
Testking_640-802_V13
.pdf
Answer: C, E, F Explanation:
OSPF, RIP v2, and EIGRP all support VLSM information, which will eliminate the problems that can arise from non contiguous networks.
Incorrect Answers:
A, D. IGRP and RIP version 1 are distance vector routing protocols that do not support VLSM information, so they are prone to problems that can arise from discontiguous network schemes.
B. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is not a routing protocol. It is used primarily for the management and monitoring of networks.
QUESTION NO: 25
Which of the following statements describe the characteristic of link state routing protocols? (Choose all that apply.)
A.The exchange of an advertisement is triggered by a change in the network.
B.All routers exchange routing tables with each other in a multipoint network.
C.Packets are routed based upon the shortest path to the destination.
D.Paths are chosen depending on the cost efficiency factor.
E.Every router in an OSPF area is capable of representing the entire network topology.
F.Only the designated router in an OSPF area can represent the entire network topology.
Answer: A, C, E Explanation:
The predominant link state routing protocols are OSPF and IS-IS. The following describes the features and functionality of OSPF:
Open Shortest Path First
*Each router discovers its neighbors on each interface. The list of neighbors is kept in a neighbor table.
*Each router uses a reliable protocol to exchange topology information with its neighbors.
*Each router places the learned topology information into its topology database.
*Each router runs the SPF algorithm against its own topology database.
*Each router runs the SPF algorithm against its own topology database to calculate the best routes to each subnet in the database.
*Each router places the best roué to each subnet into the IP routing table.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 451 -

The following list points out some of the key features of OSPF:
*Converges very quickly - from the point of recognizing a failure, it often can converge in less than 10 seconds.
*Supports VLSM.
*Uses short Hello messages on a short regular interval, with the absence of hello messages indicating that a neighbor is no longer reachable.
*Sends partial updates when link status changes and floods full updates every 30 minutes. The flooding, however, does not happened all at once, so the overhead s minimal.
*Uses cost for the metric.
Reference: CCNA Self-Study CCNA INTRO exam certification Guide (Cisco Press, ISBN 1-58720-094-5) Page 417
QUESTION NO: 26
What are the different characteristics of distance vector and link state routing protocols?
A.Distance vector protocols send the entire routing table to directly connected neighbors.
B.Distance vector protocols are responsible for sending updates to all networks listed in the routing table.
C.Link state protocols are responsible for sending the entire routing table to the whole network.
D.Link state protocols send updates regarding their own links status to all other routers on the network.
E.None of the above
Answer: A, D
Explanation:
Distance Vector Protocols:
Distance Vector Protocols advertise routing information by sending messages, called routing updates, out the interfaces on a router. These updates contain a series of entries, with each entry representing a subnet and a metric.
Link-State Protocols:
Sends partial updates when link status changes and floods full updates every 30 minutes. The flooding, however, does not happen all at once, so the overhead is minimal. Reference: CCNA Self-Study CCNA INTRO exam certification Guide (Cisco Press, ISBN 1-58720-094-5) Page 413 + 419
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 452 -

QUESTION NO: 27
Which one of the following statements best explains the split horizon rule used in distance vector routing protocols?
A.Only routers can split boundaries (horizons) between concentric networks.
B.Each AS must keep routing tables converged to prevent dead routes from being advertised across boundaries.
C.Networks can only remain fully converged if all information is sent out all active interfaces.
D.Information about a route should not be sent back in the direction from which the original update came.
E.Distance vector protocols need fall back routers that are responsible for momentary loops.
Answer: D Explanation:
Simply said, the rule of split horizons says that routing information should not be sent out the same interface that it was learned on. This is used to prevent routing loops in the network, but it can also cause problems on NBMA networks, such as a hub and spoke frame relay network. Split horizons include two related concepts that affect what routes are included in a routing update:
An update does not include the subnet of the interface out which the update is sent
All routes with outgoing interface of interface x are not included in updates sent out that same interface x.
Incorrect Answers
A. There is no such requirement
C. This is not a feature of split horizon
B. This is not a related feature for split horizon
E. Distance vector protocols updates routing table at regular intervals instead of Topology changes
Reference: Wendell Odom. CISCO CCNA Certification Guide (2000 Cisco Press) Page 369.
QUESTION NO: 28
Which of the following statements are correct in regard to classless routing protocols? (Select two)
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 453 -

A.Discontiguous subnets are not allowed.
B.Variable length subnet masks are allowed.
C.RIP v1 is a classless routing protocol.
D.IGRP supports classless routing within the same autonomous system.
E.RIP v2 supports classless routing.
Answer: B, E
Explanation:
Classless and Classful Routing Protocols
Some routing protocols must consider the Class A, B, or C network number that a subnet resides in when performing some of its tasks. Other routing protocols can ignore Class A, B, and C rules altogether. Routing protocols that must consider class rules are called classful routing protocols; those that do not need to consider class rules are called classless routing protocols.
You can easily remember which routing protocols fall into each category because of one fact:
Classful routing protocols do not transmit the mask information along with the subnet number, whereas classless routing protocols do transmit mask information.
You might recall that routing protocols that support VLSM do so because they send mask information along with the routing information. Table 7-3 lists the routing protocols and whether they transmit mast information, support VLSM, and are classless or classful.
Table 7-3 Interior IP Routing Protocol: Classless or Classful?
Reference: CCNA ICND Exam Certification Guide by Wendell Odem, Pg.233
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 454 -
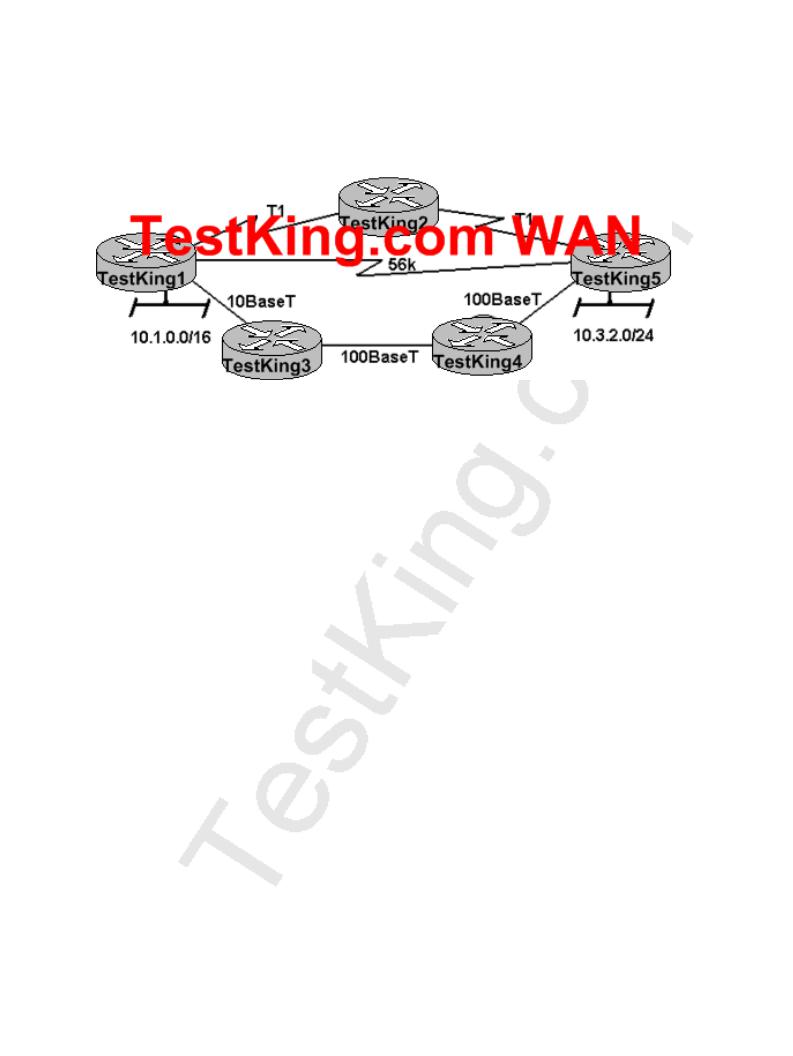
QUESTION NO: 29
The TestKing WAN is displayed below:
Assume that the routing Protocol referenced in each choice below is configuration with its default settings and the given routing protocol is running on all the routers. Which two conditional statements accurately state the path that will be chosen between network 10.1.0.0 and 10.3.2.0 for the routing protocol mentioned? (Choose Two)
A.If RIPv2 is the routing protocol; the path will be from TESTKING1 toTESTKING3 to TESTKING4 to TESTKING5.
B.If RIPv2 is the routing protocol; the path will be from TESTKING1 to TESTKING5.
C.If EIGRP is the routing protocol; the path will be from TESTKING1 toTESTKING3 to TESTKING4 to TESTKING5.
D.If EIGRP is the routing protocol, the path will be from TESTKING1 toTESTKING2 to TESTKING5.
E.If OSPF is the routing protocol; the path will be from TESTKING1 to TESTKING5.
Answer: B, C
Explanation:
RIP, IGRP both are called the distance vector Protocols. RIP uses the number of hops as a metric.
RIP:
_ Based on distance vector Logic _ Uses hop count for the metric
_ Sends periodic full routing updates every 30 seconds _ Converges slowly, often taking 3 to 5 minutes
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 455 -

_ Does not support VLSM, also making it a classful routing protocol (RIP V) IGRP
IGRP calculates the metric based on a mathematical formula that you do not really need to know for the exam. The formula uses bandwidth and delay as input and results in an integer value, the metric, between 1 and 4,294,967,295.
When RIP is used as the Routing Protocol, it selects TK1-TK5 because it has less hops. When IGRP uses as Routing Protocol, it select TK1-TK3-TK4-TK5 because having more bandwidth. IGRP uses bandwidth to calculate the path.
QUESTION NO: 30
A large corporation that frequently integrates networks from newly acquired businesses has just decided to use OSPF as the corporate routing protocol instead of EIGRP. What two benefits will the change from EIGRP to OSPF provide to the corporation? (Choose two)
A.The ability to automatically summarize networks
B.The ability to redistribute default and static routes
C.The ability to use VLSM
D.The ability to support multi-vendor routers
E.The ability to create a hierarchical design using areas
Answer: D, E
Explanation:
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol developed for Internet Protocol (IP) networks by the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Unlike, EIGRP, OSPF is standards based which is supported by multiple router vendors.
Unlike RIP and EIGRP, OSPF can operate within a hierarchy. The largest entity within the hierarchy is the autonomous system (AS), which is a collection of networks under a common administration that share a common routing strategy. OSPF is an intra-AS (interior gateway) routing protocol, although it is capable of receiving routes from and sending routes to other ASs.
An AS can be divided into a number of areas, which are groups of contiguous networks and attached hosts. Routers with multiple interfaces can participate in multiple areas. These routers, which are called Area Border Routers, maintain separate topological databases for each area.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 456 -
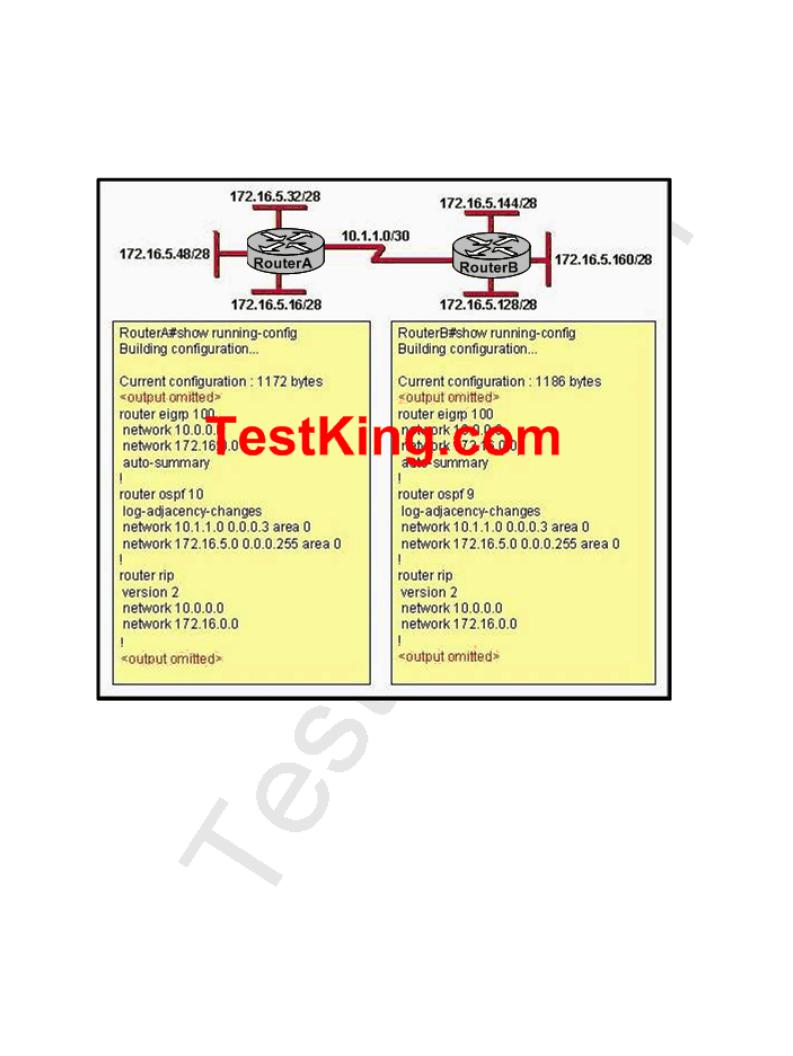
QUESTION NO: 31
Please study the exhibit shown below carefully:
Given the partial output from the show running-config command displayed on both TestKing routers, which routing protocol would be used to route packets to the 172.16.5.48/28 network from RouterB?
A.OSPF
B.RIP
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 457 -

C.EIGRP
D.No route will be installed to 172.16.5.48/28.
E.Unable to determine based on the information provided
Answer: A Explanation:
Normally, routers will choose EIGRP routes over OSPF and RIP routes because EIGRP has a lower administrative distance than the other two. However, in this case, auto summarization has been turned on, so the routers will automatically summarize at the network boundary. This will result in each router sending out only the summarized, 172.16.0.0/16 route.
However, OSPF does not summarize by default so RouterB will receive the specific 172.16.5.48/28 announcement from RouterA via OSPF. Because routers always choose the most specific route to the destination, regardless of the administrative distance, RouterB will use this OSPF route.
QUESTION NO: 32
Which characteristics are representative of link-state routing protocols? (Choose three)
A.Provides common view of entire topology
B.Utilizes event-triggered updates
C.Exchanges routing tables with neighbors
D.Calculates shortest path
E.Utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A, B, D Explanation:
Link-state algorithms (also known as shortest path first algorithms) flood routing information to all nodes in the internetwork. Each router, however, sends only the portion of the routing table that describes the state of its own links. In link-state algorithms, each router builds a picture of the entire network in its routing tables. Distance vector algorithms (also known as Bellman-Ford algorithms) call for each router to send all or some portion of its routing table, but only to its neighbors. In essence, link-state algorithms send small updates everywhere, while distance vector algorithms send larger updates only to neighboring routers. Distance vector algorithms know only about their neighbors.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 458 -

The primary advantage of link-state routing is that it reacts more quickly, and in a bounded amount of time, to connectivity changes. Also, the link-state packets that are sent over the network are smaller than the packets used in distance-vector routing. Distance-vector routing requires a node's entire routing table to be transmitted, while in link-state routing only information about the node's immediate neighbors are transmitted. Therefore, these packets are small enough that they do not use network resources to any significant degree. The primary disadvantage of link-state routing is that it requires more storage and more computing to run than distance-vector routing.
Incorrect Answers:
C, E: These are characteristics of distance vector routing protocols.
Section 12: Configure, verify, and troubleshoot OSPF (34 questions)
QUESTION NO: 1
Exhibit:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 459 -
You work as a network technician at TestKing.com. Study the exhibit carefully. A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
TestKing2(Config-router)#network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all interfaces are participating in OSPF. Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three.)
A.Serial0/1.103
B.FastEthernet 0/1
C.Serail0/1.102
D.Serial0/0
E.FastEthernet 0/0
Answer: B, C, D Explanation:
OSPF uses the concept of wildcard masks much like access list filters. OSPF network matches are done using the network number and wildcard bits. The network number is the network portion of the IP address, with the host bits all set to zero. The wildcard bits determine which portion of the address the access list will act on. Only bits set to zero are acted upon (bits set to one are ignored.) This is the exact opposite of a netmask. Remember that this number is in bits, and you will always have all zeros to the left of the first one, and all ones to the right of the last zero. The table below shows some examples of netmasks and wildcard bits.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 460 -
