
Mankiw Principles of Economics (3rd ed)
.pdf308 |
PART FIVE FIRM BEHAVIOR AND THE ORGANIZATION OF INDUSTRY |
A SHIFT IN DEMAND IN THE SHORT RUN AND LONG RUN
Because firms can enter and exit a market in the long run but not in the short run, the response of a market to a change in demand depends on the time horizon. To see this, let’s trace the effects of a shift in demand. This analysis will show how a market responds over time, and it will show how entry and exit drive a market to its long-run equilibrium.
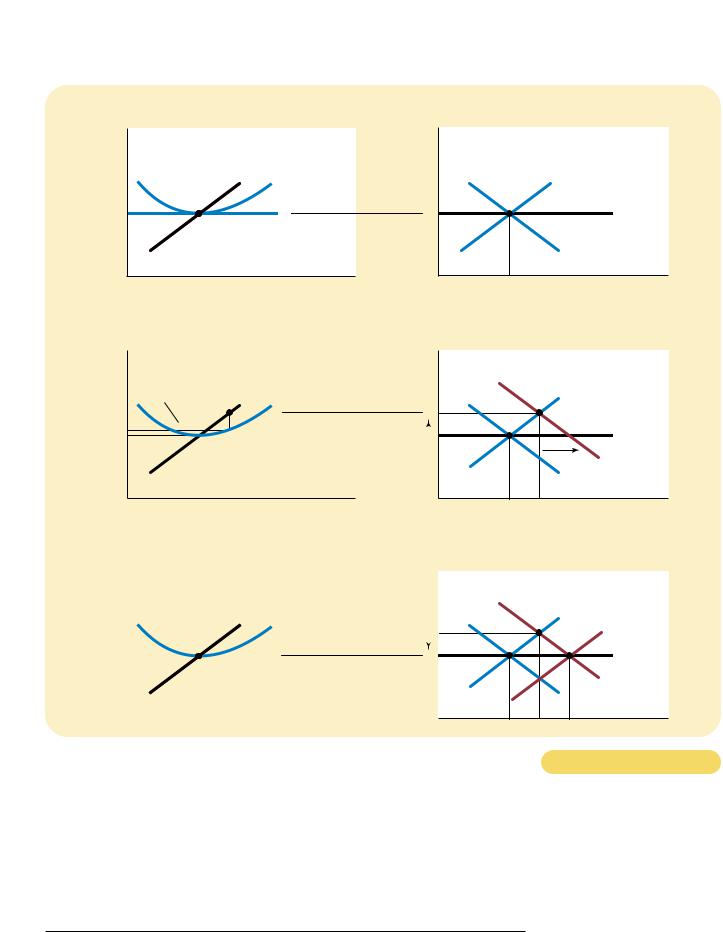
Suppose the market for milk begins in long-run equilibrium. Firms are earning zero profit, so price equals the minimum of average total cost. Panel (a) of Figure 14-8 shows the situation. The long-run equilibrium is point A, the quantity sold in the market is Q1, and the price is P1.
Now suppose scientists discover that milk has miraculous health benefits. As a result, the demand curve for milk shifts outward from D1 to D2, as in panel (b). The short-run equilibrium moves from point A to point B; as a result, the quantity rises from Q1 to Q2, and the price rises from P1 to P2. All of the existing firms respond to the higher price by raising the amount produced. Because each firm’s supply curve reflects its marginal-cost curve, how much they each increase production is determined by the marginal-cost curve. In the new, short-run equilibrium, the price of milk exceeds average total cost, so the firms are making positive profit.
Over time, the profit in this market encourages new firms to enter. Some farmers may switch to milk from other farm products, for example. As the number of firms grows, the short-run supply curve shifts to the right from S1 to S2, as in panel (c), and this shift causes the price of milk to fall. Eventually, the price is driven back down to the minimum of average total cost, profits are zero, and firms stop entering. Thus, the market reaches a new long-run equilibrium, point C. The price of milk has returned to P1, but the quantity produced has risen to Q3. Each firm is again producing at its efficient scale, but because more firms are in the dairy business, the quantity of milk produced and sold is higher.
WHY THE LONG-RUN SUPPLY CURVE
MIGHT SLOPE UPWARD
So far we have seen that entry and exit can cause the long-run market supply curve to be horizontal. The essence of our analysis is that there are a large number of potential entrants, each of which faces the same costs. As a result, the long-run market supply curve is horizontal at the minimum of average total cost. When the demand for the good increases, the long-run result is an increase in the number of firms and in the total quantity supplied, without any change in the price.
There are, however, two reasons that the long-run market supply curve might slope upward. The first is that some resource used in production may be available only in limited quantities. For example, consider the market for farm products. Anyone can choose to buy land and start a farm, but the quantity of land is limited. As more people become farmers, the price of farmland is bid up, which raises the costs of all farmers in the market. Thus, an increase in demand for farm products cannot induce an increase in quantity supplied without also inducing a rise in farmers’ costs, which in turn means a rise in price. The result is a long-run market supply curve that is upward sloping, even with free entry into farming.
A second reason for an upward-sloping supply curve is that firms may have different costs. For example, consider the market for painters. Anyone can enter

310 |
PART FIVE FIRM BEHAVIOR AND THE ORGANIZATION OF INDUSTRY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gluts, price wars, shakeouts, |
|
IN THE NEWS |
|
consolidations. . . . |
|
|
One man who attended the Pebble |
|
|
Entry or Overinvestment? |
|
meeting, Joseph Soviero, a Union |
|
|
|
bide vice president, cites an odd but |
|
|
|
problem in chemicals: the strong |
|
|
|
of the past few years. “The prof- |
|
|
|
that the industry sees during the |
|
|
|
times has always led to overinvest- |
|
|
|
and it has this time,” Mr. Soviero |
|
|
be euphoric. |
says. He adds that the chemicals busi- |
|
|
||
|
|
Instead, an undertone of concern is |
ness cycle is alive and has peaked. At |
|
|
evident among these executives from |
Union Carbide, he says, “we always talk |
|
|
Mobil Corp., Union Carbide Corp. and |
about the cycle” and try to manage it. |
|
|
other capital-intensive companies. In be- |
So far, demand isn’t a big problem. |
|
|
tween golf, fine meals and cigars, they |
In many industries, it is still growing |
|
|
hear a sobering message from their |
steadily, though slowly. What is develop- |
|
|
hosts. |
ing is too much supply, stemming from |
|
|
“I feel like the prophet of doom” is |
the recurring problem of overinvestment. |
|
|
the welcoming line of R. Duane Dickson, |
. . . The next few years will bring fierce |
|
|
a director of Mercer Management Con- |
competition and falling prices. |
|
|
sulting and host of the meeting. “It’s our |
|
|
|
belief that the downturn has started. I |
SOURCE: The Wall Street Journal, August 7, 1997, |
|
|
can’t tell you how far it’s going to go. But |
p. A1. |
|
A K e y C u l p r i t : H i g h P r o f i t s |
it could be a very ugly one.” |
|
|
|
For two days, the executives and |
|
|
BY BERNARD WYSOCKI, JR. |
their advisers discuss what they expect |
|
|
MONTEREY, CALIF.—About 20 execu- |
in their industries between now and |
|
|
tives are huddled in a conference room |
2000: growing overcapacity, world-wide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the market for painting services, but not everyone has the same costs. Costs vary in part because some people work faster than others and in part because some people have better alternative uses of their time than others. For any given price, those with lower costs are more likely to enter than those with higher costs. To increase the quantity of painting services supplied, additional entrants must be encouraged to enter the market. Because these new entrants have higher costs, the price must rise to make entry profitable for them. Thus, the market supply curve for painting services slopes upward even with free entry into the market.
Notice that if firms have different costs, some firms earn profit even in the long run. In this case, the price in the market reflects the average total cost of the marginal firm—the firm that would exit the market if the price were any lower. This firm earns zero profit, but firms with lower costs earn positive profit. Entry does not eliminate this profit because would-be entrants have higher costs than firms already in the market. Higher-cost firms will enter only if the price rises, making the market profitable for them.



316 |
PART FIVE FIRM BEHAVIOR AND THE ORGANIZATION OF INDUSTRY |
In this chapter we examine the implications of this market power. We will see that market power alters the relationship between a firm’s price and its costs. A competitive firm takes the price of its output as given by the market and then chooses the quantity it will supply so that price equals marginal cost. By contrast, the price charged by a monopoly exceeds marginal cost. This result is clearly true in the case of Microsoft’s Windows. The marginal cost of Windows—the extra cost that Microsoft would incur by printing one more copy of the program onto some floppy disks or a CD—is only a few dollars. The market price of Windows is many times marginal cost.
It is perhaps not surprising that monopolies charge high prices for their products. Customers of monopolies might seem to have little choice but to pay whatever the monopoly charges. But, if so, why does a copy of Windows not cost $500? Or $5,000? The reason, of course, is that if Microsoft set the price that high, fewer people would buy the product. People would buy fewer computers, switch to other operating systems, or make illegal copies. Monopolies cannot achieve any level of profit they want, because high prices reduce the amount that their customers buy. Although monopolies can control the prices of their goods, their profits are not unlimited.
As we examine the production and pricing decisions of monopolies, we also consider the implications of monopoly for society as a whole. Monopoly firms, like competitive firms, aim to maximize profit. But this goal has very different ramifications for competitive and monopoly firms. As we first saw in Chapter 7, selfinterested buyers and sellers in competitive markets are unwittingly led by an invisible hand to promote general economic well-being. By contrast, because monopoly firms are unchecked by competition, the outcome in a market with a monopoly is often not in the best interest of society.
One of the Ten Principles of Economics in Chapter 1 is that governments can sometimes improve market outcomes. The analysis in this chapter will shed more light on this principle. As we examine the problems that monopolies raise for society, we will also discuss the various ways in which government policymakers might respond to these problems. The U.S. government, for example, keeps a close eye on Microsoft’s business decisions. In 1994, it prevented Microsoft from buying Intuit, a software firm that sells the leading program for personal finance, on the grounds that the combination of Microsoft and Intuit would concentrate too much market power in one firm. Similarly, in 1998, the U.S. Justice Department objected when Microsoft started integrating its Internet browser into its Windows operating system, claiming that this would impede competition from other companies, such as Netscape. This concern led the Justice Department to file suit against Microsoft, the final resolution of which was still unsettled as this book was going to press.
|
WHY MONOPOLIES ARISE |
|
|
monopoly |
A firm is a monopoly if it is the sole seller of its product and if its product does not |
a firm that is the sole seller of a |
have close substitutes. The fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry: A mo- |
product without close substitutes |
nopoly remains the only seller in its market because other firms cannot enter |
|
the market and compete with it. Barriers to entry, in turn, have three main sources: |

CHAPTER 15 MONOPOLY |
317 |
A key resource is owned by a single firm.
The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good or service.
The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
Let’s briefly discuss each of these.
MONOPOLY RESOURCES
The simplest way for a monopoly to arise is for a single firm to own a key resource. |
“Rather than a monopoly, we like |
For example, consider the market for water in a small town in the Old West. If |
to consider ourselves ‘the only |
dozens of town residents have working wells, the competitive model discussed in |
game in town.’” |
Chapter 14 describes the behavior of sellers. As a result, the price of a gallon of wa- |
|
ter is driven to equal the marginal cost of pumping an extra gallon. But if there is |
|
only one well in town and it is impossible to get water from anywhere else, then |
|
the owner of the well has a monopoly on water. Not surprisingly, the monopolist |
|
has much greater market power than any single firm in a competitive market. In |
|
the case of a necessity like water, the monopolist could command quite a high |
|
price, even if the marginal cost is low. |
|
Although exclusive ownership of a key resource is a potential cause of mo- |
|
nopoly, in practice monopolies rarely arise for this reason. Actual economies are |
|
large, and resources are owned by many people. Indeed, because many goods are |
|
traded internationally, the natural scope of their markets is often worldwide. There |
|
are, therefore, few examples of firms that own a resource for which there are no |
|
close substitutes. |
|
CASE STUDY THE DEBEERS DIAMOND MONOPOLY
A classic example of a monopoly that arises from the ownership of a key resource is DeBeers, the South African diamond company. DeBeers controls about 80 percent of the world’s production of diamonds. Although the firm’s share of the market is not 100 percent, it is large enough to exert substantial influence over the market price of diamonds.
How much market power does DeBeers have? The answer depends in part on whether there are close substitutes for its product. If people view emeralds, rubies, and sapphires as good substitutes for diamonds, then DeBeers has relatively little market power. In this case, any attempt by DeBeers to raise the price of diamonds would cause people to switch to other gemstones. But if people view these other stones as very different from diamonds, then DeBeers can exert substantial influence over the price of its product.
DeBeers pays for large amounts of advertising. At first, this decision might seem surprising. If a monopoly is the sole seller of its product, why does it need to advertise? One goal of the DeBeers ads is to differentiate diamonds from other gems in the minds of consumers. When their slogan tells you that “a diamond is forever,” you are meant to think that the same is not true of emeralds, rubies, and sapphires. (And notice that the slogan is applied to all diamonds, not just DeBeers diamonds—a sign of DeBeers’s monopoly position.) If the ads are
