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
lidus to the subthalamic nucleus. C |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
omic nuclei. It influences heat regulation, glan- |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
7 Mamillothalamic fasciculus. Fasciculus mamil- |
|
||||||||||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
dular activity and circulation. D |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
lothalamicus. Fiber |
tract extending |
from the |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
21 Intermediate hypothalamic region. Regio hy- |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
mamillary body to the anterior nucleus of the |
||||||||||||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
|
pothalamica intermedia. Area situated between |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
thalamus. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
8 |
|
|
Pedunculus |
|
the |
anterior |
and posterior hypothalamic |
re- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Inferior |
thalamic |
peduncle. |
|
gions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
16 |
|
|
|
thalamicus inferior. Fibers between |
the hy- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
22 |
Arcuate |
nucleus. [[Nucleus arcuatus]]. Mural |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
pothalamus and thalamus. According to some |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
nucleus situated in the entrance to the infun- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
anatomists, it consists of fibers of the pulvinar |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
dibulum. It belongs to the tuberal nuclei, i. e., it |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
from and to the occipital lobes and its vicinity, as |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
regulates |
the release |
of |
hormones from |
the |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
well as fibers of the auditory tract. |
|
|
|
|
anterior lobe by delivering an active substance |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
18 |
|
|
9 Ansa lenticularis and fasciculus lenticularis. |
|
(neurohormone) to blood vessels of the hy- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Ansa et |
fasciculus |
lenticulares. |
Two |
fiber |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
pophysial stalk where its processes (axons) are |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
bundles from the lentiform nucleus to the ven- |
|
found. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
tral nuclei of the thalamus. One part passes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
23 |
Tuberal nuclei. Nuclei tuberales. Groups of nu- |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
around the anterior margin of the internal cap- |
|
clei in the posterior wall of the infundibulum. |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
sule (ansa lenticularis); the other part passes |
|
|||||||||||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
|
They function similar to the arcuate nucleus. D |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
through the internal capsule. Both tracts are |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
united in the thalamic fasciculus. C |
|
|
|
24 |
Lateral |
hypothalamic |
region. |
Regio |
hy- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
21 |
10 |
Ansa peduncularis and fasciculus peduncu- |
|
pothalamica lateralis. Area separated from the |
||||||||||||||||||
|
medial hypothalamus |
by |
the |
fornix, |
mamil- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
laris. Ansa et fasciculus pedunculares. Fiber |
|
lothalamic fasciculus and medial telencephalic |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tract connecting the thalamus and claustrum, |
|
|||||||||||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
fasciculus. It is occupied by the lateral preoptic |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
thereby extending between the lentiform nu- |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cleus and the amygdaloid body. B C |
|
|
|
|
nucleus and the supraoptic nucleus including its |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lateral portion. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
23 |
11 |
Intrathalamic fibers. Fibrae |
intrathalamicae. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Connections of individual thalamic nuclei. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12 Periventricular fibers. Fibrae periventriculares.
24Fibers coursing beneath the ependyma of the third ventricle between the medial nucleus and
25the hypothalamic nucleus to enter the posterior longitudinal fasciculus.
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 303
2
1
3
A Radiation of thalamus
10
5 6
4 |
9 |
B Ansa et fasciculus peduncularis
10 9
304.17
C Subthalamic pathways
24 7
19 
 17
17
20
 18
18
23
24
22
D Nuclei of hypothalamus
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
304 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus. Nucleus |
14 |
Posterior |
(dorsal) |
longitudinal |
fasciculus. |
|||||||
1 |
|
1 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
hypothalamicus ventromedialis. Lies in and |
|
Fasciculus |
longitudinalis dorsalis |
[[Schütz]]. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
above the entrance into the infundibulum. This |
|
Cranial continuation of a large portion of the |
|||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
nucleus belongs to the group of tuberal nuclei |
|
ventricular fibers. In the midbrain they lie close |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
and, like them, controls the release of regulating |
|
to the cerebral aqueduct and connect the hy- |
|||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
hormones for the anterior lobe via the hypophy- |
|
pothalamus with the rest of the brainstem. B |
|||||||||
|
|
|
sial stalk. A |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
Mamillotegmental |
fasciculus. |
Fasciculus |
|||
|
|
2 |
Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus. Nucleus |
|
mamillotegmentalis. Dissectible fiber bundle |
||||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
hypothalamicus dorsomedialis. It lies near the |
|
between the mamillary body and the tegmental |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
apex of the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus |
|
nuclei of the midbrain. It arises as a common |
|||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
and has similar functions. A |
|
|
|
|
trunk together with the mamillothalamic |
||||||
|
3 |
Dorsal hypothalamic nucleus. Nucleus hy- |
|
fasciculus and branches off into the mesen- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pothalamicus dorsalis. Group of cells located |
|
cephalic tegmentum. B |
|
||||||||
6 |
|
|
|
below |
the |
dorsal |
hypothalamic |
area |
(see |
16 |
Mamillothalamic fasciculus. Fasciculus mamil- |
||||
|
|
|
|
p. 302.14). A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
lothalamicus. It arises together with the mamil- |
||||
7 |
|
4 |
Posterior periventricular |
nucleus. Nucleus |
|
lotegmental fasciculus and passes to the ante- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
periventricularis posterior. Cell group located |
|
rior thalamic nuclei. B |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
below the ependyma in the posterior segment |
17 Fornix. It conveys fibers from the hippocampal |
||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
of the 3rd ventricle. A |
|
|
|
|
formation to the medial thalamic nuclei and hy- |
||||||
|
|
5 |
Infundibular (arcuate) nucleus. Nucleus infun- |
|
pothalamus, and projects fibers to the lateral |
||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
dibularis (arcuatus). It lies near the apex of the |
|
nuclei of the mamillary body. B |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
funnel of the infundibulum and has functions |
18 Fibers of stria terminalis. Fibrae striae termi- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
similar to those of the tuberal nuclei. A |
|
|
nalis. Fibers from the amygdaloid body which |
||||||||
10 |
|
6 |
Posterior hypothalamic area. Regio hy- |
|
communicate with the stria terminalis in the |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pothalamica posterior. It contains the lateral |
|
hypothalamus. B |
|
|
|||||||
11 |
|
|
|
and medial nuclei of the mamillary body and |
19 |
Medial prosencephalic fasciculus. Fasciculus |
|||||||||
|
|
|
other structures. |
|
|
|
|
|
prosencephalicus medialis. Fibers lying be- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
12 |
|
|
7 Medial and lateral nuclei of mamillary body. |
|
tween the medial and lateral hypothalamus. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
Nuclei corporis mamillaris mediales/laterales. |
|
They connect individual hypothalamic nuclei |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
The medial nucleus forms the mamillary body |
|
with one another and continue toward the oc- |
|||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
and is |
the |
origin |
of the |
mamillothalamic |
|
ciput in the posterior longitudinal fasciculus. B |
|||||
|
|
|
fasciculus. The lateral nucleus lies ventrolateral |
20 |
Hypothalamohypophysial tract. Tractus hy- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
and receives the fornix. A B |
|
|
|
|
pothalamohypophysialis. Bundle of neu- |
||||||
|
8 |
Posterior hypothalamic nucleus. Nucleus hy- |
|
rosecretory fibers that arises after the union of |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
pothalamicus posterior. It lies occipital to the |
|
the fiber groups from the supraoptic and para- |
|||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
dorsomedial |
and |
ventromedial |
nuclei |
and |
|
ventricular nuclei. B |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
above the mamillary body up to the hy- |
21 |
Supraoptic fibers. Fibrae supraopticae. Fibers |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
pothalamic sulcus and influences circulation, |
|
that arise in the supraoptic nucleus. B |
|||||||||
|
|
|
peristalsis and the blood sugar level. A B |
|
22 |
Paraventricular fibers. Fibrae paraventricu- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
9 Neurohypophysis. In contrast to the two other |
|
lares. Fibers that arise in the paraventricular nu- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
posterior lobes of the hypophysis, it is of neuro- |
|
cleus. B |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
genic origin; so is the continuation of the infun- |
23 |
Supraopticohypophysial tract. Tractus su- |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
dibulum. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
praopticohypophysialis. Fibers that arise in the |
||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
10 |
Hypothalamic tract and fasciculi. Tractus et |
|
supraoptic nucleus and form part of the hy- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
fasciculi hypothalamici. Tracts and fiber |
|
pothalamohypophysial tract. |
|
||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
bundles of the hypothalamus. |
|
|
24 |
Paraventriculohypophysial tract. Tractus para- |
|||||||
|
11 |
Periventricular fibers. Fibrae periventriculares. |
|
ventriculohypophysialis. Fibers that arise in the |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Fiber tract directly under the ependyma of the |
|
paraventricular nucleus and form part of the hy- |
|||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
3rd ventricle. It is permeated by cells, connects |
|
pothalamohypophysial tract. |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
the thalamus with the hypothalamus and con- |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
21tinues posteriorly into the posterior longitudinal fasciculus. B
22 |
12 Dorsal supraoptic commissure. Commissura |
|
supraoptica dorsalis [[Meynert]]. Decussation |
||
|
lying directly above the chiasm. Passes to the |
|
23 |
other side and may connect the subthalamic nu- |
|
|
cleus with the contralateral globus pallidus. |
|
|
13 Ventral supraoptic commissure. Commissura |
|
24 |
||
supraoptica ventralis [[Gudden]]. Crossing fibers |
||
|
lying partially in the chiasm. Among other |
|
25 |
things, it may connect the medial geniculate bo- |
|
|
dies with one another. |
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme |
|
|
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license. |

Brain 305
304.17 |
1 |
|
2
3
3
4 |
8 |
2 |
|
|
1
7
5
A Nuclei of hypothalamus
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
11 |
8 |
|||
14 |
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
19 |
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
15
7
20 
21
22
9
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
318.1
|
Pathways of hypothalamus |
|
B |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
306 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
ENDBRAIN. Telencephalon. The endbrain, which |
19 |
Ascending ramus. Ramus ascendens. Short |
|||||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||||
|
|
|
is formed by invagination of the prosencephalon |
|
branch of the lateral sulcus ascending into the |
|||||
|
|
|
|
(forebrain). It consists of the cerebral cortex to- |
|
frontal lobe. A |
||||
2 |
|
|
|
gether with the corpus callosum, corpus stri- |
20 |
Posterior ramus. Ramus posterior. Long poste- |
||||
|
|
|
|
atum and olfactory brain. |
|
|
|
rior branch of the lateral sulcus terminating |
||
3 |
|
|
2 CEREBRUM. In the present context, it comprises |
|
near the supramarginal gyrus. A |
|||||
|
|
|
the two cerebral hemispheres and their con- |
21 |
Interlobar sulci. Sulci interlobares. Furrows |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
tents. |
|
|
|
|
||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
which separate the cerebral lobes from one |
|
|
3 |
Cerebral cortex. Cortex cerebralis (pallium). |
|
|||||||
|
|
another. They include the central and parieto- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Paired portion of the hemispheres covering |
|
occipital sulci and the lateral sulcus together |
||||
5 |
|
|
|
most of the brainstem. |
|
|
|
|
with its posterior ramus. |
|
|
|
4 |
Cerebral gyri. Gyri cerebrales. Convolutions of |
22 |
Frontal lobe. Lobus frontalis. Lobe extending |
|||||
6 |
|
|
|
the cerebral hemispheres, about 1 cm wide. |
|
from the frontal pole to the central sulcus. A |
||||
|
5 |
Cerebral sulci. Sulci cerebrales. Fissures be- |
23 |
Frontal pole. Polus frontalis. Anterior end of the |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
tween gyri. |
|
|
|
|
|
frontal lobe. A |
|
6 |
Cerebral lobes. Lobi cerebrales. The four lobes |
24 |
Precentral sulcus. Sulcus precentralis. Furrow |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
of the cerebrum: frontal, parietal, temporal and |
|
in front of the precentral gyrus. A |
||||
|
|
|
occipital. |
|
|
|
|
25 Precentral gyrus. Gyrus precentralis. Convolu- |
||
|
|
7 |
Longitudinal |
fissure |
of |
cerebrum. Fissura |
||||
9 |
|
|
tion of the frontal lobe lying in front of the cen- |
|||||||
|
|
|
longitudinalis |
cerebralis. |
Deep |
longitudinal |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
tral sulcus. Motor area of the cerebral cortex. A |
||||||
|
|
|
|
groove between the |
right and |
left cerebral |
26 Superior frontal gyrus. Gyrus frontalis superior |
|||
10 |
|
|
|
hemispheres. It lodges the falx cerebri. B |
||||||
|
|
|
|
(primary motor area ???). A |
||||||
|
|
8 Transverse fissure of cerebrum. Fissura trans- |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
27 |
Superior frontal sulcus. Sulcus frontalis super- |
||||||
11 |
|
|
|
versa cerebralis [[fissura |
telodiencephalica]]. |
|||||
|
|
|
Fissure beneath the corpus callosum and fornix |
|
ior. Furrow below the superior frontal gyrus. A |
|||||
|
|
|
|
as well as above the thalamus and roof of the 3rd |
28 |
Middle frontal gyrus. Gyrus frontalis medius. A |
||||
12 |
|
|
|
ventricle. B |
|
|
|
|
29 |
Inferior frontal sulcus. Sulcus frontalis inferior. |
|
|
9 Lateral fossa of cerebrum. Fossa lateralis cere- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Furrow lying between the middle and inferior |
||||||
13 |
|
|
|
bralis. Space deep within the lateral sulcus. B |
|
frontal gyri. A |
||||
|
10 Superior (superomedial) margin. Margo su- |
30 Inferior frontal gyrus. Gyrus frontalis inferior. |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
perior (superomedialis). Superior border of a |
||||||
14 |
|
|
|
31 |
Opercular part (frontal operculum). Pars |
|||||
|
|
|
hemisphere between the superolateral and me- |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
dial surface. B |
|
|
|
|
|
opercularis [operculum frontale]. Part of infe- |
15 |
|
11 |
Inferior (inferolateral) margin. Margo inferior |
|
rior frontal gyrus lying behind the ascending |
|||||
|
|
ramus and covering the insula. A |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
(inferolateralis). Inferolateral border of a hemi- |
32 |
Orbital part. Pars orbitalis. Part of the inferior |
||||
16 |
|
|
|
sphere between the superolateral and inferior |
||||||
|
|
|
surfaces. B |
|
|
|
|
|
frontal gyrus located below the anterior ramus |
|
|
|
12 Medial (inferomedial) margin. Margo medialis |
|
of the lateral sulcus. A |
||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
17 |
|
33 |
Triangular part. Pars triangularis. Portion of |
|||||||
|
|
|
(inferomedialis). Inferomedial border of either |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
hemisphere between the inferior and medial |
|
the inferior frontal gyrus located between the |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
|
|
|
surfaces. B |
|
|
|
|
|
anterior and descending rami of the lateral sul- |
13 |
[[Fissura limitans]]. Fissure between the insula |
|
cus. Region of the motor speech center of Broca. |
|||||||
|
|
A |
||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
and opercula. The floor of this cleft, the sulcus |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
limitans, receives the insula. |
|
|
|
||||
|
14 |
Cerebral hemisphere. Hemispharium (cere- |
|
|
||||||
20 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
bralis). Half of the telencephalon. B |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 Superolateral surface of hemisphere. Facies
21superolateralis hemispherii. Upper and lateral surface of the hemisphere. B
2216 Central sulcus. Sulcus centralis. Furrow located between the preand postcentral gyri and between the frontal and parietal lobes. A
2317 Lateral sulcus. Sulcus lateralis. Deep cleft passing superiorly between the temporal and frontal
24lobes and inferiorly between the temporal and parietal lobes.
2518 Anterior ramus. Ramus anterior. Short anteriorly directed branch of the lateral sulcus. A
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 307
26
 16
16
27 |
25 |
28 |
24 |
22 |
|
30 |
19 |
23
29 18 31
33 20
32
A Brain, lateral view
10 7
15
14
 8 9
8 9 
11
12
B Brain, frontal section
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
308 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Parietal lobe. Lobus parietalis. It is bounded |
17 |
Transverse temporal sulci. Sulci temporales |
|||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||
|
|
|
anteriorly by the central sulcus, posteriorly by |
|
transversi. Transverse furrows between the |
|||
|
|
|
|
the parieto-occipital sulcus. A |
|
transverse temporal gyri in the floor of the post- |
||
2 |
|
2 |
Postcentral sulcus. Sulcus postcentralis. Poste- |
|
erior ramus of the lateral sulcus. C |
|||
|
18 |
Transverse temporal gyri. Gyri temporales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
rior boundary of the postcentral gyrus. A |
||||
3 |
|
3 |
Postcentral |
gyrus. Gyrus |
postcentralis. Pre- |
|
transversi [Heschl’s transverse convolutions]. |
|
|
|
2−4 transverse convolutions in the floor of the |
||||||
|
|
|
|
dominantly sensory area of the parietal lobe |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. Acoustic |
|||
4 |
|
|
|
that lies between the central and postcentral |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
center. C |
||||
|
|
|
sulci. A |
|
|
|
||
5 |
|
4 |
Superior parietal lobule. Lobulus parietalis su- |
19 |
Superior temporal gyrus. Gyrus temporalis su- |
|||
|
|
|
perior. Upper half of parietal lobe situated be- |
|
perior. A C |
|||
|
|
|
|
hind the postcentral gyrus and above the intra- |
20 |
Temporal operculum. Operculum temporale. |
||
6 |
|
|
|
parietal sulcus. A |
|
|
Part of superior temporal gyrus which covers |
|
|
|
5 Intraparietal sulcus. Sulcus intraparietalis. In- |
|
the insula. A |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
21 |
Superior temporal sulcus. Sulcus temporalis |
||||
7 |
|
|
|
constant sagittal furrow between the superior |
||||
|
|
|
and inferior parietal lobulus. A |
|
superior. Cleft between the superior and middle |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
8 |
|
|
6 Inferior parietal lobue. Lobulus parietalis infe- |
|
temporal gyri. A |
|||
|
|
22 |
Middle temporal gyrus. Gyrus temporalis me- |
|||||
|
|
|
rior. Lower half of parietal lobe situated behind |
|||||
|
|
|
|
the postcentral gyrus and below the intra- |
|
dius. A C |
||
9 |
|
|
|
parietal sulcus. A |
|
23 |
Inferior temporal sulcus. Sulcus temporalis in- |
|
|
|
7 |
Frontoparietal operculum. Operculum fron- |
|
ferior. Cleft between the middle and inferior |
|||
10 |
|
|
|
toparietale. Part of the cerebral segment located |
|
temporal gyri. A |
||
|
|
|
above the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus |
24 |
Inferior temporal gyrus. Gyrus temporalis in- |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||
11 |
|
|
|
and covering the insula. It extends toward the |
|
ferior. A |
||
|
|
|
occiput and approaches the site where the post- |
25 Insula (insular lobe). Lobus insularis (insula). |
||||
|
|
|
|
erior ramus turns upward. A |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Originally exposed cerebral cortex overlapped |
|||
12 |
|
8 |
Supramarginal gyrus. Gyrus supramarginalis. |
|
||||
|
|
during ontogenesis. It lies on the floor of the |
||||||
|
|
|
|
Convolution curving around the posterior end of |
|
lateral cerebral fossa. B |
||
13 |
|
|
|
the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. A |
26 |
Insular gyri. Gyri insulae. Gyri on the surface of |
||
|
9 |
Angular gyrus. Gyrus angularis. Convolution |
||||||
|
|
|
the insula. |
|||||
14 |
|
|
|
curving around the posterior end of the superior |
27 |
Short gyri of insula Gyri breves insulae. |
||
|
|
|
temporal sulcus. A |
|
||||
|
|
10 |
Occipital lobe. Lobus occipitalis. It is in- |
|
Short gyri located in the upper portion of the in- |
|||
15 |
|
|
sula. B |
|||||
|
|
|
completely |
bounded by |
the parietal and |
28 |
Long gyrus of insula. Gyrus longus insulae. |
|
|
|
|
|
parieto-occipital sulci and the pre-occipital in- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Long horizontal convolution located below the |
|||
16 |
|
|
|
cisure. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
short gyri. B |
||
|
11 Occipital pole. Polus occipitalis. Posterior end of |
|
||||||
|
|
29 Limen insulae. Terminal portion of the insular |
||||||
|
|
|
|
occipital lobe. A |
|
|||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
directed anteroinferiorly toward the anterior |
||
12 |
Transverse occipital sulcus. Sulcus occipitalis |
|
||||||
|
|
perforated substance. It is covered by the middle |
||||||
|
|
|
|
transversus. Continuation of the intraparietalis |
|
cerebral artery. B |
||
18 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
sulcus on the occipital lobe. A |
30 Central sulcus of insula. Sulcus centralis in- |
||||
|
13 |
Lunate sulcus. Sulcus lunatus. Sometimes con- |
||||||
|
|
sulae. Cleft between the long and short gyri of |
||||||
19 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
spicuous semilunar furrow that forms the ante- |
|
the insula. B |
|||
|
|
|
|
rior boundary of the visual cortex. It lies on the |
31 Circular sulcus of insula. Sulcus circularis in- |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||
20 |
|
|
|
superolateral surface of the cerebrum near the |
|
sulae. Limiting furrow of the insula. It is inter- |
||
|
|
|
occipital pole of the hemisphere at the posterior |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
rupted by the limen insulae. B |
|||
|
|
|
|
end of the calcarine fissure. A |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2114 Preoccipital incisure. Incisura preoccipitalis. Notch near the inferolateral edge of the cerebral
22hemisphere that marks the boundary between the occipital and temporal lobes. On the bony skull it is marked by the site where the petrous
23ridge enters the lateral wall of the skull. A
15 Temporal lobe. Lobus temporalis. It is bounded
24superiorly by the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. A
2516 Temporal pole. Polus temporalis. Anterior end of temporal lobe. A
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 309
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
5 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
11 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
7 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
16 |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
||||
18 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cerebrum, lateral view |
|
12 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heschl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
||
|
convolutions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
27 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25
30 28 31
29
B Insula
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
310 |
Brain |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Medial and inferior surfaces of a cerebral |
18 |
Collateral sulcus. Sulcus collateralis. Furrow |
||
1 |
|
1 |
|||||
|
|
|
hemisphere. Facies medialis et inferior |
|
between the parahippocampal and medial oc- |
||
|
|
|
|
hemispherii cerebri. |
|
|
cipitotemporal gyri extending into the occipital |
2 |
|
2 |
Sulcus of corpus callosum. Sulcus corporis cal- |
|
lobe. A B |
||
|
|
|
|
losi. Cleft between the corpus callosum and the |
19 |
Rhinal sulcus. Sulcus rhinalis. Continuation of |
|
3 |
|
|
|
cingulate gyrus. A |
|
|
the collateral sulcus occasionally present lateral |
|
3 |
Cingulate gyrus. Gyrus cinguli (cingulatum). |
|
to the uncus. A B |
|||
|
|
|
|||||
4 |
|
|
|
Convolution between the cingulate sulcus and |
20 |
Medial occipitotemporal gyrus. Gyrus occipi- |
|
|
|
|
sulcus of the corpus callosum coursing parallel |
|
totemporalis medialis. Basal convolution be- |
||
|
|
|
|
to the corpus callosum. It is part of the limbic |
|
tween the collateral and occipitotemporal sulci. |
|
5 |
|
|
|
cortex. A |
|
|
A B |
|
4 |
Isthmus of cingulate gyrus. Isthmus gyri cin- |
21 |
Occipitotemporal sulcus. Sulcus occipitotem- |
|||
|
|
||||||
6 |
|
|
|
guli (cingulatus). Constricted area where the |
|
poralis. Cleft between the medial and lateral oc- |
|
|
|
|
cingulate gyrus connects with the parahippo- |
|
cipitotemporal gyri located on the inferior sur- |
||
|
|
|
|
campal gyrus posterior and inferior to the |
|
face of the brain lateral to the collateral sulcus. A |
|
7 |
|
|
|
splenium of the corpus callosum. A |
|
B |
|
|
5 |
Cingulate sulcus. Sulcus cinguli (cingulatus). |
|
||||
|
|
22 |
Lateral occipitotemporal gyrus. Gyrus occipi- |
||||
8 |
|
|
|
Furrow bounding the anterior portion of cingu- |
|
totemporalis lateralis. Convolution adjoining |
|
|
|
|
late gyrus anteriorly and superiorly. A |
|
the occipitotemporal sulcus laterally. At the in- |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
9 |
|
6 |
Subparietal sulcus. Sulcus subparietalis. Fur- |
|
ferior margin of the temporal lobe it becomes |
||
|
|
|
row bounding the posterior portion of the cin- |
|
continuous with the inferior temporal gyrus |
||
|
|
|
|
gulate gyrus superiorly and posteriorly. A |
|
without interruption. A B |
|
10 |
|
7 |
Medial frontal gyrus. Gyrus frontalis medialis. |
23 |
Gyrus rectus. Elongated convolution located |
||
|
|
|
|
Convolution superior to the medial surface of |
|
above the orbit at its medial margin. B |
|
11 |
|
|
|
the frontal lobe, bounded inferiorly by the cin- |
24 Olfactory sulcus. Sulcus olfactorius. Groove for |
||
|
|
|
gulate sulcus. A |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
the olfactory tract on the inferior surface of the |
||
|
|
8 |
Paracentral lobule. Lobulus |
paracentralis. |
|
||
|
|
|
frontal lobe. B |
||||
12 |
|
|
|
Hooklike connection between the preand |
25 |
Orbital gyri. Gyri orbitales. Frontal convolu- |
|
|
|
|
|
postcentral gyri on the medial surface. A |
|
tions located lateral to the gyrus rectus. |
|
|
|
|
9 Precuneus. Precuneus.3 Area in front of the |
|
|||
13 |
|
|
26 |
Orbital sulci. Sulci orbitales. Furrows between |
|||
|
|
|
parieto-occipital sulcus. Anteriorly; it is partly |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
the oribtal gyri. B |
||
|
|
|
|
bounded by the subparietal sulcus. A |
|
||
14 |
|
|
|
26 a Olfactory brain. Rhinencephalon. |
|||
|
10 |
Parieto-occipital sulcus. Sulcus parieto-occipi- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
talis. Deep cleft in front of the cuneus separating |
27 |
Olfactory bulb. Bulbus olfactorius. Knob-like |
|
15 |
|
|
|
the occipital and parietal lobes. A |
|
|
enlargement containing dendrite-rich mitral |
|
11 Cuneus. Portion of the brain located between |
|
cells at the beginning of the olfactory tract. B |
||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
28 |
Olfactory tract. Tractus olfactorius. Connec- |
||||
16 |
|
|
|
the calcarine and parieto-occipital sulci. A |
|||
|
12 |
Calcarine sulcus. Sulcus calcarinus. Deep fur- |
|
tion between the olfactory bulb and trigone on |
|||
|
|
|
the inferior surface of the frontal lobe. B |
||||
|
|
|
|
row below the cuneus near the primary visual |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
area. Anteriorly, it meets the parieto-occipital |
29 |
Olfactory trigone. Trigonum olfactorium. Tri- |
||
|
|
|
|
sulcus at an acute angle. A |
|
|
angular widening at the end of the olfactory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
13 |
Dentate gyrus. Gyrus dentatus. Curved convo- |
|
tract. B |
|||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
lution of gray matter with a serrated appearance |
30 |
Medial and lateral olfactory striae. Striae ol- |
|
|
|
|
|
due to numerous indentations. It forms the infe- |
|
factoriae medialis et lateralis. Diverging fiber |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
rior continuation of the fasciolar gyrus, reaches |
|
bundles of the olfactory tract radiating fanlike at |
||
|
|
|
|
up to the medial surface of the uncus and lies be- |
|
the olfactory trigone. B |
|
20 |
|
|
|
tween the hippocampus and parahippocampal |
31 |
Medial and lateral olfactory gyri. Gyri olfac- |
|
|
|
|
gyrus. A |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
torii medialis et lateralis. Cellular continuations |
|
|
14 |
Hippocampal sulcus. Sulcus hippocampi (hip- |
|
||||
21 |
|
of the corresponding olfactory striae. |
|||||
|
|
|
pocampalis). Furrow situated between the para- |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
hippocampal and dentate gyri. It joins the uncus |
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
anteriorly. A |
|
|
|
|
15 |
Parahippocampal gyrus. Gyrus |
hippocampi |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||
23 |
|
|
|
(parahippocampalis). Thick convolution located |
|
|
|
|
|
|
below the hippocampal sulcus. A B |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16Uncus. Hooklike structure on the anterior end 24 of the parahippocampal gyrus. A B
17Lingual gyrus. Gyrus lingualis. Occipitally
25directed continuation of the parahippocampal gyrus. A B
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
|
|
|
Brain 311 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
5 |
|
|
|
2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
7 |
|
|
8 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
4 |
||||
|
|
|
9 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
2 |
|
6 |
10 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
6
13 |
16 |
15 |
18 |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
11 |
14 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
17 |
|
12 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
19 |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A |
Cerebrum, medial view |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
27 |
13 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
14 |
||||
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
30 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
||
22 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
22 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
B |
Base of brain |
||
|
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
312 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Olfactory brain. Its comprised of the substantia |
18 |
Gyrus fasciolaris. Convolution that passes |
|||||
1 |
|
1 |
||||||||
|
|
|
perforata anterior, stria diagonalis, area subcal- |
|
around the splenium of the corpus callosum and |
|||||
|
|
|
|
losa and gyrus paraterminalis. |
|
forms a connection between the longitudinal |
||||
2 |
|
2 |
Anterior |
perforated |
substance. Substantia |
|
striae, including the indusium griseum and den- |
|||
|
|
|
|
perforata anterior. Area posterior to the ol- |
|
tate gyrus. B |
||||
|
|
|
|
19 |
Lamina terminalis. Thin walled, anterior border |
|||||
3 |
|
|
|
factory trigone with perforations for the passage |
||||||
|
|
|
of cerebral vessels. A |
|
|
of the 3rd ventricle. A B |
||||
4 |
|
|
3 Diagonal stria (band) of Broca. Stria diagonalis |
20 |
Anterior commissure. Commissura anterior. |
|||||
|
|
|
[Broca]. Bundle of myelinated fibers often |
|
Anterior, transverse connection between the |
|||||
|
|
|
|
coursing obliquely over the anterior perforated |
|
right and left halves of the cerebrum. It lies be- |
||||
5 |
|
|
|
substance. It connects the precommissural sep- |
|
hind the lamina terminalis and is visible in the |
||||
|
|
|
|
tum with the uncus. A |
|
|
most anterior segment of the 3rd ventricle. A |
|||
6 |
|
4 |
Subcallosal area. Area subcallosa. Area on the |
21 Fornix. Curved bundle of fibers that pass in both |
||||||
|
|
|
medial surface of the frontal lobe situated below |
|
directions between the mamillary body and |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
7 |
|
|
|
the genu and rostrum of the corpus callosum. A |
|
hippocampus. B |
||||
|
5 |
Paraterminal |
gyrus. |
Gyrus paraterminalis. |
22 |
Crus of fornix. Crus. The posterior limb of the |
||||
|
|
|
|
Convolution on the medial surface below the |
|
fornix that arises from the hippocampus as the |
||||
8 |
|
|
|
rostrum and in front of the laminal terminalis. A |
|
hippocampal fimbria, circles around the pulvi- |
||||
|
|
|
|
nar and unites with the contralateral limb to |
||||||
|
|
6 |
Corpus |
callosum. Massive transverse fibers |
|
|||||
|
|
|
form the body of the fornix. B |
|||||||
9 |
|
|
|
connecting the right and left hemispheres at the |
|
|||||
|
|
|
23 |
Body of fornix. Corpus. Unparied middle part of |
||||||
|
|
|
base of the longitudinal fissure of the cerebrum. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
fornix situated below the corpus callosum and |
|||||
|
|
|
|
A B C |
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
formed by the union of both crura. B |
||
|
|
7 Splenium. Thick, free posterior end of the cor- |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
24 Tenia. Taenia. Thin, lateral margin of the fornix |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
pus callosum. B |
|
|||||
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
that gives attachment to the choroid plexus of |
||||
|
|
8 Trunk. Truncus. Portion of corpus callosum be- |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
the lateral ventricle. B |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
12 |
|
|
|
tween the splenium and genu. B |
25 Column. Columna. Anterior part of the fornix lo- |
|||||
|
9 |
Genu. Bend in the corpus callosum located ante- |
||||||||
|
|
cated partly in the lateral wall of the 3rd ven- |
||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
riorly above the rostrum. B |
|
tricle. It extends as far as the mamillary body. B |
||||
|
10 |
Rostrum. Anterior end of corpus callosum that |
26 Commissure. Commissura. Triangular connect- |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
tapers inferiorly to a point where it joins the |
|
ing plate situated between the crura of the for- |
||||
14 |
|
|
|
lamina terminalis. B |
|
|
nix below the posterior part of the corpus callo- |
|||
|
11 |
Radiation of |
corpus |
callosum. Radiatio cor- |
|
sum. It contains fibers crossing from the hippo- |
||||
|
|
|
||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
poris callosi. Fibers radiating from the corpus |
|
campal fimbriae of both sides. B |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
callosum to the cerebral cortex. A D |
27 |
Septum pellucidum (lucidum). Bilayered, thin |
|||||
|
|
12 |
Forceps |
minor. Forceps frontalis (minor). U- |
|
plate extending between the corpus callosum |
||||
16 |
|
|
and fornix. It separates the anterior horns of the |
|||||||
|
|
|
shaped fibers passing through the genu of the |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
lateral ventricles from one another. B |
||||||
|
|
|
|
corpus callosum and connecting the frontal |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
28 Cavity of septum pellucidum. Cavum septi pel- |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
17 |
|
|
|
lobes. D |
|
|
|
|||
13 |
Forceps major. Forceps occipitalis (major). U- |
|
lucidi. Enclosed cavity of variable size between |
|||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
the two laminae of the septum pellucidum. B |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
shaped fibers passing through the splenium of |
|
|||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
29 |
Lamina of septum pellucidum. Lamina septi |
||||||
|
|
|
the corpus callosum and connecting the poste- |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
rior parts of the occipital lobes. D |
|
pellucidi. Paired sheet forming the septum pel- |
||||
19 |
14 |
Tapetum. Continuous layer of fibers arching |
|
lucidum and the lateral wall of its cavity. B |
||||||
30 |
Precommissural septum. Septum precommis- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
laterally and inferiorly from the corpus callosum |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
20 |
|
|
|
and forming the lateral wall of the inferior and |
|
surale. Area on the free medial surface of the |
||||
|
|
|
posterior horns of the lateral ventricle as well as |
|
frontal lobe in front of the lamina terminalis. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
the roof of the posterior horn. C |
|
|
||||
2115 Indusium griseum. Thin layer of gray matter on the superior surface of the corpus callosum. B C
2216 Medial longitudinal stria. Stria longitudinalis medialis. A medial longitudinal band of white
23fibers in the indusium griseum. It is part of the olfactory brain. B C
17 Lateral longitudinal stria. Stria longitudinalis
24lateralis. Paired longitudinal stripe embedded in the indusium griseum and covered laterally
25by the cingulate gyrus. It is part of the olfactory brain. B C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 313
|
|
11 |
11 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
20 |
|
4 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
4 |
5 |
19 |
2 |
4 |
11 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
ARadiation of corpus callosum and cingulum
17
16
28

929
27
10
25
19
6
14
C Tapetum
6 |
16 |
17 |
8
23
26
7
21
24
18
 22
22
BFornix with crura and pellucid septum, obliquely from behind
11
12
13
D Major and minor forceps
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

|
314 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1 |
Lateral ventricle. Ventriculus lateralis. Paired |
15 |
Collateral trigone. Trigonum collaterale. |
|||||||
1 |
||||||||||||
|
|
ventricle which communicates with the third |
|
Broadened triangular area near the beginning of |
||||||||
|
|
|
ventricle via the interventricular foramen. It |
|
the collateral eminence at the border between |
|||||||
2 |
|
|
consists of the pars centralis and three horns |
|
the inferior and posterior horns. C |
|||||||
|
|
|
(anterior, posterior, inferior). A |
|
|
16 |
Hippocampus. Enlongated elevation in the infe- |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
2 |
Central part. Pars centralis. Middle portion of |
|
rior horn formed by the hippocampal sulcus. It is |
||||||||
3 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
lateral ventricle located above the thalamus and |
|
a specifically structured part of the rhinen- |
||||||||
|
|
|
below the corpus callosum. It contains a part of |
|
cephalon. C |
|||||||
4 |
|
|
the choroid plexus. A |
|
|
|
|
17 |
Pes. Foot like elevation at the anterior end of the |
|||
|
|
3 Interventricular |
foramen. |
Foramen inter- |
|
hippocampus. C |
||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
5 |
|
|
ventriculare. Passage behind |
and |
below |
the |
18 |
Alveus. Thin layer of white matter on the hippo- |
||||
|
|
genu of the fornix through which the lateral and |
|
campus. C |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
third ventricles communicate. D |
|
|
19 |
Fimbria. Bundle of white fibers emanating from |
|||||
6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
4 |
Anterior horn. Cornu frontale (anterius). Part of |
|||||||||||
|
the alveus and passing medially and upward on |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
the lateral ventricle that extends forward from |
|
the hippocampus to continue into the fornix as |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
7 |
|
|
the interventricular foramen. It is bounded me- |
|
its crus. C |
|||||||
|
|
dially by the septum pellucidum, laterally by the |
19 a |
Sections of the telencephalon. Sectiones telen- |
||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
head of the caudate nucleus, superiorly by the |
|
cephalici. |
|||||||
8 |
|
|
trunk of the corpus callosum, anteriorly and in- |
|
||||||||
|
|
20 |
Archicortex (archipallium). Archaecortex. Phy- |
|||||||||
|
|
feriorly by the genu and rostrum of the corpus |
||||||||||
|
|
|
callosum. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
logenetically speaking, this is an older part of |
||
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the cerebral cortex. Unlike the neocortex, it has |
|||
5 |
Posterior |
horn. Cornu |
occipitale |
(posterius). |
|
|||||||
|
three instead of six layers and is formed by the |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Part of the lateral ventricle that extends into the |
|
hippocampus and dentate gyrus. |
|||||||
10 |
|
|
occipital lobe. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
Paleocortex. Palaeocortex. Oldest part of cere- |
||||
6 |
Inferior horn. Cornu temporale (inferius). Part |
|||||||||||
|
|
bral cortex originally derived from the piriform |
||||||||||
11 |
|
|
of the lateral ventricle that accompanies the |
|
lobe. |
|||||||
|
|
hippocampus laterally and contains a part of the |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
22 Neocortex. The largest part of the cerebral cor- |
|||||||||
|
|
|
choroid plexus. A |
|
|
|
|
|||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tex comprised of six layers. |
||||
7 |
Stria terminalis. Longitudinal band of myeli- |
|
||||||||||
22 a Mesocortex. Incompletely differentiated zone |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
nated fibers located in the angle between the |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
in the region of the insular cortex with visceral |
||||||||
13 |
|
|
thalamus |
and |
caudate |
nucleus |
above |
the |
|
|||
|
|
|
functions. |
|||||||||
|
|
thalamostriate vein. It arises from the amyg- |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
daloid body. B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
148 Lamina affixa. Floor of lateral ventricle between the stria terminalis and tenia choroidea. B
159 Choroid fissure. Fissura choroidea. Cleft between the thalamus and fornix for passage of the choroid plexus into the lateral ventricle. In
16the inferior horn it lies between the fimbria of the hippocampus and the stria terminalis. B
1710 Tenia choroidea. Taenia choroidea. Line of attachment of the lateral choroid plexus to the thalamus. It becomes visible after removal of the
18choroid plexus. B
|
11 Choroid plexus of lateral ventricle. Plexus |
|
19 |
choroideus ventriculi lateralis. Highly vascu- |
|
|
larized, fringelike villous folds that protrude |
|
|
into the lateral ventricle through the choroid fis- |
|
20 |
||
sure. They extend anteriorly to the interventric- |
||
|
ular foramen and posteriorly into the inferior |
|
|
||
21 |
horn. B |
|
12 Bulb of posterior horn. Bulbus cornus occipi- |
talis (posterioris). Enlargement on the medial
22side of the posterior horn caused by fibers of the splenium of the corpus callosum. C
2313 Calcar avis. Enlargement on the medial side of the posterior horn produced by the calcarine fissure. C
2414 Collateral eminence. Eminentia collateralis. Elevation in the lateral floor of the inferior horn
25near the hippocampus. It is caused by the collateral sulcus. C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Brain 315 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
8 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Right and left lateral ventricles |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
10 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with left caudate nucleus |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
8 |
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interventricular foramen |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Thalamus with fornix |
|
D |
|
16 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
||||
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
19 |
16 |
|
|
22 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|||
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Left hippocampus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
24 |
||||
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

|
316 |
Brain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Sections through telencephalon. Sectiones tel- |
16 |
Superior |
longitudinal |
fasciculus. Fasciculus |
||||||||||
1 |
|
1 |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
encephali. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
longitudinalis superior. Largest bundle of asso- |
|||||
|
|
|
2 Cerebral cortex. Cortex cerebralis (pallium). |
|
ciation fibers in the cerebrum, extending from |
||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
the frontal lobe to the temporal lobe via the |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Gray |
matter, |
1.5−4.5 mm |
thick, |
consisting |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
mainly of the following six layers. A |
|
|
|
occipital lobe. E |
|
|
|||||||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
Inferior |
longitudinal |
fasciculus. |
Fasciculus |
|||||||
|
3 |
Molecular (plexiform) layer. 1st layer. Lamina |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
longitudinalis inferior. Bundle of |
association |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
molecularis (plexiformis). It contains a few tan- |
|
fibers connecting the temporal and occipital |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
gential cells and a thick network of tangential |
|
||||||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
lobes. E |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
fibers from dendrites of pyramidal cells and |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
18 |
Uncinate fasciculus. Fasciculus uncinatus. As- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
axons of other cells. None of its projections ex- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
sociation fibers connecting the inferior surface |
||||||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
tend beyond the cerebral cortex. A |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
of the frontal lobe and the anterior part of the |
|||||||||||
|
4 |
External granular layer. 2nd layer. Lamina |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
temporal lobe. E |
|
|
||||||||||||
6 |
|
|
|
granularis externa. A layer of small cells in a fine |
19 |
Radiation of corpus callosum. Radiatio cor- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
fiber network. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
poris callosi. Fibers connecting the right and left |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7 |
|
5 |
External |
pyramidal |
layer |
(pyramidal |
cell |
|
cerebral cortices. See also p. 312.11−14. C |
||||||||
|
|
|
layer). 3rd layer. Lamina pyramidalis externa. It |
20 |
Basal nuclei. Nuclei basales. Basal ganglion. |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
contains medium-sized pyramidal cells which |
21 Corpus striatum. The striate body, which is |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
do not form long tracts. A |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
comprised of basal ganglia (caudate nucleus and |
|||||||||
|
|
6 |
Internal granular layer. 4th layer. Lamina granu- |
|
putamen) united by bundles of gray matter. |
||||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
laris interna. It consists predominantly of |
|
Central synaptic station of the extrapyramidal |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
closely packed stellate cells and receives im- |
|
system. D |
|
|
|
||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
pulses primarily from thalamocortical fibers. Its |
22 |
Caudate nucleus. Nucleus caudatus. Elongated, |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
stria is comprised of densely stratified tangen- |
|
arched nucleus that arises from the ganglionic |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
tial fibers. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mass of the telencephalon and curves around |
|||||
11 |
|
7 |
Internal pyramidal (ganglionic) layer. 5th layer. |
|
the thalamus. |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Lamina pyramidalis interna (ganglionaris). It |
23 |
Head of caudate nucleus. Caput [[nuclei cau- |
|||||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
contains larger pyramidal cells and is the exit of |
|
dati]]. Anteriorly situated structure that forms |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
the corticonuclear and corticospinal tracts in |
|
the lateral wall of the anterior horn of the lateral |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
the corresponding regions of areas 4 and 6. A |
|
ventricle. B D |
|
|
|||||||||
|
8 |
Multiform (fusiform) layer. 6th |
layer. Lamina |
24 |
Body of caudate nucleus. Corpus [[nuclei cau- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
multiformis. Poorly defined layer made up of |
|
dati]]. Middle part of caudate nucleus lying on |
|||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
the thalamus. B D |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
many, mostly small, fusiform cells extending |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
25 |
Tail of caudate nucleus. Cauda [[nuclei cau- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
into the white matter. A |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
15 |
|
9 |
Tangential fibers. Neurofibrae tangentiales. Su- |
|
dati]]. It accompanies the inferior horn and |
||||||||||||
|
|
forms the tapering posterior and inferior seg- |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
perficial fiber complex comprised of the follow- |
|
ments of the caudate nucleus. D |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
ing four layers. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 Lentiform nucleus. Nucleus lentiformis (lentic- |
|||||||
|
10 |
Stria of molecular layer. Stria laminae |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
ularis). Part of the corpus striatum that arises |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
molecularis (plexiformis). Band of tangential |
|
from the telencephalon and diencephalon. D |
|||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
fibers in the 1st layer of the cerebral cortex. A |
27 |
Putamen. Lateral, telencephalic portion of the |
||||||||||||
|
11 |
Stria of external granular layer. Stria laminae |
|
lentiform nucleus. B |
|
|
|||||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
granularis externa. Thinner band of tangential |
28 |
Lateral medullary lamina. Lamina medullaris |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
fibers in the 2nd layer of the cerebral cortex. A |
|
lateralis. Medullary layer of the corpus striatum |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
19 |
12 |
Stria of internal granular layer. Stria laminae |
|
situated between the globus pallidus and puta- |
|||||||||||||
|
men. B |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
granularis interna. Band of tangential fibers in |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
29 |
Lateral globus pallidus. Globus pallidus later- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
the 4th layer of the cerebral cortex [[outer stripe |
|||||||||||||
20 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
of Baillarger]]. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
alis. Part of the diencephalic globus pallidus lo- |
|||||||
|
13 |
Stria |
of |
internal |
pyramidal |
layer. |
Stria |
|
cated between the lateral and medial medullary |
||||||||
21 |
|
laminae. B |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
laminae pyramidalis interna (ganglionaris). |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
30 |
Medial medullary lamina. Lamina medullaris |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Band of tangential fibers in the 5th layer of the |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
cerebral cortex [[inner stripe of Baillarger]]. A |
|
medialis. Medullary layer between the medial |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
and lateral parts of the globus pallidus. B |
|||||||||||||
|
14 Arcuate fibers of cerebrum. Fibrae arcuatae |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
31 |
Medial globus pallidus. Globus pallidus medi- |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
cerebri. Arcuate fibers connecting the adjacent |
|||||||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
alis. Part of the globus pallidus located medial to |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
cerebral gyri. F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the medial medullary lamina. B |
|
|||||
|
15 |
Cingulum. Fiber bundle lying in the medulla of |
|
|
|||||||||||||
24 |
32 |
Claustrum. Layer of gray matter between the |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
the cingulate gyrus. It arises from the area sub- |
|
lentiform nucleus and the insular cortex. B |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
callosa, arches |
around the |
corpus |
callosum, |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
25passes the splenium and extends anteriorly up to the uncus. C
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 317
1
310
2
4 |
|
3 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
5 |
32 |
|
27 |
2931 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
30
28
24 |
4 |
|
|
312927 |
5 |
32 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
|
|
|
30 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Horizontal and frontal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
B |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|||||
|
|
13 |
|
sections of the brain |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
11 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
12 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
A |
Cerebral cortex |
|
C |
Radiation of corpus |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Cells at left |
|
|
callosum and cingulum |
|
|
|
16 |
||
|
Medullary sheaths at right |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
23 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
20 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
Association pathways |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
D |
Lateral ventricle |
|
|
|
F |
Arcuate fibers |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
with left striate body |
|
|
|
|
|||||
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

318 Brain
1 |
Amygdaloid body (amygdala). Corpus amyg- |
1 |
daloideum. Ovoid group of nuclei in front of the in- |
ferior horn of the lateral ventricle that communi-
2cates with the medial cerebral cortex. It forms part of the rhinencephalon, has some autonomic functions, and influences emotional behavior. D
32 Anterior amygdaloid area. Area amygdaloidea
anterior. Anterior group of cells directed toward the anterior perforated substance. It receives 4 fibers from the lateral olfactory tract. The diago-
nal band of Broca arises from this area. D
53 Basolateral part. Pars basolateralis. In humans,
it contains the largest group of nuclei of the amygdala complex. It receives no olfactory fibers 6 but has projections to the hypothalamus, hippocampus and other parts of the brain, as well as
7 |
with the stria terminalis. D |
|
Corticomedial part. Pars corticomedialis [olfac- |
||
4 |
toria]. Smaller superomedially directed group of
8nuclei that receives fibers from the olfactory tract and is involved in the formation of the stria ter-
9 |
|
minalis. D |
|
5 Extreme capsule. Capsula extrema. White matter |
|||
|
|||
|
|
between the cortex of the insula and the |
|
10 |
|
||
|
claustrum. A B |
||
|
6 External capsule. Capsula externa. White matter |
||
|
|||
11 |
|
between the claustrum and lentiform nucleus. A B |
|
7 Internal capsule. Capsula interna. Very important |
|||
|
|||
|
|
conduction band lying medial to the lentiform nu- |
|
12 |
|
||
|
cleus and lateral to the thalamus and caudate nu- |
||
|
|
cleus. A |
|
|
|
||
13 |
8 Anterior limb of internal capsule. Crus anterius |
||
|
capsulae internae. Structure lying between the |
||
|
|
||
|
|
lentiform nucleus and the head of the caudate nu- |
|
14 |
9 |
cleus. A |
|
|
Anterior thalamic radiations. Radiationes |
||
|
|||
15 |
|
thalamicae anteriores. It contains fibers that con- |
|
|
nect the frontal lobe and the medial nucleus of the |
||
|
|
thalamus, as well as the anterior nucleus of the |
|
16 |
|
thalamus and the anterior region of the cingulate |
|
|
|
gyrus. B |
|
10 Frontopontine tract. Tractus frontopontinus.
17Fibers extending from the frontal lobe to the nuclei of the pons. B
1811 Genu of internal capsule. Genu capsulae internae.
It lies between the anterior and posterior limbs of the internal capsule and forms part of the lateral wall of the ventricular system. A B
12 Corticonuclear tract. Tractus corticonuclearis.
20Part of the pyramidal tract passing into the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. B
13 Posterior limb of internal capsule. Crus posterius
21capsulae internae. The part of the internal capsule that separates the lentiform nucleus from the
2214 thalamus and body of caudate nucleus. AThalamolentiform part. Pars thalamolenti-
formis. Portion of the posterior limb of the internal
23capsule that extends up to the posterior margin of the lentiform nucleus. B
15 Corticospinal fibers. Fibrae corticospinales. Part of
24the pyramidal tract that is organized somatotopically in such a way that the fibers for the most
25caudal region of the body lie farthest toward the occiput. B
16Corticorubral fibers. Fibrae corticorubrales. Fibers extending from the frontal lobe to the red nucleus. B
17Corticoreticular fibers. Fibrae corticoreticulares. Fibers passing from the region in front of and behind the central sulcus to the reticular formation. B
18Corticothalamic fibers. Fibrae corticothalamicae. Part of the thalamic radiation in the thalamus. B
19Thalamoparietal fibers. Fibrae thalamoparietales. Nerve fibers that project from the cerebral cortex to the thalamus. B
20Central thalamic radiations. Radiationes thalamicae centrales. Nerve fibers that radiate from the superior portion of the cerebral cortex to the thalamus. B See also p. 302.2.
21Sublentiform part. Pars sublentiformis. Portion of internal capsule lying below the posterior part of the lentiform nucleus. A B
22Optic radiation [[Gratioleti]]. Radiatio optica. Fiber tract that radiates from the lateral geniculate body to the area striata in the occipital lobe. A B
23Acoustic radiation. Radiatio acustica. Auditory tract that radiates from the medial geniculate body to the transverse temporal gyrus [[Heschl]]. A B
24Corticotectal fibers. Fibrae corticotectales. Connecting fibers between the cerebral cortex and the tectum. B
25Temporopontine fibers. Fibrae temporopontinae. Fibers of the cerebropontocerebellar tract that arise from the temporal lobe. B
26Retrolentiform part. Pars retrolentiformis. Portion of internal capsule situated occipital to the lentiform nucleus. A B
27Posterior thalamic radiations. Radiationes thalamicae posteriores. B
28Parieto-occipitopontine fasciculus. Fasciculus parieto-occipitopontinus. Portion of cerebropontocerebellar tract arising from the parietal and occipital lobes. B
29Corona radiata. Fibers of the internal capsule radiating fanlike in all directions toward the cerebral cortex. A
30Anterior commissure. Commisura anterior. It lies in front of the column of the fornix and is readily visible in the anterior wall of the third ventricle. A C
31Anterior part. Pars anterior. It radiates into the area subcallosa and is part of the phylogenetic rhinencephalon. C
32Posterior part. Pars posterior. Larger portion of anterior commisure that connects the two temporal lobes. C
33Association neurofibers. Neurofibrae associationes. Association fibers connecting adjacent or distant parts of the same side of the cerebrum. They form some of the above-named tracts, e. g., cingulum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, etc.
34Commissural neurofibers. Neurofibrae commissurales. They connect equivalent structures of contralateral hemispheres.
35Projecting neurofibers. Neurofibrae projectiones. They form the longer tracts, e. g., pyramidal tract, optic and acoustic radiations, thalamic radiation.
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.

Brain 319
1
2
5
AFrontal and stepped horizontal cut through cerebrum
910
|
|
12 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
15 |
11 |
|
16;17 |
|
||
6 |
|
|
|
21 |
18 |
|
|
|
19 |
14 |
|
23 |
20 |
||
|
|||
24 |
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
28 |
26 |
|
|
27 |
B |
Internal capsule |
|
22 |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
30 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6 |
8 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||||
29 |
4 |
|||||
|
|
11 |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
7 |
5 |
||
23 26 |
|
6 |
|
|||
|
|
|||||
|
6 |
|||||
|
5 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
7 |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
21 |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
8 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
13 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
14 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
32 |
15 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
C |
Fornix with anterior commissure of cerebrum |
||
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
2 |
20 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
3
D Amygdaloid body
1 |
22 |
23
24
25
Feneis, Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.
