
- •Биологическое окисление 1
- •Содержание
- •Биоэнергетика
- •История учения о БО
- •Antoine Lavoisier
- •Теория активации кислорода
- •Критическая оценка теории Баха-Энглера
- •Хромогены и гистогематины
- •Редокс-реакции, редокс потенциал
- •Maкроэргичность ATФ
- •ATФ-AДФ цикл
- •Образование субстратов БО
- •Stages 1 and 2
- •Stage 3
- •Ферменты и коферменты БО
- •Структура FAD и FMN
- •Мх: локализация
- •Общий план строения Мх
- •Internal structure of a mitochondrion
- •The Comparative Characteristics
- •Membrane Composition:
- •Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
- •Krebs’
- •Role of TCA
- •Plastic Role of
- •Regulation of
- •Regulation of the TCA Cycle (cont’d)
- •Inhibitors of Krebs Cycle
- •Content
- •Introduction
- •The Ways of Oxygen Consumption
- •Biologic Oxidation (BO)
- •Biomedical Importance of BO
- •Energy Conversion: Mitochondria
- •Chemiosmotic Coupling
- •Electron Transporting Chain, ETC
- •Electron Transporting Chain (ETC)
- •ETC functions
- •ETC Complexes: Overview
- •Complex I (NADH-CoQ reductase)
- •Coenzyme Q (CoQ) or Ubiquinone
- •Complex II (Succinate-CoQ reductase)
- •Complex II and III
- •Complex IV: Cytochrome c Oxidase
- •ATP/ADP translocase
- •Respiratory Chain Functioning
- •Functional scheme of ETC
- •Inhibitors of Oxidative Phosphorylation
- •The Structures of Several Inhibitors of
- •The Sites of Action of Several Inhibitors of ETC and/or OP
- •Several Uncouplers of OP
- •Uncoupler Action
- •Endogenous Uncouplers Enable
- •P/O Ratio
- •Disorders of Mitochondrial
- •Clinical Manifestation and
- •Some Mitochondrial Diseases
- •LHON
- •MERRF, MELAS et al.
- •Can Mitochondrial Diseases be Treated?
- •Cytochromes P450 are monooxygenases important for the detoxification of many drugs
- •Cytochrome b5
- •Monooxygenase System (Microsomal
- •Functioning of Microsomal
- •Microsomal Oxidation and Cytochrome P450

Complex IV: Cytochrome c Oxidase
Complex IV is called cytochrome c oxidase because it accepts electrons from cytochrome c and directs them to the four- electron reduction of O2 to form H2O.
07/06/19

H+-ATPase
Ion gradient across a membrane is a form of stored energy, which can do useful work when the ions are flowing back across the membrane.
H+ flows back down its electrochemical gradient through ATP synthase, which catalyzes the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
This ubiquitous enzyme plays the role of a turbine, permitting the proton gradient to drive the production of ATP.
07/06/19

ATP/ADP translocase
Outward transport of ATP (via the ATP/ADP translocase) is favored by the membrane electrochemical potential.
07/06/19
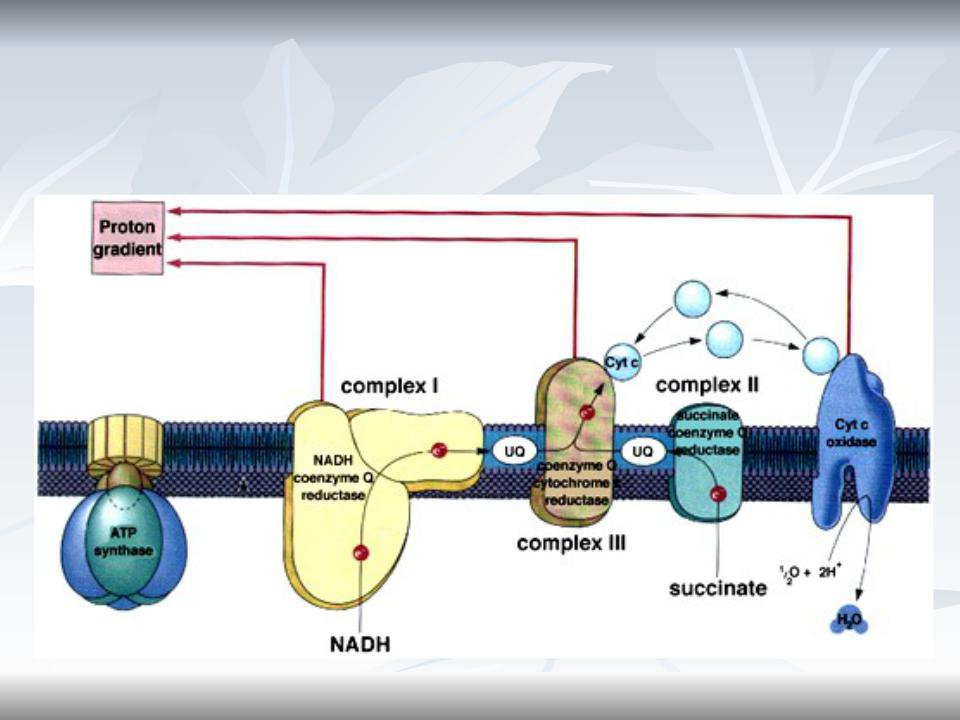
Respiratory Chain Functioning
07/06/19

Functional scheme of ETC
4H+ |
QH2 |
4H+ |
2H+ |
|
|
|
|||||
F-cycle |
Q-cycle |
O-cycle |
|||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||
NADH + H+
|
|
|
|
|
|
4H+ + O |
NAD+ |
FADH2 |
|
|
H2O |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
4H+ |
|
+ |
2H |
+ |
|
|
FAD |
|
||||
|
|
2H |
|
|
TCA 
There are 3 cycles in ETC functioning: F-cycle, Q-cycle and O- cycle.
Proton pumping result in electrochemical gradient H+ formation.
Finally it is used for ATP formation.
ADP + Pi
H+
ATP synthase
ATP
07/06/19

Inhibitors of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Name |
Function |
Site of Action |
Rotenone |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex I |
Amytal |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex I |
Antimycin A |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex III |
Cyanide |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex IV |
Carbon Monoxide |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex IV |
Azide |
e- transport inhibitor |
Complex IV |
2,4,-dinitrophenol |
Uncoupling agent |
transmembrane H+ carrier |
Pentachlorophenol |
Uncoupling agent |
transmembrane H+ carrier |
Oligomycin |
Inhibits ATP synthase |
OSCP fraction of ATP |
|
|
synthase |

The Structures of Several Inhibitors of
ETC and OP

The Sites of Action of Several  Inhibitors of ETC and/or OP
Inhibitors of ETC and/or OP
07/06/19

Several Uncouplers of OP
07/06/19

Uncoupler Action
O- |
H+ |
OH |
|
NO2 |
NO2 |
|
|
|
|
NO2 |
NO2 |
2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP) can uptake proton from the intermembrane space and transports it back to the mitochondrial matrix.
07/06/19

2,4-DNP decreases H+
H+ |
H+ |
|
H+ |
+ H |
+ H+ |
H+ |
H+ |
H |
+ H+ |
H |
+ |
H+ |
25:1 H+ |
||
Intermembrane |
H+ |
|
+ |
H+ |
H+ |
|
+ |
H+ |
|
+ |
|
||||
H+ |
H+ H |
|
H H+ |
|
|
|
H H+ |
|
H H+ |
|
|||||
space |
|
|
H+ |
|
|
O- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

 NO2
NO2
NO2
NO2
O2N 
OH
Mitochondrial matrix
 H+
H+
07/06/19
