
- •THEORY OF PHONEMES
- •PHONOLOGY
- •CONCEPTUALITY
- •PHONEME
- •phoneme
- •PHONEME
- •What sort of entity is the phoneme?
- •1.WHAT SORT OF ENTITY IS THE PHONEME?
- •2. WHAT IS THE CONTENT OF THE
- •CONTINUE…
- •3. HOW DOES ONE IDENTIFY PHONEMES
- •VIEWS OF WHAT THE PHONEME IS
- •BLOOMFIELD’S PHONEME
- •COMMON PHONEMIC RULES
- •Phonemic Awareness
- •COMMON TYPES OF PHONEMIC AWARENESS

THEORY OF PHONEMES
Phonology
ENTITY of THE PHONEME
Content of THE PHONEME
|
DIFFERENCE? |
/k/ |
|
|
|
|
|
kit |
[ko] |
[kh] |
[k] |
elsewhere |
|||
|
after s |
Initial |
|
|
skill |
|
|
|
|
|
sack
 We pronounce them differently but we know they are the same sound.
We pronounce them differently but we know they are the same sound.
 How do we know two sounds are the same or different?
How do we know two sounds are the same or different?
2
3

PHONOLOGY
Phonology is how speech sounds are organized and affect one another in pronunciation.
Key terms:
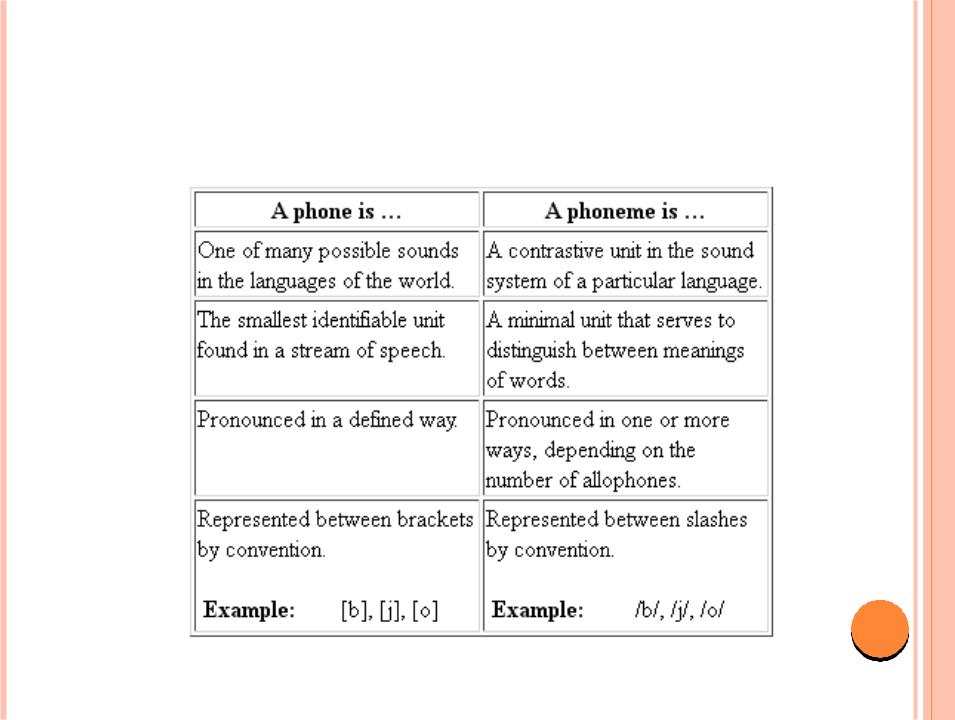
Phone
Phoneme
allophone
This organization is explained in phonological rules
4
CONCEPTUALITY
Articulatory phonetics
Real sounds = phones
•[p], [t], [k]
•[i], [æ]
•Phonology
•system and rules of sound patterns
•Abstractions = phoneme
•/p/, /t/, /k/
•/i/, /æ/
•Inventory of sounds and how they are realized.
6
PHONEME
a PHONEME is the minimal distinctive (contrastive ) linguistic sound
Phoneme |
Mental unit |
Meaningful |
Not realized |
Phone |
Physical/environmental |
Meaningless |
Realized |
|
unit |
|
|
Allophone |
Phonetic unit |
Variation of phoneme |
variations |
phoneme
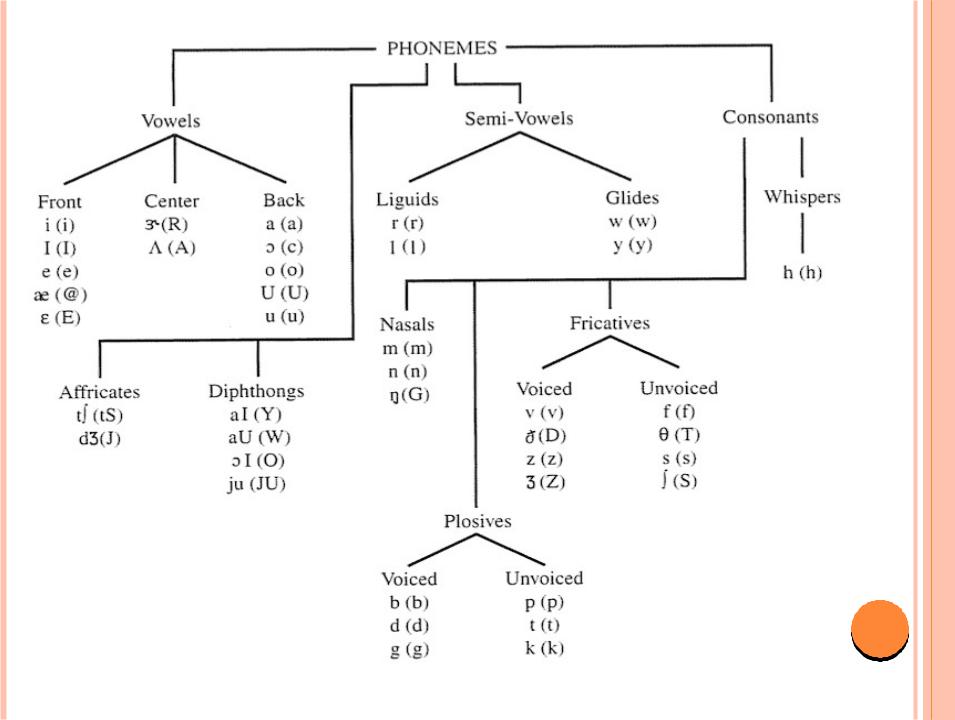
(from the Greek: φώνημα, phōnēma, "a sound uttered") is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances. (Wikipedia)
Segment: "any discrete unit that can be identified, either physically or auditorily,
speech."
multiple segments vowels, consonants
suprasegmental
tone,stress, length,intonation secondary articulations
nasalization vowel harmony
Marginal segments onomatopoeic words,
interjections, loan words
1. separate and individual,
such as consonants and vowels,
2. occur in a distinct temporal order
Source:
Wikipedia

PHONEME
A unit of speech that can be used to differentiate words(e.g.“cat”/kaet/vs.“bat”/baet/).
Phonemes identify minimal pairs in a language.
The set of phonemes in a language subject to interpretation; most languages have 20 to 40 phonemes.
The phoneme cannot therefore be acoustically defined. The
phoneme is instead a feature of language structure. |
9 |
|

What sort of entity is the phoneme?
Issues
10
