
Reference_book_on_Higher_Mathemanics_Part_I_F
.pdfLinear Algebra
Vocabulary
addition (subtraction) of matrices – сложение (вычитание матриц) adjoint matrix– присоединенная матрица
augmented matrix – расширенная матрица capital letter – заглавная буква
check the equality – проверить равенство
cofactor of an element A - алгебраическое дополнение элементаaij
column – столбец
compatible system – совместная система
Cramer’s Rule – правило Крамера determinant - определитель
diagonal matrix – диагональная матрица dimension – размерность
elementary operations on matrices – элементарные операции над матрицами general case – общий случай
homogeneous system of equations – однородная система уравнений inverse of matrix – обратная матрица
lowercase letter (small letter) – строчная буква matrix (matrices) – матрица (матрицы) matrix form – матричный метод
matrix of order n – матрица порядка n minor – минор
multiplication of matrices – умножение матриц
multiplying of a matrix by a number – умножение матрицы на число nonsingular - невырожденный
principal (main) diagonal – главная диагональ rank of matrix – ранг матрицы
row – строка
square matrix – квадратная матрица supplement – дописать, добавить
system of n linear equation in n unknowns – система n линейных уравнение с n
неизвестными the expanding determinant by – разложение определителя по transformation Z through X - преобразование Z через X transposed matrix – транспонированная матрица
triangular matrix – треугольная матрица unique solution – единственное решение unit-matrix – единичная матрица
31

Matrices, determinants, linear systems
Titles, definitions, theorems |
Algebraic form |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
• A rectangular array of numbers is called |
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
a |
L a |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
a matrix of [m× n] (read m by n) |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
dimension. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A = |
a21 |
|
|
a22 |
L a2n |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
• The element in the i-th row and j-th |
|
L |
|
|
|
L |
L |
L |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
column of a matrix can be represented as |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
j = 1, n. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
aij : A = aij |
, i = 1, m, |
|
|
|
|
am1 |
|
|
am2 |
L amn |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Transposed matrix |
|
|
|
a |
|
|
L a |
T |
a |
L a |
m1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L L L |
= L L L |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
am1 |
|
|
amn |
a1n |
|
amn |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
a |
L a |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Square matrix of order n |
A = |
a21 |
|
a22 |
L a2n |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
L L L |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
an2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
an1 |
|
L ann |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The diagonal containing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Principal (main) diagonal of a square |
a11, a22 ,K, an −1n −1, ann |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
matrix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
0 |
|
L |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Diagonal matrix |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
a21 |
L |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
L L L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L ann |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
L 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Unit-matrix E or I |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
L 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
I = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L L L L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
L 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
A = (aij ), B = (bij ), i = |
|
|
, j = |
|
then |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
Let |
1, m |
1, n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Equality of matrices |
A = B |
A = B aij = bij , i = 1, m , j = 1, n |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sum of matrices of the same dimension |
C = (cij |
), where cij |
= aij |
+ bij , |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
A+B = C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i = 1, m , j = 1, n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Difference of matrices of the same |
D = (d ij ), where d ij |
= aij |
− bij , |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
dimension A - B = D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
i = 1, m , j = 1, n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32
Product of a matrix A by a number λ : |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
λA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, i = 1, m , j = 1, n |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
λA = λaij |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Determinants: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
• det a11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• det a11 = a11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
a |
|
a |
|
= |
|
a |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
a |
|
= a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
• det |
11 |
|
12 |
|
|
11 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
11 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
a |
22 |
|
|
21 |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a21 |
a22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a21 |
a22 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
a21 |
|
a |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
a |
a |
|
a |
a |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
a |
a |
a |
a a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
11 |
|
|
12 |
13 |
|
11 |
|
12 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
|
13 |
|
11 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
• det a |
21 |
|
a22 |
a23 |
= |
a21 |
a22 |
a23 |
|
|
• |
a21 |
a22 |
a23 |
a21 a22 = |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
a32 |
|
|
|
|
|
a31 |
a32 |
a33 |
|
|
|
|
a31 |
a32 |
a33 |
a31 a32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
a32 |
|
a33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= a11a22 a33 + a12 a23 a31 + a13 a21a32 − |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− a31a22 a13 − a32 a23 a11 − a33 a21a12 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A minor M ij |
of an element aij |
of a square matrix A is a determinant obtained from a |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
given matrix deleting the i-th row and j-th column. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
A quantity |
(−1) i + j M |
ij is called a cofactor |
A |
of an element |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ij |
|
|
ij . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
The sum of the products of elements |
a |
of |
|
|
A |
= a |
A |
+ a |
i |
2 |
A |
2 |
+ ... + a |
in |
A is |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ij |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i1 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in |
||||||||||
any row (column) of a determinant and |
|
|
|
called the expanding determinant by the i- |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
their cofactors is equal to one and the same |
|
th row. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
number. This number is a value of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
given determinant. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The multiplication of a matrix A[m× n] by |
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
a matrix B[n× p] is a matrix C[m× p] whose |
|
cij = ∑aik bkj , i = |
|
|
|
, j = |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1, m |
1, p |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
element cij |
is the product of |
the i-th row |
|
|
|
|
k =1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
of A and the j-th column of B: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
A square matrix B is said to be an inverse matrix of A if |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
AB = BA = I and it is denoted by the symbol |
A−1 . So we have AA−1 = A−1 A = I |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transposed |
|
matrix |
|
of |
cofactors |
of |
the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
L A |
|
T |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
corresponding elements of the given |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
matrix A is called the adjoint of A |
|
|
|
|
adj A = A = L |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
L |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L Ann |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
|
Be sure that |
|
|
|
= |
|
A |
|
≠ 0. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Construct the matrix of corresponding |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ |
|
|
|
|
||||
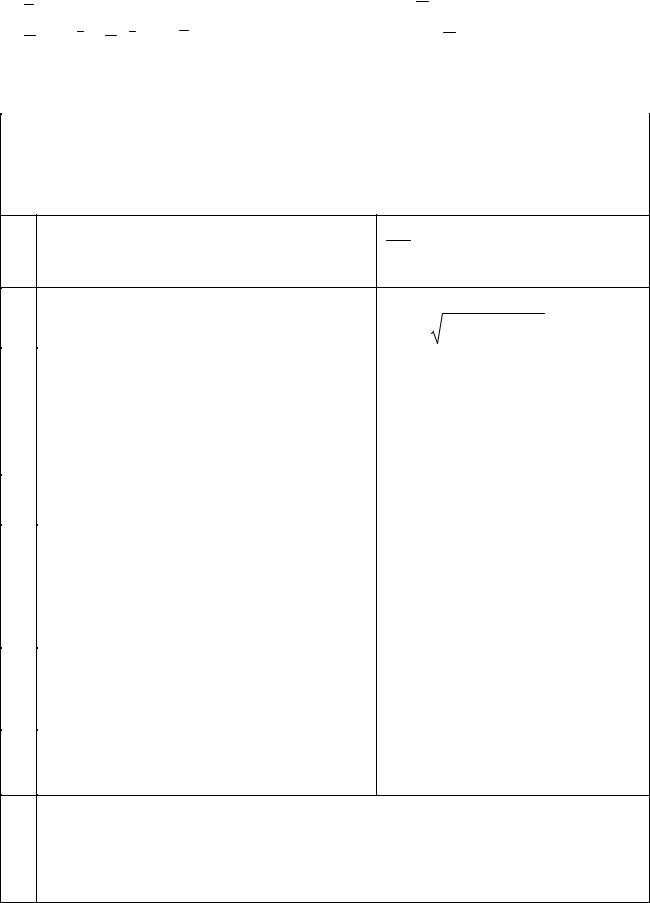
Method of finding the inverse matrix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
cofactors and transpose it (A). |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
Divide the matrix |
|
|
A by |
|
: |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A−1 = |
|
1 |
|
~ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
det A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33
|
a x + a x |
|
|
+ K + a |
|
x |
|
|
= b |
|||||
The system of n linear equation with n |
11 1 |
12 |
|
2 |
1n |
|
|
n |
1 |
|||||
unknowns |
a21x1 + a22 x2 + K + a2n xn = b2 |
|||||||||||||
....................................... |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
x + a |
n2 |
x |
2 |
+ K + a |
nn |
x |
n |
= b |
||||
|
|
n1 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|||||
|
|
|
AX = B , where |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
a |
|
|
a |
|
L a |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
|
1n |
|
||
Matrix form of a system: |
AX =B |
|
a |
21 |
|
a |
22 |
K a |
2n |
|
||
A = |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
||||||
|
|
L |
|
L L L |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
an1 |
|
an2 K ann |
|||||||
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
b |
|
|
. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
X = |
x2 |
, |
B = |
b2 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xn |
|
|
|
bn |
|
|
|
||
Methods of solution of linear systems
Matrix method solution of a square |
|
|
|
X = A−1 B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
linear system |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cramer’s Rule :If the determinant of |
x = |
|
1 |
, x |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
2 |
, K, x |
|
|
= |
n |
, |
||||||||||||||||||
the system does not equal zero then this |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2 |
|
|
n |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
system has a unique solution . |
|
|
where |
|
|
|
= |
|
A |
|
. |
|
i is |
|
the |
|
determinant |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
formed by replacing the ith column of the |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
matrix A with the column of constant |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
terms |
b1, b2 , b3 ,K, bn , i = 1, n |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
System of linear equations in the general |
• |
Matrix of a system: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Case |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
a |
|
|
|
|
L a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
a11 x1 + a12 x2 + K + a1n xn = b1 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
a |
21 |
a |
22 |
|
|
|
L a |
2n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
+ a22 x + K + a2n x2 = b2 |
|
A = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
a21 x1 |
|
|
|
L L |
L L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
....................................... |
|
(1) |
|
a |
m1 |
a |
m2 |
L a |
mn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
+ |
am2 x2 |
+ |
K |
+ |
amn xn |
= |
bm |
• Augmented matrix: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
am1 x1 |
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
L a |
|
|
|
b |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1n |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a21 |
|
a22 |
L a2n |
|
|
b2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B = |
L |
|
L |
L |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
am1 |
am2 |
L amn |
|
bm |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
34
Let an arbitrary matrix A dimension of which is [m× n] be given
Let us strike out k rows and k columns in this matrix. Then elements aij found at the
intersection of these rows and columns form the matrix of order k. Determinant of this matrix is said to be minor of the k order of the matrix A.
The highest order of the minor of matrix A different from zero is called the rank of this matrix and denoted r(A).
Matrix A is equivalent to matrix B if their ranks are equal: A ~B if r(A) = r(B).
A system (1) is compatible if and only if the rank of matrix A is equal to the rank of matrix B: r(A) = r(B)
• Gauss Method. The goal of this method is to reduce an augmented matrix to triangular form. After that it is able to answer the next questions:
1.Is the given linear system compatible or not?
2.How many solutions has this system?
3.If the system is compatible you can find its solution.
• Homogeneous System of Equations is a linear system of equations for which the constant terms are zeroes:
a11x1 + a12 x2 + K + a1n xn = 0a21x1 + a22 x2 + K + a2n xn = 0
LLLLLLLLLLL
am1x1 + am2 x2 + L + amn xn = 0
Homogeneous system is compatible as the solution (0,0,...,0) is always the solution of this system. If a homogeneous system has non-zero solutions you can find them using the Gauss method
Example. Solve the system of linear equation using Gauss method.
2x + x |
|
+ x |
|
+ 2x |
|
= 8, |
||
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
x1 |
- x2 |
+ 3x3 + x4 |
|
= 10, |
||||
|
x1 |
+ x2 |
|
|
+ x4 = 5. |
|||
|
|
|
||||||
35
Solution. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reduce the augmented matrix to triangular form: |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
2 1 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 1 0 1 |
|
5 |
|
|
||||||
|
2 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B = 1 − 1 3 |
1 |
|
10 |
|
~ |
2 1 1 2 |
|
|
|
8 R2 − 2R1 ~ |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R3 → R1 |
|
1 − 1 3 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
R2 − R1 |
|
|
1 1 0 |
1 |
5 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|||||||||
|
1 1 0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 1 0 1 |
|
5 |
|||||||
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
~ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
~ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
0 − 1 1 |
|
0 |
− 2 |
|
0 − 1 1 0 |
|
− 2 |
||||||||||
|
|
− 2 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
− 2R2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
0 |
0 |
5 |
R3 |
|
0 0 1 0 |
|
9 |
|
||||||||
As we can see r(A) = r(B) = 3 . But n = 4 > r = 3. It means that the general solution depends on n − r arbitrary constants. Here is one constant in this case. Let x4 = C , then the equivalent system is
|
x + x |
|
= 5 − C |
|
x |
3 |
= 9, |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− x2 + x3 = −2 |
|
− x2 + 9 = −2 x2 = 11, |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
x3 = 9 |
|
|
|
|
+ 11 = 5 − C x1 = −6 − C. |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
x1 |
|
|
|
||||||
Check the solution: AX = B . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
2 1 1 2 |
|
− 6 − C |
-12-2C + 11 + 9 + 2C |
|
8 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AX = 1 − 1 3 1 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
= − 6 − C − 11 + 27 + C = 10 = B . |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 6 - C + 11 + C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
1 1 0 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− 6 − C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answer: X = |
9 |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36

VECTORS
Vocabulary accordingly – соответственно
be observed - наблюдается clockwise – по часовой стрелке collinear - коллинеарный coplanar - компланарный
counterclockwise – против часовой стрелки directed – направленный
direction cosines – направляющие косинусы
expansion of the vector a through the base – разложение вектора по базису
initial point - начальная точка lefthanded triple – левая тройка
middle point of a segment – точка, делящая отрезок пополам ordered triple –упорядоченная тройка
ort of a vector (unit vector) – единичный вектор orthogonal – ортогональный
right -handed triple – правая тройка rotation – поворот
scalar – скаляр
scalar product (dot product) – скалярное произведение terminal (end) point – конечная точка
test of collinearity of vectors – признак коллинеарности векторов test of coplanarity of vectors – признак компланарности векторов test of orthogonality of vectors – признак ортогональности векторов tetrahedron – тетраэдр
torque – момент (силы) triangle – треугольник
triple scalar product – смешанное произведение vector – вектор
vector product (cross product) – векторное произведение volume of the parallelepiped – объем параллелепипеда
• Vector is a line segment. a = AB , A is the initial point. B is the terminal (end)
point.
• Let i , j, k be the unit and orthogonal vectors giving the direction of x-axis, y-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
k . Then vector |
||||||
axis and |
z-axis accordingly: |
i |
= |
j |
= |
k |
= 1, |
j |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− are the projections of the vector |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
= a x i + a y |
j + a z k , where a x , a y , a z |
|
a |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
a |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
onto the vectors i, j and k accordingly and are called the coordinates of the vector.
37
• a = (a x , a y , a z ) – the coordinate form of the vector a ;
• a = axi + a y j + az k – the vector form of the vector a , or the expansion of the
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
through the base i , j, k. |
|
|
|
||||||
vector |
a |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
№ |
|
Theorems, definitions |
Formulas for Calculation |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Let the coordinates of the points А and В and vectors |
a |
, b , |
c |
be given: |
||||||
A(x A , y A , z A ), B(xB , y B , z B ), |
|
= (a x , a y , a z ), |
|
= (bx , b y , bz ), |
|
= |
(c x , c y , c z ) then |
|||
|
b |
|||||||||
a |
c |
|||||||||
Vector’s coordinates through the |
|
1 coordinates of initial and end points |
AB = (x B − x A ; y B − y A , z B − z A ) |
2The length of a vector
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= a x2 + a 2y + a z2 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equal vectors |
( |
|
= |
|
|
) have equal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= b a x |
|
= bx , a y |
= by , a z = bz |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
corresponding coordinates |
a |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sum and difference of vectors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
a ± b = |
|
|
|
± bx ; a y |
± b y ; a z ± bz |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a x |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A product of a vector |
|
by a scalar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
(number) λ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
λ |
|
|
|
= (λa x ; λa y ; λa z ) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A scalar product (dot product) of vectors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
and b is the number equal to the product |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
of the moduli of these vectors and the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= a x bx + a y by |
+ a z bz |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
a , b |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
cosine of the angle φ between them: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
( |
|
, |
|
)= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cos ϕ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cos ϕ = |
|
( |
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Cosine of the angle φ between vectors |
a |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
b |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ϕ = ( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
, ^ b ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
The scalar product |
is the work. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A = F , S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
9The ordered triple of vectors is called a right (left)-handed triple if the shortest rotation of the first vector to the second one is observed from the end point of the third vector in the counterclockwise (clockwise)
38

|
Vector product (cross product) of two |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vectors a and b is the vector S such that |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| = | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | b | sin φ , where φ is the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
1) |
s |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
j |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
angle between a and b ; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S = |
|
|
a x |
|
|
|
a y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
a z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2) |
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
, S b ( the vector S is orthogonal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bx |
|
|
|
by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
bz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
to both of the vectors |
a |
and b ); |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3) |
|
|
|
,b , S is the right-handed triple of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
vectors. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 |
The area of the parallelogram constructed on |
|
S = |
|
[ |
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
the vectors |
|
|
|
and b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
1 |
|
|
|
|
[ |
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
The area of a triangle constructed on the |
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
vectors |
|
|
|
|
and b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
|
The vector product is the torque of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
[r |
, F ]= L 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
force |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
14 |
The triple scalar product: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
a y |
|
a z |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
( a , b , c )= |
bx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
by |
|
bz |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
( a , b , c ) = ( [a , b ], c ) ( a , [b , c ]) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
c y |
|
c z |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 |
The volume of the parallelepiped |
V = |
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
a |
b |
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
determined by vectors a, b, c is equal to the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
module of the triple scalar product of these |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
vectors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
The volume of a tetrahedron determined by |
V |
tet. |
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
b |
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
vectors a, b, c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
a y |
|
|
a |
z |
||||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tests of collinearity of vectors a |
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bx |
|
by |
|
bz |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b a = λ b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
]= 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• |
|
|
|
|
|
b |
[a |
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
|
|
|
)= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Test of orthogonality of vectors a b |
a b |
a , b |
|
||||||||||
19 |
Test of coplanarity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
b and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
are coplanar if and |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
a |
c |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
only if ( |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
)=0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
c |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
20 Coordinates of a point M dividing a segment |
|
xM |
|
= |
|
|
x A + λx B |
, |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 + λ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y A |
+ λy B |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
АВ in the given ratio λ : |
|
|
|
= λ |
|
|
y M |
= |
|
, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 + λ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
z A + λz B |
. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 + λ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xC |
= |
|
|
x A + x B |
, |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
21 |
Coordinates of a middle point of a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
y A + y B |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
segment АВ ( AC = CB) |
|
|
|
|
|
yC |
|
= |
, |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z |
|
|
= |
z A + z B |
. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cosα = |
|
|
a x |
|
, |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Direction cosines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
(α = a^ i, β = a^ j, γ = a^ k ) |
|
|
|
cos β = |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cos γ = |
|
a z |
|
. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 = (cosα; cos β ; cos γ ) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ort of a vector |
|
(the unit vector): a 0 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
a |
a |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40
