
- •Pediatric Oncology
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •Contributors
- •Abbreviations
- •Introduction
- •Incidence and Management of Childhood Cancer
- •1: General Aspects of Childhood Leukemia
- •1.1 Definition and General Characteristics
- •Abbreviations
- •1.2 Incidence
- •1.3 Etiology and Predisposing Factors
- •1.3.1 Genetics
- •1.3.2 Ionizing Radiation
- •1.3.3 Chemicals and Drugs
- •1.3.4 Infection
- •1.3.5 Immunodeficiency
- •1.3.6 Socioeconomic Situation
- •1.4.1 Molecular Pathogenesis
- •1.4.2 Minimal Residual Disease (MRD)
- •2: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- •2.1 Incidence
- •2.2 Clinical Manifestation
- •2.2.1 General Aspects
- •2.2.2 Specific Signs and Symptoms
- •2.2.2.1 Skin
- •2.2.2.2 Central Nervous System
- •2.2.2.4 Ear, Nose, and Throat
- •2.2.2.5 Cardiac Involvement
- •2.2.2.6 Mediastinum
- •2.2.2.7 Pleura/and Pericardium
- •2.2.2.8 Gastrointestinal Involvement
- •2.2.2.9 Renal Involvement
- •2.2.2.10 Testicular Involvement
- •2.2.2.11 Penis
- •2.2.2.12 Bone and Joint Involvement
- •2.3 Laboratory Findings and Classification
- •2.3.1 Hematology
- •2.3.1.1 Red Cells
- •2.3.1.2 White Blood Cell Count
- •2.3.1.3 Platelets
- •2.3.2 Coagulopathy
- •2.3.3 Serum Chemistry
- •2.3.4 Bone Marrow Analysis
- •2.4 Leukemic Cell Characterization and Classification
- •2.4.1 Morphology
- •2.4.2 Cytochemistry
- •2.4.3 Immunological Characterization
- •2.4.4 Biochemical Characterization
- •2.4.4.1 Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase
- •2.4.4.2 5-Nucleotidase
- •2.4.5 Cytogenetic Characterization
- •2.4.6 Cytometry
- •2.4.7 Cell Kinetics
- •2.5 Prognostic Factors of All
- •2.6 Characteristics and Prognosis of ALL in Infants
- •2.7 Differential Diagnosis
- •2.8 Therapy
- •2.8.1 Induction of Remission
- •2.8.2 Consolidation Treatment
- •2.8.3 Maintenance Treatment
- •2.9 Prognosis
- •2.10 Management of Complications and Side Effects
- •2.11 Relapse
- •2.12 Special Forms
- •2.12.1 CNS Leukemia
- •2.12.2 Testicular Leukemia
- •3: Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- •3.1 Epidemiology
- •3.2 Predisposing Factors
- •3.3 Differential Diagnosis
- •3.4 Classification
- •3.4.2 Histochemical Classification and Frequency
- •3.4.3 Immunophenotyping
- •3.4.4 Cytogenetics
- •3.5 Clinical Presentation
- •3.5.1 Bleeding
- •3.5.2 Leukostasis
- •3.5.3 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- •3.5.4 Infection
- •3.6 Therapy
- •3.6.1 Induction Therapy
- •3.6.2 Remission and Postremission Therapy
- •3.6.3 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- •3.6.4 Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- •3.7 Characteristics of and Therapy for AML Subtypes
- •3.7.1 Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL, M3)
- •3.7.2 Acute Myelomonocytic and Acute Monocytic Leukemia (M4, M5)
- •3.7.3 Erythroleukemia (Di Guglielmo Syndrome, M6)
- •3.7.4 Acute Megakaryocytic Leukemia (AMKL)
- •3.7.6 Eosinophilic Leukemia
- •3.7.7 Congenital Leukemias
- •3.7.8 Inherited AML
- •3.8 Relapse of AML
- •3.9 Detailed Reference
- •4: Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- •4.1 Introduction
- •4.2 Definition
- •4.3 Classification
- •4.4 Epidemiology
- •4.5 Predisposing Factors
- •4.6 Etiology
- •4.7 Clinical Manifestations
- •4.8 Laboratory Findings
- •4.9 Differential Diagnosis
- •4.10 Treatment
- •References
- •5.1 Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
- •5.1.1 Clinical Manifestations
- •5.1.2 Laboratory Findings
- •5.1.3 Natural History
- •5.1.4 Prognosis
- •5.1.5 Therapy
- •5.2 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Adult Type)
- •5.2.1 Clinical Manifestations
- •5.2.2 Laboratory Findings
- •5.2.3 Natural History
- •5.2.4 Management
- •5.3 Polycythemia Vera
- •5.3.1 Diagnosis
- •5.3.2 Clinical Manifestations
- •5.3.3 Management
- •5.4 Essential Thrombocythemia
- •5.4.1 Differential Diagnosis
- •5.4.2 Diagnosis
- •5.4.3 Management
- •5.5 Idiopathic Myelofibrosis
- •5.5.1 Clinical Manifestations
- •5.5.2 Natural History
- •5.5.3 Management
- •5.6 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- •5.7 Transient Myeloproliferative Syndrome Associated with Down Syndrome
- •5.8 Mast Cell Disease (Mastocytosis)
- •References
- •6: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- •6.1 Definition
- •6.2 Incidence
- •6.3 Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Molecular Genetics
- •6.4 Pathology and Classification
- •6.5 Histological, Immunological, and Cytogenetic Characteristics of the Different Forms of NHL
- •6.5.1 Burkitt Lymphoma (BL) and Burkitt Like Lymphoma (BLL)
- •6.5.3 Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (LL)
- •6.5.4 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)
- •6.5.5 Unclassifiable NHL
- •6.6 Clinical Manifestations
- •6.6.1 General Symptoms
- •6.6.2 Symptoms in Relation to Location of NHL
- •6.6.2.1 Abdomen
- •6.6.2.2 Mediastinum
- •6.6.2.3 Peripheral Lymph Nodes
- •6.6.2.4 Other Locations
- •6.7 Differential Diagnosis Among the Different Forms of NHL (In Ranking of Frequency)
- •6.7.1 Differential Diagnosis of Other Disorders
- •6.8 Diagnosis
- •6.8.2 Radiological Diagnosis
- •6.9 Staging (Murphy, St. Jude)
- •6.9.1 Frequency
- •6.10 Therapy
- •6.10.1 Therapy and Prognosis of BL, BLL, and LBCL
- •6.10.2 Therapy and Prognosis of LL
- •6.10.3 Therapy and Prognosis of ALCL
- •6.11 Novel Immunologic Treatment
- •6.12 Patients with Partial Response or with Relapse of NHL
- •7: Hodgkin Disease
- •7.1 Definition
- •7.2 Incidence
- •7.3 Etiology and Pathogenesis
- •7.4 Pathology and Immunology
- •7.4.1 Macroscopic Features
- •7.4.2 Microscopic Features
- •7.4.3 Molecular Biology
- •7.4.4 Immunophenotype
- •7.4.5 Histological Classification (WHO)
- •7.4.6 Approximate Frequency of Histological Subtype and Stage
- •7.5 Staging Classification
- •7.5.1 Ann Arbor Staging Classification
- •7.5.2 A/B Staging
- •7.6 Clinical Presentation
- •7.6.1 Involvement of Organs and Organ Systems
- •7.6.1.1 Spleen
- •7.6.1.2 Lungs
- •7.6.1.3 Bone Marrow
- •7.6.1.4 Bone
- •7.6.1.5 Liver
- •7.7 Laboratory Analyses
- •7.7.1 Blood
- •7.7.2 Chemistry
- •7.7.3 Immunological Analyses
- •7.8 Radiological Evaluation
- •7.8.1 Chest
- •7.8.2 Abdomen
- •7.8.3 Bone
- •7.9 Differential Diagnosis
- •7.10 Treatment
- •7.10.1 Chemotherapy
- •7.10.2 Radiotherapy
- •7.11 Prognosis
- •7.13 Relapse
- •7.14 Side Effects and Sequelae
- •7.14.1 Biochemical or Clinical Hypothyroidism
- •7.14.2 Gonadal Dysfunction
- •7.14.3 Decrease in Bone Growth of Irradiated Area
- •7.14.4 Pneumonitis and Pericarditis
- •7.14.5 Infection After Splenectomy
- •7.14.6 Secondary Tumors
- •8: Histiocytoses
- •8.1 Definition and Overview
- •8.2 Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- •8.2.1 Incidence
- •8.2.2 Etiology and Pathogenesis
- •8.2.3 Histopathology
- •8.2.4.1 Bone
- •8.2.4.2 Skin
- •8.2.4.3 Lungs
- •8.2.4.4 Lymph Nodes
- •8.2.4.5 Liver
- •8.2.4.6 Spleen
- •8.2.4.7 Endocrine Organs
- •8.2.4.8 Central Nervous System
- •8.2.4.9 Blood
- •8.2.4.10 Immune System
- •8.2.4.11 Gastrointestinal Tract
- •8.2.5 Differential Diagnosis
- •8.2.6 Prognosis
- •8.2.7 General Therapeutic Approach
- •8.2.7.1 Surgery
- •8.2.7.2 Radiotherapy
- •8.2.7.3 Chemotherapy
- •8.2.7.4 Stem Cell Transplantation
- •8.2.8.1 Endocrine Sequelae
- •8.2.8.2 Pulmonary Sequelae
- •8.2.8.3 Hepatic Sequelae
- •8.2.8.4 Psychosocial Problems
- •8.2.8.5 Secondary Tumor
- •8.2.9 Special Clinical Presentations of LCH
- •8.2.9.2 Chronic-Disseminated or Multifocal LCH (Formerly Hand–Schüller–Christian Syndrome)
- •8.2.9.3 Eosinophilic Granuloma
- •8.4 Familial Erythrophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (FEL)
- •8.4.1 Definition
- •8.4.2 Pathology and Genetics
- •8.4.3 Clinical Presentation
- •8.4.4 Laboratory Analyses
- •8.4.5 Clinical Course
- •8.4.6 Differential Diagnosis
- •8.4.7 Therapy
- •8.5 Malignant Histiocytosis
- •8.5.1 Incidence
- •8.5.2 Pathology
- •8.5.3 Clinical Presentation
- •8.5.4 Therapy
- •9: Brain Tumors
- •9.1 Overview
- •9.2 Incidence
- •9.3 Tumor Types and Frequencies
- •9.4 Etiology and Pathogenesis
- •9.5 Pathology and Classification
- •9.6 Clinical Manifestations
- •9.6.1 Hydrocephalus and Manifestations of High Intracranial Pressure
- •9.6.2 Focal Neurological Failures
- •9.6.3 Tumor Types and Symptoms According to Intracranial Location
- •9.6.3.1 Cerebral Hemisphere
- •9.6.3.2 Parasellar Optic Chiasma Area
- •9.6.3.3 Pineal Area
- •9.6.3.4 Posterior Fossa Tumors
- •9.6.3.5 Vermis Cerebelli
- •9.6.3.6 Fourth Ventricle
- •9.6.3.7 Brain Stem
- •9.6.3.8 Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors
- •9.6.3.9 Spinal Cord
- •9.7 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.7.1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT)
- •9.7.2 Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- •9.7.3 Conventional Radiography of the Skull
- •9.7.4 Special Methods for Special Indications
- •9.7.4.1 Bone Scintigraphy
- •9.7.4.2 Angiography
- •9.7.4.3 Ultrasonography (in Infancy)
- •9.7.4.4 Myelography
- •9.8 Additional Diagnostic Tools
- •9.8.1 Cerebral Fluid Analysis
- •9.8.2 Electroencephalography
- •9.8.3 Stereotactic Biopsy
- •9.9 Differential Diagnosis
- •9.10 Metastatic Spread
- •9.11 Therapy
- •9.11.1 Neurosurgical Procedure
- •9.11.2 Radiotherapy
- •9.11.3 Chemotherapy (for Details of Special Tumor Types See Below)
- •9.12 Special Tumor Types
- •9.12.1 Astrocytic Tumors
- •9.12.1.1 Incidence
- •9.12.1.2 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.1.3 Characteristics of Low-Grade Astrocytoma (LGA I and II)
- •9.12.1.4 Characteristics of High-Grade Astrocytoma (HGA III/IV)
- •9.12.2.1 Incidence
- •9.12.2.2 Pathology
- •9.12.2.3 Clinical Presentation
- •9.12.2.4 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.2.5 Histology
- •9.12.2.6 Therapy and Prognosis
- •9.12.3 Brain Stem Tumors
- •9.12.3.1 Incidence
- •9.12.3.2 Pathology
- •9.12.3.3 Location
- •9.12.3.4 Clinical Manifestations
- •9.12.3.5 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.3.6 Therapy
- •9.12.4 Medulloblastoma and PNET
- •9.12.4.1 Incidence
- •9.12.4.2 Pathology
- •9.12.4.3 Clinical Manifestation
- •9.12.4.4 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.4.5 Therapy
- •9.12.4.6 Prognosis
- •9.12.5 Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumors (ATRT)
- •9.12.6 Pineal Tumors
- •9.12.6.1 Frequency
- •9.12.6.2 Pathology
- •9.12.6.3 Clinical Manifestation
- •9.12.6.4 Laboratory Diagnosis
- •9.12.6.5 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.6.6 Therapy
- •9.12.6.7 Prognosis
- •9.12.7 Ependymoma
- •9.12.7.1 Incidence
- •9.12.7.2 Pathology and Genetics
- •9.12.7.3 Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
- •9.12.7.4 Therapy
- •9.12.7.5 Prognosis
- •9.12.8 Craniopharyngioma
- •9.12.8.1 Incidence, Pathogenesis, and Pathology
- •9.12.8.2 Differential Diagnosis
- •9.12.8.3 Clinical Manifestations
- •9.12.8.4 Radiological Diagnosis
- •9.12.8.5 Therapy
- •9.12.8.6 Prognosis
- •9.12.9 Meningioma
- •9.12.9.1 Incidence and Pathology
- •9.12.9.2 Location
- •9.12.9.3 Clinical Manifestation
- •9.12.9.4 Therapy
- •9.12.10 Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors
- •9.12.10.1 Incidence
- •9.12.10.2 Pathology
- •9.12.10.3 Symptoms
- •9.12.10.4 Prognosis
- •9.12.10.5 Therapy
- •9.13 Adverse Late Effects from Brain Tumors and Their Treatment
- •10: Neuroblastoma
- •10.1 Definition
- •10.2 Incidence
- •10.3 Etiology and Pathogenesis
- •10.4 Molecular Cytogenetics
- •10.5 Pathology
- •10.5.1 Macroscopic Features
- •10.5.2 Microscopic Features
- •10.6 Clinical Manifestations
- •10.6.1 Common Symptoms
- •10.6.2 Symptoms Associated with Catecholamine Production
- •10.6.3 Paraneoplastic Syndromes
- •10.6.4 Local Symptoms and Classic Signs
- •10.6.4.1 Eyes
- •10.6.4.2 Neck
- •10.6.4.3 Chest, Posterior Mediastinum, and Vertebrae
- •10.6.4.4 Abdomen
- •10.6.4.5 Liver
- •10.6.4.6 Skin
- •10.6.4.7 Bone
- •10.6.4.8 Bone Marrow
- •10.7 Metastatic Spread
- •10.8 Laboratory Findings
- •10.8.1 Urinary Catecholamine Metabolites (Tyrosine Metabolism)
- •10.8.2 Other Laboratory Findings
- •10.8.3 Bone Marrow
- •10.9 Diagnostic Imaging
- •10.9.1 Conventional X-Ray
- •10.9.2 Methylisobenzyl Guanidinium (MIBG) Scintigraphy
- •10.9.4 Bone Scintigraphy (Technetium)
- •10.10 Differential Diagnosis
- •10.11 International Staging (Including the Classic Evans Staging)
- •10.11.1 The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Classification
- •10.12 Therapy
- •10.12.1 Surgical Procedure
- •10.12.2 Chemotherapy
- •10.12.3 Radiotherapy
- •10.12.4.1 Low Risk
- •10.12.5 Therapy in Relapse
- •10.13 Prognosis
- •10.13.1 Futuristic Therapeutic Approaches
- •10.14 Special Forms
- •10.14.1 Ganglioneuroblastoma
- •10.14.2 Ganglioneuroma
- •10.14.3 Olfactory Neuroblastoma
- •10.14.4 Neuroblastoma Arising from Organ of Zuckerkandl (Location at the Bifurcation of the Aorta or Origin of the Inferior Mesenteric Artery)
- •10.14.5 Pheochromocytoma
- •11: Nephroblastoma (Wilms Tumor)
- •11.1 Definition
- •11.2 Incidence
- •11.3 Chromosomal Association
- •11.4 Pathology
- •11.4.1 Macroscopic Features
- •11.4.2 Microscopic Features
- •11.5 Clinical Manifestations
- •11.6 Laboratory Diagnosis
- •11.7 Radiological Diagnosis
- •11.8 Differential Diagnosis
- •11.9 Staging
- •11.10 Therapy
- •11.10.1 Surgical Procedures
- •11.10.2 Chemotherapy
- •11.10.3 Radiotherapy
- •11.11 Therapy in Relapse
- •11.12 Prognosis
- •11.13 Metastatic Nephroblastoma
- •11.14 Subtypes
- •11.14.1 Bilateral Wilms Tumor (Stage 5)
- •11.14.1.1 Therapy
- •11.14.1.2 Prognosis
- •11.14.2 Congenital Mesoblastic Nephroblastoma (Fetal Renal Hamartoma)
- •11.14.2.1 Pathology
- •11.14.2.2 Clinical Manifestations
- •11.14.2.3 Therapy
- •11.14.3 Renal Cell Carcinoma
- •11.14.3.1 Pathology
- •11.14.3.2 Clinical Manifestations
- •11.14.3.3 Therapy
- •11.14.3.4 Prognosis
- •11.14.4 Renal Rhabdoid Tumor
- •12: Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- •12.1 Overview
- •12.1.1 Definition
- •12.1.2 Incidence
- •12.2 Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
- •12.2.1 Incidence and Localization
- •12.2.2 Etiology and Pathogenesis
- •12.2.3 Histopathology
- •12.2.3.1 Four Subtypes of Rhabdomyosarcoma
- •12.2.4 Cytogenetics
- •12.2.5 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.2.5.1 Head and Neck Area
- •12.2.5.2 Genitourinary Tract Including Sarcoma Botryoides
- •12.2.5.3 Extremities and Trunk
- •12.2.5.4 Retroperitoneal Area
- •12.2.5.5 Rare Locations
- •12.2.6 Laboratory Diagnosis
- •12.2.7 Radiological Diagnosis
- •12.2.8 Staging/Grouping
- •12.2.9 Metastatic Spread
- •12.2.10 Therapy
- •12.2.10.1 Overview
- •12.2.10.2 Surgical Procedure
- •12.2.10.3 Radiotherapy
- •12.2.10.4 Chemotherapy
- •12.2.11 Special Locations
- •12.2.11.1 Head and Neck Area
- •12.2.11.2 Parameningeal Site
- •12.2.11.3 Orbit
- •12.2.11.4 Pelvic Area
- •12.2.11.5 Paratesticular Rhabdomyosarcoma
- •12.2.11.6 Retroperitoneal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- •12.2.11.7 Extremities
- •12.2.12 Prognosis
- •12.2.13 Therapy and Prognosis in Nonresponding or Relapsing Rhabdomyosarcoma
- •12.2.14 Secondary Tumors
- •12.3 Fibrosarcoma
- •12.3.1 Incidence
- •12.3.2 Location
- •12.3.3 Pathology and Cytogenetics
- •12.3.4 Differential Diagnosis
- •12.3.5 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.3.6 Therapy
- •12.3.6.1 Surgical Procedures
- •12.3.6.2 Radiotherapy
- •12.3.6.3 Chemotherapy
- •12.3.7 Follow-Up
- •12.3.8 Prognosis
- •12.4 Synovial Sarcoma
- •12.4.1 Incidence
- •12.4.2 Location
- •12.4.3 Pathology and Cytogenetics
- •12.4.4 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.4.5 Radiological Diagnosis
- •12.4.6 Therapy
- •12.4.6.1 Surgical Procedure
- •12.4.6.2 Radiotherapy
- •12.4.6.3 Chemotherapy
- •12.4.7 Prognosis
- •12.5 Liposarcoma
- •12.5.1 Incidence
- •12.5.2 Pathology and Cytogenetics
- •12.5.3 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.5.4 Therapy
- •12.5.4.1 Surgical Procedure
- •12.5.4.2 Radiotherapy
- •12.5.4.3 Chemotherapy
- •12.5.5 Prognosis
- •12.6 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
- •12.6.1 Incidence
- •12.6.2 Location
- •12.6.3 Pathology and Cytogenetics
- •12.6.4 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.6.5 Therapy
- •12.7 Leiomyosarcoma
- •12.7.1 Incidence
- •12.7.2 Location
- •12.7.3 Pathology
- •12.7.4 Clinical Manifestations
- •12.7.5 Therapy
- •12.7.6 Prognosis
- •12.8 Hemangiopericytoma
- •12.8.1 Incidence
- •12.8.2 Location
- •12.8.3 Pathology and Cytogenetics
- •12.8.4 Therapy
- •12.8.5 Prognosis
- •12.8.6 Congenital Hemangiopericytoma Variant
- •12.9 Malignant Fibrohistiocytoma
- •13: Osteosarcoma
- •13.1 Definition
- •13.2 Epidemiology
- •13.3 Location
- •13.4 Etiology and Tumor Genetics
- •13.5 Pathology
- •13.6 Clinical Manifestations
- •13.7 Metastasis
- •13.8 Evaluation
- •13.9 Radiology
- •13.10 Differential Diagnosis
- •13.11 Treatment
- •13.11.1 Treatment of Relapsed Disease
- •13.12 Prognosis
- •13.13 Complications
- •14: Ewing Sarcoma Family of Tumors
- •14.1 Definition
- •14.2 Epidemiology
- •14.3 Localization
- •14.4 Pathogenesis
- •14.5 Genetics
- •14.6 Pathology
- •14.6.1 Macroscopic Aspects
- •14.6.2 Microscopic Aspects
- •14.6.3 Immunohistochemistry
- •14.7 Clinical Manifestations
- •14.8 Metastases
- •14.9 Evaluation
- •14.10 Differential Diagnosis
- •14.11 Treatment
- •14.12 Prognosis
- •14.12.1 Complications
- •15: Retinoblastoma
- •15.1 Definition
- •15.2 Incidence
- •15.3 Etiology, Genetics, and Pathogenesis
- •15.4.1 Macroscopic Features
- •15.4.2 Microscopic Features
- •15.5 Clinical Manifestations
- •15.6 Differential Diagnosis
- •15.7 Therapy
- •15.7.1 Surgical Management
- •15.7.2 Chemotherapy
- •15.7.3 Chemothermotherapy
- •15.7.4 Radiotherapy
- •15.7.5 Laser Photocoagulation
- •15.7.6 Cryotherapy
- •15.7.7 Brachytherapy
- •15.8 Management of the Different Manifestations of Retinoblastoma
- •15.8.1 Unilateral Intraocular Retinoblastoma
- •15.8.2 Unilateral Extraocular Retinoblastoma
- •15.8.3 Bilateral Retinoblastoma
- •15.9 Prognosis
- •15.9.1 Risk of Secondary Tumors
- •16: Germ Cell Tumors
- •16.1 Definition
- •16.2 Incidence
- •16.3 Pathogenesis
- •16.4 Genetics
- •16.5 Histological Classification
- •16.6 Diagnostics
- •16.7 Therapy: Overview
- •16.8 Testicular Germ Cell Tumors and Subtypes
- •16.8.1 Testicular Yolk Sac Tumor
- •16.8.1.1 Macroscopic Features
- •16.8.1.2 Microscopic Features
- •16.8.1.3 Therapy
- •16.8.2 Testicular Teratoma
- •16.8.2.1 Histopathology
- •16.8.2.2 Therapy
- •16.8.3 Testicular Embryonal Carcinoma
- •16.8.4 Testicular Teratocarcinoma
- •16.8.5 Testicular Seminoma (in Adults)
- •16.9 Ovarian Tumors and Subtypes
- •16.9.1 Ovarian Teratoma
- •16.9.2 Ovarian Dysgerminoma
- •16.9.2.1 Macroscopic Features
- •16.9.2.2 Microscopic Features
- •16.9.2.3 Therapy
- •16.9.3 Ovarian Yolk Sac Tumor
- •16.9.5 Embryonal Carcinoma of the Ovary
- •16.9.6 Ovarian Gonadoblastoma
- •16.10 Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Subtypes
- •16.10.1 Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
- •16.10.2 Intracranial Teratoma
- •16.10.3 Mediastinal Teratoma
- •17: Hepatic Tumors
- •17.1 Forms and Frequencies
- •17.2 Incidence (Except Benign Hepatic Tumors)
- •17.3 Pathology and Genetics
- •17.3.1 Macroscopic Features
- •17.3.2 Microscopic Features
- •17.4 Clinical Manifestations
- •17.5 Laboratory Diagnosis
- •17.6 Radiological Diagnosis
- •17.7 Differential Diagnosis of Hepatoblastoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- •17.8 Staging
- •17.9 Therapy
- •17.9.1 Surgical Management
- •17.9.2 Liver Transplantation
- •17.9.3 Radiotherapy
- •17.9.4 Chemotherapy
- •17.10 Prognosis
- •18: Emergencies in Pediatric Oncology
- •18.1 Tumor Lysis and Hyperleukocytosis
- •18.1.1 General
- •18.1.2 Diagnosis
- •18.1.3 Treatment
- •18.2 Fever and Netropenia
- •18.2.1 General
- •18.2.2 Diagnosis
- •18.2.3 Treatment
- •18.2.4 Outlook
- •18.3 Hyperkalemia
- •18.3.1 General
- •18.3.2 Diagnosis
- •18.3.3 Treatment
- •18.4 Hypercalcemia
- •18.4.1 General
- •18.4.2 Diagnosis
- •18.4.3 Treatment
- •18.5 Airway Compression
- •18.5.1 General
- •18.5.2 Diagnosis
- •18.5.3 Treatment
- •18.6 Spinal Cord Compression
- •18.6.1 General
- •18.6.2 Diagnosis
- •18.6.3 Treatment
- •18.7.1 General
- •18.7.2 Diagnosis
- •18.7.3 Treatment
- •18.8 Pleural and Pericardial Effusion
- •18.8.1 General
- •18.8.2 Diagnosis
- •18.8.3 Treatment
- •18.9 Cardiac Tamponade
- •18.9.1 General
- •18.9.2 Diagnosis
- •18.9.3 Treatment
- •18.10 Hemolysis
- •18.10.1 General
- •18.10.2 Diagnosis
- •18.10.3 Treatment
- •18.11 Abdominal Emergencies and Abdominal Tumor
- •18.11.1 General
- •18.11.2 Diagnosis
- •18.11.3 Treatment
- •18.12 Hemorrhagic Cystitis, Dysuria
- •18.12.1 General
- •18.12.2 Diagnosis
- •18.12.3 Treatment
- •18.13 Acute Alteration of Consciousness
- •18.13.1 General
- •18.13.2 Diagnosis
- •18.13.3 Treatment
- •18.14 Seizures
- •18.14.1 General
- •18.14.2 Diagnosis
- •18.14.3 Treatment
- •19: Oncological Nursing Care
- •19.1 The Role of the Nurse in Pediatric Oncology
- •19.1.1 Direct Care
- •19.1.2 Nursing Care
- •19.2 Side Effects of Treatment
- •19.2.1 Nausea and Vomiting
- •19.2.1.1 Cause
- •19.2.1.2 Forms of Nausea and Vomiting
- •19.2.1.3 Symptoms
- •19.2.1.4 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.1.5 Treatment
- •19.2.2 Hair Loss
- •19.2.2.1 Causes
- •19.2.2.2 Symptoms
- •19.2.2.3 Treatment
- •19.2.2.4 Nursing Tips Concerning Hair Loss
- •Coverage of Costs for Hair Substitution
- •19.2.3 Stomatitis and Mucitis
- •19.2.3.1 Cause
- •19.2.3.2 Risk Factors
- •19.2.3.3 Symptoms
- •19.2.3.4 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.3.5 General Tips on Nursing Care
- •19.2.3.6 Treatment
- •19.2.4 Myelosuppression
- •19.2.4.1 Causes
- •19.2.4.2 Leukopenia
- •Prophylactic Care
- •Risk Factors
- •Treatment
- •19.2.4.3 Thrombocytopenia
- •Symptoms
- •Prophylactic Care
- •Treatment
- •19.2.4.4 Anemia
- •Symptoms
- •Prophylactic Care
- •Treatment
- •19.2.5 Loss of Appetite
- •19.2.5.1 Causes
- •19.2.5.2 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.6 Digestive Disorders (Constipation and Diarrhea)
- •19.2.6.1 Constipation
- •Causes
- •Prophylactic Care
- •Treatment
- •19.2.6.2 Diarrhea
- •Causes
- •Treatment
- •19.2.7 Neuropathy
- •19.2.7.1 Symptoms
- •19.2.7.2 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.7.3 Treatment
- •19.2.8 Fatigue
- •19.2.8.1 Causes
- •19.2.8.2 Symptoms
- •19.2.8.3 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.8.4 Treatment
- •Significance of Fatigue Nursing Care
- •19.2.9 Pain
- •19.2.9.1 Causes
- •19.2.9.2 Symptoms
- •19.2.9.3 Prophylactic Care
- •19.2.9.4 Treatment
- •19.3 Central Catheter Care
- •19.3.1.1 Complications
- •19.3.1.2 Considerations for Domestic PAC Management
- •19.3.1.3 Managing PAC
- •19.3.2 Broviac and Hickman Catheters
- •19.4 Chemotherapy
- •19.4.1 General
- •19.4.2 Administration
- •19.4.3 Protective Measures When Handling Chemotherapeutic agents
- •19.4.4 Extravasation
- •19.5 Giving Information to the Child and Parents
- •19.6 Care at Home
- •20.1 Significance for Contemporary Pediatric Oncology
- •20.2 Structure
- •20.2.1 Concepts
- •20.2.2 Staff
- •20.2.2.1 Medical and Nursing Staff
- •20.2.2.2 Child Psychiatry and Psychology
- •20.2.2.3 Social Work
- •20.2.2.4 Education in Hospital
- •20.3.1 Objectives
- •20.3.2 Procedure
- •20.3.2.1 Investigative Phase
- •Areas Investigated
- •20.3.2.2 Treatment Phase
- •20.3.3 Basic Attitudes
- •20.4 Problems and Possible Interventions
- •20.4.1 Before Diagnosis
- •20.4.1.1 Problems
- •20.4.1.2 Requirements
- •20.4.1.3 Reactions
- •20.4.1.4 Interventions
- •20.4.2 After Diagnosis
- •20.4.2.1 Problems
- •20.4.2.2 Requirements
- •20.4.2.3 Reactions
- •20.4.2.4 Interventions
- •20.4.3 Start of Therapy
- •20.4.3.1 Problems
- •20.4.3.2 Requirements
- •20.4.3.3 Reactions
- •20.4.3.4 Interventions
- •20.4.4 Course of Therapy
- •20.4.4.1 Problems
- •20.4.4.2 Requirements
- •20.4.4.3 Reactions
- •20.4.4.4 Interventions
- •20.4.5 Surgical Intervention
- •20.4.5.1 Problems
- •20.4.5.2 Requirements
- •20.4.5.3 Reactions
- •20.4.5.4 Interventions
- •20.4.6 Radiotherapy
- •20.4.6.1 Problems
- •20.4.6.2 Requirements
- •20.4.6.3 Reactions
- •20.4.6.4 Interventions
- •20.4.7 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- •20.4.7.1 Problems
- •20.4.7.2 Requirements
- •20.4.7.3 Reactions
- •20.4.7.4 Interventions
- •20.4.8 End of Therapy
- •20.4.8.1 Problems
- •20.4.8.2 Requirements
- •20.4.8.3 Reactions
- •20.4.8.4 Interventions
- •20.4.9 Long-Term Remission and Cure
- •20.4.9.1 Problems
- •20.4.9.2 Requirements
- •20.4.9.3 Reactions
- •20.4.9.4 Interventions
- •20.4.10 Relapse
- •20.4.10.1 Problems
- •20.4.10.2 Requirements
- •20.4.10.3 Reactions
- •20.4.11 Dying, Death, Mourning
- •20.4.11.1 Problems
- •20.4.11.2 Requirements
- •20.4.11.3 Reactions
- •20.4.11.4 Interventions
- •20.5 Treatment Team
- •20.6 Further Reading
- •Index
9 Brain Tumors |
97 |
|
|
•Extradural tumors
–Neuroblastoma
–Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
–Tumor of the vertebrae: eosinophilic granuloma, Ewing sarcoma (differential diagnosis: hematoma, inflammatory abscess, etc.)
•Symptoms:
–Compression symptoms: back pain, paraspinal muscle spasm, resistance to
trunk flexion, scoliosis, changes of reflexes, disturbances of walking, sensory deficiencies at dermatome level, decreased perspiration below tumor level, muscle weakness, positive Babinski sign, urinary or anal sphincter impairment (incontinence, urinary retention, obstipation), priapism
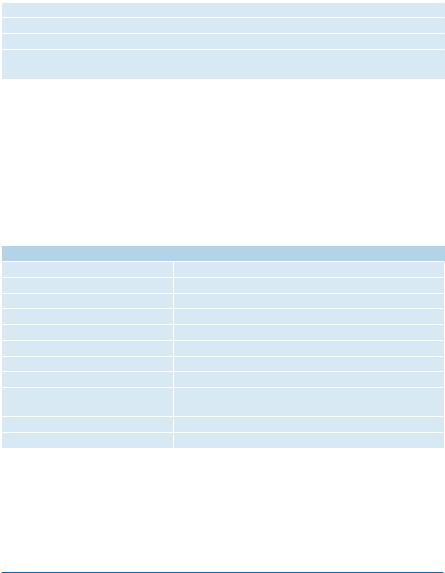
–The following list summarizes neurological signs, corresponding to different levels of spinal cord tumors
Neurological signs corresponding to different level of spinal cord tumors
C1–C3 |
Phrenic nerve paralysis (apnea) |
C3–C4 |
Weakness or inability to raise shoulders |
C5–C6 |
Weakness of arm abduction |
C7–C8 |
Weakness of elbow extension, of fingers |
T2–T12 |
Scoliosis, trunk weakness |
L1 |
Weakness of hip flexion |
L2 |
Weakness of hip abduction |
L3–L4 |
Weakness of knee extension |
L4–L5 |
Weakness of abduction and extension as well as dorsal |
|
flexion of ankle |
L5–S1 |
Weak hamstrings |
S1–S2 |
Ankle plantar flexion weakness |
–Tumor in foramen magnum area: stiffness of the neck, torticollis, cervical pain
–Tumor in cervical spinal channel: nystagmus
–Tumor in cauda equina area: negative reflexes of the lower extremities, muscle atrophy of the legs, urinary and defecation problems
9.7Radiological Diagnosis
9.7.1Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT)
•MRI and CT are the basic imaging techniques for brain tumors, with demonstration of intracranial structures, lesions, and solid and liquid components
•Intravenous application of contrast liquids provides detailed information
