
Reference_book_on_Higher_Mathemanics_Part_I_F
.pdf
A function f(x) is decreasing if |
|
f (x1 ) > f (x2 ) |
whenever x1 < x2 |
|||
A function f(x) is constant |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( f (x) = C ) if |
|
f (x1 ) = f (x2 ) |
for all x1 and x2 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
A function f (x) is an even |
|
f (− x) = f (x) for x D(x) and − x D(y) |
||||
function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A function f (x) is called an odd |
|
f (− x) = − f (x) for x D(x) and − x D(y) |
||||
function if |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A function f (x) is a periodic |
|
f (x + P) = f (x) for x D(x) |
||||
function with period P if |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Composite function |
|
f (g(x)) − function of function |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
The graphs of the given function |
f (x) and its inverse f −1 (x) are symmetric one to |
|||||
other with respect to the line y = x. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linear function |
|
y = ax + b |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Quadratic function |
|
y = ax 2 + bx + c |
||||
The graph of a quadratic function |
|
parabola |
|
|
||
Standard form of a quadratic |
|
y = a(x − x0 ) |
2 |
+ y0 |
||
function |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hyperbola |
|
y = |
a |
, n N |
||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
x n |
|
|
|
An exponential function |
|
y = a x , a > 0, a ≠ 1 |
||||
Logarithmic function |
|
y = loga x , a > 0, a ≠ 1 |
||||
Table for Finding the Domain of a Composite Function
y = |
|
|
( |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
f |
x |
2k f (x) |
|
x |
tan f |
x |
cot f |
x |
arcsin f |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
loga f |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x , |
||||||||||||||
|
|
g(x) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
arccos f (x) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
D(y ): |
g(x) ≠ 0 |
f (x) ≥ 0 |
f (x) > 0, |
|
f (x) |
≠ π + πn, |
f (x) ≠ πn, |
|
f (x) |
|
≤ 1 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a > 0, a ≠ 1 |
n Z |
|
|
n Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21
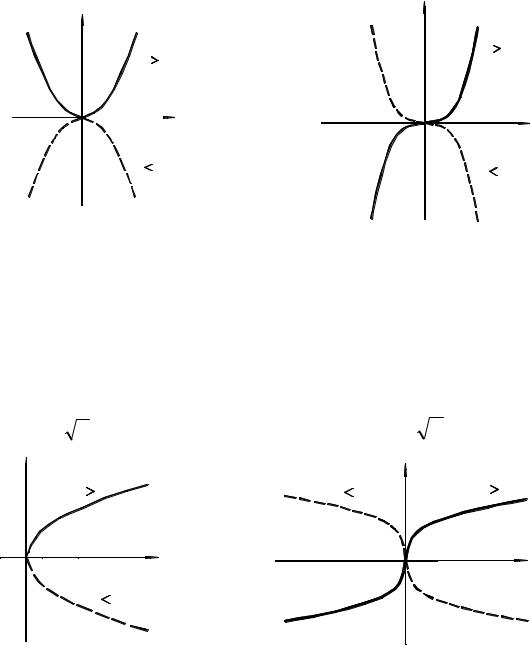
A.Graphs in the Cartesian System of Co-ordinates
I.Power Functions
1. Parabolas
a). y = ax2n , n = 1,2,K |
|
y |
|
a |
0 |
|
x |
0 |
|
a |
0 |
Domain of definition:
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞)
Range of values
[0, ∞), a > 0
E(y) = (− ∞ ] <
,0 , a 0
b). y = ax2n+1 , n = 1,2,K |
|
y |
|
a |
0 |
|
x |
0 |
|
a |
0 |
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞) |
|
E(y) = (− ∞,+∞)
c). y = a2 n x , n = 1,2,L |
||
y |
|
|
a |
0 |
|
|
|
x |
0 |
|
|
|
a |
0 |
d). y = a 2 n +1 x , n = 1,2,L |
|||
a 0 |
y |
a |
0 |
|
|||
|
|
|
x |
|
0 |
|
|
D(y) = [0,+∞) |
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞) |
E(y) = [0,+∞), a ≥ 0 |
E(y) = (− ∞,+∞) |
|
|
(− ∞,0], a ≤ 0 |
|
22

2. Hyperbolas
a). y = |
a |
, n |
= 1,2,K |
|
x 2n−1 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
a 0 |
a |
0 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
D(y) = (− ∞,0) (0,+∞) |
|
|||
E(y) = (− ∞,0) (0,+∞)
II. Exponential Function
y = a x , a > 0, a ≠ 1 |
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
a |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
a |
1 |
|
|
|
x |
0 |
|
|
|
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞) |
|
|
|
E(y) = (0,+∞)
b). y = |
a |
, n = 1,2,K |
|
|
x 2n |
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
a |
0 |
|
|
|
x |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
a |
0 |
D(y)= (− ∞,0) (0,+∞)
(0,+∞), a > 0
E(y) = (− ∞ ) <
,0 , a 0
III. Logarithm Function
y = log a |
x, a > 0, a ≠ 1 |
||||
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
a |
1 |
D(y) = (0,+∞)
E(y) = (− ∞,+∞)
23

IY. Trigonometric Functions
1). Sinusoid (sine curve, harmonic curve) y = sin x
|
|
y |
|
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞), |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E(y) = [−1,+1] |
|
|
|
|
x |
-π |
π |
0 |
π |
π |
|
--- |
|
-- |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
2). Cosine curve |
y = cos x |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
D(y) = (− ∞,+∞), |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
E(y) = [− 1,+1] |
|
-π |
π |
0 |
π |
π |
|
--- |
-- |
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
3). Tangent curve |
y = tan x |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
π |
π |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D(y) = |
|
+ kπ , |
+ kπ , k = 0,±1,±2,K |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
E(y ) = (− ∞,+∞) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-π |
π |
0 |
π |
π |
|
|
|
|
|
|
--- |
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4). Cotangent curve |
y = cot x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
y |
|
|
D(y) = (kπ , (k + 1π )), k = 0,±1,±2,K |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
x |
E(y) = (− ∞,+∞) |
||||
-π |
π |
0 |
π |
π |
|
|
|
|
|
|
--- |
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24
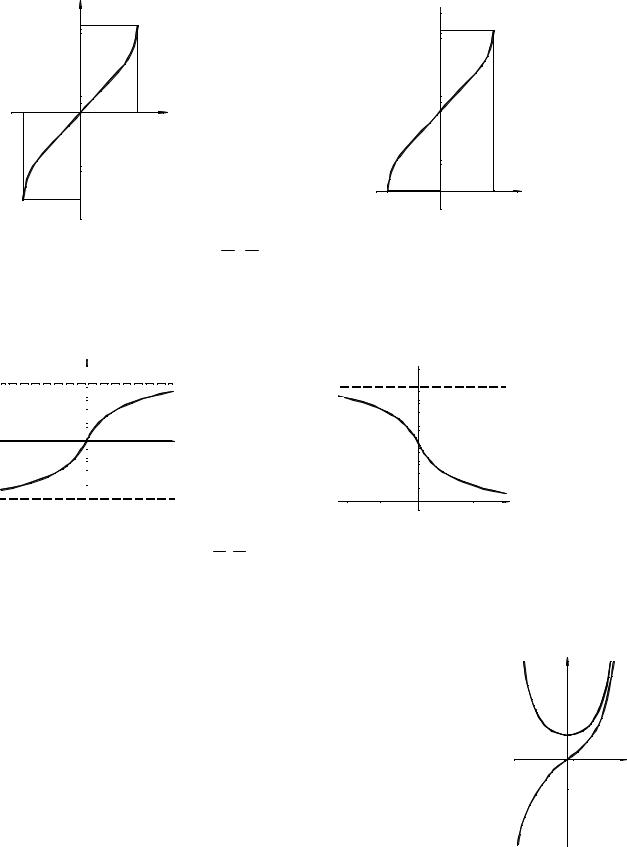
Y. Inverse Trigonometric Functions
1). y = sin −1 x = arcsin x |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
π |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
π |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
--- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
( |
y |
) |
[ |
] |
E(y) = |
− π |
, |
π |
||
|
|
= − |
1;1 |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
3). y = tan −1 x = arctan x |
|
|
y |
|
|
π |
|
|
-- |
|
|
2 |
|
|
x |
|
|
0 |
|
|
π |
|
|
--- |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
π |
π |
D(y ) = (− ∞,+∞), E(y) = − |
, |
|
|
2 |
2 |
2). y = cos −1 x = arccos x |
||
|
y |
|
|
π |
|
|
π |
|
|
-- |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
x |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
D(y) = [− 1;1], E(y) = [0;π ] |
||
4). y = cot −1 x = arc cot x |
y |
π |
π |
-- |
2 |
x |
0 |
D(y ) = (− ∞,+∞), E(y) = (0,π )
YI. Hyperbolic Functions |
|
|
|||
1). y = sinh x (shx) |
2). y = cosh x (chx) |
||||
sinh x = |
e x − e− x |
cosh x = |
e x + e − x |
||
2 |
|
2 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
D(sinh x) = (− ∞,+∞) |
D(cosh x) = (− ∞,+∞) |
||||
E(sinh x) = (− ∞,+∞) |
E(cosh x) = [1,+∞) |
||||
y |
y=chx |
x |
0 |
y=shx |
25
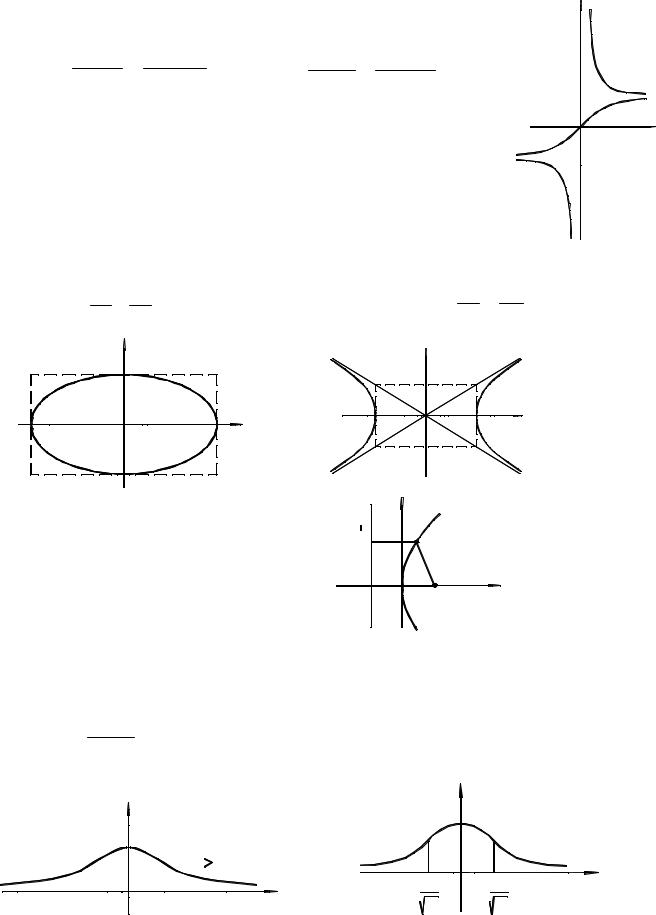
3). y = tanh x |
(thx) |
|
|
4). y = coth x |
(cthx) |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
tanh x = sinh x = e x |
− e− x |
|
coth x = cosh x = e x + e − x |
|
|
|
|
y=cthx |
||||
cosh x |
e x |
+ e− x |
|
sinh x |
e x − e − x |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
D (tanh x ) = (− ∞ ,+∞ ) |
|
D(coth x) = (− ∞,0) (0,+∞) |
|
|
y=thx |
0 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
E(tanh x) = (− 1,+1) |
|
|
E(coth x) = (− ∞,−1) (1, ∞) |
|
y=cthx |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
YII. Curves of the Second Order |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
x 2 |
|
y 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
x 2 |
|
y 2 |
|
|
1. Ellipse: a 2 |
+ b 2 = 1 |
|
2.Hyperbola: |
a 2 |
− b 2 |
= 1 |
|
|||||
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-a |
|
|
a |
x |
|
-a |
|
|
a |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
y 2 = 4 px |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
p |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Parabola |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
F (0, |
p) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4. Witch of Agnesi:
y =
k
1 + x 2
|
y |
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
|
k |
0 |
|
|
|
x |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
|
5.Curve of Gauss:
y = e− x2 |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
x |
- |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
||
26
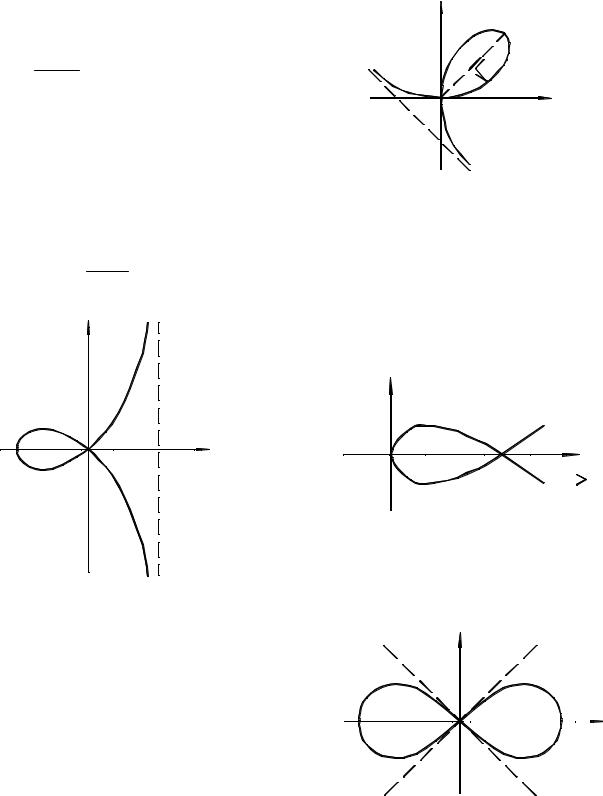
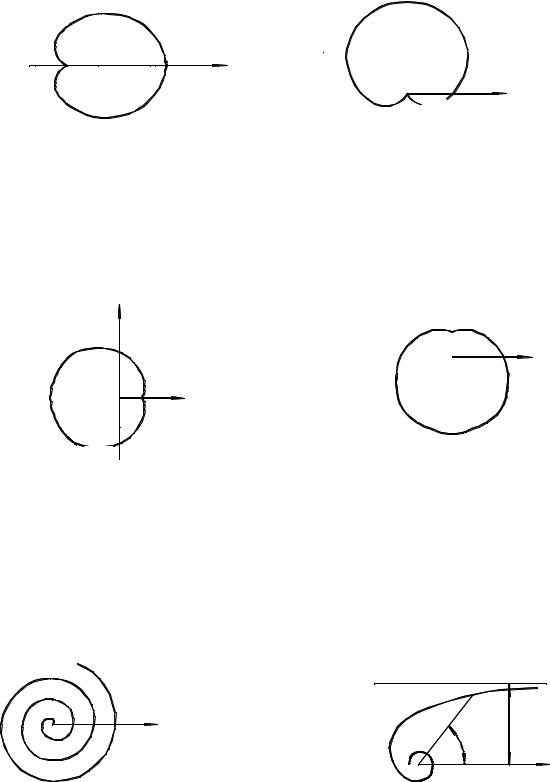
6. Loops
a). Folium of Descartes
x3 + y 3 − 3axy = 0 , or
3at
1 + t 3x =
|
3at 2 |
|
|
||
y = |
|
|
1 + t |
2 |
|
|
|
|
b) |
y 2 |
= x 2 a + x |
|
|
|
a − x |
|
|
|
y |
|
-a |
|
a |
x |
|
|
0 |
|
7. Lemniscate of Bernoulli
(x 2 + y 2 )2 = a 2 (x 2 − y 2 )
or
r 2 = a 2 cos 2ϕ
|
y |
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
0 |
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
c). a 2 y 2 = x(a − x 2 ), a > 0
|
y |
|
|
|
|
x |
|
0 |
a |
a |
0 |
|
|
|
y |
|
x |
0 |
a |
|
27
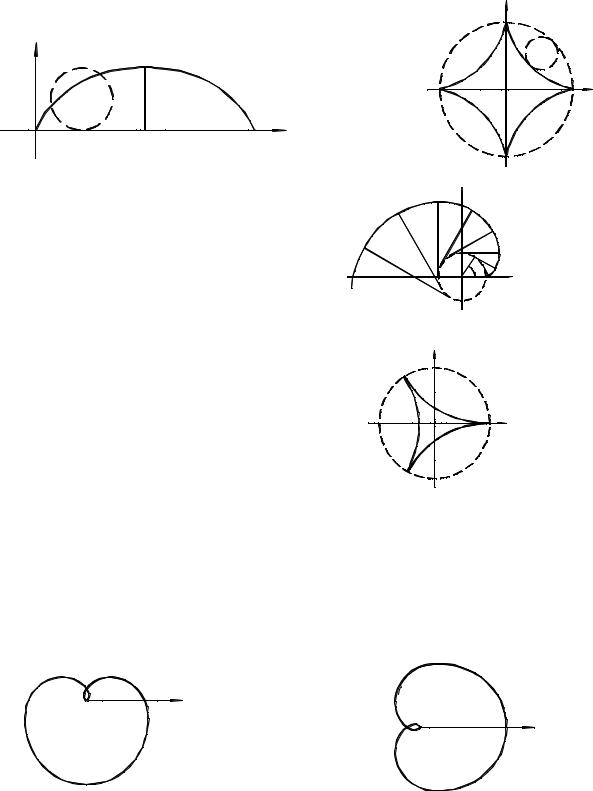
B. Curves Given by Parametric Equations
I. Cycloid:
x = a(t − sin t ) |
|
|
, a > 0 |
y = a(1 |
− cost ) |
y
|
2 a |
|
x |
0 |
2π a |
III. Evolvent of Circle:
x = a(cos t + t sin t ) |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, a > 0 |
|
||||
y |
= a(sin t − t cos t ) |
|
|
|
||||||||
IY. |
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|||
|
x = R cos |
|
|
|
|
2 |
+ cos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
t |
|
||||
|
y = R sin |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
− sin |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
3 |
t |
x = a cos |
|
||
II. Astroid: |
3 |
, a > 0 |
|
|
|
|
t |
y = a sin |
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
a |
|
-a |
a |
x |
|
0 |
|
|
-a |
|
y |
|
a |
|
t |
x |
0 |
|
y |
x |
0 |
C. Curves in the Polar System of Coordinates
1. ρ = a sin |
3 |
ϕ |
II. ρ = a cos |
3 |
ϕ , |
||||||
|
|
|
, |
|
|||||||
|
3 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
a > 0,ϕ [0,3π ] |
|
3π |
3π |
|
|
||||||
a > 0,ϕ − |
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
0 |
ρ |
0 |
ρ |
28
|
III. Cardioids |
1) ρ = a(1 + cosϕ ), a > 0 |
2) ρ = a(1 + sin ϕ ), a > 0 |
|
2 a |
|
0 |
ρ |
0 |
|

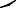
 a ρ
a ρ
IY. Limacons
`1). ρ = a − cosϕ , a > 1
y |
a |
ρ |
0 |
2). ρ = a − sinϕ , a > 1
ρ
|
Y. Spirals |
||
1). ρ = aϕ, a > 0 |
2). ρ = |
a |
, a > 0 |
|
|||
|
ϕ |
||
0 |
|
M |
ρ |
a |
|
ρ |
|
ϕ |
|
|
|
0 |
|
ρ |
29
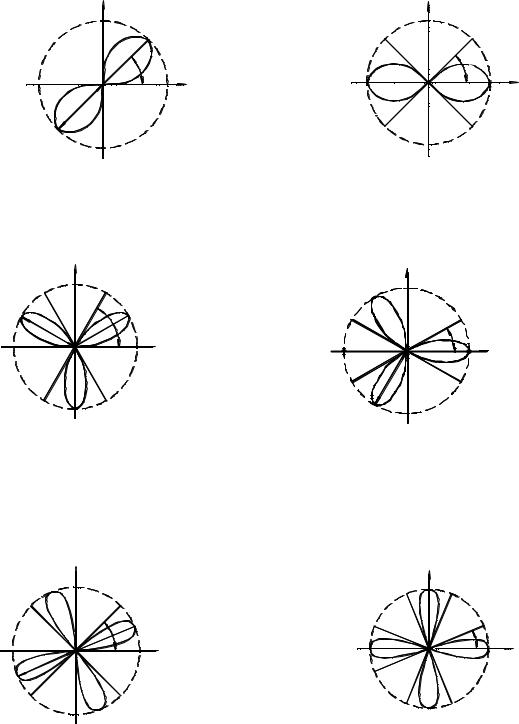
1). ρ = a sin 2ϕ , a > 0 |
|
y |
|
π |
|
-- |
x |
4 |
|
0 |
ρ |
a |
|
3). ρ = a sin 3ϕ, a > 0 |
|
y |
|
π |
|
-- |
|
3 |
|
a |
x |
|
|
0 |
ρ |
YI. Roses
2). ρ = a cos 2ϕ , a > 0 |
|
y |
|
π |
|
-- |
|
4 |
|
a |
x |
0 |
ρ |
|
4). ρ = a cos 3ϕ , a > 0 |
||
y |
|
|
|
π |
|
|
- |
|
|
6 |
x |
|
|
|
0 |
|
ρ |
|
|
|
a |
|
|
5). ρ = a sin 4ϕ, a > 0 |
6). ρ = a cos 4ϕ , a > 0 |
|
|
y |
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
π |
|
|
|
|
-- |
π |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
x |
a |
x |
a |
0 |
ρ |
0 |
ρ |
|
||||
|
|
30
