
ECHO 2013 / When (and how) to use Stress Testing in Valvular Heart Disease
.pdf
Rest
25 W
75 W
Supine Bike Study
Mean Gradient |
7 mmHg |
Heart rate |
69 BPM |
TR velocity |
2.8 m/sec |
Mean Gradient |
10 mmHg |
Heart rate |
76 BPM |
TR velocity |
3.2 m/sec |
Mean Gradient |
17 mmHg |
Heart rate |
105 BPM |
TR velocity |
4.2 m/sec |
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-11

Exercise in Mitral Stenosis
•Mean gradient > 15 mmHg: Severe
•TR velocity > 3.5 m/sec
( PASP >60 mmHg): Severe
•PHT shortens and does not work
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-12

Exercise test in Aortic Stenosis
To assess the accuracy of exercise testing in predicting symptom onset in patients with asymptomatic AS.
European Heart J. 2005
CP1217054-21
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-13

Exercise Testing in AS
125Patients
•Asymptomatic
•AVA 0.9 0.2 cm2
•Exercise-induced symptoms were only independent predictors of outcome
•BP response or ST-segment depression did not improve
•Positive predictive value 57%
Das et al: EHJ, 2005 CP1217054-6
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-14

Exercise Study in Aortic Stenosis
Symptom-Free Survival
1.0 |
No symptoms |
0.8 |
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mean AVA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limiting |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0.9 cm |
|
|
|
|
symptoms |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
3 |
|
6 |
|
9 |
|
12 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
At risk |
|
6 |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Months |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
No symptoms |
79 |
77 |
|
73 |
|
71 |
|
70 |
|||||||||
Limiting symptoms |
46 |
41 |
|
33 |
|
28 |
|
25 |
|||||||||
Das et al: Eur Ht J, 2005 CP1217054-20
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-15

European Hear Journal 2010
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-16

•Increase in MG>20 mmHg had 3.8 fold increase in risk of events
•Resting MG> 35 mmHg and increase in MG>20 mmHg had 9.6 fold increase
•Resting gradient did not predict the degree of increase in MG with exercise
European Hear Journal 2010
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-17

©2013 MFMER | 3259292-18

Lancelloti et al Circulation 2012
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-19
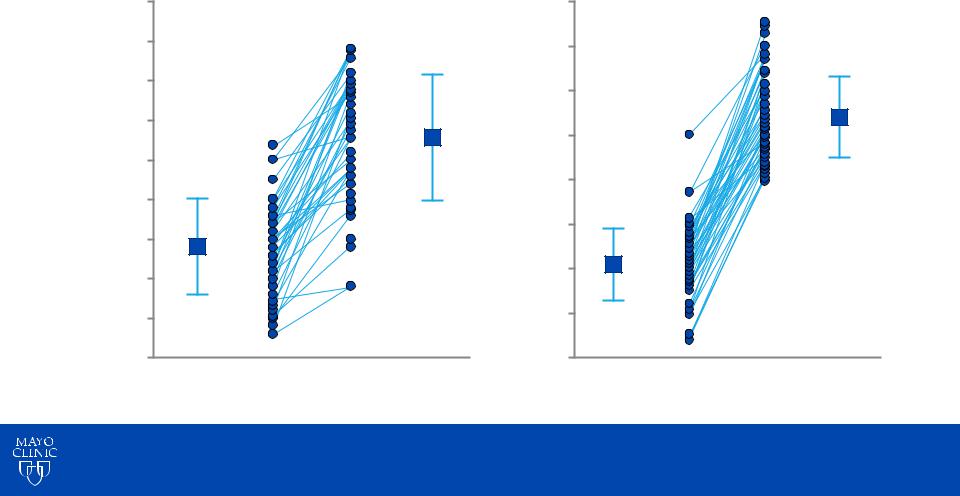
Impact of Exercise on Systolic Pulmonary
Arterial Pressure
|
Without Exercise Pulmonary |
|
|
Hypertension |
|
|
65 |
|
|
P<0.0001 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
49±8 |
|
Hg) |
55 |
|
|
||
(mm |
50 |
|
45 |
||
PAP |
||
34±6 |
||
|
||
Systolic |
40 |
|
35 |
||
|
||
|
30 |
25
20
Mean±SD Rest Exercise Mean±SD
Systolic PAP (mm Hg)
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
With Exercise Pulmonary
Hypertension
P<0.0001
74.5±9
40.9±8
Mean±SD Rest Exercise Mean±SD
Lancellotti et al: Circ 126:851, 2012
©2013 MFMER | 3259292-20
