
- •Table of Contents
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Audience
- •How to Read this Book
- •Conventions Used in This Book
- •Typographic Conventions
- •Icons
- •Organization of This Book
- •New in Subversion 1.1
- •This Book is Free
- •Acknowledgments
- •From Ben Collins-Sussman
- •From Brian W. Fitzpatrick
- •From C. Michael Pilato
- •Chapter 1. Introduction
- •What is Subversion?
- •Subversion's History
- •Subversion's Features
- •Subversion's Architecture
- •Installing Subversion
- •Subversion's Components
- •A Quick Start
- •Chapter 2. Basic Concepts
- •The Repository
- •Versioning Models
- •The Problem of File-Sharing
- •The Lock-Modify-Unlock Solution
- •The Copy-Modify-Merge Solution
- •Subversion in Action
- •Working Copies
- •Revisions
- •How Working Copies Track the Repository
- •The Limitations of Mixed Revisions
- •Summary
- •Chapter 3. Guided Tour
- •Help!
- •Import
- •Revisions: Numbers, Keywords, and Dates, Oh My!
- •Revision Numbers
- •Revision Keywords
- •Revision Dates
- •Initial Checkout
- •Basic Work Cycle
- •Update Your Working Copy
- •Make Changes to Your Working Copy
- •Examine Your Changes
- •svn status
- •svn diff
- •svn revert
- •Resolve Conflicts (Merging Others' Changes)
- •Merging Conflicts by Hand
- •Copying a File Onto Your Working File
- •Punting: Using svn revert
- •Commit Your Changes
- •Examining History
- •svn diff
- •Examining Local Changes
- •Comparing Working Copy to Repository
- •Comparing Repository to Repository
- •svn list
- •A Final Word on History
- •Other Useful Commands
- •svn cleanup
- •svn import
- •Summary
- •Chapter 4. Branching and Merging
- •What's a Branch?
- •Using Branches
- •Creating a Branch
- •Working with Your Branch
- •The Key Concepts Behind Branches
- •Copying Changes Between Branches
- •Copying Specific Changes
- •The Key Concept Behind Merging
- •Best Practices for Merging
- •Tracking Merges Manually
- •Previewing Merges
- •Merge Conflicts
- •Noticing or Ignoring Ancestry
- •Common Use-Cases
- •Merging a Whole Branch to Another
- •Undoing Changes
- •Resurrecting Deleted Items
- •Common Branching Patterns
- •Release Branches
- •Feature Branches
- •Switching a Working Copy
- •Tags
- •Creating a Simple Tag
- •Creating a Complex Tag
- •Branch Maintenance
- •Repository Layout
- •Data Lifetimes
- •Summary
- •Chapter 5. Repository Administration
- •Repository Basics
- •Understanding Transactions and Revisions
- •Unversioned Properties
- •Repository Data-Stores
- •Berkeley DB
- •FSFS
- •Repository Creation and Configuration
- •Hook Scripts
- •Berkeley DB Configuration
- •Repository Maintenance
- •An Administrator's Toolkit
- •svnlook
- •svnadmin
- •svndumpfilter
- •svnshell.py
- •Berkeley DB Utilities
- •Repository Cleanup
- •Managing Disk Space
- •Repository Recovery
- •Migrating a Repository
- •Repository Backup
- •Adding Projects
- •Choosing a Repository Layout
- •Creating the Layout, and Importing Initial Data
- •Summary
- •Chapter 6. Server Configuration
- •Overview
- •Network Model
- •Requests and Responses
- •Client Credentials Caching
- •svnserve, a custom server
- •Invoking the Server
- •Built-in authentication and authorization
- •Create a 'users' file and realm
- •Set access controls
- •SSH authentication and authorization
- •SSH configuration tricks
- •Initial setup
- •Controlling the invoked command
- •httpd, the Apache HTTP server
- •Prerequisites
- •Basic Apache Configuration
- •Authentication Options
- •Basic HTTP Authentication
- •SSL Certificate Management
- •Authorization Options
- •Blanket Access Control
- •Per-Directory Access Control
- •Disabling Path-based Checks
- •Extra Goodies
- •Repository Browsing
- •Other Features
- •Supporting Multiple Repository Access Methods
- •Chapter 7. Advanced Topics
- •Runtime Configuration Area
- •Configuration Area Layout
- •Configuration and the Windows Registry
- •Configuration Options
- •Servers
- •Config
- •Properties
- •Why Properties?
- •Manipulating Properties
- •Special Properties
- •svn:executable
- •svn:mime-type
- •svn:ignore
- •svn:keywords
- •svn:eol-style
- •svn:externals
- •svn:special
- •Automatic Property Setting
- •Peg and Operative Revisions
- •Externals Definitions
- •Vendor branches
- •General Vendor Branch Management Procedure
- •svn_load_dirs.pl
- •Localization
- •Understanding locales
- •Subversion's use of locales
- •Subversion Repository URLs
- •Chapter 8. Developer Information
- •Layered Library Design
- •Repository Layer
- •Repository Access Layer
- •RA-DAV (Repository Access Using HTTP/DAV)
- •RA-SVN (Custom Protocol Repository Access)
- •RA-Local (Direct Repository Access)
- •Your RA Library Here
- •Client Layer
- •Using the APIs
- •The Apache Portable Runtime Library
- •URL and Path Requirements
- •Using Languages Other than C and C++
- •Inside the Working Copy Administration Area
- •The Entries File
- •Pristine Copies and Property Files
- •WebDAV
- •Programming with Memory Pools
- •Contributing to Subversion
- •Join the Community
- •Get the Source Code
- •Become Familiar with Community Policies
- •Make and Test Your Changes
- •Donate Your Changes
- •Chapter 9. Subversion Complete Reference
- •The Subversion Command Line Client: svn
- •svn Switches
- •svn Subcommands
- •svn blame
- •svn checkout
- •svn cleanup
- •svn commit
- •svn copy
- •svn delete
- •svn diff
- •svn export
- •svn help
- •svn list
- •svn merge
- •svn mkdir
- •svn move
- •svn propedit
- •svn proplist
- •svn resolved
- •svn revert
- •svn status
- •svn switch
- •svn update
- •svnadmin
- •svnadmin Switches
- •svnadmin Subcommands
- •svnadmin create
- •svnadmin deltify
- •svnadmin dump
- •svnadmin help
- •svnadmin list-dblogs
- •svnadmin list-unused-dblogs
- •svnadmin load
- •svnadmin lstxns
- •svnadmin recover
- •svnadmin rmtxns
- •svnadmin setlog
- •svnadmin verify
- •svnlook
- •svnlook Switches
- •svnlook
- •svnlook author
- •svnlook changed
- •svnlook date
- •svnlook help
- •svnlook history
- •svnlook tree
- •svnlook uuid
- •svnserve
- •svnserve Switches
- •svnversion
- •svnversion
- •mod_dav_svn Configuration Directives
- •Appendix A. Subversion for CVS Users
- •Revision Numbers Are Different Now
- •Directory Versions
- •More Disconnected Operations
- •Distinction Between Status and Update
- •Branches and Tags
- •Metadata Properties
- •Conflict Resolution
- •Binary Files and Translation
- •Versioned Modules
- •Authentication
- •Converting a Repository from CVS to Subversion
- •Appendix B. Troubleshooting
- •Common Problems
- •Problems Using Subversion
- •Every time I try to access my repository, my Subversion client just hangs.
- •Every time I try to run svn, it says my working copy is locked.
- •I'm getting errors finding or opening a repository, but I know my repository URL is correct.
- •How can I specify a Windows drive letter in a file:// URL?
- •I'm having trouble doing write operations to a Subversion repository over a network.
- •Under Windows XP, the Subversion server sometimes seems to send out corrupted data.
- •What is the best method of doing a network trace of the conversation between a Subversion client and Apache server?
- •Why does the svn revert command require an explicit target? Why is it not recursive by default? This behavior differs from almost all the other subcommands.
- •On FreeBSD, certain operations (especially svnadmin create) sometimes hang.
- •I can see my repository in a web browser, but svn checkout gives me an error about 301 Moved Permanently.
- •Appendix C. WebDAV and Autoversioning
- •Basic WebDAV Concepts
- •Just Plain WebDAV
- •DeltaV Extensions
- •Subversion and DeltaV
- •Mapping Subversion to DeltaV
- •Autoversioning Support
- •The mod_dav_lock Alternative
- •Autoversioning Interoperability
- •Win32 WebFolders
- •Unix: Nautilus 2
- •Linux davfs2
- •Appendix D. Third Party Tools
- •Clients and Plugins
- •Language Bindings
- •Repository Converters
- •Higher Level Tools
- •Repository Browsing Tools
- •Appendix E. Copyright

Chapter 1. Introduction
Version control is the art of managing changes to information. It has long been a critical tool for programmers, who typically spend their time making small changes to software and then undoing those changes the next day. But the usefulness of version control software extends far beyond the bounds of the software development world. Anywhere you can find people using computers to manage information that changes often, there is room for version control. And that's where Subversion comes into play.
This chapter contains a high-level introduction to Subversion—what it is; what it does; how to get it.
What is Subversion?
Subversion is a free/open-source version control system. That is, Subversion manages files and directories over time. A tree of files is placed into a central repository. The repository is much like an ordinary file server, except that it remembers every change ever made to your files and directories. This allows you to recover older versions of your data, or examine the history of how your data changed. In this regard, many people think of a version control system as a sort of “time machine”.
Subversion can access its repository across networks, which allows it to be used by people on different computers. At some level, the ability for various people to modify and manage the same set of data from their respective locations fosters collaboration. Progress can occur more quickly without a single conduit through which all modifications must occur. And because the work is versioned, you need not fear that quality is the trade-off for losing that conduit—if some incorrect change is made to the data, just undo that change.
Some version control systems are also software configuration management (SCM) systems. These systems are specifically tailored to manage trees of source code, and have many features that are specific to software develop- ment—such as natively understanding programming languages, or supplying tools for building software. Subversion, however, is not one of these systems. It is a general system that can be used to manage any collection of files. For you, those files might be source code—for others, anything from grocery shopping lists to digital video mixdowns and beyond.
Subversion's History
In early 2000, CollabNet, Inc. (http://www.collab.net) began seeking developers to write a replacement for CVS. CollabNet offers a collaboration software suite called SourceCast, of which one component is version control. Although SourceCast used CVS as its initial version control system, CVS's limitations were obvious from the beginning, and CollabNet knew it would eventually have to find something better. Unfortunately, CVS had become the de facto standard in the open source world largely because there wasn't anything better, at least not under a free license. So CollabNet determined to write a new version control system from scratch, retaining the basic ideas of CVS, but without the bugs and misfeatures.
In February 2000, they contacted Karl Fogel, the author of Open Source Development with CVS (Coriolis, 1999), and asked if he'd like to work on this new project. Coincidentally, at the time Karl was already discussing a design for a new version control system with his friend Jim Blandy. In 1995, the two had started Cyclic Software, a company providing CVS support contracts, and although they later sold the business, they still used CVS every day at their jobs. Their frustration with CVS had led Jim to think carefully about better ways to manage versioned data, and he'd already come up with not only the name “Subversion”, but also with the basic design of the Subversion repository. When CollabNet called, Karl immediately agreed to work on the project, and Jim got his employer, RedHat Software, to essentially donate him to the project for an indefinite period of time. CollabNet hired Karl and Ben Collins-Sussman, and detailed design work began in May. With the help of some well-placed prods from Brian Behlendorf and Jason Robbins of CollabNet, and Greg Stein (at the time an independent developer active in the WebDAV/DeltaV specification process), Subversion quickly attracted a community of active developers. It turned out that many people had had the same frustrating experiences with CVS, and welcomed the chance to finally do something about it.
1

Introduction
The original design team settled on some simple goals. They didn't want to break new ground in version control methodology, they just wanted to fix CVS. They decided that Subversion would match CVS's features, and preserve the same development model, but not duplicate CVS's most obvious flaws. And although it did not need to be a drop-in replacement for CVS, it should be similar enough that any CVS user could make the switch with little effort.
After fourteen months of coding, Subversion became “self-hosting” on August 31, 2001. That is, Subversion developers stopped using CVS to manage Subversion's own source code, and started using Subversion instead.
While CollabNet started the project, and still funds a large chunk of the work (it pays the salaries of a few full-time Subversion developers), Subversion is run like most open-source projects, governed by a loose, transparent set of rules that encourage meritocracy. CollabNet's copyright license is fully compliant with the Debian Free Software Guidelines. In other words, anyone is free to download, modify, and redistribute Subversion as he pleases; no permission from CollabNet or anyone else is required.
Subversion's Features
When discussing the features that Subversion brings to the version control table, it is often helpful to speak of them in terms of how they improve upon CVS's design. If you're not familiar with CVS, you may not understand all of these features. And if you're not familiar with version control at all, your eyes may glaze over unless you first read Chapter 2, Basic Concepts, in which we provide a gentle introduction to version control in general.
Subversion provides:
Directory versioning
CVS only tracks the history of individual files, but Subversion implements a “virtual” versioned filesystem that tracks changes to whole directory trees over time. Files and directories are versioned.
True version history
Since CVS is limited to file versioning, operations such as copies and renames—which might happen to files, but which are really changes to the contents of some containing directory—aren't supported in CVS. Additionally, in CVS you cannot replace a versioned file with some new thing of the same name without the new item inheriting the history of the old—perhaps completely unrelated—file. With Subversion, you can add, delete, copy, and rename both files and directories. And every newly added file begins with a fresh, clean history all its own.
Atomic commits
A collection of modifications either goes into the repository completely, or not at all. This allows developers to construct and commit changes as logical chunks, and prevents problems that can occur when only a portion of a set of changes is successfully sent to the repository.
Versioned metadata
Each file and directory has a set of properties—keys and their values—associated with it. You can create and store any arbitrary key/value pairs you wish. Properties are versioned over time, just like file contents.
Choice of network layers
Subversion has an abstracted notion of repository access, making it easy for people to implement new network mechanisms. Subversion can plug into the Apache HTTP Server as an extension module. This gives Subversion a big advantage in stability and interoperability, and instant access to existing features provided by that server—authentication, authorization, wire compression, and so on. A more lightweight, standalone Subversion server process is also available. This server speaks a custom protocol which can be easily tunneled over SSH.
Consistent data handling
Subversion expresses file differences using a binary differencing algorithm, which works identically on both text (human-readable) and binary (human-unreadable) files. Both types of files are stored equally compressed in the repository, and differences are transmitted in both directions across the network.
2

Introduction
Efficient branching and tagging
The cost of branching and tagging need not be proportional to the project size. Subversion creates branches and tags by simply copying the project, using a mechanism similar to a hard-link. Thus these operations take only a very small, constant amount of time.
Hackability
Subversion has no historical baggage; it is implemented as a collection of shared C libraries with well-defined APIs. This makes Subversion extremely maintainable and usable by other applications and languages.
Subversion's Architecture
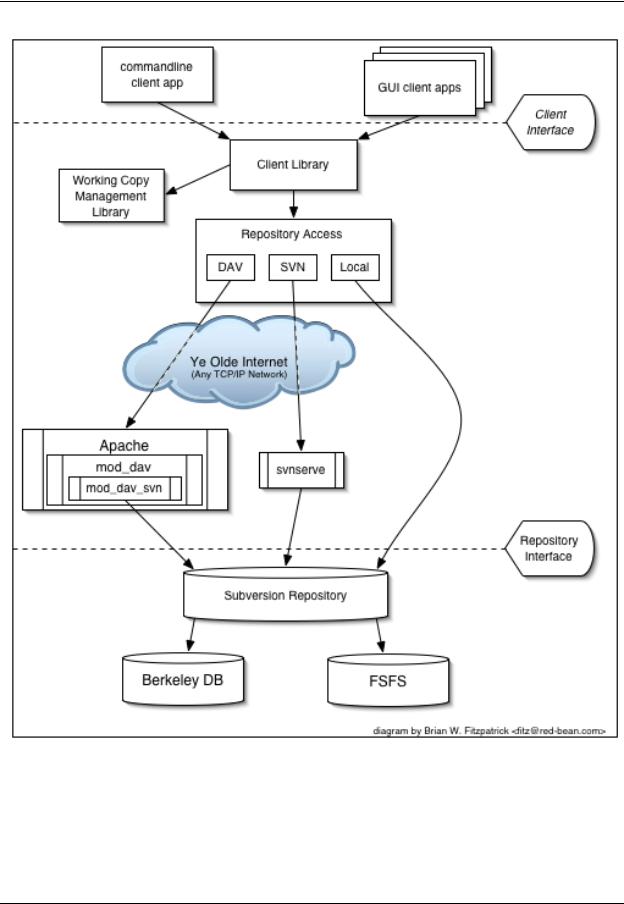
Figure 1.1, “Subversion's Architecture” illustrates what one might call a “mile-high” view of Subversion's design.
Figure 1.1. Subversion's Architecture
3
Introduction
On one end is a Subversion repository that holds all of your versioned data. On the other end is your Subversion client program, which manages local reflections of portions of that versioned data (called “working copies”). Between these extremes are multiple routes through various Repository Access (RA) layers. Some of these routes go across computer networks and through network servers which then access the repository. Others bypass the network altogether and access the repository directly.
Installing Subversion
4
