
Testking_640-802_V13
.pdf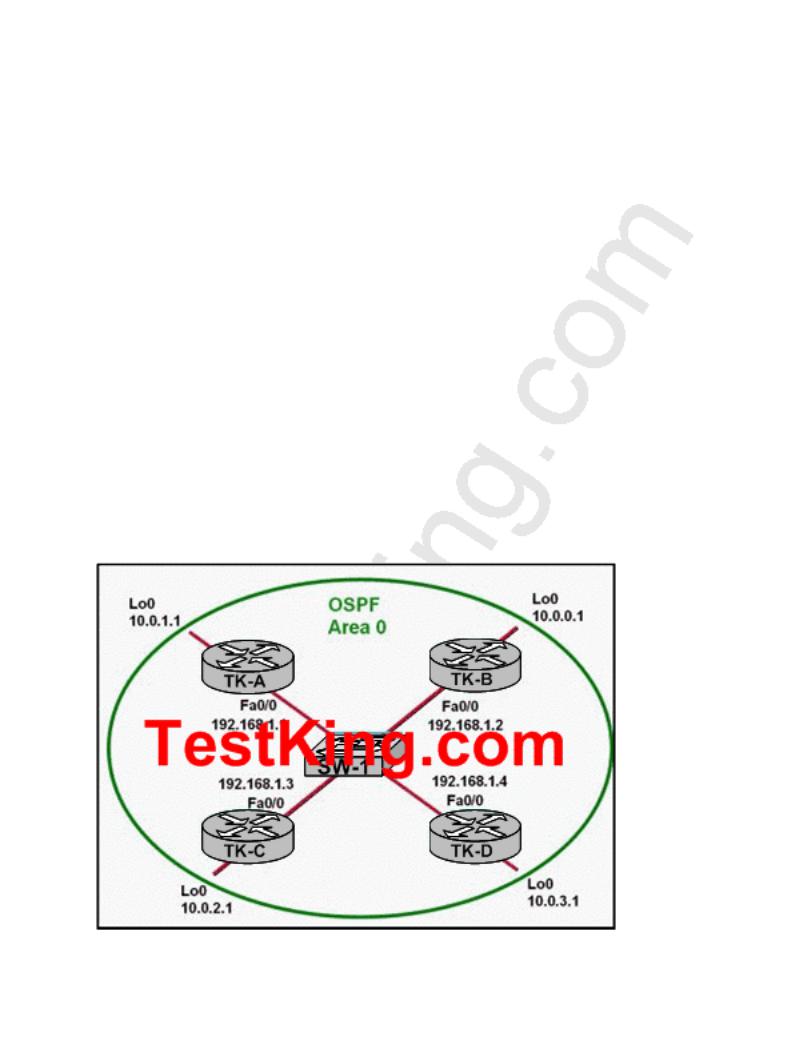
S* 0.0.0.0/0[1/0] via 10.10.10.6
E. None of the above
Answer: A Explanation:
The key to this question lies in the cost of the route to the 192.168.2.0/24 network. With OSPF, the cost of a link is 10,000,000/BW. Here we can see that the best path is over the two T1 links instead of the single 64K circuit. The OSPF cost of a link on a 1544kbps T1 line is 64. Since there are two T1 links, the cost now becomes 128. Finally, when we add the cost of the Ethernet link (10) the cost then becomes 138. Since choice A is the only option with the correct cost to this network it is correct. The other answers assume that the single 64K link is best, which is why the cost to the 192.168.2.0/24 network shows as 1572.
Note: If this were a RIP network, then the best path would indeed be over the single slower link as RIP does not consider the bandwidth of the link, only the number of hops.
QUESTION NO: 34
Please study the exhibit carefully.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 491 -

Based on the information shown above, which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on TK-B? (Choose two)
A.It indicates that TK-B should be elected the DR for the LAN.
B.It provides stability for the OSPF process on TK-B.
C.It ensures that data will be forwarded by TK-B.
D.It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from TK-B.
E.It specifies that the router ID for TK-B should be 10.0.0.1.
Answer: B, E
Explanation:
A loopback interface is virtual in nature, and thus will never go down as long as the router is powered on. It doesn't rely on any physical network or cable to be plugged in. This makes it a prime choice for any good reference point. That brings us to the "why" about using it.
When OSPF routers talk to one another, they all identify themselves. That is done by a RID, or Router ID value. An OSPF router may talk to many neighbors out multiple interfaces, but it only has one Router ID it uses for all conversations.
How does a router choose its identifier? Well, there are a couple ways. Typically, the router chooses its highest IP address of all physical interfaces. However, if there's a loopback interface (seen as a manual intervention), the OSPF process will always use the loopback address as its RID value.
In this network, stability is ensured for TK-B as it will not become the DR or the BDR because the other routers will have a higher router ID since the have a higher loopback IP address. The DR/BDR election process is as follows:
A designated router (DR) is the router elected by the network by elections. The DR is elected based on the following default criteria:
*If the priority setting on a OSPF router is set to 0, that means it can NEVER become a DR or BDR.
*When a DR fails and the BDR takes over, there is another election to see who becomes the replacement BDR.
*The router sending the Hello packets with the highest priority.
*If two or more routers tie with the highest priority setting, the router sending the Hello with the highest RID (Router ID) wins.
*(NOTE) A RID is the highest logical (loopback) IP address configured on a router, if no logical/loopback IP address is set then the Router uses the highest IP address configured on its interfaces. (e.g. 192.168.0.1 would be higher than 10.1.1.2)
*Usually the router with the second highest priority number becomes the BDR (Backup Designated Router)
*
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 492 -

The range of priority values range from 1 - 255, with a higher value increasing its chances of becoming DR or BDR.
* IF a HIGHER priority OSPF router comes online AFTER the election has taken place, it will not become DR or BDR until (at least) the DR and BDR fail.
Section 13: Configure, verify, and troubleshoot EIGRP (23 questions)
QUESTION NO: 1
Network topology exhibit:
Configuration exhibit (Routing Table):
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 493 -

You work as a network technician at TestKing and you need to troubleshoot an issue with the network.
Based on the information provided above, what can be determined from the router output shown in the graphic?
A.200.1.1.64 is a default route
B.EIGRP is in use in this network
C.The output came from a router that has four physical interfaces
D.The output shows that there are three default routes
E.The output came from router TestKing2
F.None of the above
Answer: B Explanation:
In the routing table the "D" letter marks the route learned from EIGRP routing protocol. Based on the routing table above, there are 4 directly connected IP interfaces, 2 EIGRP learned routes (which means that EIGRP is in use on this network) and a static default route was also configured.
QUESTION NO: 2
You are troubleshooting a routing issue in the TestKing EIGRP network. In this network, which statements are true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two)
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 494 -

A.Successor routes are flagged as "active" in the routing table
B.Successor routes are saved in the topology table to be used if the primary route fails
C.A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination
D.A successful route may be backed up by a feasible successor route
Answer: C, D
Explanation:
The DUAL finite state machine embodies the decision process for all route computations. It tracks all routes advertised by all neighbors. The distance information, known as a metric, is used by DUAL to select efficient loop free paths. DUAL selects routes to be inserted into a routing table based on feasible successors. A successor is a neighboring router used for packet forwarding that has a least cost path to a destination that is guaranteed not to be part of a routing loop. When there are no feasible successors but there are neighbors advertising the destination, a recomputation must occur. This is the process where a new successor is determined. The amount of time it takes to recompute the route affects the convergence time. Even though the recomputation is not processor-intensive, it is advantageous to avoid recomputation if it is not necessary. When a topology change occurs, DUAL will test for feasible successors. If there are feasible successors, it will use any it finds in order to avoid any unnecessary recomputation. Feasible successors are defined in more detail later in this document.
Feasible Successors
A destination entry is moved from the topology table to the routing table when there is a feasible successor. All minimum cost paths to the destination form a set. From this set, the neighbors that have an advertised metric less than the current routing table metric are considered feasible successors.
Feasible successors are viewed by a router as neighbors that are downstream with respect to the destination. These neighbors and the associated metrics are placed in the forwarding table.
When a neighbor changes the metric it has been advertising or a topology change occurs in the network, the set of feasible successors may have to be re-evaluated. However, this is not categorized as a route recomputation.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/tk207/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml#feasible
QUESTION NO: 3
Three TestKing routers are connected as show below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 495 -

Part of their configurations are shown below:
IP Addresses and routing for the network are configured as shown above. The TestKing network administrator issued the "show ip eigrp neighbors" command from router TestKing1 and receives the output shown. Based on all the information provided above, which statement is true?
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 496 -

A.It is normal for TestKing1 to show once active neighbor at a time to prevent routing loops
B.The IP addresses are not configured properly on the TestKing1 and TestKing3 interfaces
C.The "no auto-summary" command configured on the routers prevents TestKing1 and TestKing2 from forming a neighbor relationship
D.Routing is not completely configured on TestKing3
E.None of the above
Answer: D Explanation:
The Router TestKing3 is connected to three different networks: 192.168.3.1/30, 192.168.2.2/30, and 10.0.4.0/24 but only 10.0.4.0 and 192.168.2.0 are being advertised via EIGRP. In TestKing3, the "network 192.168.3.0" command should be placed under the EIGRP 10 process.
QUESTION NO: 4
The topology table for the TestKing EIGRP network is shown below from router TestKing3:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 497 -

You are troubleshooting a routing issue with the TestKing network. Why does Router TestKing3 show multiple unequal cost paths to network 192.168.81.0/24?
A.Because the EIGRP topology table displays all routes to a destination
B.Because the EIGRP topology table shows only backup routes to a destination
C.Because variance was configured for EIGRP autonomous system 109
D.Because multiple floating static routes were configured to network 192.168.81.0 via interface Serial0
E.None of the above
Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 5
The routing table of router TK1 is shown below:
Based on the routing table of TK1 shown above, which address and mask combination represents a summary of the routes learned by EIGRP?
A.192.168.25.28 255.255.255.252
B.192.168.25.28 255.255.255.240
C.192.168.25.16 255.255.255.252
D.192.168.25.0 255.255.255.252
E.192.168.25.16 255.255.255.240
F.192.168.25.0 255.255.255.240
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 498 -

Answer: E
QUESTION NO: 6
You need to configure EIGRP on a new TestKing router. What parameters must you specify when you enable EIGRP routing?
A.The broadcast address, and AS number
B.The network number and AS number
C.EIGRP routing, network number and passive interface
D.EIGRP routing, network number, and AS
E.None of the above.
Answer: D Explanation:
To enable EIGRP on your router, you must specify EIGRP routing, the network number, and the AS system number.
Example:
Router EIGRP 33
Network 10.0.0.0
In the case above the AS process number is 33.
QUESTION NO: 7
The TestKing router has been configured for EIGRP. Information relating to the configuration is displayed in the output shown below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 499 -

The EIGRP configuration in the TestKing router used a single network statement. From the output shown in the graphic, which network statement was used to advertise these networks in EIGRP?
A.network 172.26.168.128 0.0.0.127
B.network 172.26.168.128 area 478
C.network 172.26.0.0
D.network 172.26.168.0 area 478
E.None of the above
Answer: C
Explanation:
The correct configuration statements used in the above were:
Router eigrp 478
Network 172.26.0.0
Incorrect Answers:
A. A wildcard mask is not required at the end of the network statement in order to configure EIGRP. It is only required for an OSPF configuration. Although a wildcard mask is now supported with EIGRP, the mask used in this example is incorrect.
B, D: In EIGRP, the concept of an area does not exist. This is only used by OSPF.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 500 -
