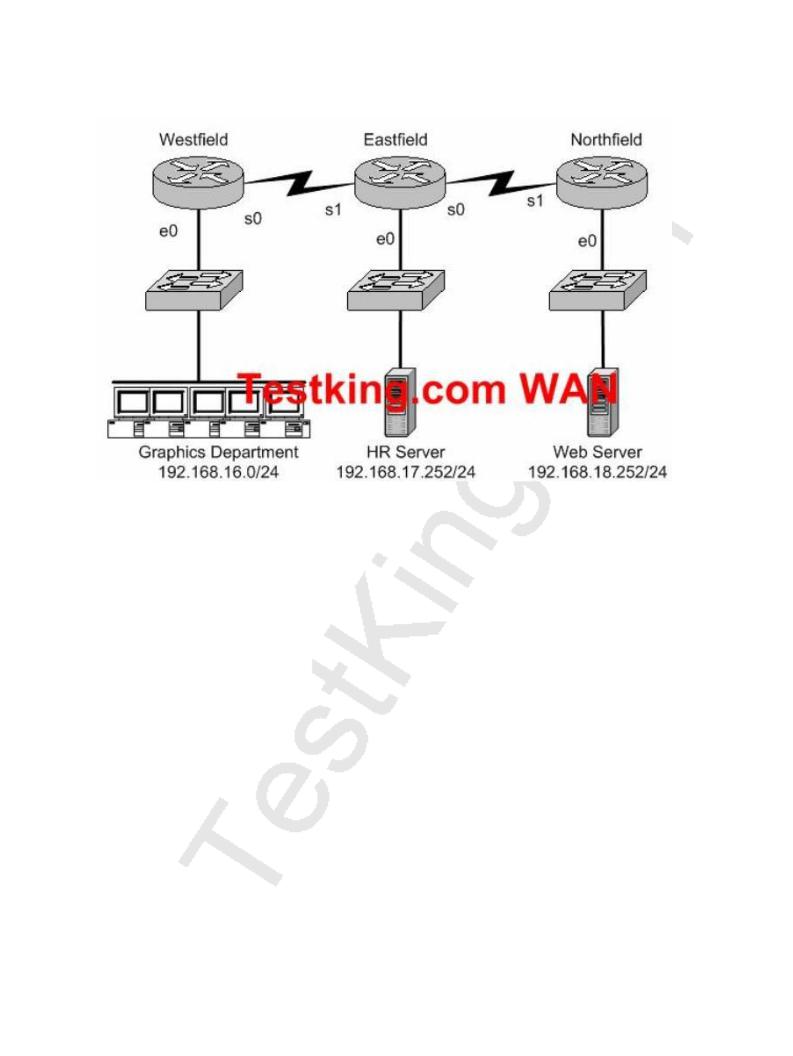
In order to control access on the Testking network, the following access list is created:
access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.15 192.168.2 16 0.0.0.15 eq 23
What would happen if you applied the following ACL to any one of the TestKing routers in the above exhibit? On what interface and what direction should you apply it? Once applied, what will this access list accomplish? (Select all valid answer choices)
A.Telnet traffic from 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.15 to 168.2.16 0.0.0.15 is allowed.
B.SMTP traffic from 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.15 to 168.2.16 0.0.0.15 is allowed.
C.The ACL is configured to allow traffic from one specific host to another.
D.The ACL should be applied inbound to the e0 interface of Router TestKing1.
E.The ACL should be applied outbound to the e0 interface of Router TestKing1.
Answer: A, D
Explanation:
This is a two part question. The first part is the type of traffic that will match this specific access list entry. Since telnet uses TCP port 23, choice B is correct.
Next, to determine which interface and which direction to apply the access list, we see that the source of the traffic is the 192.168.1.16/28 network, while the destination is the 192.168.2.16/28 network. Therefore, only choice D makes sense.
Incorrect Answers:
B.SMTP uses TCP port 25.
C.There is a /15 network mask for both the source and destination in this access list, which translates to a /28 network.
E.This would not be useful if applied to the outbound, as no traffic would match then. Note that if this answer had stated that the access list be placed on the outbound serial (WAN) interface, then this would have been an acceptable choice.
QUESTION NO: 11
The TestKing network is subnetted using 29 bits for the subnet mask. Which wild card mask should be used to configure an extended access list to permit or deny access to an entire subnetwork?
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com