
Testking_640-802_V13
.pdf
QUESTION NO: 8
Router TK1 is configured to run EIGRP. Which tables of EIGRP route information are held in RAM and maintained through the use of hello and update packets in this router? (Choose two)
A.SPF table
B.Query table
C.RTP table
D.Neighbor table
E.DUAL table
F.Topology table
G.State Table
Answer: D, F
Explanation:
In EIGRP the only two tables of significance are the neighbor table and the topology table.
Reference: Sybex CCNA Study Guide edition 4, Page 271.
QUESTION NO: 9
The TestKing network is shown in the following exhibit:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 501 -

Based on the TestKing router configurations shown above, why has this network failed to converge?
A.The no auto-summary command needs to be applied to the routers
B.The network numbers have not been properly configured on the router s
C.The subnet masks for the network numbers have not been properly con figured
D.The autonomous system number has not been properly configured
E.The bandwidth values have not been properly configured on the serial interfaces
Answer: A Explanation:
To restore the default behavior of automatic summarization of subnet routes into network-level routes, use the auto-summary command in router configuration mode. To disable this function and transmit subprefix routing information across classful network boundaries, use the no form of this command. Without disabling auto summarization, each router will advertise the 192.168.20.0/24 route, and the specific /26 networks will not be known.
QUESTION NO: 10
Which statements are true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two)
A.A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination.
B.Successor routes are saved in the topology table to be used if the primary route fails.
C.Successor routes are flagged as "active" in the routing table.
D.A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route.
E.Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process.
F.Successors are not used in EIGRP.
Answer: A, D
Explanation:
The following are some terms relating to EIGRP:
1.Feasible Distance: The lowest calculated metric to each destination
2.Feasibility Condition: A condition that is met if a neighbor's advertised distance to a destination is lower that the router's Feasible Distance to that same destination.
3.Successor: The neighbor that has been selected as the next hop for a given destination based on the Feasibility Condition.
Reference: Jeff Doyle, Routing TCP/IP, Volume I, Chapter 8: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), p.336-337, Cisco Press, (ISBN 1-57870-041-8)
Additional info:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 502 -

The Feasible Condition is met when the receiving router has a Feasible Distance (FD) to a particular network and it receives an update from a neighbor with a lower advertised or Reported Distance (RD) to that network. The neighbor then becomes a Feasible Successor (FS) for that route because it is one hop closer to the destination network. There may be a number of Feasible Successors in a meshed network environment.
The RD for a neighbor to reach a particular network must always be less than the FD for the local router to reach that same network. In this way EIGRP avoids routing loops. This is why routes that have RD larger than the FD are not entered into the Topology table. Reference: Ravi Malhotra, IP Routing, Chapter 4: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), O'Reilly Press, January 2002 (ISBN 0-596-00275-0)
QUESTION NO: 11
Which one of the following EIGRP commands can check the IP addresses of the adjacent neighbors, as well as verifying the EIGRP retransmit intervals and queue counts?
A.TK1#show ip eigrp adjacency
B.TK1#show ip eigrp topology
C.TK1#show ip eigrp interfaces
D.TK1#show ip eigrp neighbors
E.None of the above
Answer: D Explanation:
The topology database contains information from all of the LSA packets that have been received for an area. The topology database is updated by the LSAs. Each router within the area has exactly the same topology database. All routers must have the same vision of the networks; otherwise, confusion, routing loops, and loss of connectivity will result. Note: The topology database is the router's view of the network within the area. It includes every OSPF router within the area and all the connected networks. This database is indeed a routing table, but a routing table for which no path decisions have been made; it is at present a topology database.
Reference: "CCNP BSCI Exam Certification Guide Third Edition" by Clare Gough, CCIE No. 2893, Page 197.
QUESTION NO: 12
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 503 -

The Testking network consists of two routers as shown below:
Both routers Testking and HG are configured for EIGRP. Unfortunately, users on the Testking networks are unable to reach users on the HG networks. Which command could you enter on Testking to correct this problem?
A.Testking(config-router)# version 2
B.Testking(config-router)# no auto-summary
C.Testking(config-router)# redistribute eigrp 44
D.Testking(config-router)# EIGRP log-neighbor-changes
E.Testking(config-router)# default-information originate
Answer: B Explanation:
By default, EIGRP will auto-summarize IP information at the network boundaries. In this example, the 192.168.10.0 network is subnetted into 6 separate networks. Therefore, each router will only advertise the 192.168.10.0/24 network to each other by default. To disable this function and transmit sub-prefix routing information across classful network boundaries, auto summarization must be disabled.
Incorrect Answers:
A. There is only one version of EIGRP.
C.Based on the diagram, each router is already configured for EIGRP 44.
D.This will have no impact on the routes.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 504 -

E. This will generate a default route, which will be advertised to the other router. However, a default route is not needed, as the individual subnets need to be advertised, not a default route.
QUESTION NO: 13
TestKing.com has a large corporate network that uses multiple routing protocols. Hosts in a portion of the network that uses EIGRP have become unreachable. Which router command will allow you, the network technician, to view the status of these routes?
A.TestKing# show eigrp entries
B.TestKing# show protocols
C.TestKing# debug eigrp routes
D.TestKing# show ip route eigrp
E.TestKing# show route eigrp
Answer: D Explanation:
The show ip route and show ip route eigrp commands both list the EIGRP-learned routes with a D beside them. D signifies EIGRP. The letter E was already being used for Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) when Cisco created EIGRP, so it choose the next-closest letter to denote EIGRP-learned routes. You can see information about EIGRP neighbors with the show ip eigrp neighbors command, and the number of active neighbors (called peers in the command ouput) with the show ip eigrp interfaces command.
Reference: Cisco CCNA ICND 640-811 p.211
QUESTION NO: 14
Which command displays EIGRP-related router activities as they occur?
A.TestKing# show ip route *
B.TestKing# debug eigrp route
C.TestKing# debug ip eigrp
D.TestKing# debug ip protocols eigrp
E.TestKing# show ip route eigrp
F.None of the above
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 505 -

Answer: C Explanation:
The debug ip eigrp command helps you analyze the packets that are sent and received on an interface. Because the debug ip eigrp command generates a substantial amount of output, only use it when traffic on the network is light.
Examples:
The following is sample output from the debug ip eigrp command:
TestKing# debug ip eigrp
IP-EIGRP: Processing incoming UPDATE packet
IP-EIGRP: Ext 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 M 386560 - 256000 130560 SM 360960 - 256000 104960
IP-EIGRP: Ext 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 M 386560 - 256000 130560 SM 360960 - 256000 104960
IP-EIGRP: Ext 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 M 386560 - 256000 130560 SM 360960 - 256000 104960
IP-EIGRP: 172.69.43.0 255.255.255.0, - do advertise out Ethernet0/1
IP-EIGRP: Ext 172.69.43.0 255.255.255.0 metric 371200 - 256000 115200
IP-EIGRP: 192.135.246.0 255.255.255.0, - do advertise out Ethernet0/1
IP-EIGRP: Ext 192.135.246.0 255.255.255.0 metric 46310656 - 45714176 596480
IP-EIGRP: 172.69.40.0 255.255.255.0, - do advertise out Ethernet0/1
IP-EIGRP: Ext 172.69.40.0 255.255.255.0 metric 2272256 - 1657856 614400
IP-EIGRP: 192.135.245.0 255.255.255.0, - do advertise out Ethernet0/1
IP-EIGRP: Ext 192.135.245.0 255.255.255.0 metric 40622080 - 40000000 622080
IP-EIGRP: 192.135.244.0 255.255.255.0, - do advertise out Ethernet0/1
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 506 -

QUESTION NO: 15
Refer to the TestKing network shown below:
In this network, TK1 can ping across the serial link to 172.168.10.5, but cannot ping the FastEthernet interface of TK2 (172.168.10.65). The routing protocol being used is EIGRP, and the routing table of TK2 is shown. Which two statements could be the cause of this problem? (Choose two)
A.The serial interface does not have the clockrate set.
B.EIGRP is not enabled on one of the routers.
C.The IP addressing scheme has overlapping subnetworks.
D.The IP addressing scheme is using subnet zero but the ip subnet-zero command has not been enabled on one or both of the routers.
E.The FastEthernet interface of TK2 is administratively shutdown.
F.The EIGRP autonomous system numbers configured on the two routers do not match.
Answer: B, F
Explanation:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 507 -

You can successfully ping over the serial link, which tells us the serial interface is properly configured, but you are unable to ping a network that is not directly connected. Since no EIGRP routes appear in the routing table, this tells us there is something wrong with the EIGRP configuration on either router. The most likely problem is that EIGRP is not enabled on one of the routers, or the EIGRP AS numbers do not match on each router.
QUESTION NO: 16
The TestKing EIGRP network is displayed in the following diagram:
Refer to the graphic. TestKing is running EIGRP. Hosts from the 200.1.1.0/26 subnet cannot access a server located on the 200.1.1.64 subnet. The users have previously been able to access this server. After router Testking1 is accessed with the use of Telnet, which of the following commands would be a logical first choice in troubleshooting this problem?
A.Testking1# show interface s0/0
B.Testking1# show controllers
C.Testking1# show ip route
D.Testking1# show hosts
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 508 -

E. None of the above
Answer: C Explanation:
Since the network was previously accessible, and users are only unable to reach a specific subnet, it can be safely assumed that a routing issue is the problem, so viewing the routing table to see how traffic destined to the 200.1.1.64/26 subnet is being routed would be a logical first step.
Incorrect Answers:
A, B. These commands would be used if we had a reason to believe that there was a physical problem with the circuit itself. However, since we can safely telnet into the router remotely, and users appear to be able to reach other networks, we can assume that the physical serial interface is working properly.
D. The "show hosts" command is used to display the default domain name, the style of name lookup service, a list of name server hosts, and the cached list of host names and addresses on the network to which you can connect. It will not help us in any way in this example.
QUESTION NO: 17
Three TestKing routers are connected as shown below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 509 -
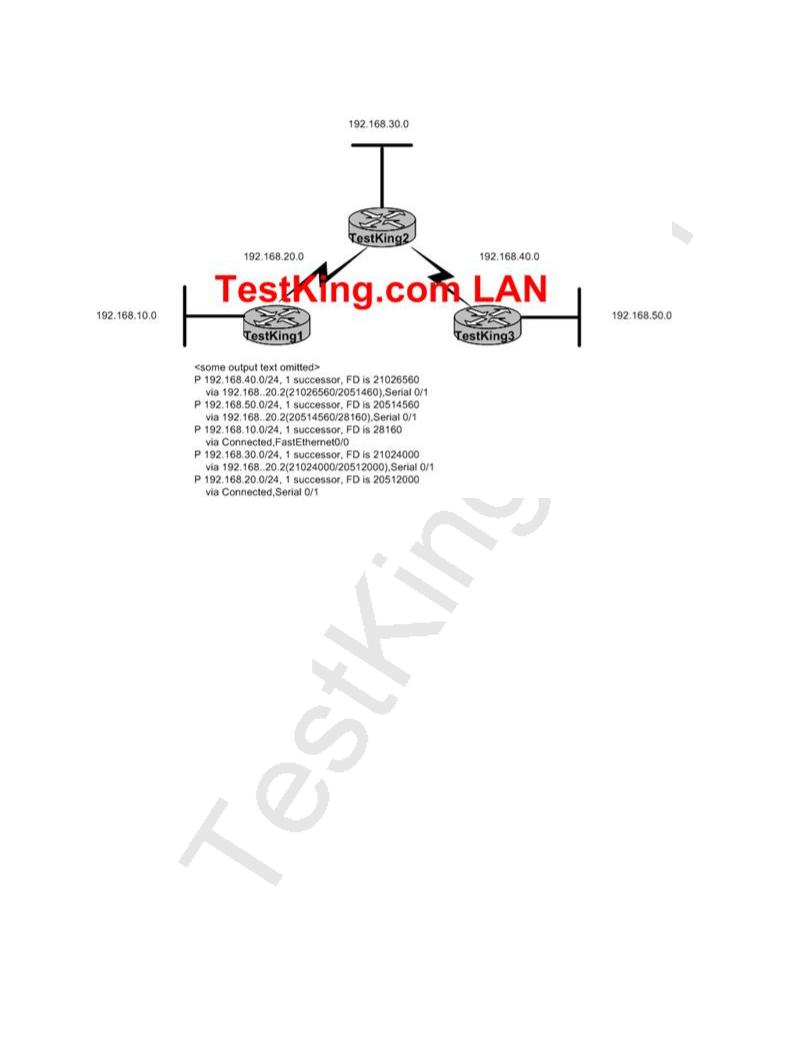
Based on the information shown above, which of the routers shown could produce the output shown?
A.TestKing1
B.TestKing2
C.TestKing3
D.Cannot be determined from the information shown
Answer: A Explanation:
The following is sample output from the show ip eigrp topology command: Router# show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for process 77
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
