
ECHO 2013 / Systolic Heart Failure Review of Cardiomyopathy
.pdf
Systolic heart failure: Review of Cardiomyopathy
Michael H. Picard, M.D.
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
No disclosures

What does the heart failure specialist want to know from the echo ?
•LV size
•LV function
–Systolic vs. Diastolic
•RV function
•Presence and severity of functional MR + TR
•Does the patient need anticoagulation (LV thrombus)
•Clues to Etiology
•Response to therapy
•Eligibility for specialized therapies
– dysynchrony

Diagnosis by echo: Cardiomyopathy examples
•Dilated (congestive)
–Idiopathic, Ischemic, toxins (alcohol), myocarditis (end stage), hypertensive (end stage), substrate deficiencies, musc dystrophies
•Hypertrophic
–With obstruction
–Without obstruction
–Apical variant
•Restrictive/infiltrative
–Amyloid
–Sarcoid
–Endomyocardial Fibrosis, Eosinophilic myocarditis
–Storage diseases – Fabry’s
•RV cardiomyopathy (ARVC/D)
•Other
–Post infectious – Chagas cardiomyopathy
–Noncompaction
–Post Chemotherapy

2D echo features of cardiomyopathies
Echo |
Hypertrophic |
Dilated |
Restrictive |
Infiltrative |
ARVC/D |
Isolated |
|
cmpty |
cmpty |
cmpty |
cmpty |
|
non- |
|
|
|
|
(amyloid) |
|
compaction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LVEDD |
N, |
|
N |
+/- |
N |
N, |
LA |
|
|
N, |
|
N |
N, |
LV wall |
|
N, |
N, |
|
N |
N, focal |
thickness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LVEF |
N, |
|
N, |
N, |
N |
N, |
RV fnctn |
N |
N, |
N |
N, |
|
N, |

Assessment of LV systolic function
•Covered yesterday
•Caveats
–Common echo measures are load dependent
•Less load dependent
–Elastance, strain/strain rate, MV annular velocities
•Influence of significant MR on LVEF
–Effects of tachycardia

LVEF REMAINS A STRONG PREDICTOR OF OUTCOME IN HEART FAILURE PATIENTS ACROSS A
BROAD SPECTRUM OF EF’s AND ETIOLOGIES
DIG Trial |
CHARM Trial |
|
Curtis et al. JACC 2003;42:736-42 |
Solomon et al, Circ 2005;112:3738-44 |

2o Valvular regurgitation and prognosis
additive prognostic value when symptomatic HF and LV systolic dysfunction
•“Functional” mitral regurgitation
–LV remodeling
•“Functional” tricuspid regurgitation
–primary right ventricular systolic dysfunction
–pulmonary hypertension

Valvular regurgitation: prognostic factor in ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
TR |
MR |
|
|
TR |
MR |
NYHA II |
LVEF 35% |
Hung et al, Am J Cardiol 1998;82:1302 |
Koelling et al, Am Heart J |
|
2002;144:524-9 |

differentiating scar from viable myocardium
Dobutamine echo: Low dose augmentation
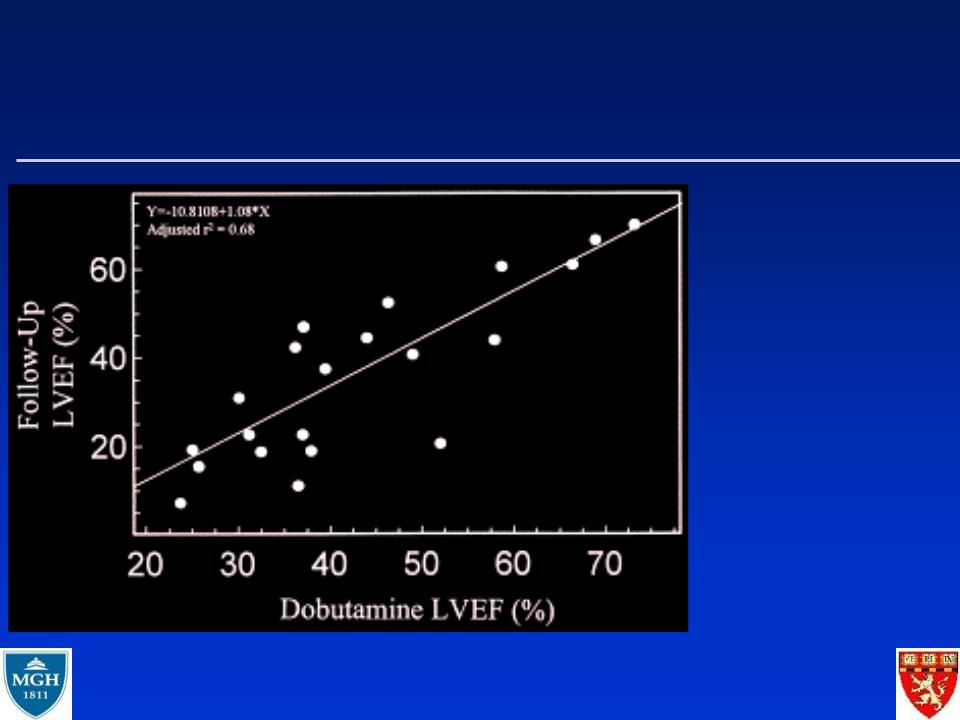
IS THE VENTRICULAR SYSTOLIC DYSFUNCTION LIKELY TO IMPROVE IN NEW ONSET DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY?
Myocardial contractile reserve predicts improvement in dilated cardiomyopathy
Naqvi TS et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 1999;34:1537-44
