
Reference_book_on_Higher_Mathemanics_Part_I_F
.pdfANALYTIC GEOMETRY
Vocabulary
angular relations – угловые соотношения asymptote - асимптота
axis of the parabola - ось параболы
canonical equations – канонические уравнения directrix - директриса
distance from a point to – расстояние от точки до eccentricity – эксцентриситет
ellipse - эллипс
ellipse’s focal axis – фокальные оси эллипса ellipsoid - эллипсоид
elliptic cone – эллиптический конус elliptic cylinder – эллиптический цилиндр
elliptic paraboloid – эллиптический параболоид general equation – общее уравнение
hyperbolic cylinder – гиперболический цилиндр hyperbolic paraboloid – гиперболический параболоид
intercept form of the equation of a plane – уравнение плоскости в отрезках major axis – большая ось
normal vector - нормальный вектор
one-sheeted hyperboloid – однополостный гиперболоид parabola – парабола
parabolic cylinder – параболический цилиндр position vector - направляющий вектор quadric surface – поверхность второго порядка second order curves – кривые второго порядка semimajor axis - большая полуось
slope equation - уравнение с угловым коэффициентом standard parametric equations – параметрические уравнения
two-points equation of a straight line – уравнение прямой через две точки two-sheeted hyperboloid – двуполостный гиперболоид
vector equation – векторное уравнение vertex of the parabola – вершина параболы
41
№ |
Names, definitions, theorems |
|
|
|
|
Equations and formulas |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A plane in a space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
The equation for the plane through the |
|
A(x − x0 ) + B(y − y0 ) + C(z − z0 ) = 0 |
|||||||||||||||||||
1. |
point M (x0 ; y0 ; z0 ) normal to the |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
vector |
|
= (A, B, C ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Standard equation of a plane π |
|
π : Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 |
|||||||||||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
= (A; B; C ) π |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
n |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
3 |
Equation of a plane passing through |
|
x − x1 |
|
y − y1 |
z − z1 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
points P (x ; y ; z ), |
P (x |
|
; y |
|
; z ), |
|
x2 − x1 |
y2 − y1 |
z2 − z1 |
= 0 |
|||||||||||
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
P3 (x3 ; y3 ; z3 ). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x3 − x1 |
y3 − y1 |
z3 − z1 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
4 |
Intercept form of the equation of a |
|
|
|
x |
+ |
y |
+ |
z |
= 1 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
plane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
b c |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
5The distance from the point
|
|
P(x0 ; y0 ; z0 ) to the |
plane |
d (P,π ) = |
|
|
Ax0 + By0 + Cz0 + D |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
π : Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
A2 + B 2 + C 2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Let |
|
1 = (A1 ; B1 ; C1 ) - normal vector of a plane π1 , аnd |
|
|
|
2 = (A2 ; B2 ; C2 ) - normal |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
n |
n |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
vector of a plane π 2 , then there are relations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Conditions of the perpendicularity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
6 |
|
of the planes: π1 π 2 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
π1 π 2 A1 A2 + B1 B2 + C1C2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
n |
n |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conditions of the parallelism of |
π1 |
|
|
|
π 2 A1 |
= B1 = C1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
the planes: π1 |
|
|
|
|
π 2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
|
B2 C2 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
|
The angle between |
the planes |
cos (π1 ^π 2 ) = |
|
cos ( |
|
1 , ^ |
|
2 ) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
n |
n |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
(π1 ^π 2 ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
A straight line in a space
Let a straight line lpasses the point M (x0 ; y0 ; z0 ) parallel to a vector s = (m; n; p),
( |
|
− directed vector of l) |
then: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
9 |
|
|
Vector equation of a |
straight line l |
r = r0 |
+ t s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
l : |
x − x |
0 |
= |
|
y − y |
0 |
= |
z − z |
0 |
|
||||||
10 |
Canonical equations of a straight line l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
m |
|
|
|
n |
|
p |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42
|
|
x = x0 |
+ mt |
11 |
Standard parametric equations of a |
l : y = y0 |
+ nt |
|
straight line l |
z = z0 |
+ pt |
|
|
Let s1 = (m1 ; n1 ; p1 )- direction vector of a straight line l1 , аnd s2 direction vector of a straight line l 2 , then there are relations:
= (m2 ; n2 ; p2 ) -
12 |
Conditions of the parallelism of the |
l |
1 |
|
l |
2 |
|
m1 |
= |
|
n1 |
= |
p1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
m2 |
|
n2 |
p2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
straight lines: l1 |
|
l 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
s |
1 |
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
Conditions of the |
|
perpendicularity of |
l1 l 2 m1m2 + n1n2 + p1 p2 = 0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
the straight lines: |
|
l1 l 2 |
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
s |
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
14 |
The angle |
|
between |
the straight |
cos (l1^ l 2 ) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
m1m2 + n1n2 + p1 p2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
lines: cos (l |
|
^ l |
|
) = |
|
cos ( |
|
, ^ |
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
s |
s |
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m 2 |
+ n 2 |
+ p 2 |
|
|
m 2 + n |
2 |
+ p |
2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A plane and a straight line in a space
Let l : |
x − x0 |
= |
y − y0 |
= |
|
z − z0 |
and π : Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 be given, then: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
m |
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
p |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
Parallelism of a straight line l and a |
π |
|
|
l Am + Bn + Cp = 0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
plane π : π |
|
|
l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
n |
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
π l |
A |
= |
B |
= |
C |
|
|
|
|
||||||
16 |
|
Conditions of the perpendicularity of |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m n |
p |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
a straight line l and a plane π : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
π l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
n |
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Angle ϕ between a straight line l |
sin (π ^ l) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17 |
|
and a plane π : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Am + Bn + Cp |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
sin (π ^ l) = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
cos (n, ^ s ) |
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 + B 2 + C 2 |
|
m 2 + n 2 + p 2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43

A straight line in a plane
The first group of equations of a straight line (with normal vector n = (A, B))
|
The equation of a straight line |
|
A(x − x0 ) + B(y − y0 ) = 0 |
|||||||||
18 |
through the point P0 (x0 ; y0 ) with the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
normal vector |
|
= (A; B). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
19 |
A general equation of a straight |
|
Ax + By + C = 0 |
|||||||||
|
line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
20 |
A distance from a point P0 (x0 ; y0 ) to a |
d = |
|
Ax0 + By0 + C |
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
straight line Ax + By + C = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
A2 + B 2 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Intercept form of the equation of a |
|
x |
+ |
y |
= 1 |
||||||
21 |
straight line |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
a b |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
The second group of equations of a straight line (with direction vector s = (m, n))
22 |
A vector equation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r = r0 + t s , |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
x = x0 + mt |
|||||||||||
23 |
A parametric equations |
|
|
+ nt |
||||||||||
|
|
|
y = y0 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
x − x0 |
= |
y − y0 |
|
|
|||||||
24 |
A canonical equation |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
m |
|
|
|
|
n |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
x − x1 |
= |
y − y1 |
|
||||||||
25 |
A two-points equation |
|
x2 − x1 |
y2 − y1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The third group of equations of a straight line in a plane: |
|
|
the straight line with a slope ( k = tan ϕ , ϕ = l Ox ) |
|
|
|
|
26 |
the point – slope equation of a straight |
y − y0 = k (x − x0 ) |
|
line |
|
27 |
the slope-intercept equation of a straight |
y = kx + b |
|
line |
|
|
44 |
|
Angular relations between straight lines l1 and l 2
A1 |
= |
B1 |
||
|
|
|
||
A2 |
B2 |
|||
|
||||
Conditions of parallelism of straight lines |
l1 |
|
|
|
l 2 |
m1 |
|
= |
|
n1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
28 l1 and l 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m2 |
|
|
|
|
n2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k |
1 |
= k |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Conditions of |
the |
|
|
|
|
perpendicularity of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
lines l1 and l 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 A2 + B1 B2 = 0 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
l1 l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 m1m2 + n1n2 = 0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= − |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k1 |
|
k 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Finding an angle θ between straight lines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 A2 + B1 B2 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
l1 and l 2 : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cosθ = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A12 |
+ B12 |
|
|
|
|
A22 + B22 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
n2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
cosθ |
|
cos n1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m1m2 + n1n2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
= |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
cosθ |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
cosθ |
|
cos s1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m1 |
|
+ n1 |
|
|
m2 |
+ n2 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
tan ϕ1 − tan ϕ 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
− k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
tanθ = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tanθ |
= |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
1 + tan ϕ1 tan ϕ 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 + k |
|
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
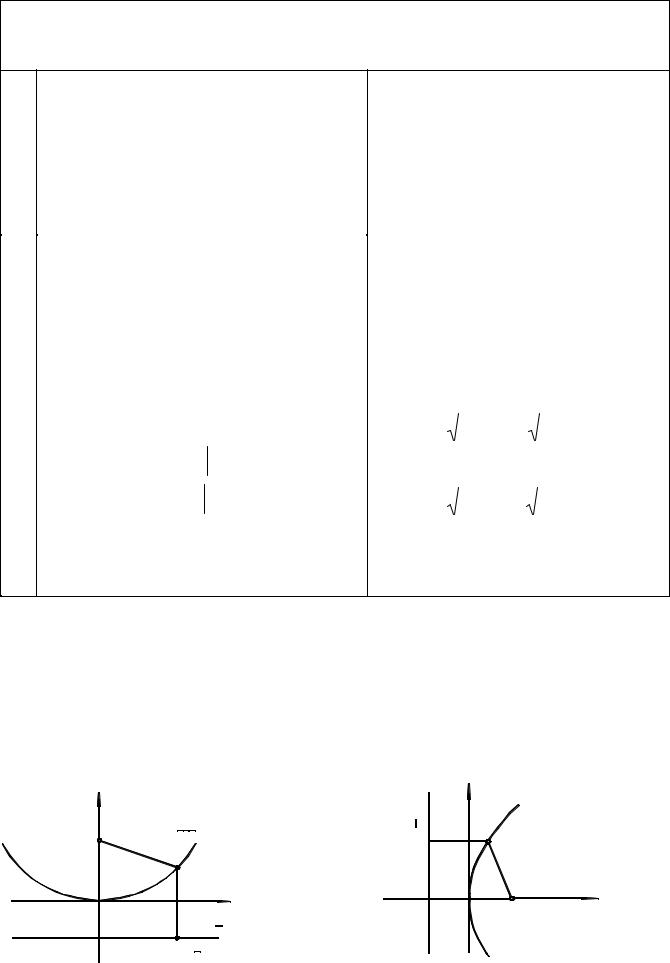
SECOND ORDER CURVES
Parabolas
x 2 = 4 py |
y 2 = 4 px |
y |
|
|
|
|
|
y |
y2 = 4 px |
|
|
|
|
|
|
p |
|||
|
|
|
x2 |
|
|
|
|
|
F(0, p) |
y = |
|
|
= |
|
|
||
4p |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
P(x, |
y) |
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
x |
Elli |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
|
|
F (0, |
p) |
||
|
|
|
Q (x, |
p) |
pse: |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Directrix |
y = p |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
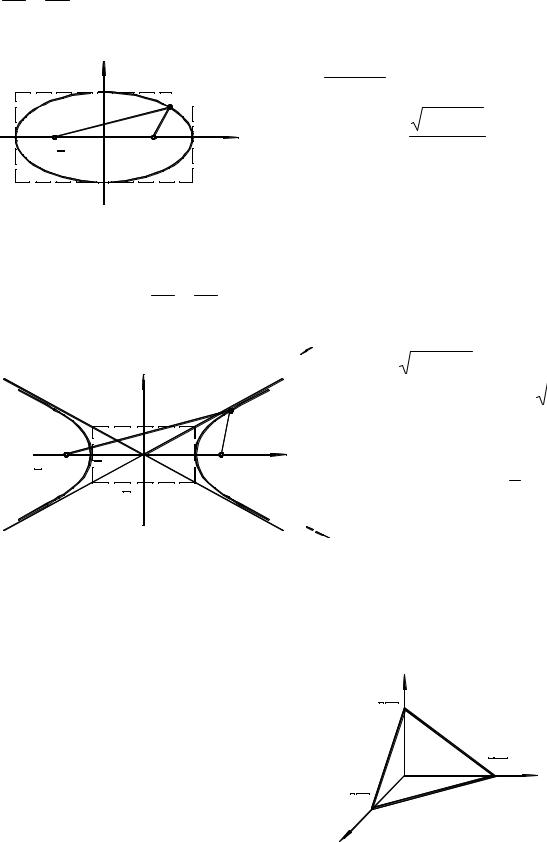
x 2 |
+ |
y |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a 2 |
|
b |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
P(x, y) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
F |
( |
c, 0) |
0 |
F |
( , |
) |
a |
||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
c |
0 |
|
|
|||
foci F1 (− c,0) and F2 (c,0) , where c = 
 a 2 − b 2
a 2 − b 2
a 2 − b 2
eccentricity: e =
a
Hyperbola: |
x 2 |
− |
y |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
a 2 |
|
b |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bx |
|
||
|
|
y |
|
|
y |
= |
a |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
b |
|
|
|
P(x , y) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
F ( c, 0) |
a |
0 |
a |
|
F(c, 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
= |
b |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
1.Planes
1)A General Equation of a Plane
Ax + By + Cz + D = 0
Foci F1 (− c,0) and F2 (c,0), where
c = a 2 + b 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eccentricity: |
e = |
c |
= |
|
a 2 |
+ b 2 |
|
a |
|
|
a |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Asymptotes y = ± b x
a
|
z |
D |
|
C |
|
|
D |
O |
B |
|
D |
y |
A |
|
x
46
2) Planes which are Parallel to One of the Coordinat Axis
a) π1 |
|
Oy |
b)π 2 |
|
Oz |
c)π 3 |
|
Ox |
π1 :Ax + Cz + D = 0 |
π 2 :Ax + By + D = 0 |
π 3 :By + Cz + D = 0 |
||||||
|
z |
|
|
z |
|
|
|
D |
|
||
D |
|
z |
|
||
|
C |
|
|||
C |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
D |
|
D |
|
|
|
|
B |
||
O |
O |
B |
O |
||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
D |
y |
y |
|
y |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
x |
x |
D |
x |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
3) Planes which are Passing through One of the Axis of Coordinates
a) Oy π 1 |
b)π 2 Oz |
c)π 3 Ox |
π1 :Ax + Cz = 0 |
π 2 :Ax + By = 0 |
π 3 :By + Cz = 0 |
z |
O |
y |
x
z |
z |
O |
O |
y |
y |
x |
x |
4) Planes which are Parallel to One of the Coordinat Planes
a) π 1 |
|
xOz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b)π 2 |
|
yOz |
|
c)π 3 |
|
xOy |
||||||
π1 : y = D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
π 2 : x = D |
|
π 3 : z = D |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z |
|
z |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
O |
|
|
y |
||
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
D |
x |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
47
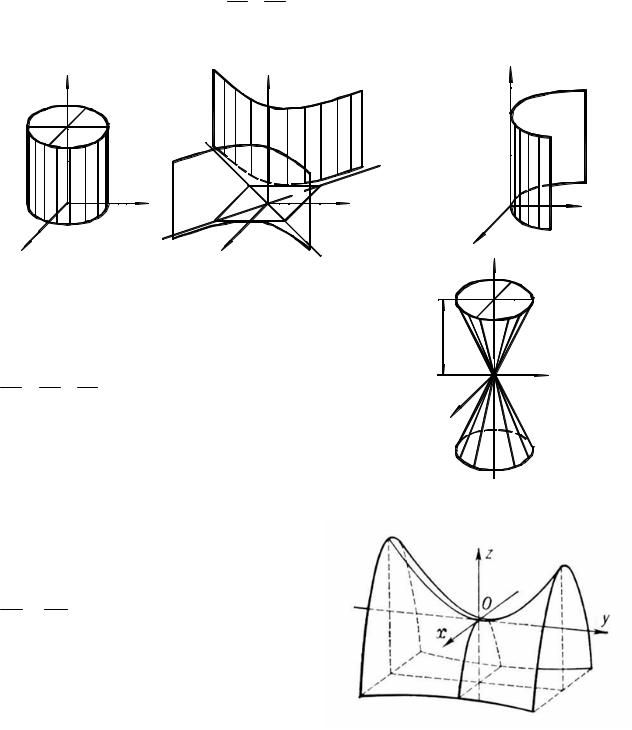
2. Quadric Surfaces
Elliptic Cylynder
х |
2 |
+ |
у |
2 |
= 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
а2 |
b2 |
|||||
|
|
|||||
z |
b |
a |
y |
x |
Elliptic Cone
х2 + у2 − z 2 = 0 а2 b2 c2
Hyperbolic Cylinder
х2 − у2 = 1
а2 b2
z |
|
b |
y |
|
|
a |
|
x |
|
Parabolic Cylinder
x 2 = 2 py |
z |
y |
x |
z |
b |
a |
c |
y |
x |
Hyperbolic Paraboloid
х2 − у2 = 2z
pq
48
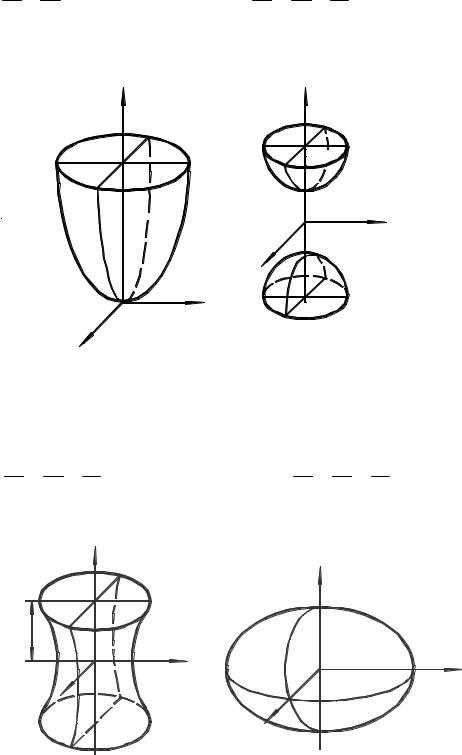
Elliptic Paraboloid
х2 |
+ у2 |
= z |
а2 |
b2 |
|
|
|
z |
|
|
b |
|
|
a |
|
|
y |
|
|
x |
Two-sheeted Hyperboloid
х2 + у2 − z 2 = −1
а2 b2 c2
|
z |
a |
b |
|
y |
x |
|
One-sheeted Hyperboloid |
Ellipsoid |
х2 |
у2 |
z 2 |
х2 |
+ |
у2 |
+ |
z 2 |
= 1 |
+ |
− |
= 1 |
а2 |
b2 |
c2 |
|||
а2 |
b2 |
c2 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
z |
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c |
|
|
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y |
|
|
y |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
x |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
49
LIMITS
Vocabulary approach x0 - достигать x0
arbitrarily number – произвольное число
comparison of infinitesimals – сравнение бесконечно малых deleted neighborhood – выколотая окрестность
equivalent infinitesimals – эквивалентные бесконечно малые however small – как угодно малый
indeterminacy - неопределенность
infinitely large function – бесконечно большая функция infinitesimal – бесконечно малая
infinitesimal of higher order – бесконечно малая более высокого порядка infinitesimal of the same order – бесконечно малые одного порядка left-hand limit - левосторонний предел
limit of a sequence – предел последовательности neighborhood – окрестность
one-sided limits – односторонние пределы reciprocal – обратный по величине remarkable limit – замечательный предел right-hand limit - правосторонний предел strip - полоса
tend to x0 - стремиться к x0
Definition of a Limit of a Function
y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lim f (x ) = L : L is the limit of the function |
f (x) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
ε |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x→ x0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f(x) lies in here |
as x tends to x0 (approaches x0 ) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Remember: lim f (x) = f (x0 ) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ε |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x0 |
x |
|
x→ xo |
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x0 D |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
x0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
δ |
|
|
|
x0 |
|
|
|
δ |
|
|
|
|
& |
(x0 ): |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
for all x=x0 in here |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lim f (x ) = L ε > 0 U δ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
x→ x0 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
& |
|
f (x ) − L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
< ε |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x U δ (x0 ) |
|
|
||
where |
& |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
U δ (x0 )is deleted neighborhood of a point x0 . |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
50
